This topic describes how to use TPC-H, a decision support benchmark, to run performance tests for OLAP query and Key/Value point query scenarios.
Introduction to TPC-H
The following description is quoted from the TPC Benchmark™ H (TPC-H) specification:
"TPC-H is a decision support benchmark. It consists of a suite of business-oriented ad-hoc queries and concurrent data modifications. The queries and the data populating the database have been chosen to have broad industry-wide relevance. This benchmark illustrates decision support systems that examine large volumes of data, execute queries with a high degree of complexity, and provide answers to critical business questions."
For more information, see the TPC-H Specification.
The TPC-H implementation in this topic is based on TPC-H benchmarking. The results cannot be compared with published TPC-H benchmark results. The tests in this topic do not comply with all the requirements of TPC-H benchmarking.
Dataset introduction
TPC-H is a test set developed by the Transaction Processing Performance Council (TPC) to simulate decision support applications. It is widely used in academia and industry to evaluate the performance of decision support technologies.
TPC-H models a real production environment and simulates a data warehouse for a sales system. It contains eight tables, and the data volume can be scaled from 1 GB to 3 TB. The benchmark includes 22 queries. The primary evaluation method is the response time for each query, defined as the time from query submission to result retrieval. The test results reflect the system's overall query processing capability. For more information, see TPC-H Benchmark.
Scenario description
This test scenario includes the following parts:
-
OLAP query scenario test: Uses column-oriented tables and runs the 22 query statements from the TPC-H test.
-
Key/Value point query scenario test: Uses row-oriented tables and performs point queries with primary key filtering on the ORDERS table.
-
Data update scenario: Tests the data update performance of the OLAP engine when a primary key exists.
The data volume directly affects the test results. The TPC-H generation tool uses a scale factor (SF) to control the size of the generated data. 1 SF corresponds to 1 GB.
The data volume mentioned applies only to the raw data. It does not include space for indexes. Therefore, reserve additional space when you prepare the environment.
Notes
To reduce variables that might affect the test results, create a new instance for each test. Do not use instances that have been upgraded or downgraded.
OLAP query scenario test
-
Preparations
Prepare the basic environment for the OLAP query scenario.
-
Create a Hologres instance. For more information, see Purchase a Hologres instance. This test uses a dedicated pay-as-you-go instance. Because the instance is only for testing, the compute resources are set to 96 cores and 384 GB. Select the compute resource specifications based on your business needs.
-
Create an ECS instance. For more information, see Create an ECS instance. The ECS instance type used in this topic is as follows:
Parameter
Specification
Specification
ecs.g6.4xlarge
Image
Alibaba Cloud Linux 3.2104 LTS 64-bit
Data disk
Type: enterprise SSD. The specific data capacity depends on the test data volume.
-
-
Download and configure the Hologres Benchmark test toolkit.
-
Log on to the ECS instance. For more information, see Connect to an ECS instance.
-
Install the PSQL client.
yum update -y yum install postgresql-server -y yum install postgresql-contrib -y -
Download and decompress the Hologres Benchmark test toolkit.
wget https://oss-tpch.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/hologres_benchmark.tar.gz tar xvf hologres_benchmark.tar.gz -
Go to the hologres_benchmark directory.
cd hologres_benchmark -
Run the
vim group_vars/allcommand to configure the benchmark parameters.# DB config login_host: "" login_user: "" login_password: "" login_port: "" # Benchmark run cluster: hologres cluster: "hologres" RUN_MODE: "HOTRUN" # Benchmark config scale_factor: 1 work_dir_root: /your/working_dir/benchmark/workdirs dataset_generate_root_path: /your/working_dir/benchmark/datasetsParameter descriptions:
Type
Parameter
Description
Hologres service connection parameters
login_host
The VPC domain name of the Hologres instance.
Log on to the Management Console, go to the instance details page, and obtain the domain name for the specified VPC from the Domain Name column in the Network Information section.
NoteThe domain name does not include the port. Example:
hgpostcn-cn-nwy364b5v009-cn-shanghai-vpc-st.hologres.aliyuncs.comlogin_port
The VPC port of the Hologres instance.
Log on to the Management Console, go to the instance details page, and obtain the port from the Domain Name column in the Network Information section.
login_user
The AccessKey ID of your account.
Click AccessKey Management to obtain the AccessKey ID.
login_password
The AccessKey secret of your account.
Benchmark configuration parameters
scale_factor
The scale factor of the dataset, which controls the size of the generated data. The default value is 1. The unit is GB.
work_dir_root
The root directory of the working directory. It stores TPC-H related data such as table creation statements and SQL statements to be executed. The default value is
/your/working_dir/benchmark/workdirs.dataset_generate_root_path
The path where the generated test dataset is stored. The default value is
/your/working_dir/benchmark/datasets.
-
-
Run the following command to perform an end-to-end automated TPC-H test.
The end-to-end automated TPC-H test includes generating data, creating a test database named tpc_h_sf<scale_factor> (for example, tpc_h_sf1000), creating tables, and importing data.
bin/run_tpch.shYou can also run the following command to perform only the TPC-H query test.
bin/run_tpch.sh query -
View the test results.
