Database Autonomy Service (DAS) provides the storage analysis feature. You can use this feature to view the storage usage of a database instance and the expected number of days after which the remaining storage may be insufficient. You can also view information about the storage usage, fragments, and anomaly diagnosis results of a tablespace in a database. This topic provides an example to describe how to use the storage analysis feature. In this example, an ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance is used.
Prerequisites
A database instance is connected to DAS. Make sure that the database instance is one of the following types:- ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL, PolarDB for MySQL, ApsaraDB MyBase for MySQL, and self-managed MySQL databases
- ApsaraDB for MongoDB and self-managed MongoDB databases
- ApsaraDB RDS for PostagreSQL and PolarDB for PostgreSQL databases
- PolarDB for PostgreSQL (Compatible with Oracle)
- PolarDB-X 2.0
View global storage usage
If you use DAS to manage multiple database instances of the same type, you can view the storage usage of the database instances on the Global Storage Usage page. This helps you find the database instance that has the highest storage usage.
- ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL
- Self-managed MySQL
- ApsaraDB for MongoDB
- Self-managed MongoDB
- Log on to the DAS console.
- In the left-side navigation pane, click Storage Analysis. Then, the Global Storage Usage page appears. You can view information about the storage usage of all database instances of the same type.
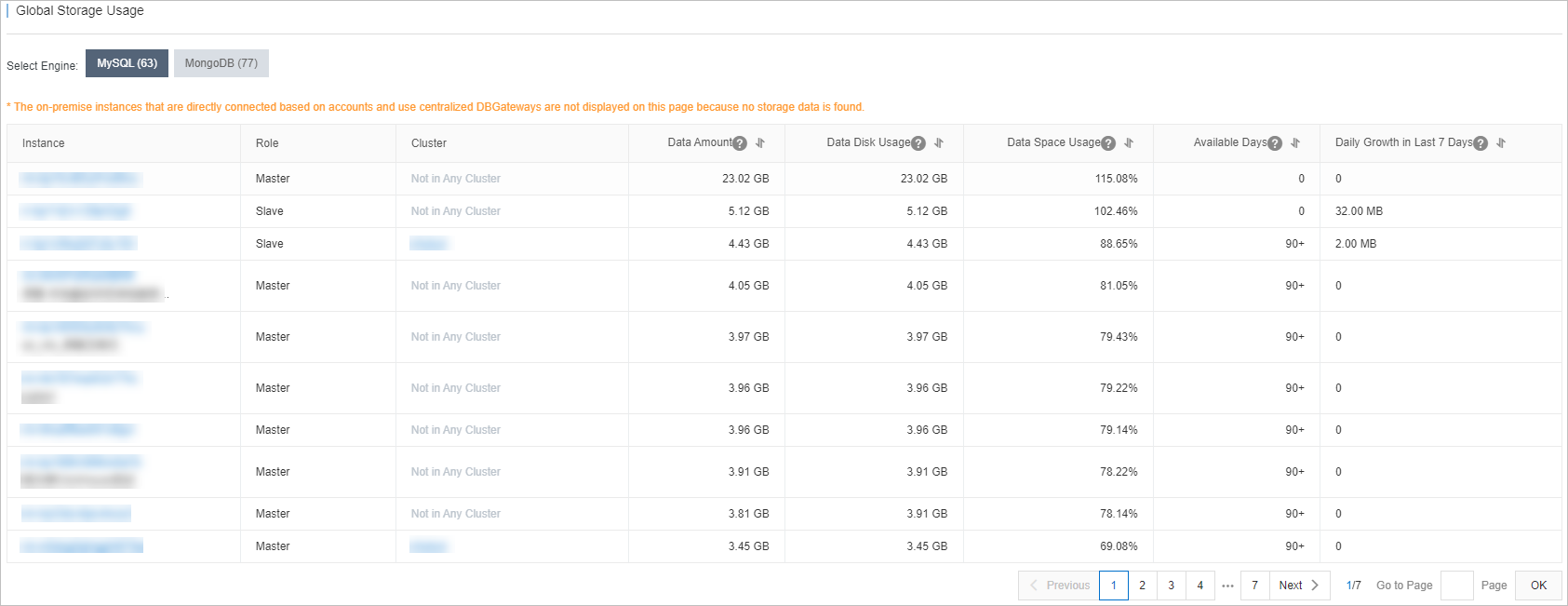
Self-managed database instances that are connected to DAS by using the Direct Access or Centralized DBGateway method are not displayed on the Global Storage Usage page because DAS cannot collect their storage data.
NoteSelf-managed databases can be connected to DAS by using multiple methods. For more information about how to connect self-managed databases to DAS, see Access instances.
- Direct Access: Self-managed databases are directly connected to DAS.
- Centralized DBGateway: Self-managed databases are connected to DAS by using DBGateway in centralized mode.
View the storage analysis results of a single database instance
- Log on to the DAS console.
- In the left-side navigation pane, click Instance Monitoring.
- On the page that appears, find the database instance that you want to manage and click the instance ID. The instance details page appears.
- In the left-side navigation pane, click Storage Analysis.
- On the Storage Overview and Data Space tabs, you can view the storage usage of the database instance.
Tab Section Description Storage Overview Storage You can view the following storage information: Exception, Avg Daily Increase in Last Week, Available Days of Storage, and Used Storage. Exceptions You can view the exception information of tables or collections in the database instance. If the automatic space optimization feature is enabled for the database instance, you can also view the space optimization history. DAS can identify the following exceptions:- Potential overflows of auto-increment primary keys: DAS can automatically identify potential overflows of auto-increment primary keys in ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instances and PolarDB for MySQL clusters.
- Duplicate indexes: DAS can automatically identify duplicate indexes in ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instances and PolarDB for MySQL clusters.
- Tablespace fragments: For more information, see Automatic tablespace fragment recycling.
Storage Trend You can view the usage trend of data space, used storage, log space, and temporary space over the last week. Tablespaces You can view the detailed information and storage usage of each table in the database instance. Click the name of a table to view the fields and indexes of the table. Data Space You can view the storage usage of each database in the RDS instance and the storage usage of tables in the database. Click the name of a table to view the fields and indexes of the table.