The continuous profiling feature of Application Monitoring can effectively discover bottlenecks caused by CPU, memory, or I/O in Go programs, and display statistics data by method name, class name, and line number. This helps developers optimize programs, reduce latency, increase throughput, and save costs. This topic describes how to enable the continuous profiling feature, and how to view the profiling data.
Prerequisites
Your application is monitored by Application Monitoring.
The version of the ARMS agent for Go is 1.3.0 or later. You can view the agent version by choosing on the application details page.
Enable continuous profiling
Log on to the ARMS console. In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Application List page, select a region in the top navigation bar and click the name of the application you want to manage.
NoteIcons displayed in the Language column indicate languages in which applications are written.
 : Java application
: Java application : Go application
: Go application : Python application
: Python applicationHyphen (-): application monitored in Managed Service for OpenTelemetry.
In the top navigation bar, choose .
In the Ongoing Profiling Settings section, turn on Master switch and other switches as needed.
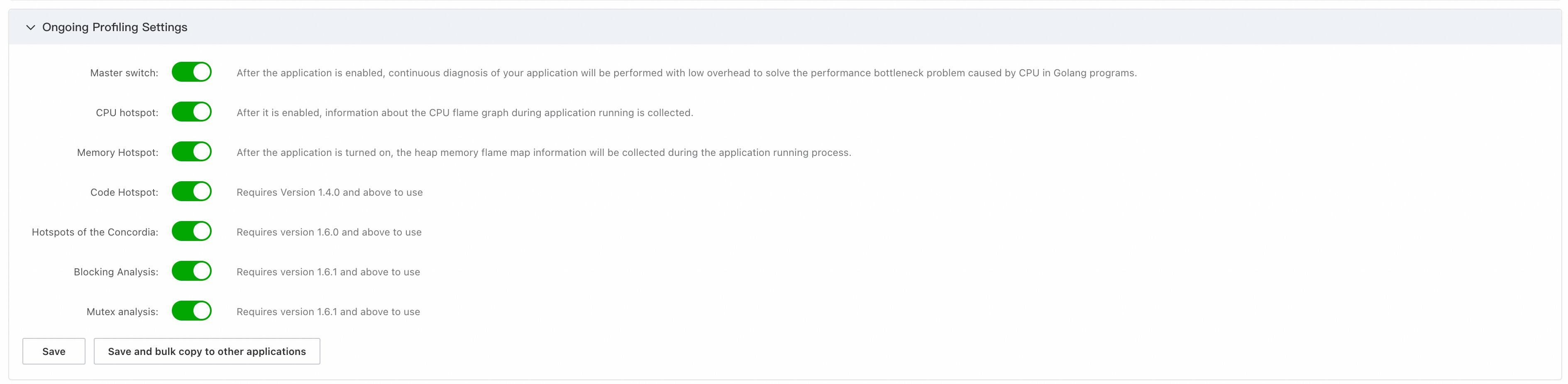
Click Save and wait 2 minutes for the changes to take effect.
View profiling data
Log on to the ARMS console. In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Application List page, select a region in the top navigation bar and click the name of the application you want to manage.
NoteIcons displayed in the Language column indicate languages in which applications are written.
 : Java application
: Java application : Go application
: Go application : Python application
: Python applicationHyphen (-): application monitored in Managed Service for OpenTelemetry.
In the top navigation bar, choose .
In the application instance list, select the application instance. On the right side of the page, set the time period.
On the Single View tab in the right-side pane, perform the following operations to query data and view aggregation analysis results.