-
Test result overview
After the
bin/run_tpch.shcommand is run, the test results are displayed directly. The results resemble the following output.TASK [tpc_h : debug] ************************************************************************************************** skipping: [worker-1] ok: [master] => { "command_output.stdout_lines": [ "[info] 2024-06-28 14:46:09.768 | Run sql queries started.", "[info] 2024-06-28 14:46:09.947 | Run q10.sql started.", "[info] 2024-06-28 14:46:10.088 | Run q10.sql finished. Time taken: 0:00:00, 138 ms", "[info] 2024-06-28 14:46:10.239 | Run q11.sql started.", "[info] 2024-06-28 14:46:10.396 | Run q11.sql finished. Time taken: 0:00:00, 154 ms", "[info] 2024-06-28 14:46:10.505 | Run q12.sql started.", "[info] 2024-06-28 14:46:10.592 | Run q12.sql finished. Time taken: 0:00:00, 85 ms", "[info] 2024-06-28 14:46:10.703 | Run q13.sql started.", "[info] 2024-06-28 14:46:10.793 | Run q13.sql finished. Time taken: 0:00:00, 88 ms", "[info] 2024-06-28 14:46:10.883 | Run q14.sql started.", "[info] 2024-06-28 14:46:10.981 | Run q14.sql finished. Time taken: 0:00:00, 95 ms", "[info] 2024-06-28 14:46:11.132 | Run q15.sql started.", "[info] 2024-06-28 14:46:11.266 | Run q15.sql finished. Time taken: 0:00:00, 131 ms", "[info] 2024-06-28 14:46:11.441 | Run q16.sql started.", "[info] 2024-06-28 14:46:11.609 | Run q16.sql finished. Time taken: 0:00:00, 165 ms", "[info] 2024-06-28 14:46:11.728 | Run q17.sql started.", "[info] 2024-06-28 14:46:11.818 | Run q17.sql finished. Time taken: 0:00:00, 88 ms", "[info] 2024-06-28 14:46:12.017 | Run q18.sql started.", "[info] 2024-06-28 14:46:12.184 | Run q18.sql finished. Time taken: 0:00:00, 164 ms", "[info] 2024-06-28 14:46:12.287 | Run q19.sql started.", "[info] 2024-06-28 14:46:12.388 | Run q19.sql finished. Time taken: 0:00:00, 98 ms", "[info] 2024-06-28 14:46:12.503 | Run q1.sql started.", "[info] 2024-06-28 14:46:12.597 | Run q1.sql finished. Time taken: 0:00:00, 93 ms", "[info] 2024-06-28 14:46:12.732 | Run q20.sql started.", "[info] 2024-06-28 14:46:12.888 | Run q20.sql finished. Time taken: 0:00:00, 154 ms", "[info] 2024-06-28 14:46:13.184 | Run q21.sql started.", "[info] 2024-06-28 14:46:13.456 | Run q21.sql finished. Time taken: 0:00:00, 269 ms", "[info] 2024-06-28 14:46:13.558 | Run q22.sql started.", "[info] 2024-06-28 14:46:13.657 | Run q22.sql finished. Time taken: 0:00:00, 97 ms", "[info] 2024-06-28 14:46:13.796 | Run q2.sql started.", "[info] 2024-06-28 14:46:13.935 | Run q2.sql finished. Time taken: 0:00:00, 136 ms", "[info] 2024-06-28 14:46:14.051 | Run q3.sql started.", "[info] 2024-06-28 14:46:14.155 | Run q3.sql finished. Time taken: 0:00:00, 101 ms", "[info] 2024-06-28 14:46:14.255 | Run q4.sql started.", "[info] 2024-06-28 14:46:14.341 | Run q4.sql finished. Time taken: 0:00:00, 83 ms", "[info] 2024-06-28 14:46:14.567 | Run q5.sql started.", "[info] 2024-06-28 14:46:14.799 | Run q5.sql finished. Time taken: 0:00:00, 230 ms", "[info] 2024-06-28 14:46:14.881 | Run q6.sql started.", "[info] 2024-06-28 14:46:14.950 | Run q6.sql finished. Time taken: 0:00:00, 67 ms", "[info] 2024-06-28 14:46:15.138 | Run q7.sql started.", "[info] 2024-06-28 14:46:15.320 | Run q7.sql finished. Time taken: 0:00:00, 180 ms", "[info] 2024-06-28 14:46:15.572 | Run q8.sql started.", "[info] 2024-06-28 14:46:15.831 | Run q8.sql finished. Time taken: 0:00:00, 256 ms", "[info] 2024-06-28 14:46:16.081 | Run q9.sql started.", "[info] 2024-06-28 14:46:16.322 | Run q9.sql finished. Time taken: 0:00:00, 238 ms", "[info] 2024-06-28 14:46:16.325 | ----------- HOT RUN finished. Time taken: 3255 mill_sec -----------------" ] } skipping: [worker-2] skipping: [worker-3] skipping: [worker-4] TASK [tpc_h : clear Env] ********************************************************************************************** skipping: [worker-1] skipping: [worker-2] skipping: [worker-3] skipping: [worker-4] ok: [master] TASK [tpc_h : debug] ************************************************************************************************** ok: [master] => { "work_dir": "/your/working_dir/benchmark/workdirs/tpc_h/sf1" } skipping: [worker-1] skipping: [worker-2] skipping: [worker-3] skipping: [worker-4] -
