JindoFS是一种云原生的文件系统,结合OSS和本地存储,成为E-MapReduce产品的新一代存储系统,为上层计算提供了高效可靠的存储。本文主要说明JindoFS的配置使用方式,以及介绍一些典型的应用场景。
概述
JindoFS 提供了块存储模式(Block)和缓存模式(Cache)的存储模式。
JindoFS采用了本地存储和OSS的异构多备份机制,Storage Service提供了数据存储能力,首先使用OSS作为存储后端,保证数据的高可靠性,同时利用本地存储实现冗余备份,利用本地的备份,可以加速数据读取;另外,JindoFS 的元数据通过本地服务Namespace Service管理,从而保证了元数据操作的性能(和HDFS元数据操作性能相似)。
- E-MapReduce-3.20.0及以上版本支持Jindo FS,您可以在创建集群时勾选相关服务来使用JindoFS。
- 本文主要是E-MapReduce-3.22.0 及以上版本的介绍;E-MapReduce-3.20.0及以上版本至E-MapReduce-3.22.0(但不包括)版本的JindoFS 使用说明,请参见JindoFS 使用说明(E-MapReduce-3.20.0~3.22.0版本)。

环境准备
- 创建集群
选择 E-MapReduce-3.22.0 及以上版本,勾选可选服务中的SmartData,具体操作步骤请参见创建集群。
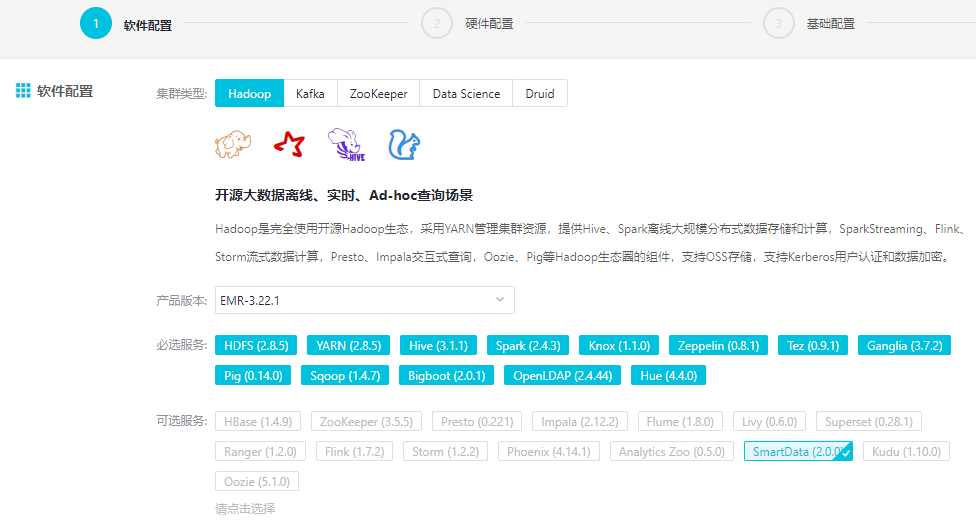
- 配置集群
SmartData提供的JindoFS文件系统使用OSS作为存储后端,因此在使用JindoFS之前需配置一些OSS相关参数。下面提供两种配置方式,第一种是先创建好集群,修改Bigboot相关参数,需重启SmartData服务生效;第二种是创建集群过程中添加自定义配置,这样集群创建好后相关服务就能按照自定义参数启动:
- 集群创建好后初始化参数
所有JindoFS相关配置都在Bigboot组件中,配置如下图所示:
-
在服务配置页面,单击bigboot页签。
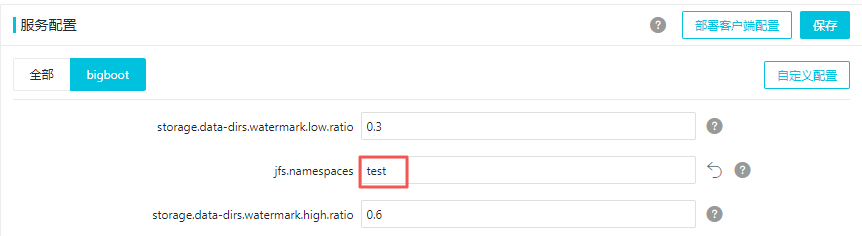
- 单击自定义配置。
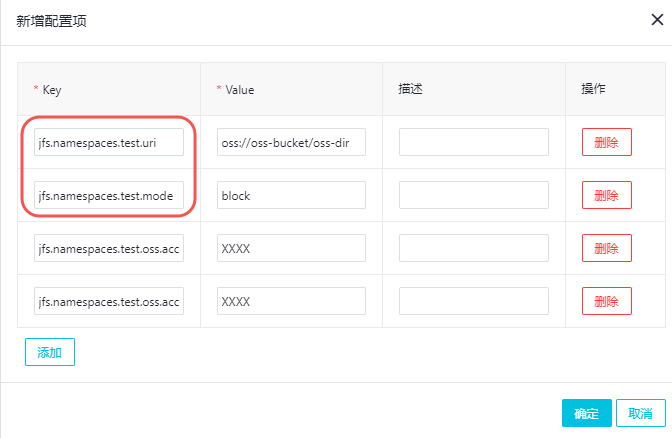
说明- 红框中为必填的配置项。
- JindoFS支持多命名空间,本文命名空间以test为例。
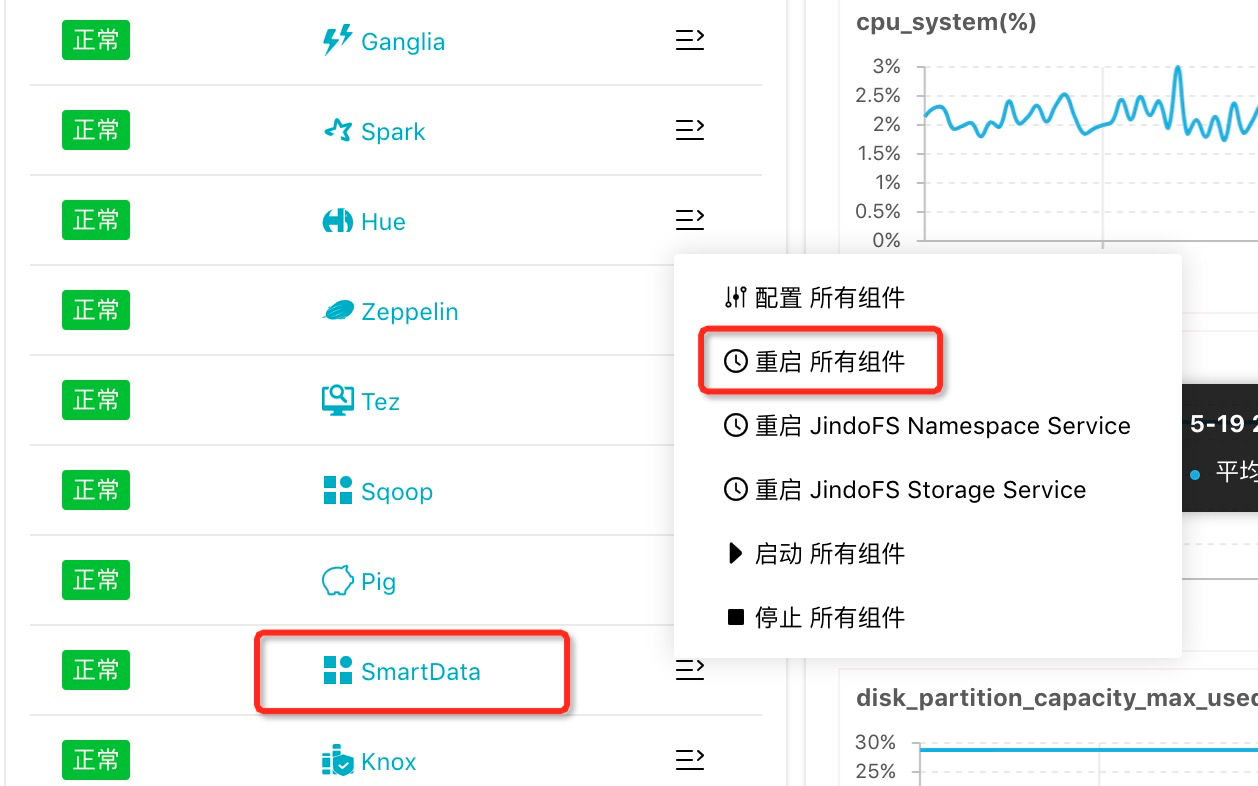