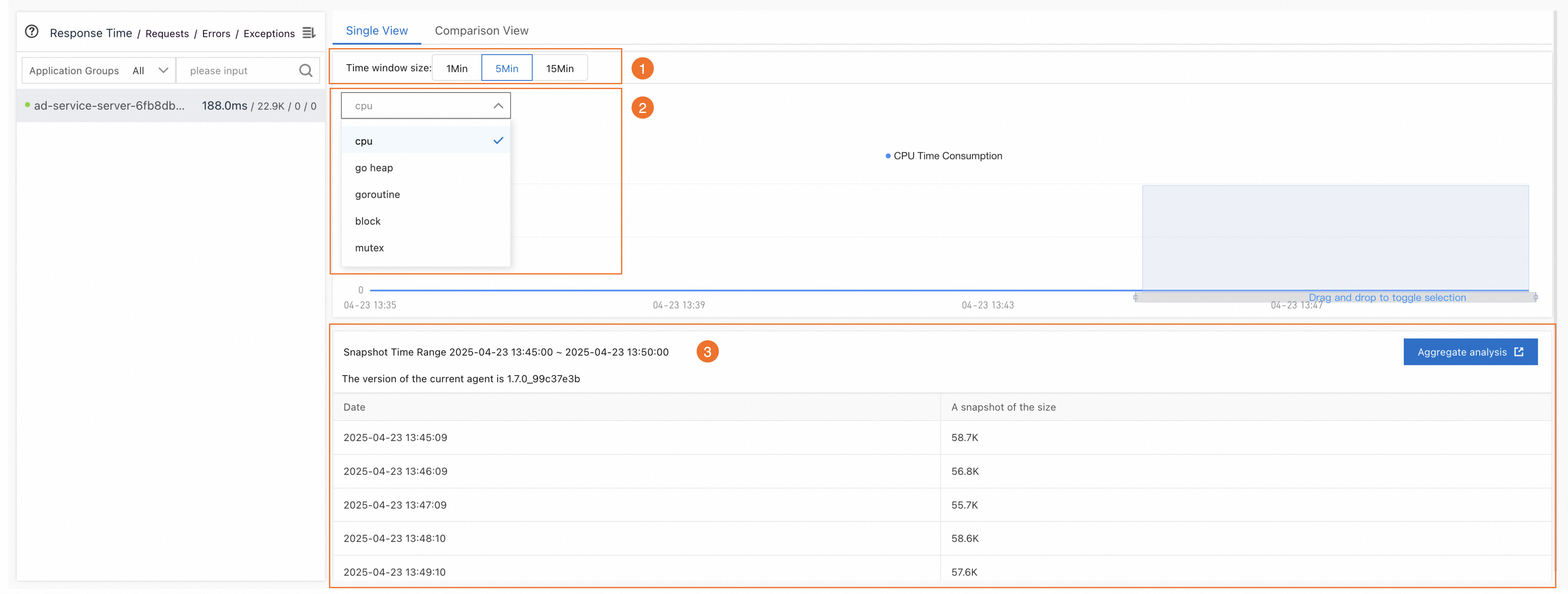
In the Time window size section (icon 1), select a snapshot duration, and drag on the line chart to select a time period.
From the drop-down list (icon 2), select the data that you want to view: CPU, Go heap, Goroutine, Mutex, and block.
As shown in the figure, data within the time period (icon 3) is displayed. You can click Aggregate analysis to view the snapshot details.