Test result details
After you run the
bin/run_tpch.shcommand, the system builds the entire TPC-H test working directory and outputs the path of the<work_dir>directory. You can switch to this path to view related information such as query statements, table creation statements, and execution logs. The following figure shows an example.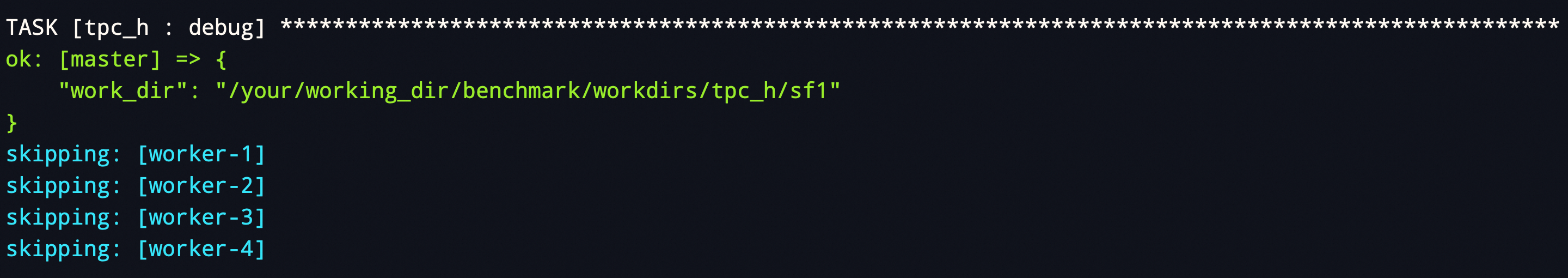
Run the
cd <work_dir>/logscommand to go to the logs directory in the working directory. You can view the test results and the detailed results of the executed SQL statements.The directory structure of
<work_dir>is as follows.working_dir/ `-- benchmark |-- datasets | `-- tpc_h | `-- sf1 | |-- worker-1 | | |-- customer.tbl | | `-- lineitem.tbl | |-- worker-2 | | |-- orders.tbl | | `-- supplier.tbl | |-- worker-3 | | |-- nation.tbl | | `-- partsupp.tbl | `-- worker-4 | |-- part.tbl | `-- region.tbl `-- workdirs `-- tpc_h `-- sf1 |-- config |-- hologres | |-- logs | | |-- q10.sql.err | | |-- q10.sql.out | | |-- q11.sql.err | | |-- q11.sql.out | | |-- q12.sql.err | | |-- q12.sql.out | | |-- q13.sql.err | | |-- q13.sql.out | | |-- q14.sql.err | | |-- q14.sql.out | | |-- q15.sql.err | | |-- q15.sql.out | | |-- q16.sql.err | | |-- q16.sql.out | | |-- q17.sql.err | | |-- q17.sql.out | | |-- q18.sql.err | | |-- q18.sql.out | | |-- q19.sql.err | | |-- q19.sql.out | | |-- q1.sql.err | | |-- q1.sql.out | | |-- q20.sql.err | | |-- q20.sql.out | | |-- q21.sql.err | | |-- q21.sql.out | | |-- q22.sql.err | | |-- q22.sql.out | | |-- q2.sql.err | | |-- q2.sql.out | | |-- q3.sql.err | | |-- q3.sql.out | | |-- q4.sql.err | | |-- q4.sql.out | | |-- q5.sql.err | | |-- q5.sql.out | | |-- q6.sql.err | | |-- q6.sql.out | | |-- q7.sql.err | | |-- q7.sql.out | | |-- q8.sql.err | | |-- q8.sql.out | | |-- q9.sql.err | | |-- q9.sql.out | | `-- run.log | `-- logs-20240628144609 | |-- q10.sql.err | |-- q10.sql.out | |-- q11.sql.err | |-- q11.sql.out | |-- q12.sql.err | |-- q12.sql.out | |-- q13.sql.err | |-- q13.sql.out | |-- q14.sql.err | |-- q14.sql.out | |-- q15.sql.err | |-- q15.sql.out | |-- q16.sql.err | |-- q16.sql.out | |-- q17.sql.err | |-- q17.sql.out | |-- q18.sql.err | |-- q18.sql.out | |-- q19.sql.err | |-- q19.sql.out | |-- q1.sql.err | |-- q1.sql.out | |-- q20.sql.err | |-- q20.sql.out | |-- q21.sql.err | |-- q21.sql.out | |-- q22.sql.err | |-- q22.sql.out | |-- q2.sql.err | |-- q2.sql.out | |-- q3.sql.err | |-- q3.sql.out | |-- q4.sql.err | |-- q4.sql.out | |-- q5.sql.err | |-- q5.sql.out | |-- q6.sql.err | |-- q6.sql.out | |-- q7.sql.err | |-- q7.sql.out | |-- q8.sql.err | |-- q8.sql.out | |-- q9.sql.err | |-- q9.sql.out | `-- run.log |-- queries | |-- ddl | | |-- hologres_analyze_tables.sql | | `-- hologres_create_tables.sql | |-- q10.sql | |-- q11.sql | |-- q12.sql | |-- q13.sql | |-- q14.sql | |-- q15.sql | |-- q16.sql | |-- q17.sql | |-- q18.sql | |-- q19.sql | |-- q1.sql | |-- q20.sql | |-- q21.sql | |-- q22.sql | |-- q2.sql | |-- q3.sql | |-- q4.sql | |-- q5.sql | |-- q6.sql | |-- q7.sql | |-- q8.sql | `-- q9.sql |-- run_hologres.sh |-- run_mysql.sh |-- run.sh `-- tpch_tools |-- dbgen |-- qgen `-- resouces |-- dists.dss `-- queries |-- 10.sql |-- 11.sql |-- 12.sql |-- 13.sql |-- 14.sql |-- 15.sql |-- 16.sql |-- 17.sql |-- 18.sql |-- 19.sql |-- 1.sql |-- 20.sql |-- 21.sql |-- 22.sql |-- 2.sql |-- 3.sql |-- 4.sql |-- 5.sql |-- 6.sql |-- 7.sql |-- 8.sql `-- 9.sql
-
Key/Value point query scenario test
For the Key/Value point query scenario test, you can continue to use the hologres_tpch database and the orders table created in the OLAP query scenario test. The steps are as follows:
-
Create a table
Because the Key/Value point query scenario uses a row-oriented table, you cannot directly use the orders table from the OLAP query scenario test. You must create a new table. Connect to Hologres using a PSQL client and run the following command to create the orders_row table.
