This topic describes how to deploy a Keycloak Service in a Container Service for Kubernetes (ACK) cluster and use Keycloak as a Kubernetes OpenID Connect (OIDC) authentication server to verify identities.
Prerequisites
An ACK managed cluster is created, and the cluster is version 1.22 or later.
You have obtained the cluster's kubeconfig file and connected to the cluster with kubectl.
(Optional) jwt-cli is installed, which is used to parse JSON Web Tokens (JWTs).
Set up the environment
Prepare a domain name for the Keycloak Service.
Certificates
To ensure the security of Keycloak in a production environment, run the following command to generate a root certificate and a server certificate. The Subject Alternate Name (SAN) of the server certificate must contain the domain name that you prepared for the Keycloak Service.
openssl genrsa -out rootCA.key 2048 #Generate a CA key. openssl req -x509 -new -nodes -key rootCA.key -sha256 -days 3650 -out rootCA.crt #Generate a CA certificate. openssl genrsa -out server.key 2048 #Generate a server key. openssl req -new -key server.key -out server.csr openssl x509 -req -in server.csr -CA rootCA.crt -CAkey rootCA.key -CAcreateserial -out server.crt -days 3650 -sha256 -extensions v3_req -extfile <(echo '[v3_req]'; echo 'subjectAltName = DNS:${Service domain name}')Databases
By default, Keycloak data is persisted to local files. In a production environment, you need to persist the data to a database. The following table describes the database engines and versions supported by Keycloak.
Database
Option value
Version
MariaDB Server
mariadb
10.11
Microsoft SQL Server
mssql
2022
MySQL
mysql
8.0
Oracle Database
oracle
19.3
PostgreSQL
postgres
15
In this example, ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL is used to persist Keycloak data. A database named Keycloak is created. For more information about how to create and use database instances, see Create and configure an ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance.
Step 1: Deploy Keycloak in an ACK managed cluster
Deploy a Keycloak Service in an ACK managed cluster.
Create a file named keycloak.yaml and add the following content to the file:
apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: labels: app: keycloak name: keycloak namespace: default spec: ports: - name: http port: 80 protocol: TCP targetPort: 8080 selector: app: keycloak type: ClusterIPRun the following command to deploy a Keycloak Service in an ACK managed cluster and expose the Service to internal access:
kubectl apply -f keycloak.yaml
Deploy relevant configurations.
Create a file named keycloak-secret.yaml and add the following content to the file.
The following database configuration is used to connect to the database named Keycloak. The administrator configuration is used to log on to Keycloak for the first time.
apiVersion: v1 data: db_passwd: ${Base64-encoded database password} db_username: ${Base64-encoded database username} db_url: ${Base64-encoded database URL/host} keycloak_admin: ${Base64-encoded Keycloak administrator username} keycloak_admin_password: ${Base64-encoded Keycloak administrator password} kind: Secret metadata: name: keycloak-secret namespace: default type: OpaqueRun the following command to deploy the configurations:
kubectl apply -f keycloak-secret.yamlCreate a file named keylock-pki.yaml and add the following content to the file:
apiVersion: v1 data: tls.crt: ${Server certificate encoded by Base64} tls.key: ${Server private key encoded by Base64} kind: Secret metadata: name: keycloak-pki namespace: default type: IngressTLSRun the following command to deploy the server certificate:
kubectl apply -f keycloak-pki.yaml
Create an Ingress.
Create a file named keycloak-ingress.yaml and add the following content to the file.
Replace the Service domain name in the following code block with the domain name that you prepared for the Keycloak Service:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: Ingress metadata: labels: ingress-controller: nginx name: keycloak namespace: default spec: ingressClassName: nginx rules: - host: ${Service domain name} http: paths: - backend: service: name: keycloak port: number: 80 path: / pathType: ImplementationSpecific tls: - hosts: - ${Service domain name} secretName: keycloak-pkiRun the following command to deploy the Ingress:
kubectl apply -f keycloak-ingress.yamlAfter the Ingress is deployed, a publicly accessible IP address is generated. The Service domain name is resolved to the IP address.
Deploy the Keycloak Deployment.
Create a file named keycloak-deploy.yaml and add the following content to the file:
Run the following command to deploy a Keycloak Deployment:
kubectl apply -f keycloak-deploy.yaml
In a browser, enter
https://${Keycloak Service domain name}to access the Keycloak Service. If the following page appears, the Service is successfully deployed.
Step 2: Deploy Keycloak
User settings
On the Keycloak service page, click Administration Console and enter the username and password to log on to the Admin console.
The username and password are the administrator logon information that you configured in the keycloak-secret.yaml file in Step 2.a.
In the upper-left corner of the page, select master from the drop-down list, and then click Create Realm.