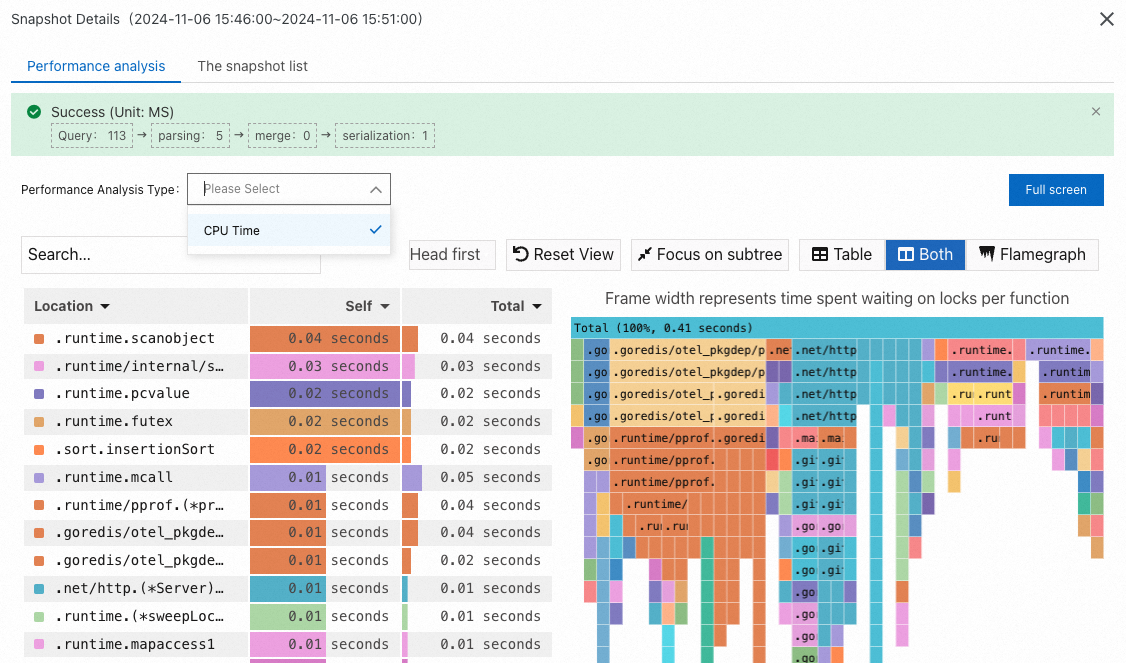
Performance analysis
CPU Time: the number of CPU cores requested.
Allocated Memory: the size of memory requested.
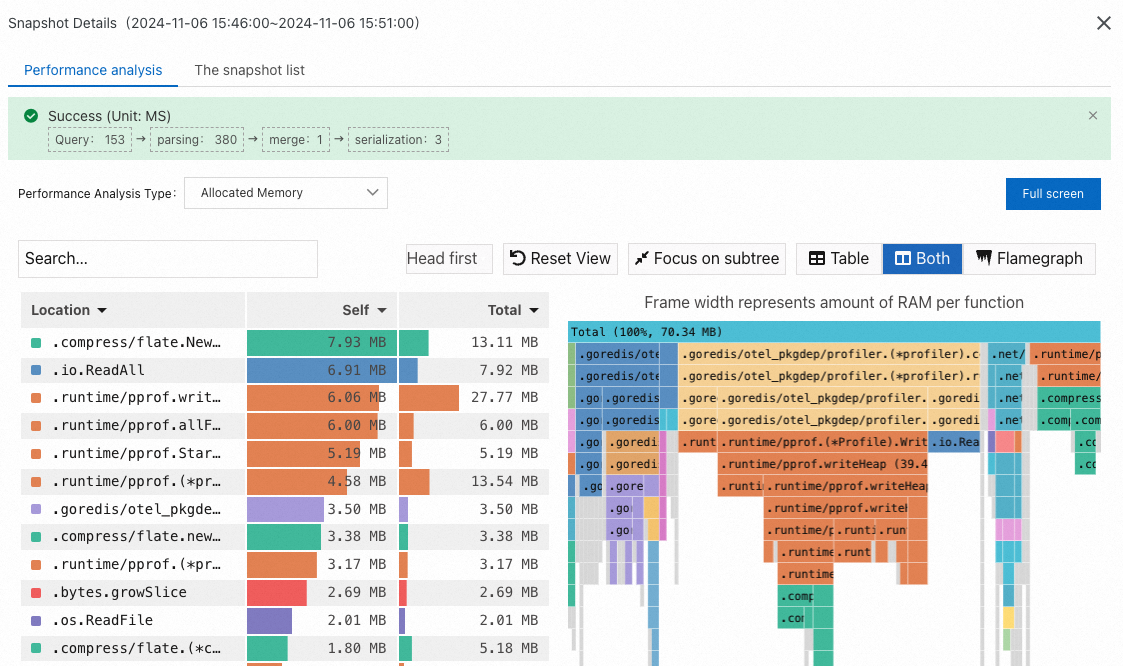
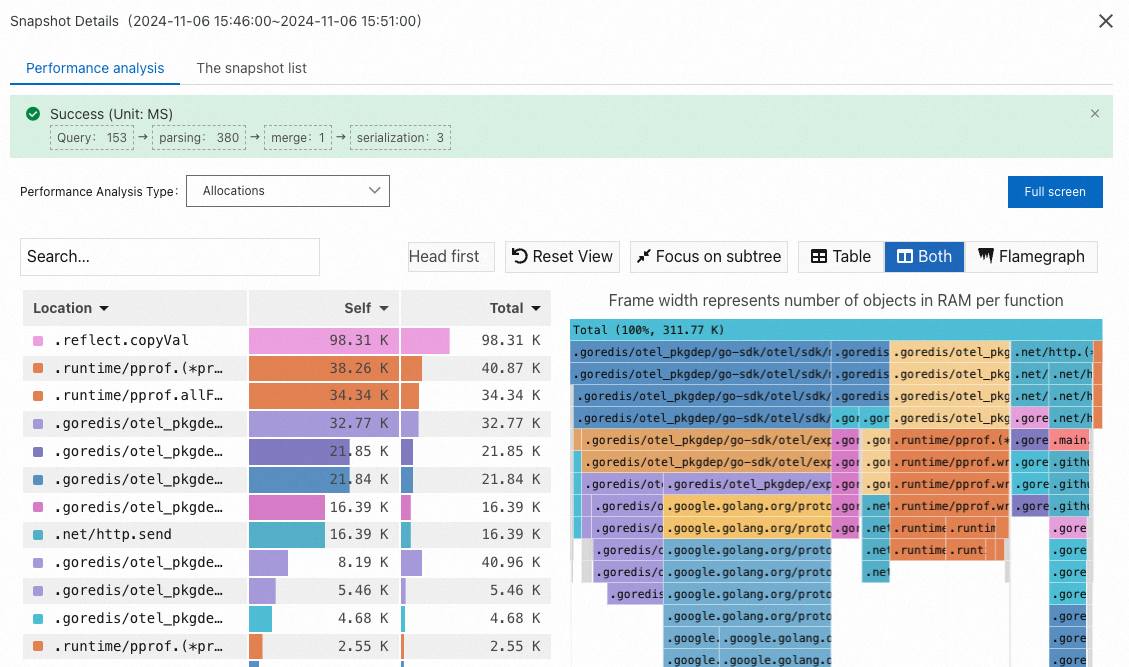
