You can configure custom cache keys by creating rules that generate cache keys based on different parts of an HTTP request, such as the URI, request parameters, HTTP request headers, or custom variables. This feature converts requests for the same file into a single cache key, which prevents the same request from being cached as different files. As a result, this improves the cache hit rate, reduces origin fetches, and decreases response times and bandwidth consumption.
Notes
The custom cache key and ignore parameter features are mutually exclusive. If you have configured ignore parameters, CDN points of presence (POPs) remove parameters that follow the question mark (
?) in request URLs. This makes the request parameters configured in the cache key unavailable. Before you enable custom cache keys, make sure that you have not configured any ignore parameter settings.The custom cache key feature modifies only the cache identifier of a request and does not change the origin fetch URL. The content of the origin fetch request remains the same as the client request.
The URL purge feature cannot purge cached content after you configure a custom cache key.
Use cases
The custom cache key feature modifies only the cache identifier of a request and does not change the origin fetch URL. The content of the origin fetch request remains the same as the client request.
A cache key is the unique identifier (ID) for a file cached on a CDN node. By default, a file's cache key is the request URL, including its parameters.
Use case 1
Request URLs can contain complex parameters. If multiple requests are for the same file but have different URL parameters, POPs treat them as requests for different files. This results in multiple cached copies and an increase in origin fetches.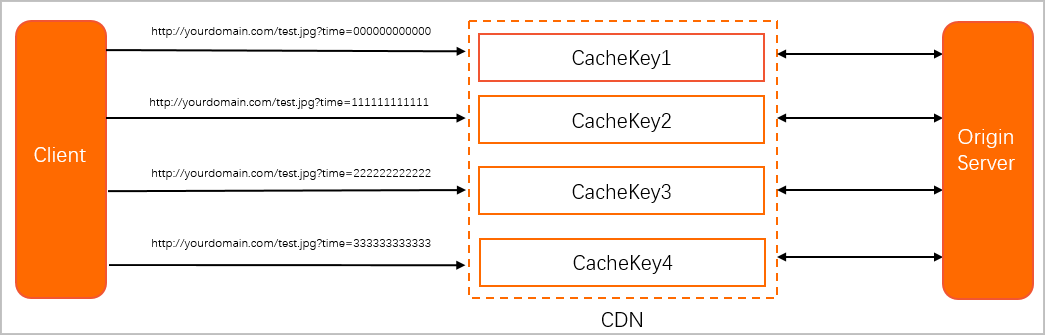
You can create a custom cache key rule to unify the cache key for these requests to reduce origin fetches.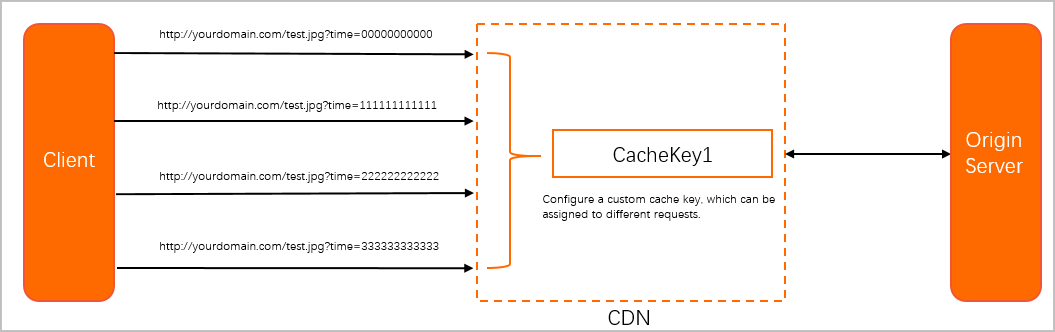
Use case 2