NoteFor more information about how to connect to Hologres using a PSQL client, see Connect to Hologres for development.
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS public.orders_row; BEGIN; CREATE TABLE public.orders_row( O_ORDERKEY BIGINT NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY ,O_CUSTKEY INT NOT NULL ,O_ORDERSTATUS TEXT NOT NULL ,O_TOTALPRICE DECIMAL(15,2) NOT NULL ,O_ORDERDATE TIMESTAMPTZ NOT NULL ,O_ORDERPRIORITY TEXT NOT NULL ,O_CLERK TEXT NOT NULL ,O_SHIPPRIORITY INT NOT NULL ,O_COMMENT TEXT NOT NULL ); CALL SET_TABLE_PROPERTY('public.orders_row', 'orientation', 'row'); CALL SET_TABLE_PROPERTY('public.orders_row', 'clustering_key', 'o_orderkey'); CALL SET_TABLE_PROPERTY('public.orders_row', 'distribution_key', 'o_orderkey'); COMMIT; -
Import data
Use the following INSERT INTO statement to import data from the orders table in the TPC-H dataset to the orders_row table.
NoteHologres V2.1.17 and later support Serverless Computing. For scenarios such as large-scale offline data import, large extract, transform, and load (ETL) jobs, and large-volume queries on foreign tables, you can use Serverless Computing to execute these tasks. This feature uses additional serverless resources instead of your instance's own resources. You do not need to reserve extra compute resources for your instance. This significantly improves instance stability, reduces the probability of out-of-memory (OOM) errors, and you are charged only for the individual tasks. For more information about Serverless Computing, see Serverless Computing. For information about how to use Serverless Computing, see Guide to using Serverless Computing.
-- (Optional) Use Serverless Computing to perform large-scale offline data import and ETL jobs. SET hg_computing_resource = 'serverless'; INSERT INTO public.orders_row SELECT * FROM public.orders; -- Reset the configuration to ensure that unnecessary SQL statements do not use serverless resources. RESET hg_computing_resource; -
Run queries
-
Generate query statements.
The Key/Value point query scenario has two main query types. The query statements are as follows:
Query method
Query statement
Description
Single-value filter
SELECT column_a ,column_b ,... ,column_x FROM table_x WHERE pk = value_x ;This query statement is used for single-value filtering, where the
WHEREclause of the SQL statement has a unique value.Multi-value filter
SELECT column_a ,column_b ,... ,column_x FROM table_x WHERE pk IN ( value_a, value_b,..., value_x ) ;This query statement is used for multi-value filtering, where the
WHEREclause of the SQL statement can have multiple values.Use the following script to generate the required SQL statements.
rm -rf kv_query mkdir kv_query cd kv_query echo " \set column_values random(1,99999999) select O_ORDERKEY,O_CUSTKEY,O_ORDERSTATUS,O_TOTALPRICE,O_ORDERDATE,O_ORDERPRIORITY,O_CLERK,O_SHIPPRIORITY,O_COMMENT from public.orders_row WHERE o_orderkey =:column_values; " >> kv_query_single.sql echo " \set column_values1 random(1,99999999) \set column_values2 random(1,99999999) \set column_values3 random(1,99999999) \set column_values4 random(1,99999999) \set column_values5 random(1,99999999) \set column_values6 random(1,99999999) \set column_values7 random(1,99999999) \set column_values8 random(1,99999999) \set column_values9 random(1,99999999) select O_ORDERKEY,O_CUSTKEY,O_ORDERSTATUS,O_TOTALPRICE,O_ORDERDATE,O_ORDERPRIORITY,O_CLERK,O_SHIPPRIORITY,O_COMMENT from public.orders_row WHERE o_orderkey in(:column_values1,:column_values2,:column_values3,:column_values4,:column_values5,:column_values6,:column_values7,:column_values8,:column_values9); " >> kv_query_in.sqlAfter the script is run, two SQL files are generated:
-
kv_query_single.sql: The SQL for single-value filtering. -
kv_query_in.sql: The SQL for multi-value filtering. This script randomly generates an SQL statement that filters for 10 values.
