
So what is blockchain exactly? In general, a blockchain implements a brand new credit system. Another synonymous saying goes like this: the blockchain system is a "trustless" system that implements its own credit. The credit system is not subject to any laws or regulations but implemented through machine languages. The credit is insulated from influences from users during system runtime and cannot be damaged. With the aid of the internet, the blockchain system can cover every corner of the world and is easy to use. In short, a blockchain refers to a chain composed of blocks organized in some way.
In this text, the blockchain technology we mentioned is actually a distributed database technology. In the blockchain, information or records are stored in blocks, and chained to the next block using cipher signatures. These blockchains have full copies on each node in the system, and all the information is timestamped and traceable. When the blockchain concept was initiated, it mainly talked about the underlying implementation methods of bitcoin. So many will interchange the concepts of bitcoin and blockchain.
After quarreling about bitcoin development, Satoshi Nakamoto vanished from the community. No matter who Satoshi Nakamoto was, we can stop being curious about him, because a common saying prevails among Geeks that: “The code matters, no matter who wrote it. Some steal or cheat in bitcoin transactions, and some give up on bitcoin, but the code is always there.” Actually, bitcoin didn't pop up overnight. A long time ago, liberal economists Friedrich August von Hayek and Milton Friedman once proposed to abolish central banks, adopt de-nationalization of and promote non-sovereign currency. In 1998 when Southeast Asia was plagued by the financial crisis, Dai Wei expounded for the first time a new form of currency, proposing to adopt cryptography principles to control currency issuance and transactions, rather than relying on the central authority. Bitcoin makes this conception true technically.
The DACT feature of blockchain makes blockchain-based systems much different from other systems. We hold that systems with blockchain technology as the core have three major features as below: decentralization, no management organizations needed and no third-party arbitration needed. Decentralization of blockchain refers to the fact that the nodes on the entire system are equivalent and every node can join or leave freely without any impact on the entire system operation; A synonym for "no management organizations needed" is "autonomous", that is to say, all nodes follow a rule and reach a consensus; "No third-party arbitration needed" means all the transactions and processes in the system observe a certain rule or contract, and all the transactions are traceable and irreversible. The blockchain system is global. Other than the network connection speed it makes no difference whether nodes of the system run on laptops on an island in the Pacific Ocean or on a server in a town in western United States. The underlying blockchain system is open-source software and is open to all. Anyone can view the code, but if they want to edit the code, they need to get the approval from other programmers in the open-source community. Although the blockchain nodes are available around the world, this won't affect its execution efficiency. Because the distributed design of the system means applications don't need to connect to all the nodes, but to the nearest node to get the information they need. To sum up, we can describe the features of blockchain with four words: Distributed, Autonomous, Contractual, Trackable. In this text, we will use DACT, the initial letters of the four words, namely Distributed, Autonomous, Contractual and Trackable, to represent the features of blockchain technology. Some once mentioned that the four features of the internet are "fairness, sharing, openness and transparency". DACT exactly corresponds to the four features of the internet: Distributed—Sharing, Autonomous—Transparency, Contractual—Fairness, Trackable—Openness.
The blockchain technology is fully compliant with the internet features, and systems implemented by the blockchain technology happen to fit with the four features of internet.
In the later part of this article, we will see that after the data is stored in the blockchain system, all transactions are traceable, full copies of timestamped transactions are available on each node in the system and the addition of transaction information requires consensus of the system, so the system data cannot be tampered with.
When our applications are based on the blockchain, we do not have to worry about data tampering, loss or wrong transaction results, because all the operations are automatically completed by the system. As a matter of fact, when using blockchain-based systems, people's trust in central organizations is replaced by their trust in mathematics.
Data openness does not mean that data on blockchain-based systems is accessible to all. On the contrary, blockchain-based systems can have the strictest permission settings. After a protocol agreed on is written into code, the contractual feature of the system makes encrypted data only accessible to users with appropriate permissions, and even nodes participating in system operation cannot access the data. Therefore, blockchain-based systems are safe.
There have been a lot of communities and discussions about blockchain. Fundamentally, I think there are two schools in the blockchain sector:
(1) Blockchain is a technology serving bitcoin or other virtual currencies.
(2) Blockchain technology can be applied to the financial or other fields.
There is a saying in bitcoin circles that the rise of blockchain technology gradually differentiates the money circle - one side is the bitcoin conservatives who hold blockchain in detestation, and the other side is the new blockchain school who won't take bitcoin into account.
If I must choose between the two, I will join the latter. But we don't class ourselves in the bitcoin circle, so our ideas may be more radical, thus not necessarily accepted by mainstream blockchain communities. We are more interested in the blockchain technology and the design philosophy behind it, as well as its application in various fields.
We are the third school who are neutral on bitcoin but highly interested in blockchain technology. We are the trend school and hold that the blockchain technology will lead the wave of information technology in the decade to come. If we can transform an industry system with the blockchain design philosophy, we think that is the contribution of the blockchain to the industry.