On the Create realm page, set Realm name to myrealm and then click Create to create a new realm named myrealm. In Keycloak, a realm represents a tenant.
In the drop-down list in the upper-left corner of the page, select myrealm. In the navigation pane on the left, select Users, and then click Add user.

On the Create user page, set Username to myuser and click Create to create a user named myuser. The other parameters are optional.
On the myuser page, click Attributes, set Key to name and Value to ack, and then click Save. The attribute can be injected into an ID token.

On the myuser page, click Credentials, and then click Set Password.
Set Temporary to On and then click Save. You must change your password after you log on for the first time.

The logon URL for Keycloak is
https://${Keycloak Service domain name}/realms/${your realm}/account.
Client settings
Clients are the entities that request Keycloak to verify user identities. After configuring user settings, you need to configure client settings.
In the navigation pane on the left of the myrealm page, select Clients, and then on the Clients page, click Create client.
On the Create client page, configure General Settings, Capability config, and Login settings.
On the General Settings page, set both Client ID and Name to ack, and then click Next.

On the Capability config page, set Client authentication to on to set the client access type to confidential, keep the default settings for other parameters, and then click Next.

On the Login settings page, set Valid redirect URIs to http://*. This setting specifies the valid redirect URIs to use after a successful logon. In this example, http://* matches all HTTP redirect URIs. Then, click Save.

Client scope settings
Client scopes can be used to share common protocol and role mappings between multiple clients within a realm.
In the navigation pane on the left of the myrealm page, select Client scopes, and then on the Client scopes page, click Create client scope.
On the Create client scope page, set Name to ack-kubernetes, keep the default settings for other parameters, and then click Save.

On the ack-kubernetes page, click Mappers, and then click Configure a new mapper.
On the Configure a new mapper page, create a User Attribute. This attribute is used to inject the name and ack fields that you added in Step 6 into the ID token.

On the Add mapper page, set Name to name, User Attribute to name (the name: ack attribute set in the preceding step), and Token Claim Name to name (the name of the attribute in the ID token). Keep the default settings for other parameters. Then, click Save.

In the navigation pane on the left, click Clients to return to the Clients page and select the Client named ack.
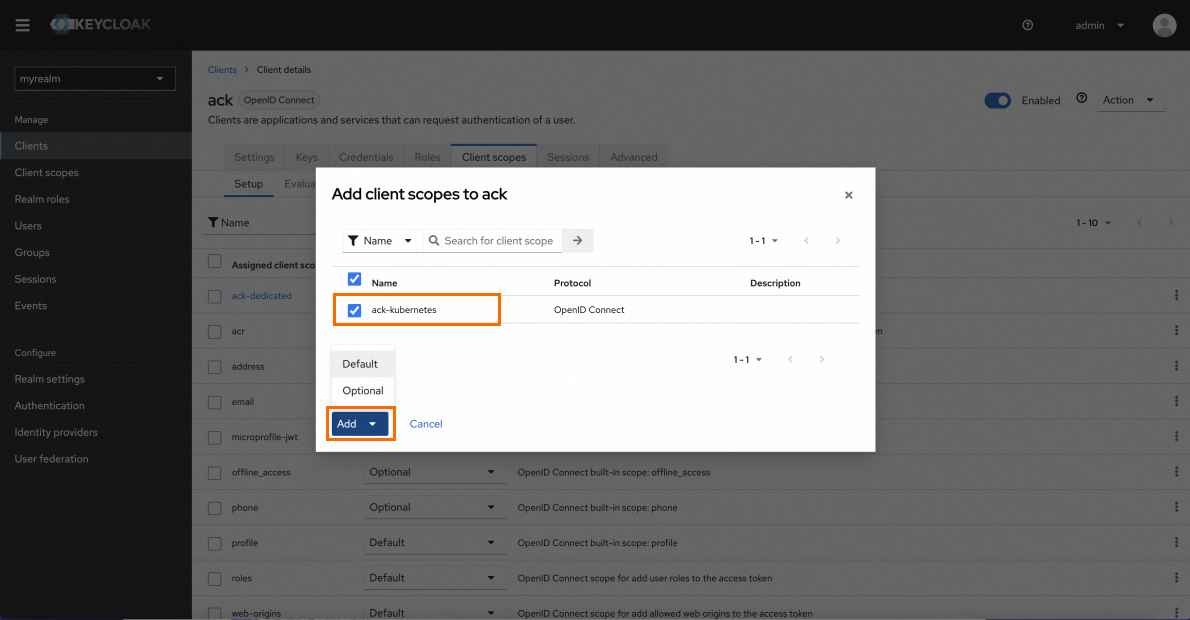
On the client page of the ack client, click Client scopes, and then click Add client scope. In the dialog box that appears, select the client scope to add, and then click Add.
Step 3: Configure Kube API Server parameters
Kubernetes supports the OIDC protocol and can be interfaced with external identity providers (IdPs) to verify identities. To enable identity verification, you need to configure OIDC parameters related to the Kube API Server component of the ACK managed cluster.
Log on to the ACK console. In the left navigation pane, click Clusters.
On the Clusters page, find the one you want to manage and click its name. In the left navigation pane, click Add-ons.
On the Add-ons page, find the Kube API Server component on the Core Components tab and click Configuration in the lower-right corner of the card.
On the Kube API Server Parameters page, configure the following parameters, keep the default settings for the other parameters, and then click OK.

