By Cloud-Native SIG

In the previous article, we described how Anolis OS is the first native Linux kernel that supports image acceleration. The Nydus image acceleration service has re-optimized the existing OCIv1 container image format, redefined the image file system, separated data from metadata, and loaded on demand. This article is a tutorial on Nydus, introducing how to deploy Nydus on Anolis OS to help users get familiar with the basic deployment of Nydus.
This tutoria uses EC2 virtual machines purchased on Alibaba Cloud. You can deploy Nydus locally or in other cloud environments.
Operating system: Anolis OS 8.4 (ANCK 64-bit)
Kernel version: Linux 4.19
CPU: 2 vCPU@3.5GHz
memory: 8GB
software dependency: Nydus currently only supports Containerd, so you need to use Containerd as the container engine.
dnf --enablerepo Plus install -y containerdOpenAnolis Community has integrated the latest stable version of Nydus, so we recommend using the OpenAnolis integrated software package to install Nydus. If you want to install the specified version of Nydus, you can download the code package of the upstream open-source version. You can use one of the following installation methods.
dnf --enablerepo Plus install -y nydus-rs nydus-snapshotterGet the latest compressed package from the release page and decompress it.
wget https://github.com/dragonflyoss/image-service/releases/download/v2.1.0-alpha.4/nydus-static-v2.1.0-alpha.4-linux-amd64.tgz
tar -xzvf nydus-static-v2.1.0-alpha.4-linux-amd64.tgzGet the latest package from the release page and decompress it.
wget https://github.com/containerd/nydus-snapshotter/releases/download/v0.2.4/nydus-snapshotter-v0.2.4-x86_64.tgz
tar -xzvf nydus-snapshotter-v0.2.4-x86_64.tgz
mv nydus-snapshotter/containerd-nydus-grpc nydus-static/containerd-nydus-grpcThe Nydus acceleration framework supports three running modes to support on-demand image loading in different scenarios:
Since the first mode has the least environmental dependency, it is suitable for demonstration. Here, we choose the fuse mode and rename the nydusd-fusedev in the nydusd binary file to nydusd:
cd nydus-static
mv nydusd-fusedev nydusdsudo cp nydusd nydus-image /usr/bin sudo cp nydusify containerd-nydus-grpc /usr/bin sudo cp ctr-remote nydus-overlayfs /usr/ cd ..Nydus provides a containerized remote snapshot manager containerd-nydus-grpc to prepare container rootfs and nydus images. Save the nydusd configuration to the /etc/nydusd-config.json to begin:
sudo tee /etc/nydusd-config.json > /dev/null << EOF
{
"device": {
"backend": {
"type": "registry",
"config": {
"scheme": "https",
"skip_verify": false,
"timeout": 5,
"connect_timeout": 5,
"retry_limit": 2
}
},
"cache": {
"type": "blobcache",
"config": {
"work_dir": "cache"
}
}
},
"mode": "direct",
"digest_validate": false,
"iostats_files": false,
"enable_xattr": true,
"fs_prefetch": {
"enable": true,
"threads_count": 4
}
}
EOFOpen a new terminal to operate containerd-nydus-grpc:
sudo /usr/bin/containerd-nydus-grpc \
--config-path /etc/nydusd-config.json \
--shared-daemon \
--log-level info \
--root /var/lib/containerd/io.containerd.snapshotter.v1.nydus \
--cache-dir /var/lib/nydus/cache \
--address /run/containerd/containerd-nydus-grpc.sock \
--nydusd-path /usr/bin/nydusd \
--nydusimg-path /usr/bin/nydus-image \
--log-to-stdoutThe cache-dir parameter indicates the local blob cache root directory. If it is not set, the default value is root + "/cache". It overrides the device.cache.config.work_dir in the nydusd-config.json.
/etc/containerd/config.toml):[proxy_plugins]
[proxy_plugins.nydus]
type = "snapshot"
address = "/run/containerd/containerd-nydus-grpc.sock"
[plugins."io.containerd.grpc.v1.cri".containerd]
snapshotter = "nydus"
disable_snapshot_annotations = falseAfter the configuration is updated, you need to restart the Contained service.
Systemctl restart containerdThis is how to use crictl to start a container in the Nydus image format.
nydus-sandbox.yaml and Pass Nydus Annotation to PODmetadata:
attempt: 1
name: nydus-sandbox
namespace: default
log_directory: /tmp
linux:
security_context:
namespace_options:
network: 2
annotations:
"io.containerd.osfeature": "nydus.remoteimage.v1"nydus-container.yaml to Specify the Container Image to Usemetadata:
name: nydus-container
image:
image: cloud-native-sig-registry.cn-hangzhou.cr.aliyuncs.com/openanolis/anolisos:8.6-x86_64-nydus
command:
- /bin/sleep
args:
- 600
log_path: container.1.logHere, we use the image of Anolis 8.6 that has been integrated with the OpenAnolis cloud-native image repository as the test image.
date
crictl pull cloud-native-sig-registry.cn-hangzhou.cr.aliyuncs.com/openanolis/anolisos:8.6-x86_64-nydus
pod=`crictl runp nydus-sandbox.yaml`
container=`crictl create $pod nydus-container.yaml nydus-sandbox.yaml`
crictl start $container
crictl ps
date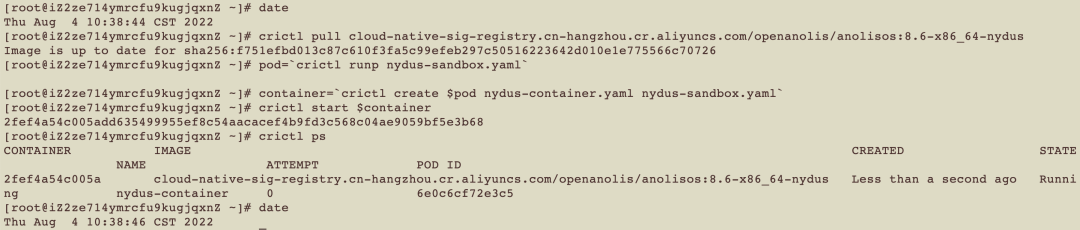
It takes only two seconds to pull and start the container image using the Nydus image. Under the same conditions, we create an OCIv1 image for comparison. We still use the Anolis 8.6 image, and the content of the image is the same Nydus mentioned above. The following is the yaml file writing:
metadata:
attempt: 1
name: normal-sandbox
namespace: default
log_directory: /tmp
linux:
security_context:
namespace_options:
network: 2metadata:
name: normal-container
image:
image: cloud-native-sig-registry.cn-hangzhou.cr.aliyuncs.com/openanolis/anolisos:8.6
command:
- /bin/sleep
args:
- 600
log_path: container.1.logUse the following command:
date
crictl pull cloud-native-sig-registry.cn-hangzhou.cr.aliyuncs.com/openanolis/anolisos:8.6
pod=`crictl runp normal-sandbox.yaml`
container=`crictl create $pod normal-container.yaml normal-sandbox.yaml`
crictl start $container
crictl ps
date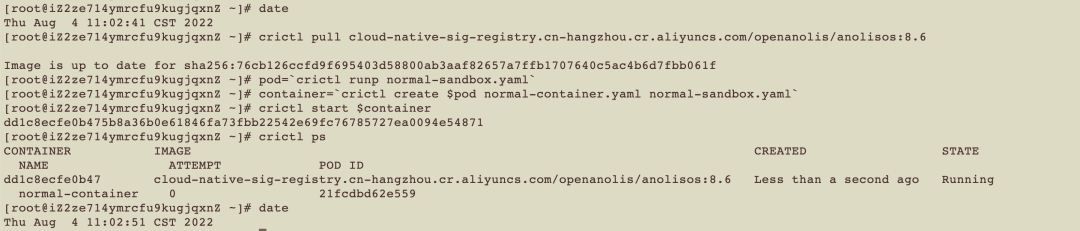
In the same environment, it takes ten seconds to start the version of Anolis 8.6 using the OCIv1 image format, which is five times that of Nydus.
This shows how to convert the Nydus image and push it to your image repository. Log into the image repository and use the nerdctl tool for configuration.
Nerdctl is a command line compatible with Docker. Since it can support starting Nydus images, we choose to use it here. Since the container may need to rely on some plug-ins during operation, we install the CNI plugin at the same time.
dnf update -y anolis-repos && yum install -y anolis-experimental-release && yum install -y nerdctl
dnf install -y containernetworking-pluginsUse nerdctl login to log on to the repository for authentication. You also can use a Docker login to log on to the repository.
nerdctl login --username ${your username} --password xxxnydusify convert --nydus-image /usr/bin/nydus-image -- source ${your image} --target ${your registry address} /${image name}: ${tag}Follow these steps. Congratulations, you have successfully deployed the Nydus image acceleration solution on Anolis OS.

99 posts | 6 followers
FollowOpenAnolis - January 11, 2024
OpenAnolis - March 8, 2022
OpenAnolis - August 3, 2022
OpenAnolis - January 10, 2023
OpenAnolis - December 7, 2022
OpenAnolis - June 15, 2022

99 posts | 6 followers
Follow Alibaba Cloud Linux
Alibaba Cloud Linux
Alibaba Cloud Linux is a free-to-use, native operating system that provides a stable, reliable, and high-performance environment for your applications.
Learn More CT Image Analytics Solution
CT Image Analytics Solution
This technology can assist realizing quantitative analysis, speeding up CT image analytics, avoiding errors caused by fatigue and adjusting treatment plans in time.
Learn More Offline Visual Intelligence Software Packages
Offline Visual Intelligence Software Packages
Offline SDKs for visual production, such as image segmentation, video segmentation, and character recognition, based on deep learning technologies developed by Alibaba Cloud.
Learn More ACK One
ACK One
Provides a control plane to allow users to manage Kubernetes clusters that run based on different infrastructure resources
Learn MoreMore Posts by OpenAnolis