Ray is an open-source framework for building scalable AI and Python applications, widely used in the machine learning field. This guide shows how to deploy a Ray Cluster on Alibaba Cloud Container Service for Kubernetes (ACK).
Create a cluster
To create a cluster, see Create an ACK managed cluster. To upgrade your cluster, see Manually upgrade a cluster. Create an ACK Managed Cluster Pro that meets the following requirements.
Cluster version: v1.24 or later.
Instance Type: Requires at least one node with a minimum of 8 vCPUs and 32 GB of memory.
The recommended minimum specifications are for a test environment. For production environments, use specifications that match your actual workload. If you require GPU acceleration, configure GPU-accelerated nodes.
For more information about supported ECS instance types, see Instance family.
You have kubectl installed on your local machine and are connected to your Kubernetes cluster. For more information, see Obtain the KubeConfig file of a cluster and connect to the cluster by using kubectl.
Install the Kuberay-Operator component
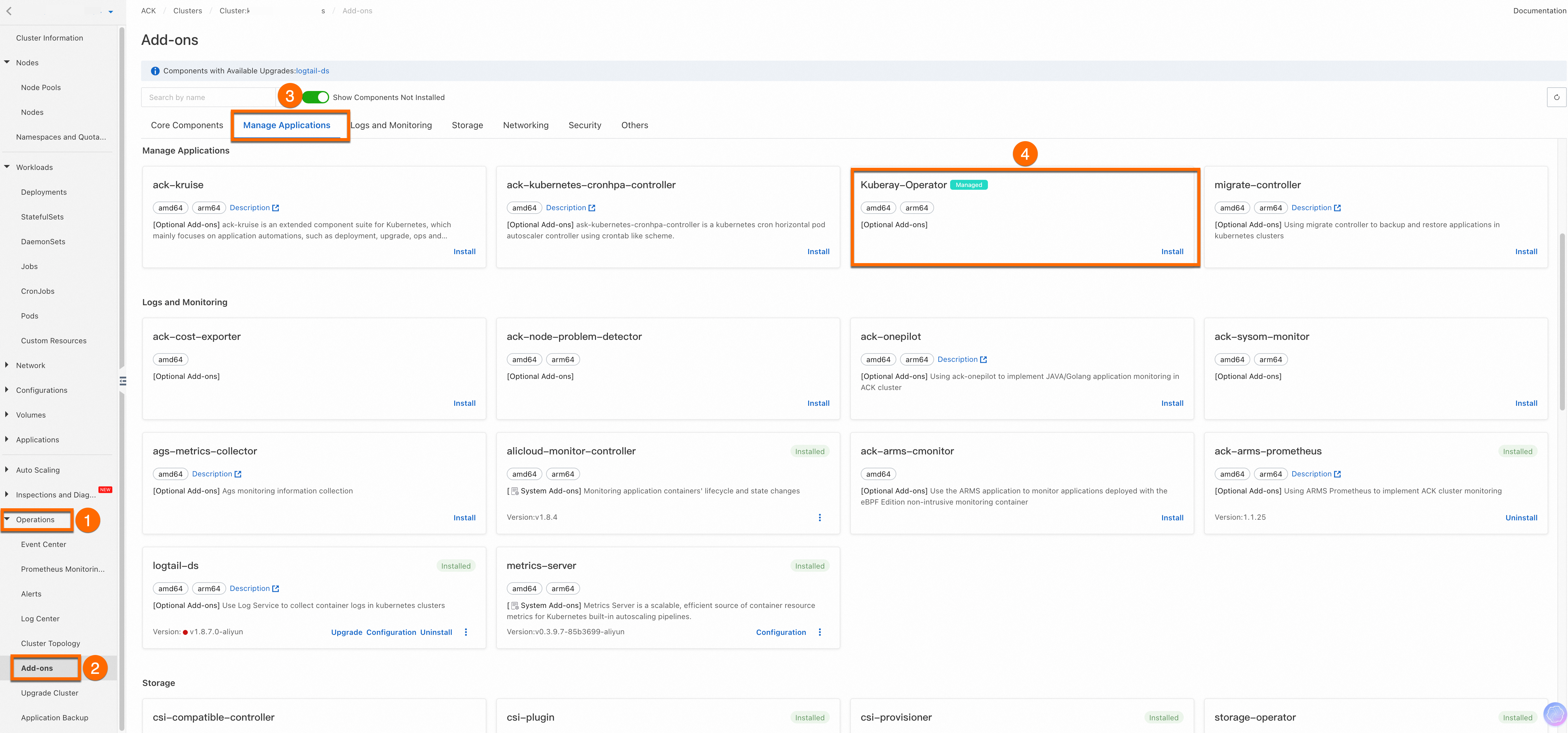
Log on to the Container Service for Kubernetes (ACK) console. In the left-side navigation pane, click Clusters. Click the name of your target cluster. Navigate to Operations > Add-ons > Manage Applications, then click Install under Kuberay-Operator.
Deploy the Ray Cluster
Solution for Docker Hub pull failures
Due to network instability, such as issues with carrier networks, image pulls from Docker Hub may fail. We recommend using images that rely on Docker Hub with caution in production environments. This example uses the official Ray image rayproject/ray:2.36.1. If you cannot pull this image, use one of the following solutions:
Subscribe to images from registries outside the Chinese mainland through Container Registry. For more information, see Subscribe to images outside China.
To directly pull images from overseas sources, create a Global Accelerator instance and use its global network acceleration service. For more information, see Use GA to accelerate cross-domain container image pulling in ACK.
Run the following commands to create a Ray Cluster named myfirst-ray-cluster and check its deployment status.
Run the following command to create the Ray Cluster resource.
Run the following commands to check the deployment status.
Check the status of the Ray Cluster.
kubectl get rayclusterExpected output:
NAME DESIRED WORKERS AVAILABLE WORKERS CPUS MEMORY GPUS STATUS AGE myfirst-ray-cluster 1 1 5 5G 0 ready 4m19sCheck the pods for the Ray Cluster.
kubectl get podExpected output:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE myfirst-ray-cluster-head-5q2hk 1/1 Running 0 4m37s myfirst-ray-cluster-work1-worker-zkjgq 1/1 Running 0 4m31sCheck the services for the Ray Cluster.
kubectl get svcExpected output:
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE kubernetes ClusterIP 192.168.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 21d myfirst-ray-cluster-head-svc ClusterIP None <none> 10001/TCP,8265/TCP,8080/TCP,6379/TCP,8000/TCP 6m57s