Parameter
Description
oidcIssuerURLOIDC
The URL of the OIDC provider
Access
https://${Keycloak Service domain name}/realms/myrealm/.well-known/openid-configuration, and enter the value corresponding to issuer into oidcIssuerURL. In this example:https://${Keycloak Service domain name}/realms/myrealm.ImportantThe API Server in the cluster will access the address specified in the oidcIssuerURL configuration item. If your service domain name is a public domain name, make sure that the cluster has Internet access enabled. For more information, see Enable Internet access for a cluster.
If the API Server still cannot access the address specified in the oidcIssuerURL configuration item after Internet access is enabled for the cluster, you can use
kubectl get endpointsto check the number of IP addresses in the Kubernetes backend.If there are more than one IP address, log on to the Worker node and try to access the oidcIssuerURL, then check the Internet configuration, security group rules, and other settings.
If there is only one IP address, please submit a ticket for assistance.
oidcClientIdOIDC
The client ID of the OIDC token
Enter the client ID specified in Step 2 of the Client settings section. In this example, ack is entered.
oidcUsernameClaim
The JWT claim that is used as the username
Enter the value of the Token Claim Name parameter specified in Step 5 of the Client scope settings section. In this example, name is entered, which is the identity of the user in the cluster.
oidcUsernamePrefix
The prefix of the username
Enter a hyphen (-), which means that no prefix is specified.
oidcCAContent
The CA certificate that is required for sending requests to the URL of the OIDC provider. You must specify a Base64-encoded certificate
Enter the Base64-encoded root certificate generated in Certificates in the Set up the environment section.
Step 4: Verify identities
Run the following command to request an ID token. Then, obtain the ID token from the request body.
curl -ks -X POST https://${Keycloak Service domain name}/realms/myrealm/protocol/openid-connect/token \ -d grant_type=password -d client_id=ack \ -d username=myuser -d password=${Password used to log on to Keycloak} -d scope=openid \ -d client_secret=${client credential}You need to replace the following variables:
Variable to replace
Description
Keycloak Service domain name
Replace it with the domain name that you prepared for the Keycloak Service.
password
Replace it with the password specified in Step 2.a of Step 1.
client_secret
Log on to the Keycloak console. On the Clients page, select the client named ack, click Credentials, and then copy the value of the Client secret parameter.

Optional: When you parse the token using jwt-cli, the output shows that
issis the oidcIssuerURL configured for the API server, and thenamefield is the User Attribute set in Step 5 of the preceding Client scopes section.Use the following YAML content to create a ClusterRole:
kind: ClusterRole apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 metadata: name: keycloak-example rules: - apiGroups: [""] resources: ["namespaces"] verbs: ["get","list"] # Allow the role to read namespace information. --- kind: ClusterRoleBinding apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 metadata: name: ack-crb roleRef: apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io kind: ClusterRole name: keycloak-example subjects: - kind: User name: ack apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.ioRun the following command to send a request to the API server:
curl -k https://${API server address}/api/v1/namespaces -H "Authorization: Bearer ${id token}"API server address: Enter the API server address based on the network where your cluster is deployed. On the Cluster Information page of the Container Service Management Console, go to the Basic Information tab and view the API server Public Endpoint and API server Internal Endpoint in the Network section.id token: Specify the ID token obtained in Step 1.
After the request is sent, the following namespace information is returned.

Send another request to request a resource that the current user is unauthorized to access. The output indicates that Kubernetes identifies the ack user and verifies the permissions of the user.