参数 参数说明 示例 jfs.namespaces 表示当前JindoFS支持的命名空间,多个命名空间时以逗号隔开。 test jfs.namespaces.test.uri 表示test命名空间的后端存储。 oss://oss-bucket/oss-dir 说明 该配置也可以配置到OSS bucket下的具体目录,该命名空间即以该目录作为根目录来读写数据。jfs.namespaces.test.mode 表示test命名空间为块存储模式。 block 说明 JindoFS支持block和cache两种存储模式。jfs.namespaces.test.oss.access.key 表示存储后端OSS的AK。 xxxx 说明 考虑到性能和稳定性,推荐使用同账户、同region下的OSS bucket作为存储后端,此时,E-MapReduce集群能够免密访问OSS,无需配置 AK和secret。jfs.namespaces.test.oss.access.secret 表示存储后端OSS的secret。 配置完成后保存并部署,然后在SmartData服务中重启所有组件,即开始使用JindoFS。
-
- 创建集群时添加自定义配置
E-MapReduce集群在创建集群时支持添加自定义配置,以同region下免密访问OSS为例,如下图勾选软件自定义配置,配置命名空间test的相关配置,详情如下:
[ { "ServiceName":"BIGBOOT", "FileName":"bigboot", "ConfigKey":"jfs.namespaces","ConfigValue":"test" },{ "ServiceName":"BIGBOOT", "FileName":"bigboot", "ConfigKey":"jfs.namespaces.test.uri", "ConfigValue":"oss://oss-bucket/oss-dir" },{ "ServiceName":"BIGBOOT", "FileName":"bigboot", "ConfigKey":"jfs.namespaces.test.mode", "ConfigValue":"block" } ]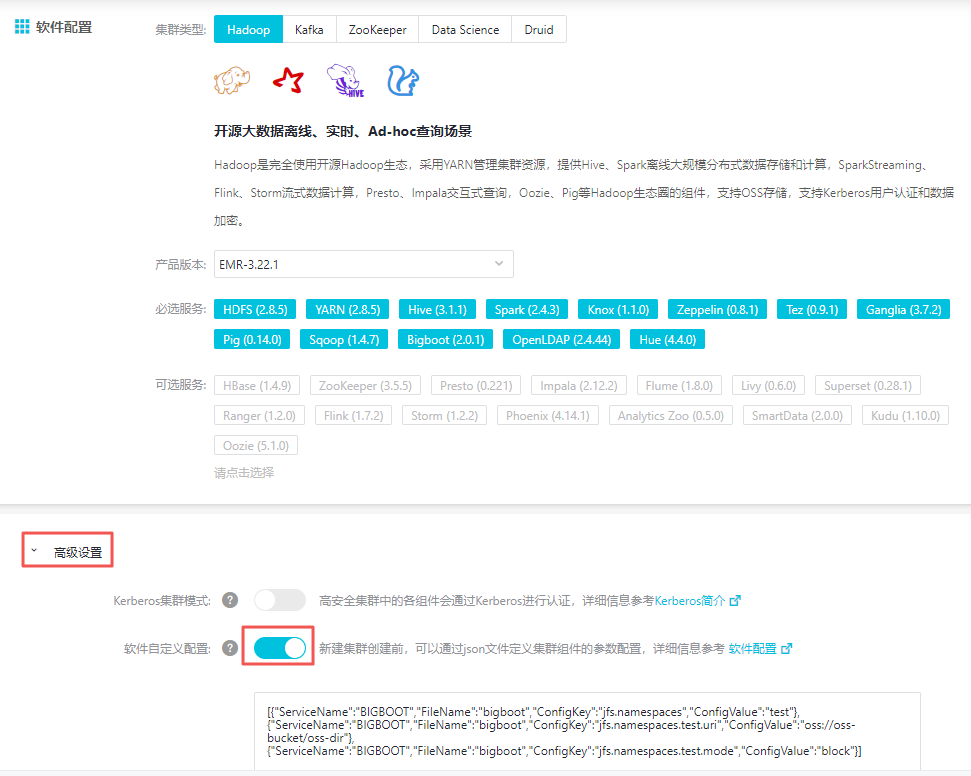
- 集群创建好后初始化参数
使用 JindoFS
JindoFS使用上与HDFS类似,提供jfs前缀,将jfs替代hdfs即可使用。
目前,JindoFS能够支持 EMR 集群上的大部分计算组件,包括 Hadoop、Hive、Spark、Flink、Presto、Impala。
简单示例:
- Shell命令
