ビッグデータプラットフォームの開発により、複数のタイプの非構造化データと半構造化データを処理できます。 たとえば、IPアドレスをジオロケーションに変換できます。 このトピックでは、MaxComputeユーザー定義関数 (UDF) を使用してIPv4またはIPv6アドレスをジオロケーションに変換する方法について説明します。
前提条件
次の要件が満たされていることを確認してください。
MaxComputeクライアントがインストールされています。
MaxComputeクライアントのインストールと設定方法の詳細については、「MaxComputeクライアントのインストールと設定」をご参照ください。
MaxCompute Studioがインストールされています。 詳細については、「MaxCompute Studioのインストール」をご参照ください。
背景情報
IPv4またはIPv6アドレスをジオロケーションに変換するには、IPアドレスを含むIPアドレスライブラリファイルをダウンロードし、そのファイルをリソースとしてMaxComputeプロジェクトにアップロードする必要があります。 IPアドレスライブラリファイルに基づいてMaxCompute UDFを開発および作成した後、SQL文でUDFを呼び出してIPアドレスをジオロケーションに変換できます。
使用上の注意
このトピックで提供されるIPアドレスライブラリファイルは、参照専用です。 ビジネス要件に基づいてIPアドレスライブラリファイルを維持する必要があります。
手順
MaxCompute UDFを使用してIPv4またはIPv6アドレスをジオロケーションに変換するには、次の手順を実行します。
IPアドレスライブラリファイルをリソースとしてMaxComputeプロジェクトにアップロードします。 このリソースは、後続の手順でMaxCompute UDFを作成するときに使用されます。
MaxComputeプロジェクトに接続し、MaxCompute Javaモジュールを作成します。
IntelliJ IDEAを使用してMaxCompute UDFを作成します。
MaxCompute UDFを作成します。
手順5: MaxCompute UDFを呼び出してIPアドレスをジオロケーションに変換
SQL文で作成したMaxCompute UDFを呼び出して、IPアドレスをジオロケーションに変換します。
手順1: IPアドレスライブラリファイルのアップロード
ダウンロードしてIPアドレスライブラリファイルをオンプレミスマシンに追加し、ファイルを解凍してipv4.txtおよびipv6.txtファイルを取得し、MaxComputeクライアントのインストールディレクトリにファイルを配置します。
. ..\odpscmd_public\bin.このトピックで提供されるIPアドレスライブラリファイルは、参照専用です。 ビジネス要件に基づいてIPアドレスライブラリファイルを維持する必要があります。
MaxComputeクライアントを起動し、ipv4.txtおよびipv6.txtファイルをアップロードするMaxComputeプロジェクトに移動します。
add fileコマンドを実行して、2つのファイルをファイルリソースとしてMaxComputeプロジェクトにアップロードします。(ローカルデバッグ) ipv4.txtファイルとipv6.txtファイルをローカルプロジェクトの
warehouse/example_project/_resources_ディレクトリに保存します。
ステップ2: MaxComputeプロジェクトへの接続
MaxComputeプロジェクトに接続します。 詳細については、「プロジェクト接続の管理」をご参照ください。
MaxCompute Javaモジュールを作成します。 詳細については、「MaxCompute Javaモジュールの作成」をご参照ください。
ステップ3: MaxCompute UDFの書き込み
Javaクラスを作成します。
Javaクラスは、次のサブステップでMaxCompute UDFを書き込むために使用されます。
IntelliJ IDEAを開始します。 [Project] タブの左側のナビゲーションウィンドウで、 を選択し、[java] を右クリックして、 を選択します。
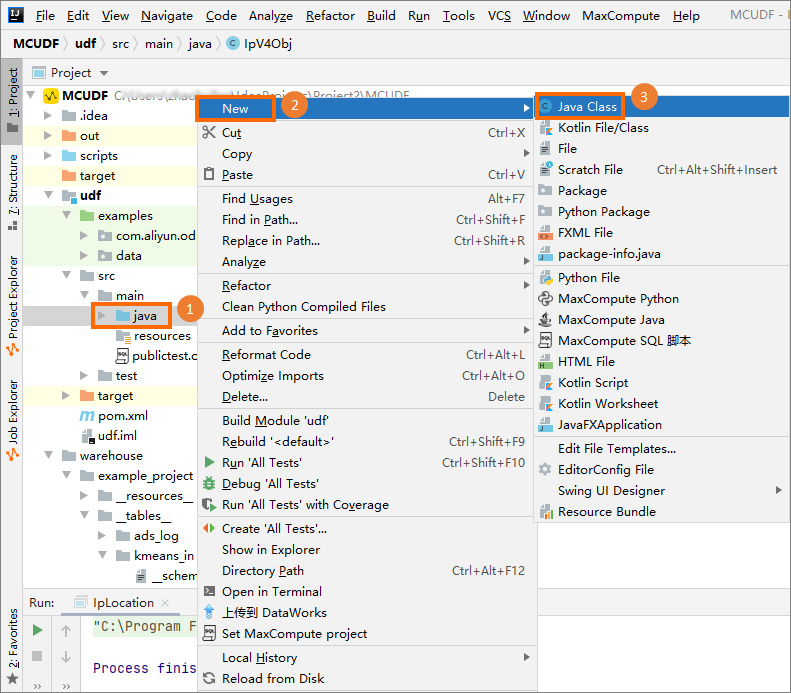
[新しいJavaクラス] ダイアログボックスで、クラス名を入力し、enterキーを押して、コードエディターにコードを入力します。
3つのJavaクラスを作成する必要があります。 次のセクションでは、これらのクラスの名前とコードを示します。 コードを変更せずに再利用できます。
IpUtils
package com.aliyun.odps.udf.utils; import java.math.BigInteger; import java.net.Inet4Address; import java.net.Inet6Address; import java.net.InetAddress; import java.net.UnknownHostException; import java.util.Arrays; public class IpUtils { /** * Convert the data type of IP addresses from STRING to LONG. * * @param ipInString * IP addresses of the STRING type. * @return Return the IP addresses of the LONG type. */ public static long StringToLong(String ipInString) { ipInString = ipInString.replace(" ", ""); byte[] bytes; if (ipInString.contains(":")) bytes = ipv6ToBytes(ipInString); else bytes = ipv4ToBytes(ipInString); BigInteger bigInt = new BigInteger(bytes); // System.out.println(bigInt.toString()); return bigInt.longValue(); } /** * Convert the data type of IP addresses from STRING to LONG. * * @param ipInString * IP addresses of the STRING type. * @return Return the IP addresses of the STRING type that is converted from BIGINT. */ public static String StringToBigIntString(String ipInString) { ipInString = ipInString.replace(" ", ""); byte[] bytes; if (ipInString.contains(":")) bytes = ipv6ToBytes(ipInString); else bytes = ipv4ToBytes(ipInString); BigInteger bigInt = new BigInteger(bytes); return bigInt.toString(); } /** * Convert the data type of IP addresses from BIGINT to