When requests have the same URL, CDN considers them requests for the same file. However, the HTTP header might contain a client field that specifies different client systems, which means the requests are for different files.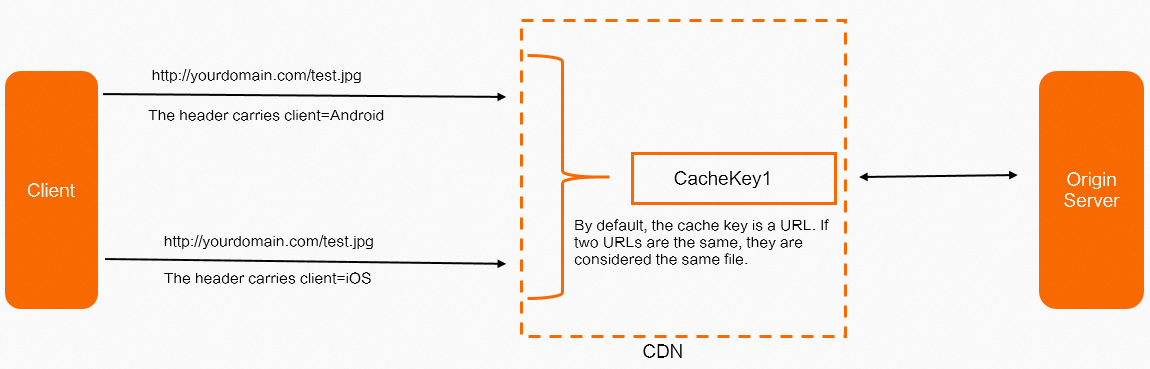
In this case, you can create a custom cache key that includes the value of the client field. This allows the two requests to be identified by two different cache keys.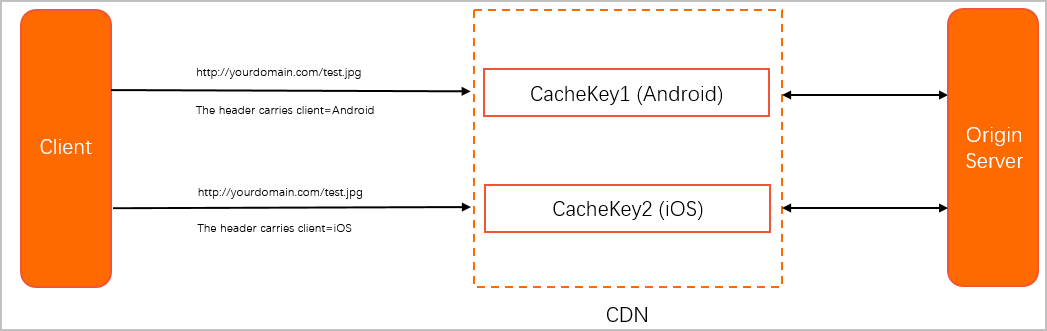
Procedure
Log on to the CDN console.
In the left navigation pane, click Domain Names.
On the Domain Names page, find the target domain name and click Manage in the Actions column.
In the domain's navigation pane, click Cache.
On the Custom Cache Key tab, click Configure to configure cache keys.
Parameter Type
Instructions
Rule Condition
Rule conditions identify various parameters in a user request to determine whether a configuration applies to the request.
Do not use: Do not use rule conditions.
To add or edit rule conditions, manage them in the Rules Engine.
URIs
When the client-requested URI matches the configured Source URI, the system replaces the Source URI with the configured Final URI to construct the cache key.
You can configure multiple URI replacement policies. If multiple policies exist, they are matched in top-down order. Once a Source URI is matched, the system executes the replacement operation using the corresponding Final URI and stops evaluating subsequent policies.
Source URI: The URI must start with a forward slash (/) and not include the http:// prefix or the domain name.
PCREregular expressions are supported.Final URI: The URI starts with a forward slash (/). It does not include the `http://` prefix or the domain name.
Request Parameter
The object of the operation is the parameters in the original request URL. You can Add, Delete, Modify, or Reserve parameters. The result is appended to the cache key. You can configure multiple operations. When multiple operations are configured, they are executed sequentially from top to bottom.