-
-
To facilitate the collection of query statistics, use the pgbench tool. Run the following command to install the pgbench tool.
yum install postgresql-contrib -yTo avoid test issues caused by tool incompatibility, install pgbench 13 or later. If you have already installed the pgbench tool, make sure its version is 9.6 or later. Run the following command to check the current tool version.
pgbench --version -
Run the test statements.
NoteRun the following commands in the directory where the query statements were generated.
-
For the single-value filtering scenario, use the pgbench tool for stress testing.
PGUSER=<AccessKey_ID> PGPASSWORD=<AccessKey_Secret> PGDATABASE=<Database> pgbench -h <Endpoint> -p <Port> -c <Client_Num> -T <Query_Seconds> -M prepared -n -f kv_query_single.sql -
For the multi-value filtering scenario, use the pgbench tool for stress testing.
PGUSER=<AccessKey_ID> PGPASSWORD=<AccessKey_Secret> PGDATABASE=<Database> pgbench -h <Endpoint> -p <Port> -c <Client_Num> -T <Query_Seconds> -M prepared -n -f kv_query_in.sql
The following table describes the parameters.
Parameter
Description
AccessKey_ID
The AccessKey ID of your Alibaba Cloud account.
Click AccessKey Management to obtain the AccessKey ID.
AccessKey_Secret
The AccessKey secret of your Alibaba Cloud account.
Click AccessKey Management to obtain the AccessKey secret.
Database
-
The name of the Hologres database.
-
After you activate a Hologres instance, the system automatically creates the postgres database.
-
You can use the postgres database to connect to Hologres. However, this database is allocated few resources. For business development, create a new database. For more information, see Create a database.
Endpoint
The network address (Endpoint) of the Hologres instance.
Go to the instance details page in the Hologres console and obtain the network address from the Network Information section.
Port
The network port of the Hologres instance.
Go to the Instance Details page in the Hologres console to obtain the network port.
Client_Num
The number of clients, which is the concurrency.
For example, this test only evaluates query performance, not concurrency. Set the concurrency to 1.
Query_Seconds
The stress testing duration (in seconds) for each query run by each client. For example, this parameter is set to 300 in this topic.
-
-
Data update scenario
This scenario tests the data update performance of the OLAP engine when a primary key exists and the performance of updating an entire row when a primary key conflict occurs.
-
Generate a query
echo " \set O_ORDERKEY random(1,99999999) INSERT INTO public.orders_row(o_orderkey,o_custkey,o_orderstatus,o_totalprice,o_orderdate,o_orderpriority,o_clerk,o_shippriority,o_comment) VALUES (:O_ORDERKEY,1,'demo',1.1,'2021-01-01','demo','demo',1,'demo') on conflict(o_orderkey) do update set (o_orderkey,o_custkey,o_orderstatus,o_totalprice,o_orderdate,o_orderpriority,o_clerk,o_shippriority,o_comment)= ROW(excluded.*); " > /root/insert_on_conflict.sql -
Insert and update. For more information about the parameters, see Parameter description.
PGUSER=<AccessKey_ID> PGPASSWORD=<AccessKey_Secret> PGDATABASE=<Database> pgbench -h <Endpoint> -p <Port> -c <Client_Num> -T <Query_Seconds> -M prepared -n -f /root/insert_on_conflict.sql -
Sample result
transaction type: Custom query scaling factor: 1 query mode: prepared number of clients: 249 number of threads: 1 duration: 60 s number of transactions actually processed: 1923038 tps = 32005.850214 (including connections establishing) tps = 36403.145722 (excluding connections establishing)
Flink real-time write scenario
This scenario tests the real-time data write capability.
-
Hologres DDL
In this scenario, the Hologres table has 10 columns, and the
keycolumn is the primary key. The Hologres DDL is as follows.DROP TABLE IF EXISTS flink_insert; BEGIN ; CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS flink_insert( key INT PRIMARY KEY ,value1 TEXT ,value2 TEXT ,value3 TEXT ,value4 TEXT ,value5 TEXT ,value6 TEXT ,value7 TEXT ,value8 TEXT ,value9 TEXT ); CALL SET_TABLE_PROPERTY('flink_insert', 'orientation', 'row'); CALL SET_TABLE_PROPERTY('flink_insert', 'clustering_key', 'key'); CALL SET_TABLE_PROPERTY('flink_insert', 'distribution_key', 'key'); COMMIT; -
Flink job script
Use the random number generator that comes with fully managed Flink to write data to Hologres. If a primary key conflict occurs, the entire row is updated. The data volume of a single row exceeds 512 B. The Flink job script is as follows.
CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE flink_case_1_source ( key INT, value1 VARCHAR, value2 VARCHAR, value3 VARCHAR, value4 VARCHAR, value5 VARCHAR, value6 VARCHAR, value7 VARCHAR, value8 VARCHAR, value9 VARCHAR ) WITH ( 'connector' = 'datagen', -- optional options -- 'rows-per-second' = '1000000000', 'fields.key.min'='1', 'fields.key.max'='2147483647', 'fields.value1.length' = '57', 'fields.value2.length' = '57', 'fields.value3.length' = '57', 'fields.value4.length' = '57', 'fields.value5.length' = '57', 'fields.value6.length' = '57', 'fields.value7.length' = '57', 'fields.value8.length' = '57', 'fields.value9.length' = '57' ); -- Create a Hologres sink table. CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE flink_case_1_sink ( key INT, value1 VARCHAR, value2 VARCHAR, value3 VARCHAR, value4 VARCHAR, value5 VARCHAR, value6 VARCHAR, value7 VARCHAR, value8 VARCHAR, value9 VARCHAR ) WITH ( 'connector' = 'hologres', 'dbname'='<yourDbname>', --The name of the Hologres database. 'tablename'='<yourTablename>', --The name of the Hologres table that receives data. 'username'='<yourUsername>', --The AccessKey ID of your Alibaba Cloud account. 'password'='<yourPassword>', --The AccessKey secret of your Alibaba Cloud account. 'endpoint'='<yourEndpoint>', --The VPC endpoint of the Hologres instance. 'connectionSize' = '10', --The default value is 3. 'jdbcWriteBatchSize' = '1024', --The default value is 256. 'jdbcWriteBatchByteSize' = '2147483647', --The default value is 20971520. 'mutatetype'='insertorreplace' --Inserts data or replaces an entire existing row. ); -- Perform ETL operations and write data. insert into flink_case_1_sink select key, value1, value2, value3, value4, value5, value6, value7, value8, value9 from flink_case_1_source ;For parameter descriptions, see Hologres sink table.
-
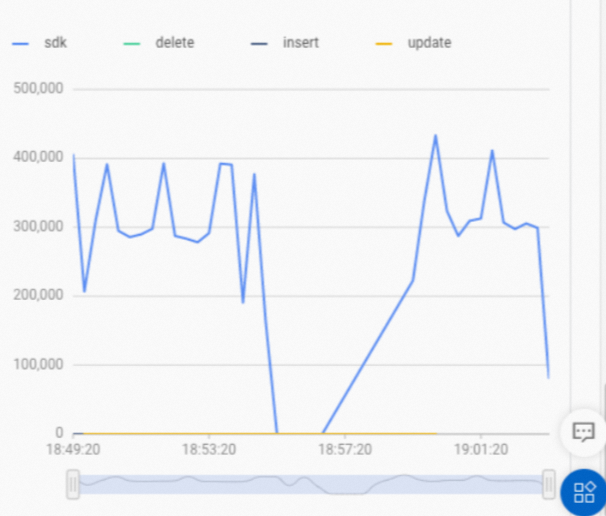
Sample result
On the Monitoring Information page of the Hologres console, you can view the RPS value.
The 22 TPC-H query statements
The 22 TPC-H query statements are as follows. You can click the links in the table to view them.
|
Name |
Query statement |
|||
|
The 22 TPC-H query statements |
||||
|
- |
- |
|||
-
Q1
select l_returnflag, l_linestatus, sum(l_quantity) as sum_qty, sum(l_extendedprice) as sum_base_price, sum(l_extendedprice * (1 - l_discount)) as sum_disc_price, sum(l_extendedprice * (1 - l_discount) * (1 + l_tax)) as sum_charge, avg(l_quantity) as avg_qty, avg(l_extendedprice) as avg_price, avg(l_discount) as avg_disc, count(*) as count_order from lineitem where l_shipdate <= date '1998-12-01' - interval '120' day group by l_returnflag, l_linestatus order by l_returnflag, l_linestatus; -
Q2
select s_acctbal, s_name, n_name, p_partkey, p_mfgr, s_address, s_phone, s_comment from part, supplier, partsupp, nation, region where p_partkey = ps_partkey and s_suppkey = ps_suppkey and p_size = 48 and p_type like '%STEEL' and s_nationkey = n_nationkey and n_regionkey = r_regionkey and r_name = 'EUROPE' and ps_supplycost = ( select min(ps_supplycost) from partsupp, supplier, nation, region where p_partkey = ps_partkey and s_suppkey = ps_suppkey and s_nationkey = n_nationkey and n_regionkey = r_regionkey and r_name = 'EUROPE' ) order by s_acctbal desc, n_name, s_name, p_partkey limit 100; -
Q3
select l_orderkey, sum(l_extendedprice * (1 - l_discount)) as revenue, o_orderdate, o_shippriority from customer, orders, lineitem where c_mktsegment = 'MACHINERY' and c_custkey = o_custkey and l_orderkey = o_orderkey and o_orderdate < date '1995-03-23' and l_shipdate > date '1995-03-23' group by l_orderkey, o_orderdate, o_shippriority order by revenue desc, o_orderdate limit 10; -
Q4
select o_orderpriority, count(*) as order_count from orders where o_orderdate >= date '1996-07-01' and o_orderdate < date '1996-07-01' + interval '3' month and exists ( select * from lineitem where l_orderkey = o_orderkey and l_commitdate < l_receiptdate ) group by o_orderpriority order by o_orderpriority; -
Q5