Allocations: the number of memory requests. Based on the number of memory requests, you can view the methods that frequently request memory.
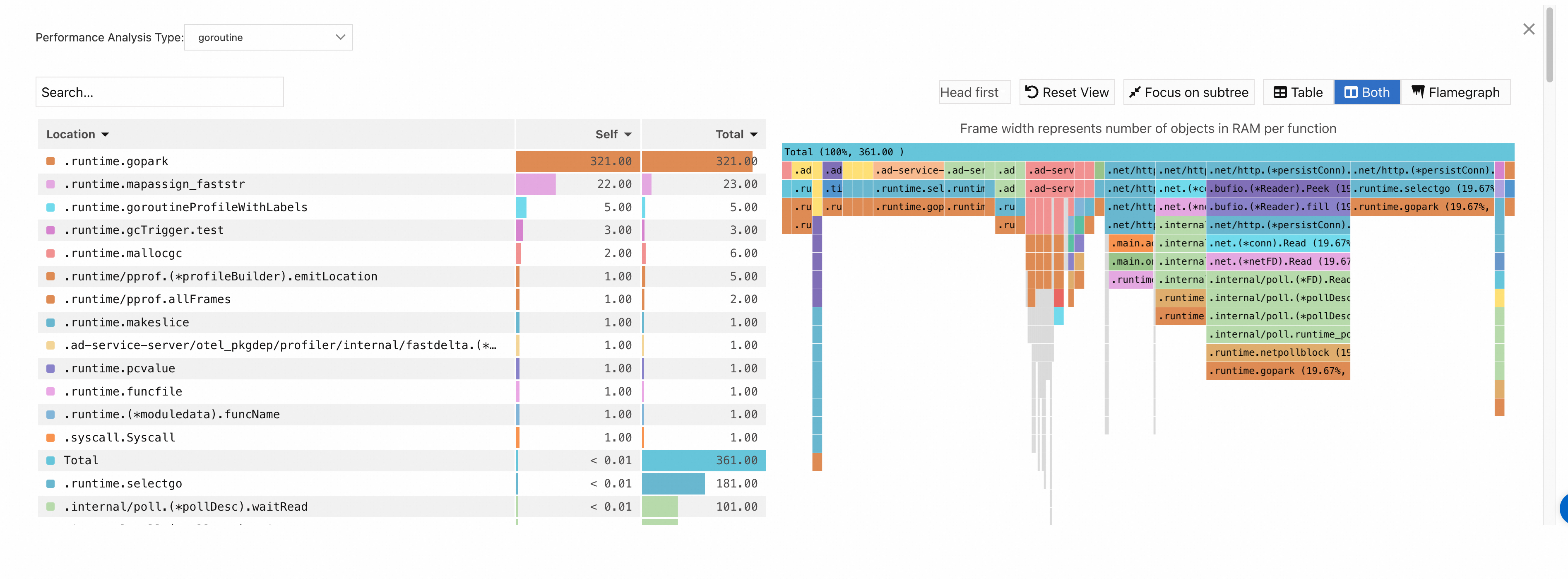
goroutine:
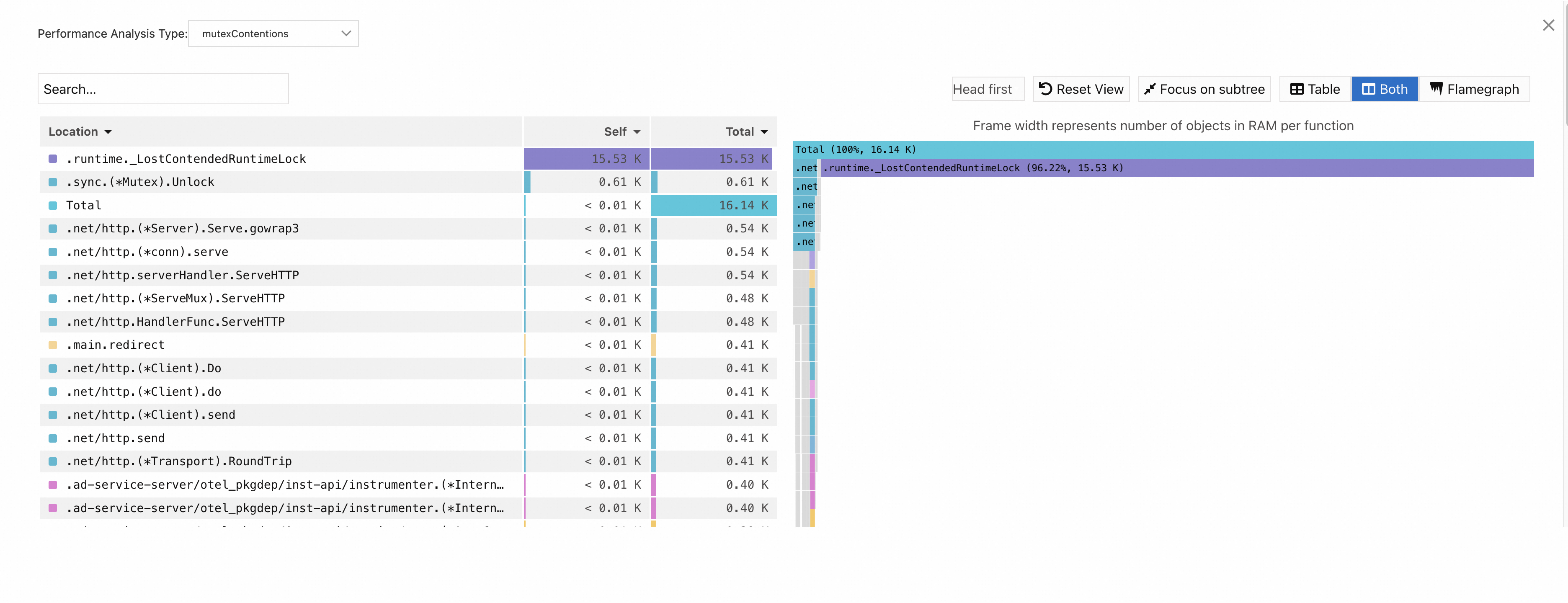
Mutex:
mutexContentions:
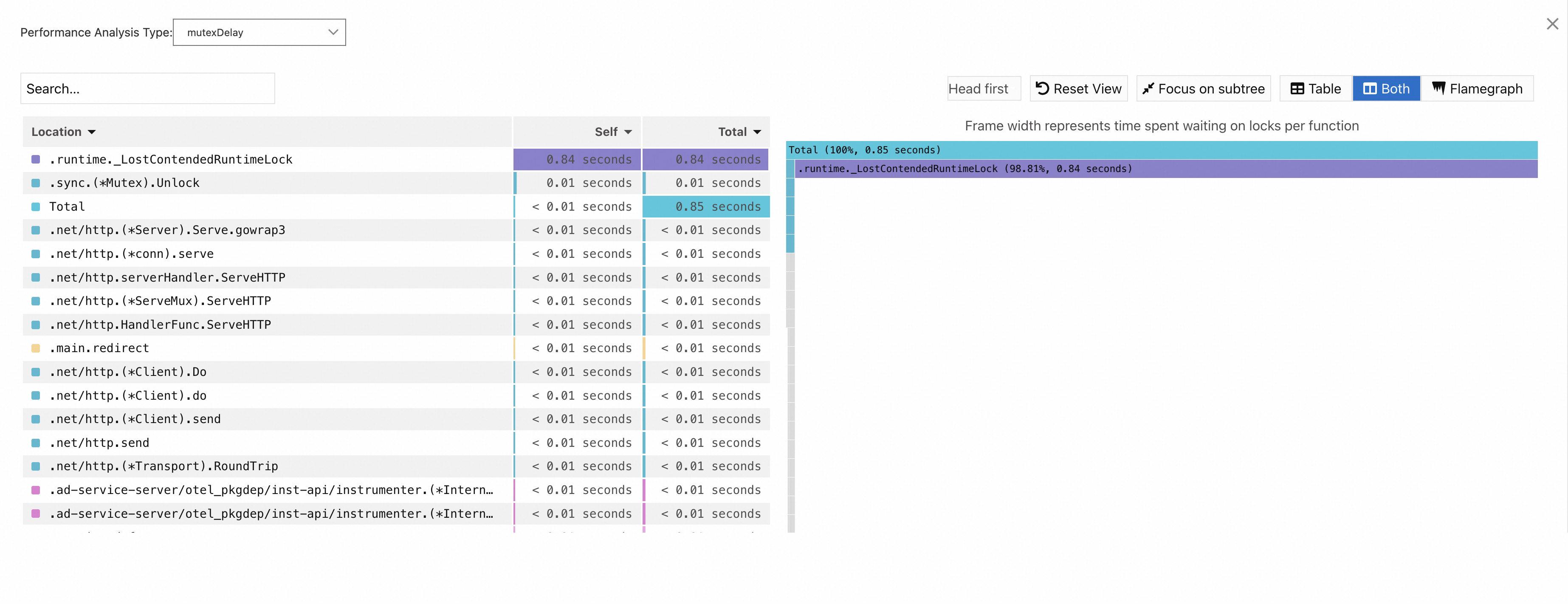
