You can use preStop hooks to seamlessly terminate a backend pod associated with an Application Load Balancer (ALB) Ingress, ensuring that the pod is only shut down after they have been completely removed. The preStop hooks allow you to ensure seamless traffic switchover and prevent service interruptions during rolling updates of your service.
Prerequisites
An ACK managed cluster or ACK dedicated cluster is created and the Kubernetes version of the cluster is 1.18 or later. For more information, see Create an ACK managed cluster or Create an ACK dedicated cluster (discontinued). If you want to update the cluster, see Manually upgrade ACK clusters.
The ALB Ingress controller is installed in the cluster. For more information, see Manage the ALB Ingress controller.
NoteTo use an ALB Ingress to access Services deployed in an ACK dedicated cluster, you need to first grant the cluster the permissions required by the ALB Ingress controller. For more information, see Authorize an ACK dedicated cluster to access the ALB Ingress controller.
How it works
Pod lifecycle
A pod may contain the following types of containers:
Init container: Init containers run before main containers to complete specific initialization operations.
Main container: Main containers run the processes of applications.
The following figure shows the lifecycle of a pod.

Run init containers: Init containers run before main containers to complete specific initialization operations.
Run main containers:
The main container invokes the postStart hook function after the container is started.
The system performs a liveness check (liveness probe) and a readiness check (readiness probe) on the main container.
The main container invokes the preStop hook function before the container is terminated.
Pod termination procedure and traffic routing rule update procedure
When you delete a pod, the system performs the pod termination procedure and the traffic routing rule update procedure at the same time. The following list describes the procedures:
Pod termination procedure
kube-apiserver receives the deletion request and marks the pod as
Terminating.If a preStop hook is configured for the pod, the system executes the preStop hook.
The cluster sends a SIGTERM signal to the container.
The system waits until the container is terminated or until the graceful shutdown process of the pod times out.
NoteThe default grace period (
terminationGracePeriodSeconds) of a pod is 30 seconds.If the pod is not terminated within the grace period, the system sends a SIGKILL signal to the container.
The pod is deleted.
Traffic routing rule update procedure
kube-apiserver receives the deletion request and marks the pod as
Terminating.The endpoint controller deletes the IP address of the pod from the endpoint.
The ALB Ingress controller reconciles the backend servers and removes the Service endpoint from the backend server group. This way, traffic is no longer routed to the deleted pod.
Use a preStop hook to seamlessly terminate a pod
During a rolling update, if the old pod is not seamlessly terminated, the following status codes may be returned when you send requests to the service. This compromises the service availability.
Status code | Cause |
504 | The old pod was processing a non-idempotent request when the pod was deleted. |
502 | The old pod is deleted after receiving the SIGTERM signal from the system. However, the reconciliation is not completed by the ALB Ingress controller when the old pod is deleted. As a result, the pod still exists in the backend server group when the request is processed. |
To prevent the preceding issues, perform the following operations:
Add a preStop hook to the Deployment to specify a sleep duration that starts after kube-apiserver receives the deletion request. The sleep duration ensures a sufficient period of time for the container to update traffic routing rules and the ALB Ingress controller to reconcile the backend servers and remove the old pod from the backend server group before the pod receives the SIGTERM signal. This way, the pod can be seamlessly terminated to prevent service interruptions during rolling updates and restarts.
The default grace period (terminationGracePeriodSeconds) of a pod is 30 seconds. This indicates that the pod can continue running for 30 seconds after it receives the SIGTERM signal. If the sum of the program shutdown duration and the amount of time required to complete the operations defined by the preStop hook exceeds 30 seconds, the graceful shutdown of the pod times out. After the grace period ends, the kubelet waits 2 seconds and sends a SIGKILL signal to the pod to forcefully terminate the pod.
In this case, we recommend that you increase the grace period (terminationGracePeriodSeconds) to ensure a sufficient period of time to complete the preceding operations.
Step 1: Configure a preStop hook for a pod
Create a file named tea-service.yaml and copy the following content to the file. The file includes the preStop hook that is added to ensure seamless pod termination.
apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: tea spec: replicas: 3 selector: matchLabels: app: tea template: metadata: labels: app: tea spec: containers: - name: tea image: registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/acs-sample/nginxdemos:latest ports: - containerPort: 80 lifecycle: # Specify a preStop hook function that requires kube-apiserver to wait 10 seconds before sending the SIGTERM signal to the pod. preStop: # The preStop hook configurations. exec: # Perform the operations defined by the preStop hook by running commands. command: # The command to run. - /bin/sh - -c - "sleep 10" # Sleep for 10 seconds. terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 45 # Specify the grace period of the pod. --- apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: tea-svc spec: ports: - port: 80 targetPort: 80 protocol: TCP selector: app: tea type: NodePortRun the following command to deploy a test Deployment and a test Service:
kubectl apply -f tea-service.yamlCreate a file named tea-ingress.yaml and copy the following content to the file. The file is used to create an Ingress.