Many articles about blockchain technology mention the concept of smart contract, as if it is the twin brother of blockchain. However, I have read the articles by Satoshi Nakamoto a dozen of times, finding no trace of "smart contract", "smart" or "contract", even words with similar definitions to "smart contract".
It is actually blockchain researchers and practitioners who associate the concepts of blockchain technology and smart contract, because they think that blockchain technology is the best technology to implement smart contract.
According to Wikipedia, the first person documented to propose the word "smart contract" is a computer scientist Nick Szabo. He intended to realize e-commerce relationships on the internet between strangers like legal contracts. On his own page, Nick Szabo defined smart contract as follows:
A smart contract is a computerized transaction protocol that executes the terms of a contract.
The objective of designing the smart contract is: satisfy contract terms, exclude the possibility of unexpected situations, whether malicious or unintentional, no intermediate third-party required. Nick Szabo thinks that, through cryptology protocol and digital safety technology, smart contract can be effectively implemented on the internet to reduce fraud, lower arbitration costs and transaction costs.
In his article titled Distributing Authorities and Verifying Their Claims, he cited a sentence by the former US president Ronald Reagan: “Trust but verify.”
So what is smart contract exactly? We can explain this concept with share transaction as an example. Peter has 100 Facebook shares in his account, with each share valuing around 100 US dollars, and Jeff has 4,000 US dollars of savings in his account. The status of their accounts is as follows:
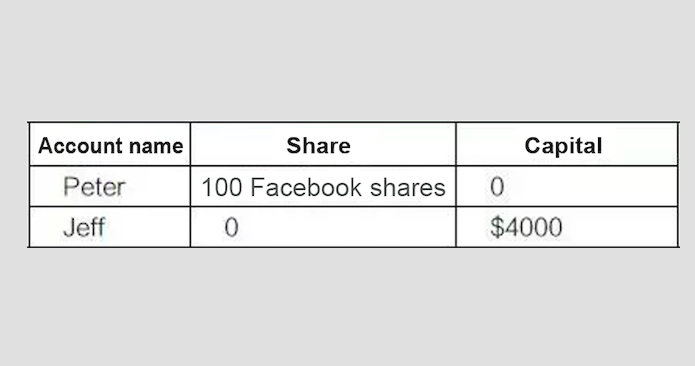
They signed a smart
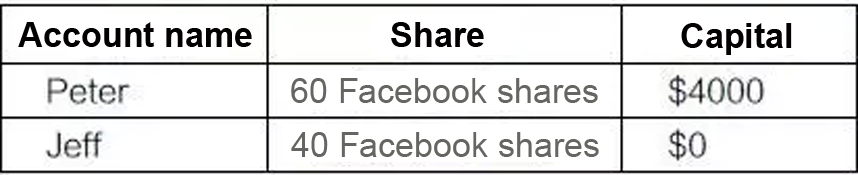
contract: Jeff bought 40 Facebook shares from Peter at 100 US dollars per
share. So when the 4,000 US dollars is transferred from Jeff's account to
Peter's account, smart contract will find the condition met, and transfer 40
shares from Peter's account to Jeff's account. After the smart contract is
executed, their account status is like this:
The smart contract will complete the transaction as agreed. If the smart contract does not exist, an intermediate third party will be required for this transaction. If we want to utilize the cryptography principle and electronic contract to protect data from third-party tampering in the blockchain system, it will be smart contract. Smart contract boasts a wide use. All transactions that require authenticity identification, multiple-party involvement, source tracing and compliance can adopt smart contract to maintain reliability of data in the system and ensure the data is not tampered with. The Economic Times predicted in 2015 that ten positions may be replaced by robots in the near future, including bank staff and intermediaries of financial transaction systems, and also mentioned that the blockchain technology is one of the crucial technologies that boost such replacement.
Smart contract can be applied to a wide range of fields, including: finance, health and medicine, medicinal herbs, food, energy, electricity, transport, real estate, agriculture, government, military. Now you may have your own ideas about smart contract. In fact, any action that can be achieved by code can be called a smart contract. The first implemented smart contract on the blockchain is the action to move the bitcoin from one account to another.
Operating Principle and Implementation of Flink: Memory Management

2,593 posts | 793 followers
FollowAlibaba Cloud Indonesia - October 25, 2022
Alibaba Clouder - December 6, 2016
vic - August 30, 2019
Alibaba Clouder - September 27, 2018
Alibaba Clouder - November 26, 2019
Alibaba Clouder - August 12, 2019

2,593 posts | 793 followers
Follow LedgerDB
LedgerDB
A ledger database that provides powerful data audit capabilities.
Learn More Blockchain as a Service
Blockchain as a Service
BaaS provides an enterprise-level platform service based on leading blockchain technologies, which helps you build a trusted cloud infrastructure.
Learn MoreMore Posts by Alibaba Clouder