mutexDelay:
Block:
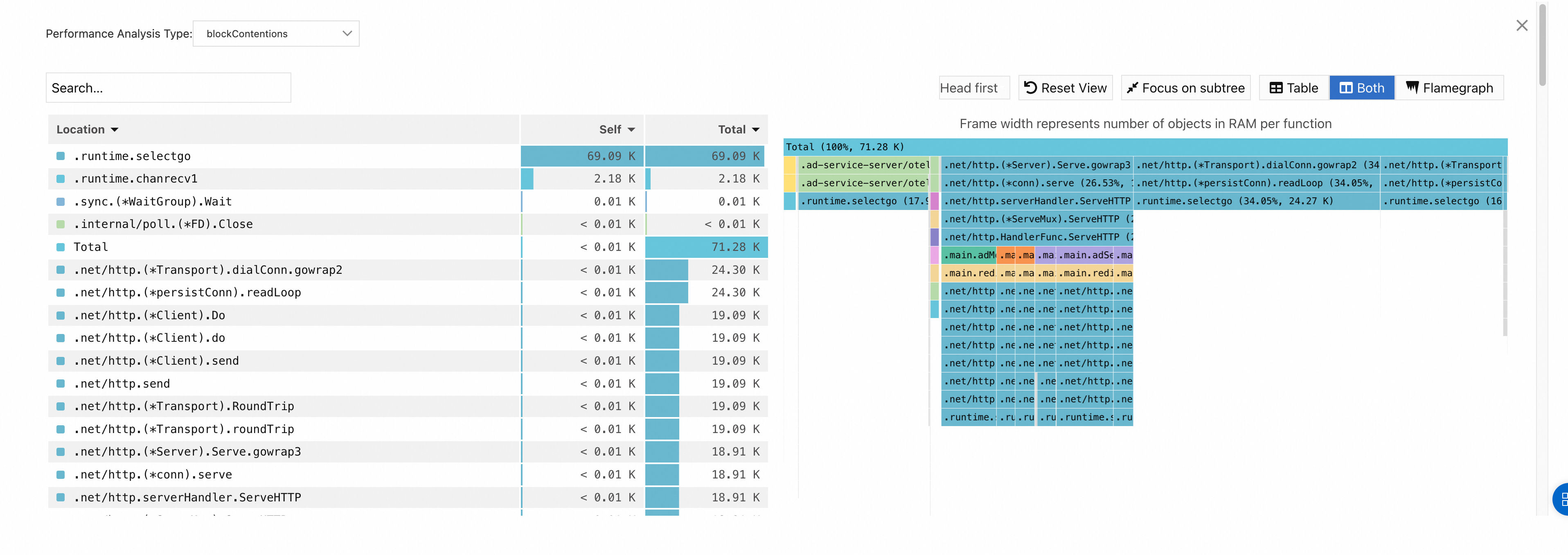
blockContentions:
blockDelay:
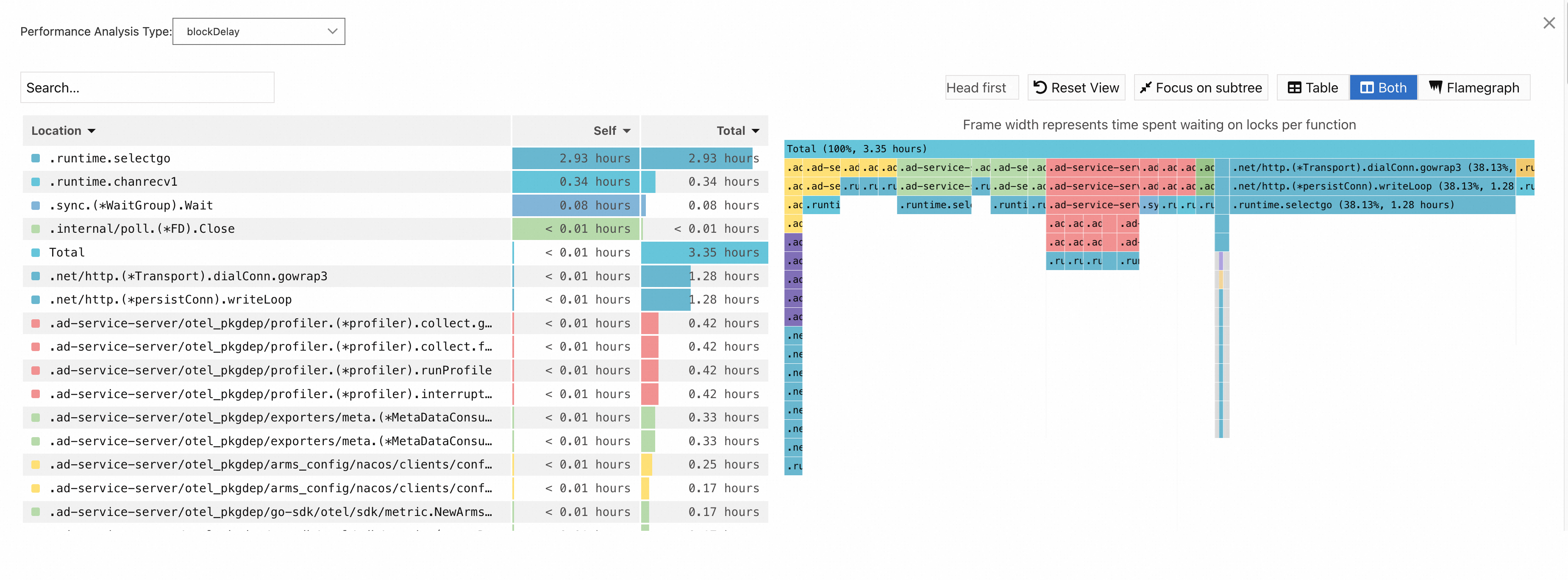
NoteThe Self column displays the time or resources that each method consumes within the stack, excluding the time or