select n_name, sum(l_extendedprice * (1 - l_discount)) as revenue from customer, orders, lineitem, supplier, nation, region where c_custkey = o_custkey and l_orderkey = o_orderkey and l_suppkey = s_suppkey and c_nationkey = s_nationkey and s_nationkey = n_nationkey and n_regionkey = r_regionkey and r_name = 'EUROPE' and o_orderdate >= date '1996-01-01' and o_orderdate < date '1996-01-01' + interval '1' year group by n_name order by revenue desc; -
Q6
select sum(l_extendedprice * l_discount) as revenue from lineitem where l_shipdate >= date '1996-01-01' and l_shipdate < date '1996-01-01' + interval '1' year and l_discount between 0.02 - 0.01 and 0.02 + 0.01 and l_quantity < 24; -
Q7
select supp_nation, cust_nation, l_year, sum(volume) as revenue from ( select n1.n_name as supp_nation, n2.n_name as cust_nation, extract(year from l_shipdate) as l_year, l_extendedprice * (1 - l_discount) as volume from supplier, lineitem, orders, customer, nation n1, nation n2 where s_suppkey = l_suppkey and o_orderkey = l_orderkey and c_custkey = o_custkey and s_nationkey = n1.n_nationkey and c_nationkey = n2.n_nationkey and ( (n1.n_name = 'CANADA' and n2.n_name = 'BRAZIL') or (n1.n_name = 'BRAZIL' and n2.n_name = 'CANADA') ) and l_shipdate between date '1995-01-01' and date '1996-12-31' ) as shipping group by supp_nation, cust_nation, l_year order by supp_nation, cust_nation, l_year; -
Q8
select o_year, sum(case when nation = 'BRAZIL' then volume else 0 end) / sum(volume) as mkt_share from ( select extract(year from o_orderdate) as o_year, l_extendedprice * (1 - l_discount) as volume, n2.n_name as nation from part, supplier, lineitem, orders, customer, nation n1, nation n2, region where p_partkey = l_partkey and s_suppkey = l_suppkey and l_orderkey = o_orderkey and o_custkey = c_custkey and c_nationkey = n1.n_nationkey and n1.n_regionkey = r_regionkey and r_name = 'AMERICA' and s_nationkey = n2.n_nationkey and o_orderdate between date '1995-01-01' and date '1996-12-31' and p_type = 'LARGE ANODIZED COPPER' ) as all_nations group by o_year order by o_year; -
Q9
select nation, o_year, sum(amount) as sum_profit from ( select n_name as nation, extract(year from o_orderdate) as o_year, l_extendedprice * (1 - l_discount) - ps_supplycost * l_quantity as amount from part, supplier, lineitem, partsupp, orders, nation where s_suppkey = l_suppkey and ps_suppkey = l_suppkey and ps_partkey = l_partkey and p_partkey = l_partkey and o_orderkey = l_orderkey and s_nationkey = n_nationkey and p_name like '%maroon%' ) as profit group by nation, o_year order by nation, o_year desc; -
Q10
select c_custkey, c_name, sum(l_extendedprice * (1 - l_discount)) as revenue, c_acctbal, n_name, c_address, c_phone, c_comment from customer, orders, lineitem, nation where c_custkey = o_custkey and l_orderkey = o_orderkey and o_orderdate >= date '1993-02-01' and o_orderdate < date '1993-02-01' + interval '3' month and l_returnflag = 'R' and c_nationkey = n_nationkey group by c_custkey, c_name, c_acctbal, c_phone, n_name, c_address, c_comment order by revenue desc limit 20; -
Q11
select ps_partkey, sum(ps_supplycost * ps_availqty) as value from partsupp, supplier, nation where ps_suppkey = s_suppkey and s_nationkey = n_nationkey and n_name = 'EGYPT' group by ps_partkey having sum(ps_supplycost * ps_availqty) > ( select sum(ps_supplycost * ps_availqty) * 0.0001000000 from partsupp, supplier, nation where ps_suppkey = s_suppkey and s_nationkey = n_nationkey and n_name = 'EGYPT' ) order by value desc; -
Q12
select l_shipmode, sum(case when o_orderpriority = '1-URGENT' or o_orderpriority = '2-HIGH' then 1 else 0 end) as high_line_count, sum(case when o_orderpriority <> '1-URGENT' and o_orderpriority <> '2-HIGH' then 1 else 0 end) as low_line_count from orders, lineitem where o_orderkey = l_orderkey and l_shipmode in ('FOB', 'AIR') and l_commitdate < l_receiptdate and l_shipdate < l_commitdate and l_receiptdate >= date '1997-01-01' and l_receiptdate < date '1997-01-01' + interval '1' year group by l_shipmode order by l_shipmode; -
Q13
select c_count, count(*) as custdist from ( select c_custkey, count(o_orderkey) as c_count from customer left outer join orders on c_custkey = o_custkey and o_comment not like '%special%deposits%' group by c_custkey ) c_orders group by c_count order by custdist desc, c_count desc; -
Q14