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: Ingress metadata: name: tea-ingress spec: ingressClassName: alb rules: - host: demo.ingress.top http: paths: - path: / pathType: Prefix backend: service: name: tea-svc port: number: 80Run the following command to create the Ingress:
kubectl apply -f tea-ingress.yamlRun the following command to query the
ADDRESSparameter of the ALB Ingress:kubectl get ingressExpected output:
NAME CLASS HOSTS ADDRESS PORTS AGE tea-ingress alb demo.ingress.top alb-110zvs5nhsvfv*****.cn-chengdu.alb.aliyuncs.com 80 7m5s
Step 2: Test whether the preStop hook takes effect
Execute a test script.
Create a script named
test.shand copy the following content to the script. The script is used to test the service availability by sending requests to the NGINX service on a per-second basis and recording the returned status codes.#!/bin/bash HOST="demo.ingress.top" DNS="alb-110zvs5nhsvfv*****.cn-chengdu.alb.aliyuncs.com" # Set the value to the value of the ADDRESS parameter of the ALB Ingress. printf "Response Code|| TIME \n" >> log.txt while true; do RESPONSE=$(curl -H Host:$HOST -s -o /dev/null -w "%{http_code}" -m 1 http://$DNS/) TIMESTAMP=$(date +%Y-%m-%d_%H:%M:%S) echo "$TIMESTAMP - $RESPONSE" >> log.txt sleep 1 doneRun the following command to execute the
test.shscript:bash test.sh
Run the following command to start a rolling update for the application and redeploy the application:
kubectl rollout restart deploy teaVerify the update.
The number of replicated pods before the rolling update is three.

During the redeployment, two old pods still run when new pods are not ready to process requests.
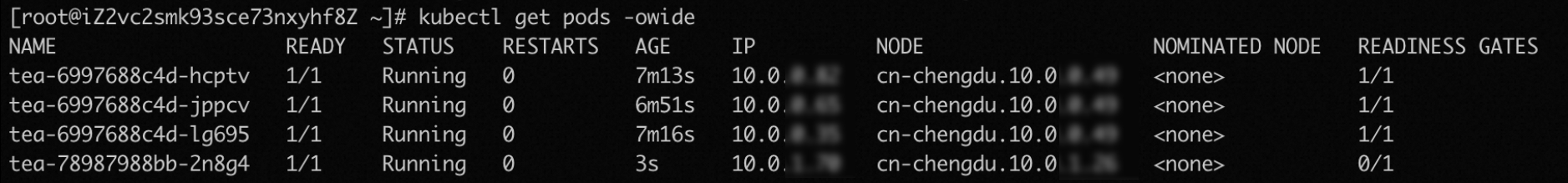
After the new pods are ready to process requests and added to the backend server group of the ALB instance, the old pods are terminated.
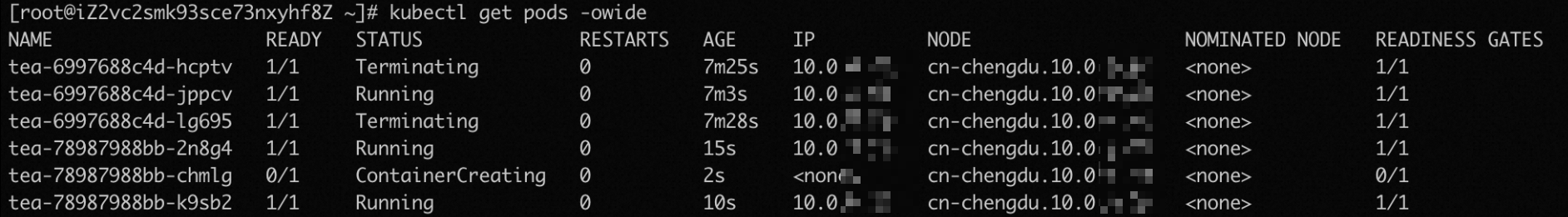
After all old pods complete running the preStop hook function or the
graceful shutdownof the pods times out, thekubectlsends a signal to the old pods to terminate them. After the pods are terminated, the rolling update is completed.
View the execution result of the test script. If 200 is returned for each request, no service interruption occurs during the rolling update.
Run the following command to view the execution result of the test script:
cat log.txtExpected output:
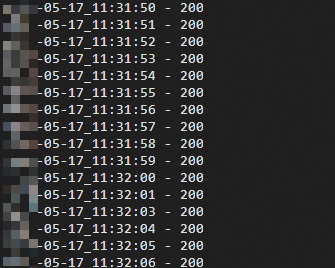
References
You can use the ALB Ingress to forward requests, redirect HTTP requests to HTTPS, and implement canary releases. For more information, see Advanced ALB Ingress configurations.
To configure readiness gates to ensure the readiness of pods before they are launched, see Use readiness gates to seamlessly launch pods that are associated with ALB Ingresses during rolling updates.
If errors occur when you use ALB Ingresses, refer to ALB Ingress FAQ and ALB Ingress controller troubleshooting.