Add: Append new request parameters to the cache key. For example, if the original URL is
http://image.example.com/cat.jpgand you add the request parametertype=jpg, the cache key becomeshttp://image.example.com/cat.jpg?type=jpg.Delete: Delete specified parameters from the original request URL when generating the cache key. For example, if the original URL is
http://image.example.com/cat.jpg?type=jpgand you delete the parametertype, the cache key becomeshttp://image.example.com/cat.jpg.Modify: When generating the CacheKey, modify the specified parameter in the original request URL. For example: the original URL is
http://image.example.com/cat.jpg?type=jpg, modify the parametertype=png, then the CacheKey is.Reserve: Retain only specified parameters from the original request URL when generating the cache key. For example, if the original URL is
http://image.example.com/cat.jpg?type=jpg&path=imageand you retain the parametertype, the cache key becomeshttp://image.example.com/cat.jpg?type=jpg.
HTTP Headers
Append the values of specified HTTP headers from the client's original request to the cache key. Configure multiple HTTP header names (separate them with spaces). The values of each HTTP header are appended to the cache key in order.
For example, if the original URL is
http://image.example.com/cat.jpgand the client request includes anHTTP header (path: image), the cache key becomeshttp://image.example.com/cat.jpgimagewhen the HTTP Headers includes thepathheader.Custom Variables
You can use a regular expression to match the value of a specified request parameter, HTTP header, or cookie, or a specified URI in the original client request. When a match is found, the matched value is appended to the cache key. For more information, see Configuration examples.

Click OK.
Configuration examples
URIs
Requests for http://aliyundoc.com/a/b/image.jpg and http://aliyundoc.com/a/b/c/image.jpg are treated as requests for the same file. The cache key for the file is http://aliyundoc.com/c/image.jpg.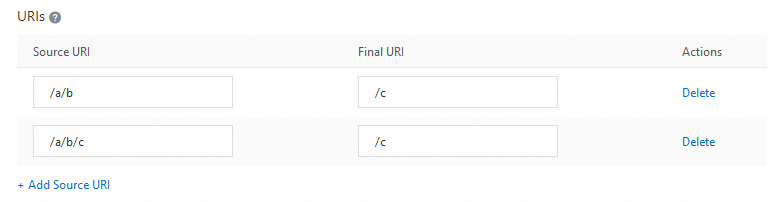
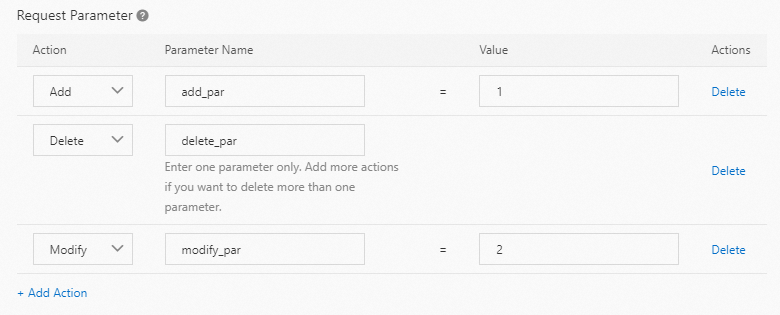
Request Parameter
For a request to http://aliyundoc.com/a/b/image.jpg?delete_par=1&modify_par=1 , the rule adds add_par=1, deletes delete_par, and changes the value of modify_par to 2. The final cache key is based on the URL http://aliyundoc.com/a/b/image.jpg?modify_par=2&add_par=1.
If multiple operations are performed on the same variable, the order of priority is: Add > Delete > Retain > Modify.
HTTP Headers
The values of the User-Agent and Accept-Language HTTP headers are appended to the cache key. For example, if a request for http://aliyundoc.com/a/b/image.jpg has User-Agent=Mozilla/5.0 (Linux; X11) and Accept-Language=en, the cache key for this request is http://aliyundoc.com/a/b/image.jpgMozilla/5.0(Linux;X11)en.