resources that their child methods consume. The data can be used to identify methods that spend excessive time or resources for their own.
The Total column displays the time or resources consumed by each method, including the time or resources consumed by all of its child methods. The data can be used to identify methods that contribute the most time or resources.
When you analyze hotspot code, you can locate the time-consuming methods by focusing on the Self column or the wide flame at the bottom of the right-side flame graph. Generally, wide flame indicates a system performance bottleneck.
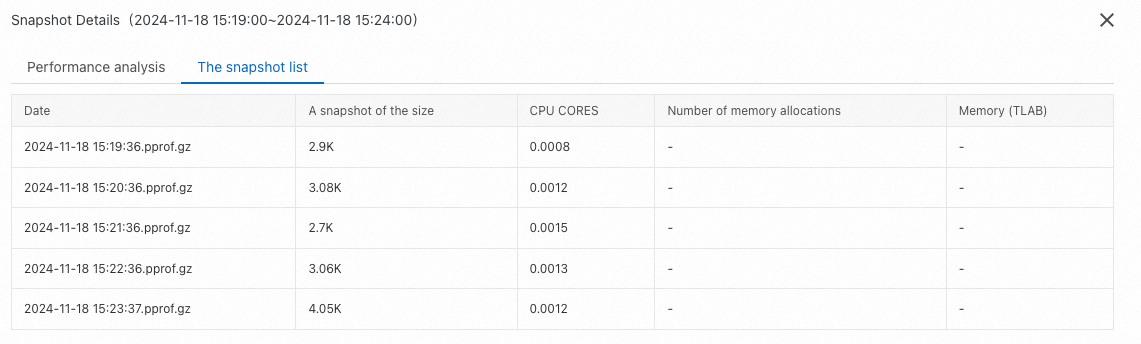
Snapshot list
References
You can use the continuous profiling feature to troubleshoot high CPU utilization and memory usage. Refer to the following topics: