Managed Service for Prometheus は、ServiceMonitor カスタムリソース定義 (CRD) を使用したサービスディスカバリをサポートしています。ServiceMonitor を使用して、Pod ディスカバリの名前空間を定義し、matchLabel でモニタリングするサービスを選択できます。本トピックでは、Spring Boot フレームワーク上に構築されたアプリケーションに対して、ServiceMonitor を使用してサービスディスカバリ構成を作成する方法について説明します。
デモ
デモプロジェクトをダウンロードして、ServiceMonitor を使用したサービスディスカバリ構成の作成方法の完全な例をご参照ください。
ステップ 1:依存関係の追加
Maven アプリケーションを作成し、次の依存関係を pom.xml ファイルに追加します。
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>io.micrometer</groupId> <artifactId>micrometer-registry-prometheus</artifactId> <version>1.6.6</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId> <optional>true</optional> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> <artifactId>lombok</artifactId> <optional>true</optional> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies>プロジェクトの src/resources/applications.properties ファイルに次の構成を追加します。
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=prometheusプロジェクトを開始し、ブラウザで
http://{host}:{port}/actuator/prometheusにアクセスします。対応する Java 仮想マシン (JVM) のモニタリングデータが表示されます。下図に例を示します。
ステップ 2:Kubernetes クラスターのデプロイ
イメージをビルドし、イメージリポジトリにアップロードします。詳細については、「ソースコードホスティングプラットフォームのバインド」をご参照ください。
次の YAML 構成を使用して Deployment を作成します。
apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: micrometer-prometheus namespace: default labels: app: demo-prometheus spec: replicas: 3 selector: matchLabels: app: demo-prometheus template: metadata: labels: app: demo-prometheus spec: containers: - name: micrometer-prometheus image: manjusakalza/micrometer-prometheus:latest ports: - containerPort: 8080次の YAML 構成を使用してサービスを作成します。
apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: prometheus-metrics-demo namespace: default labels: micrometer-prometheus-discovery: 'true' spec: selector: app: demo-prometheus ports: - protocol: TCP port: 8080 targetPort: 8080 name: metrics
ステップ 3:ServiceMonitor の作成
YAML ファイルをコンピューターに保存し、
kubectl apply -f {path/to/the/YAML/file}を実行してファイルを適用します。
以下は、ServiceMonitor の YAML ファイルのサンプルです:
apiVersion: monitoring.coreos.com/v1
kind: ServiceMonitor
metadata:
name: micrometer-demo
namespace: default
spec:
endpoints:
- interval: 15s
path: /actuator/prometheus
port: metrics # 注:ポート番号ではなく、ポート名を設定してください。
namespaceSelector:
any: true
selector:
matchLabels:
micrometer-prometheus-discovery: 'true'この YAML ファイルの各フィールドの説明は次のとおりです:
metadataフィールドのnameとnamespaceは、ServiceMonitor の主要なメタデータを指定します。specフィールドのendpointsは、Prometheus がメトリックをスクレイピングするサーバーエンドポイントを指定します。endpointsは、複数のendpointsを作成できる配列です。各endpointには、次の 3 つのフィールドが含まれます:interval:Prometheus が現在のendpointをスクレイピングする間隔を指定します。単位は秒です。この例では、値は15sに設定されています。path:Prometheus のスクレイピングパスを指定します。この例では、値は/actuator/prometheusに設定されています。port: メトリックの収集元となるサービスポートの名前。このパラメーターには、ステップ 2 で作成した Service で指定されているnameパラメーターの値を設定します。この例では、このパラメーターはmetricsに設定されています。重要ポート番号ではなく、ポート名を設定してください。