hadoop fs -ls jfs://your-namespace/ hadoop fs -mkdir jfs://your-namespace/test-dir hadoop fs -put test.log jfs://your-namespace/test-dir/ hadoop fs -get jfs://your-namespace/test-dir/test.log ./ - MapReduce作业
hadoop jar /usr/lib/hadoop-current/share/hadoop/mapreduce/hadoop-mapreduce-examples-2.8.5.jar teragen -Dmapred.map.tasks=1000 10737418240 jfs://your-namespace/terasort/input hadoop jar /usr/lib/hadoop-current/share/hadoop/mapreduce/hadoop-mapreduce-examples-2.8.5.jar terasort -Dmapred.reduce.tasks=1000 jfs://your-namespace/terasort/input jfs://your-namespace/terasort/output - Spark-SQL
CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE IF NOT EXISTS src_jfs (key INT, value STRING) location 'jfs://your-namespace/Spark_sql_test/';
磁盘空间水位控制
JindoFS后端基于OSS,可以提供海量的存储,但是本地盘的容量是有限的,因此JindoFS会自动淘汰本地较冷的数据备份。我们提供了node.data-dirs.watermark.high.ratio 和 node.data-dirs.watermark.low.ratio 这两个参数用来调节本地存储的使用容量,值均为0~1 的小数表示使用比例,JindoFS 默认使用所有数据盘,每块盘的使用容量默认即为数据盘大小。前者表示使用量上水位比例,每块数据盘的JindoFS占用的空间到达上水位即会开始清理淘汰;后者表示使用量下水位比例,触发清理后会将JindoFS 的占用空间清理到下水位。用户可以通过设置上水位比例调节期望分给JindoFS的磁盘空间,下水位必须小于上水位,设置合理的值即可。