select 100.00 * sum(case when p_type like 'PROMO%' then l_extendedprice * (1 - l_discount) else 0 end) / sum(l_extendedprice * (1 - l_discount)) as promo_revenue from lineitem, part where l_partkey = p_partkey and l_shipdate >= date '1997-06-01' and l_shipdate < date '1997-06-01' + interval '1' month; -
Q15
with revenue0(SUPPLIER_NO, TOTAL_REVENUE) as ( select l_suppkey, sum(l_extendedprice * (1 - l_discount)) from lineitem where l_shipdate >= date '1995-02-01' and l_shipdate < date '1995-02-01' + interval '3' month group by l_suppkey ) select s_suppkey, s_name, s_address, s_phone, total_revenue from supplier, revenue0 where s_suppkey = supplier_no and total_revenue = ( select max(total_revenue) from revenue0 ) order by s_suppkey; -
Q16
select p_brand, p_type, p_size, count(distinct ps_suppkey) as supplier_cnt from partsupp, part where p_partkey = ps_partkey and p_brand <> 'Brand#45' and p_type not like 'SMALL ANODIZED%' and p_size in (47, 15, 37, 30, 46, 16, 18, 6) and ps_suppkey not in ( select s_suppkey from supplier where s_comment like '%Customer%Complaints%' ) group by p_brand, p_type, p_size order by supplier_cnt desc, p_brand, p_type, p_size; -
Q17
select sum(l_extendedprice) / 7.0 as avg_yearly from lineitem, part where p_partkey = l_partkey and p_brand = 'Brand#51' and p_container = 'WRAP PACK' and l_quantity < ( select 0.2 * avg(l_quantity) from lineitem where l_partkey = p_partkey ); -
Q18
select c_name, c_custkey, o_orderkey, o_orderdate, o_totalprice, sum(l_quantity) from customer, orders, lineitem where o_orderkey in ( select l_orderkey from lineitem group by l_orderkey having sum(l_quantity) > 312 ) and c_custkey = o_custkey and o_orderkey = l_orderkey group by c_name, c_custkey, o_orderkey, o_orderdate, o_totalprice order by o_totalprice desc, o_orderdate limit 100; -
Q19
select sum(l_extendedprice* (1 - l_discount)) as revenue from lineitem, part where ( p_partkey = l_partkey and p_brand = 'Brand#52' and p_container in ('SM CASE', 'SM BOX', 'SM PACK', 'SM PKG') and l_quantity >= 3 and l_quantity <= 3 + 10 and p_size between 1 and 5 and l_shipmode in ('AIR', 'AIR REG') and l_shipinstruct = 'DELIVER IN PERSON' ) or ( p_partkey = l_partkey and p_brand = 'Brand#43' and p_container in ('MED BAG', 'MED BOX', 'MED PKG', 'MED PACK') and l_quantity >= 12 and l_quantity <= 12 + 10 and p_size between 1 and 10 and l_shipmode in ('AIR', 'AIR REG') and l_shipinstruct = 'DELIVER IN PERSON' ) or ( p_partkey = l_partkey and p_brand = 'Brand#52' and p_container in ('LG CASE', 'LG BOX', 'LG PACK', 'LG PKG') and l_quantity >= 21 and l_quantity <= 21 + 10 and p_size between 1 and 15 and l_shipmode in ('AIR', 'AIR REG') and l_shipinstruct = 'DELIVER IN PERSON' ); -
Q20
select s_name, s_address from supplier, nation where s_suppkey in ( select ps_suppkey from partsupp where ps_partkey in ( select p_partkey from part where p_name like 'drab%' ) and ps_availqty > ( select 0.5 * sum(l_quantity) from lineitem where l_partkey = ps_partkey and l_suppkey = ps_suppkey and l_shipdate >= date '1996-01-01' and l_shipdate < date '1996-01-01' + interval '1' year ) ) and s_nationkey = n_nationkey and n_name = 'KENYA' order by s_name; -
Q21
select s_name, count(*) as numwait from supplier, lineitem l1, orders, nation where s_suppkey = l1.l_suppkey and o_orderkey = l1.l_orderkey and o_orderstatus = 'F' and l1.l_receiptdate > l1.l_commitdate and exists ( select * from lineitem l2 where l2.l_orderkey = l1.l_orderkey and l2.l_suppkey <> l1.l_suppkey ) and not exists ( select * from lineitem l3 where l3.l_orderkey = l1.l_orderkey and l3.l_suppkey <> l1.l_suppkey and l3.l_receiptdate > l3.l_commitdate ) and s_nationkey = n_nationkey and n_name = 'PERU' group by s_name order by numwait desc, s_name limit 100; -
Q22
select cntrycode, count(*) as numcust, sum(c_acctbal) as totacctbal from ( select substring(c_phone from 1 for 2) as cntrycode, c_acctbal from customer where substring(c_phone from 1 for 2) in ('24', '32', '17', '18', '12', '14', '22') and c_acctbal > ( select avg(c_acctbal) from customer where c_acctbal > 0.00 and substring(c_phone from 1 for 2) in ('24', '32', '17', '18', '12', '14', '22') ) and not exists ( select * from orders where o_custkey = c_custkey ) ) as custsale group by cntrycode order by cntrycode;