specフィールドのnamespaceSelectorは、サービスディスカバリの範囲を指定します。namespaceSelectorには、相互に排他的な 2 つのフィールドが含まれています。各フィールドの説明は次のとおりです:any:値はtrueのみです。このフィールドを `true` に設定すると、システムはすべての名前空間でセレクターのフィルター条件に一致するすべてのサービスをモニタリングします。matchNames:モニタリングするnamespacesを指定する配列です。たとえば、default と arms-prom の名前空間のサービスのみをモニタリングするには、matchNamesを次のように設定します:namespaceSelector: matchNames: - default - arms-prom
specフィールドのselectorは、サービスの選択に使用されます。この例で使用されるサービスには、micrometer-prometheus-discovery: 'true' というラベルが付いています。したがって、
selectorを次のように設定します:selector: matchLabels: micrometer-prometheus-discovery: 'true'
Basic 認証機能を使用するには、次のサンプル YAML ファイルをご参照ください。
apiVersion: monitoring.coreos.com/v1
kind: ServiceMonitor
metadata:
name: cloud-open-api-monitor # ServiceMonitor に一意の名前を設定します。
namespace: default # ServiceMonitor が存在する名前空間を設定します。
spec:
endpoints:
- interval: 30s
# Prometheus が現在のエンドポイントをスクレイピングする間隔を指定します。
port: tcp-8080
# Prometheus エクスポーターのコードで公開されているパスを入力します。
path: /api/actuator/prometheus
basicAuth:
password:
name: basic-auth
key: <password>
username:
name: basic-auth
key: <userName>
scheme: http
namespaceSelector:
any: true
selector:
matchLabels:
# 次のラベルを持つサービスに一致させます。
edas.oam.acname: cloud-open-apiBasic 認証機能を使用するために必要な権限がない場合は、必要な権限を持つ ClusterRole をクラスターに追加します。次に、ClusterRoleBinding を使用して、この ClusterRole を arms-prom 名前空間の arms-prom-operator という名前の ServiceAccount にバインドします。これにより、Prometheus エージェントに必要な権限が付与されます。
ClusterRole の YAML ファイル
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 kind: ClusterRole metadata: name: prometheus-agent-role labels: app: prometheus-agent rules: - apiGroups: [""] resources: ["pods", "services", "endpoints", "nodes"] verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"] # 必要に応じて調整します。 - apiGroups: ["monitoring.coreos.com"] # 必要に応じて apiGroups を調整します。 resources: ["*"] verbs: ["get", "list", "watch", "create", "update", "delete"] # 必要に応じて調整します。ClusterRoleBinding の YAML ファイル
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 kind: ClusterRoleBinding metadata: name: prometheus-agent-binding subjects: - kind: ServiceAccount name: arms-prom-operator # サービスアカウント名 namespace: arms-prom # サービスアカウントが存在する名前空間。 roleRef: kind: ClusterRole name: prometheus-agent-role # 上記で定義した ClusterRole の名前。 apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
ステップ 4:ServiceMonitor の検証
次の手順を実行して、Prometheus がサービスを正常に検出したことを確認します。
Managed Service for Prometheus コンソールにログインします。左側のナビゲーションウィンドウで、[統合管理] をクリックします。
[統合済み環境] タブで、[コンテナサービス] リストにあるターゲットコンテナ環境の名前をクリックします。
[セルフモニタリング] タブをクリックします。
[ターゲット] タブで、{namespace}/{serviceMonitorName}/x という名前のターゲットが存在するかどうかを確認します。
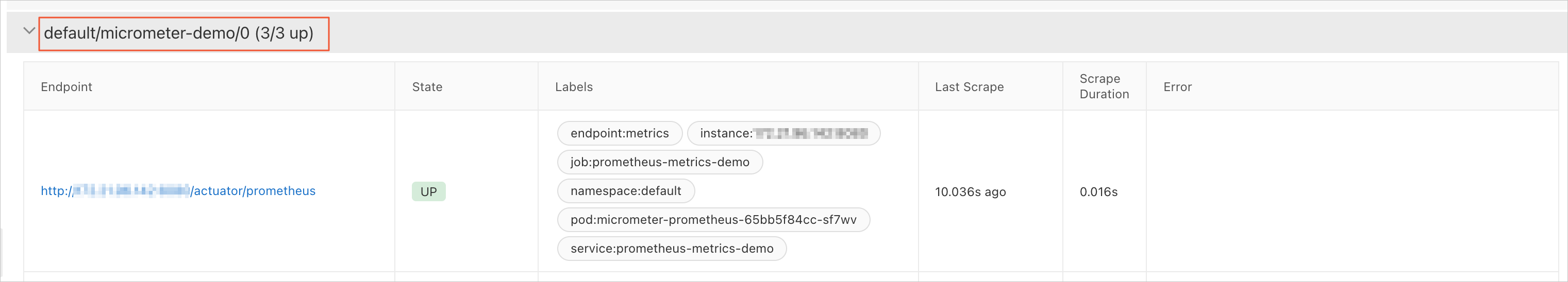
{namespace}/{serviceMonitorName}/x ターゲットの行をクリックして展開し、エンドポイントのリンクをクリックします。
メトリックが正しく表示されることを確認します。