Custom Variables
Example 1
Set the variable name to language, the source to Request Header, the source field to Accept-Language, the match rule to ([%w]+),([%w]+), and the variable expression to $1aa.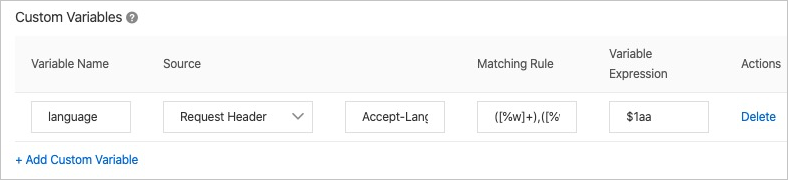
A client requests http://aliyundoc.com/a/b/image.jpg with the HTTP header Accept-Language=en,ch . The match rule captures en as $1. The variable expression uses this capture group and appends aa to produce the value enaa. This value, which uses the alias language, is appended to the URL to form the final cache key: http://aliyundoc.com/a/b/image.jpgenaa.
In a variable expression, $n refers to the content captured by the n-th group in the rule. For example, if the string is Accept-Language=en,ch and the rule is ([%w]+),([%w]+), then $1 is en and $2 is ch.
Example 2
Set the variable name to expired, the source to Request Cookie, the source field to a, the match rule to [%w]+:(.*), and the variable expression to $1.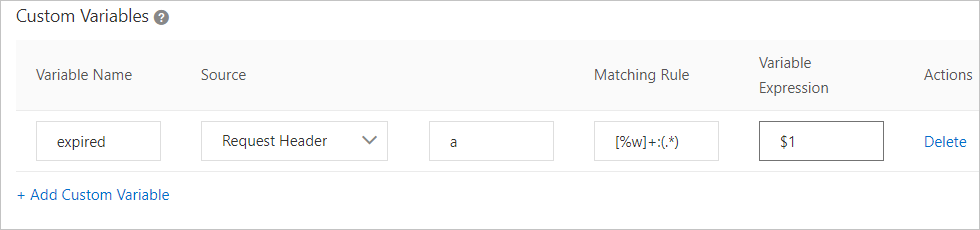
A client requests http://aliyundoc.com/a/b/image.jpg with the cookie Cookie a=expired_time:12635187. The match rule extracts the value 12635187 and assigns it to the variable expression $1. The alias for this variable is expired. This value is then appended to the URL to create the final cache key: http://aliyundoc.com/a/b/image.jpg12635187.
Example 3
Set a URI rule and a custom variable.
URI:
Merge all requests whose URIs match /abc/.*/abc into /abc.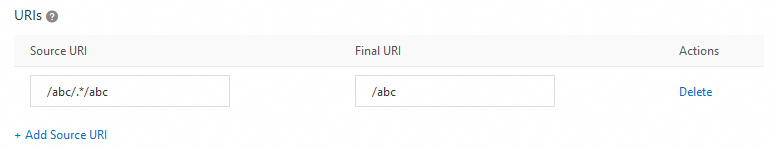
Custom variable:
Set the variable name to testname, the source to Path, the match rule to /abc/xyz/(.*), and the variable expression to $1.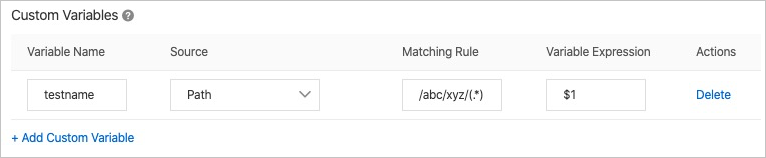
A client requests the URL http://aliyundoc.com/abc/xyz/abc/image.jpg. Based on the URI configuration, the URL is merged to produce the cache key http://aliyundoc.com/abc/image.jpg. Then, based on the custom variable configuration, the original URL matches the pattern /abc/xyz/(.*). In this case, the variable $1 is assigned the value abc and appended to the cache key. The final cache key is http://aliyundoc.com/abc/image.jpgabc. This combination of two rules allows for more complex caching logic.