存储策略
JindoFS提供了Storage Policy功能,提供更加灵活的存储策略适应不同的存储需求,可以对目录设置以下四种存储策略:
| 策略 | 策略说明 |
|---|---|
| COLD | 表示数据仅在OSS上有一个备份,没有本地备份,适用于冷数据存储。 |
| WARM |
默认策略。 表示数据在OSS和本地分别有一个备份, 本地备份能够有效的提供后续的读取加速。 |
| HOT | 表示数据在OSS 上有一个备份,本地有多个备份,针对一些最热的数据提供更进一步的加速效果。 |
| TEMP | 表示数据仅有一个本地备份,针对一些临时性数据,提供高性能的读写,但降低了数据的高可靠性,适用于一些临时数据的存取。 |
JindoFS 提供了Admin工具设置目录的Storage Policy(默认为 WARM),新增的文件将会以父目录所指定的 Storage Policy 进行存储,使用方式如下:
jindo dfsadmin -R -setStoragePolicy [path] [policy]通过以下命令,获取某个目录的存储策略:
jindo dfsadmin -getStoragePolicy [path]Admin 工具
-
Admin工具提供archive命令,实现对冷数据的归档。
此命令提供了一种用户显式淘汰本地数据块的方式。Hive分区表按天分区,假如业务上对一周前的分区数据认为不会再经常访问,那么就可以定期将一周前的分区目录执行archive,淘汰本地备份,文件备份将仅仅保留在后端OSS 上。
Archive命令的使用方式如下:
jindo dfsadmin -archive [path]说明 [path]为需要归档文件的所在目录路径。 -
Admin工具提供jindo命令,为Namespace Service提供了一些管理员功能命令。
jindo dfsadmin [-options]说明 可以通过jindo dfsadmin --help命令获取帮助信息。
- diff命令主要用来显示本地数据与后端存储系统数据之间的差异。
jindo dfsadmin -R -diff [path]说明 默认情况下比较[path]目录的子目录中元数据之间的差异,-R选项表示递归比较[path]目录下所有的路径。 - sync命令用于同步本地与后端存储之前的元数据。
jindo dfsadmin -R -sync [path]说明[path]表示需要同步元数据的路径,默认只会同步[path]的下一级目录,-R选项表示递归比较[path]目录下所有的路径。