If the request does not meet the custom variable's match rule, the variable expression $1 is not appended to the cache key.
Example 4
You can set a rule condition and a custom variable to generate different cache keys for requests from mobile and PC clients.
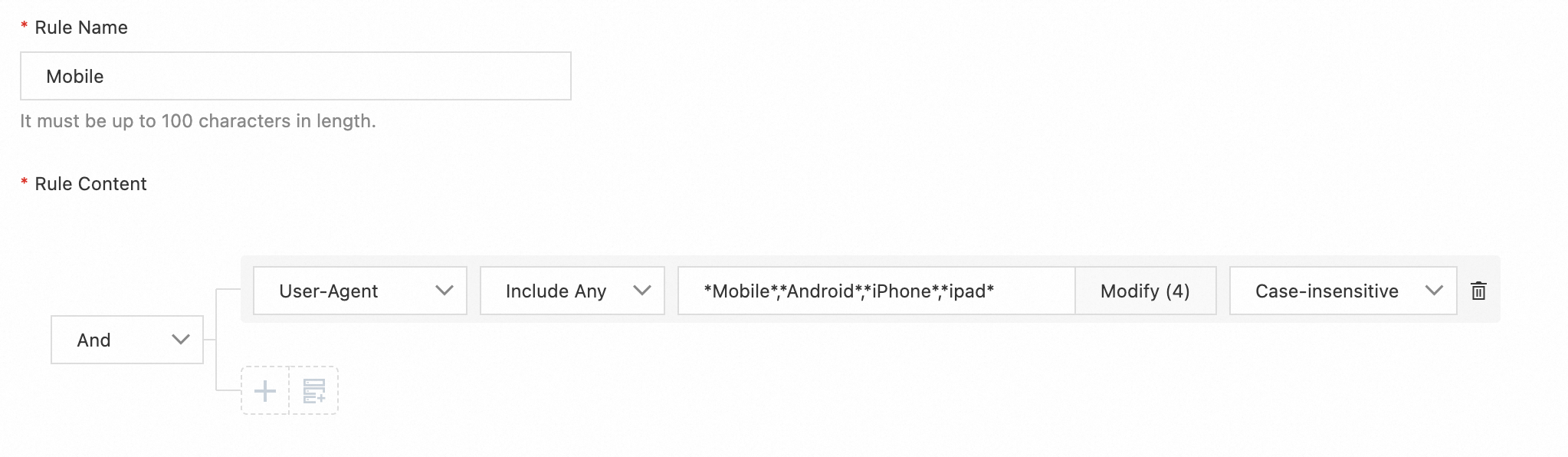
Mobile rule condition:
User-Agent contains any of *Mobile*,*Android*,*iPhone*,*ipad*
PC rule condition:
User-Agent does not contain any of *Mobile*,*Android*,*iPhone*,*ipad*

Mobile custom cache key:
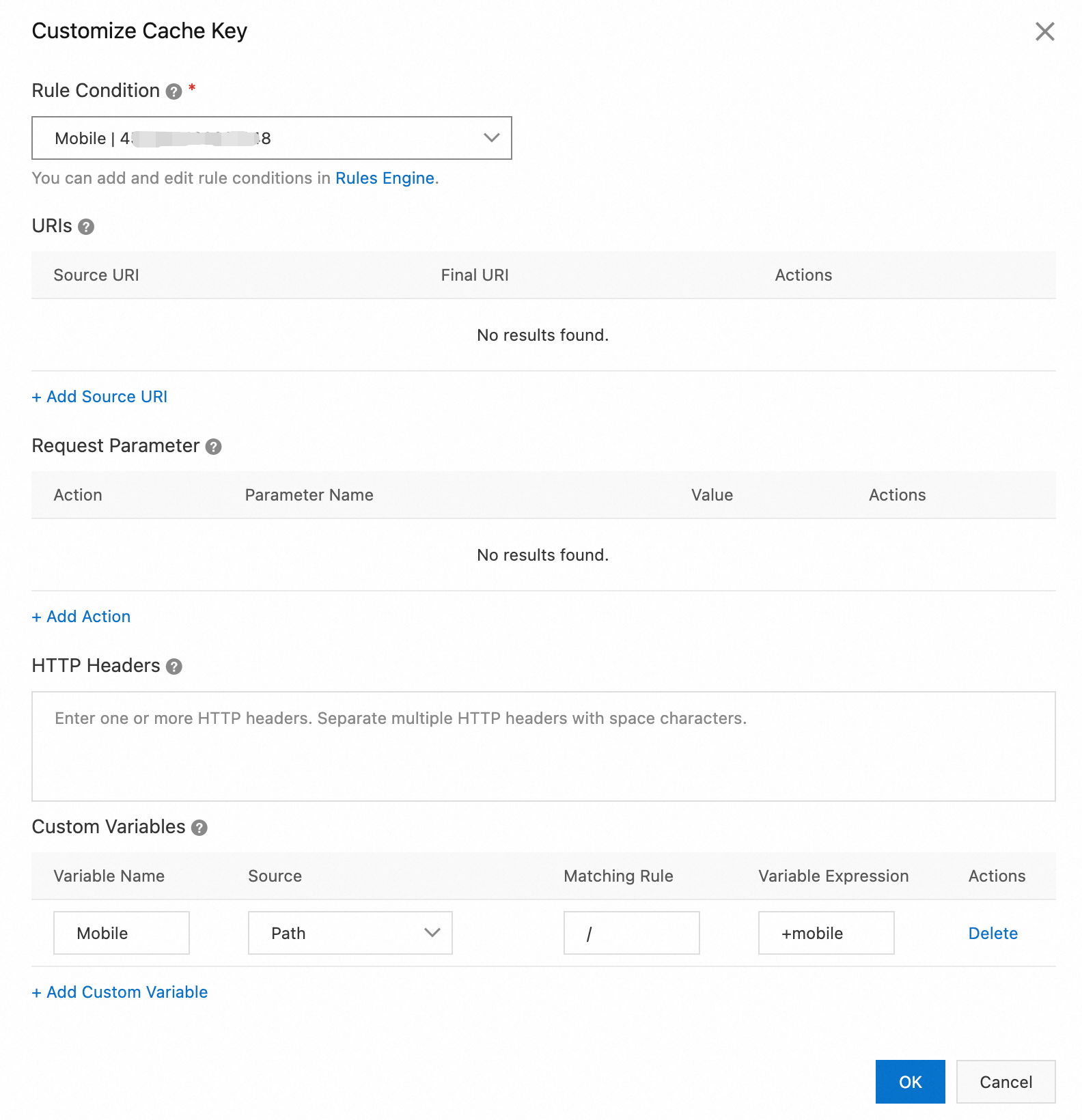
Set Rule Condition to Mobile. Then, for Custom Variables, set Variable Name to Mobile, Source to Path, Matching Rule to /, and Variable Expression to +mobile.
PC custom cache key:
Set Rule Condition to PC. For Custom Variables, set Variable Name to PC, Source to Path, Matching Rule to /, and Variable Expression to +pc.

A client requests the URL http://aliyundoc.com/image.jpg. Based on the User-Agent value, the request matches either the Mobile or PC custom cache key rule. The final cache key for a Mobile client is http://aliyundoc.com/image.jpg+mobile. The final cache key for a PC client is http://aliyundoc.com/image.jpg+pc.