STRING. * * @param ipInBigInt * IP addresses of the BIGINT type. * @return Return the IP addresses of the STRING type. */ public static String BigIntToString(BigInteger ipInBigInt) { byte[] bytes = ipInBigInt.toByteArray(); byte[] unsignedBytes = Arrays.copyOfRange(bytes, 1, bytes.length); // Remove the sign bit. try { String ip = InetAddress.getByAddress(unsignedBytes).toString(); return ip.substring(ip.indexOf('/') + 1).trim(); } catch (UnknownHostException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } /** * Convert the data type of IPv6 addresses into signed byte 17. */ private static byte[] ipv6ToBytes(String ipv6) { byte[] ret = new byte[17]; ret[0] = 0; int ib = 16; boolean comFlag=false;// IPv4/IPv6 flag. if (ipv6.startsWith(":"))// Remove the colon (:) from the start of IPv6 addresses. ipv6 = ipv6.substring(1); String groups[] = ipv6.split(":"); for (int ig=groups.length - 1; ig > -1; ig--) {// Reverse scan. if (groups[ig].contains(".")) { // Both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses exist. byte[] temp = ipv4ToBytes(groups[ig]); ret[ib--] = temp[4]; ret[ib--] = temp[3]; ret[ib--] = temp[2]; ret[ib--] = temp[1]; comFlag = true; } else if ("".equals(groups[ig])) { // Zero-length compression. Calculate the number of missing groups. int zlg = 9 - (groups.length + (comFlag ? 1 : 0)); while (zlg-- > 0) {// Set these groups to 0. ret[ib--] = 0; ret[ib--] = 0; } } else { int temp = Integer.parseInt(groups[ig], 16); ret[ib--] = (byte) temp; ret[ib--] = (byte) (temp >> 8); } } return ret; } /** * Convert the data type of IPv4 addresses into signed byte 5. */ private static byte[] ipv4ToBytes(String ipv4) { byte[] ret = new byte[5]; ret[0] = 0; // Find the positions of the periods (.) in the IP addresses of the STRING type. int position1 = ipv4.indexOf("."); int position2 = ipv4.indexOf(".", position1 + 1); int position3 = ipv4.indexOf(".", position2 + 1); // Convert the IP addresses of the STRING type between periods (.) into INTEGER. ret[1] = (byte) Integer.parseInt(ipv4.substring(0, position1)); ret[2] = (byte) Integer.parseInt(ipv4.substring(position1 + 1, position2)); ret[3] = (byte) Integer.parseInt(ipv4.substring(position2 + 1, position3)); ret[4] = (byte) Integer.parseInt(ipv4.substring(position3 + 1)); return ret; } /** * @param ipAdress IPv4 or IPv6 addresses of the STRING type. * @return 4:IPv4, 6:IPv6, 0: Invalid IP addresses. * @throws Exception */ public static int isIpV4OrV6(String ipAdress) throws Exception { InetAddress address = InetAddress.getByName(ipAdress); if (address instanceof Inet4Address) return 4; else if (address instanceof Inet6Address) return 6; return 0; } /* * Check whether the IP address belongs to a specific IP section. * * ipSection The IP sections that are separated by hyphens (-). * * The IP address to check. */ public static boolean ipExistsInRange(String ip, String ipSection) { ipSection = ipSection.trim(); ip = ip.trim(); int idx = ipSection.indexOf('-'); String beginIP = ipSection.substring(0, idx); String endIP = ipSection.substring(idx + 1); return getIp2long(beginIP) <= getIp2long(ip) && getIp2long(ip) <= getIp2long(endIP); } public static long getIp2long(String ip) { ip = ip.trim(); String[] ips = ip.split("\\."); long ip2long = 0L; for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) { ip2long = ip2long << 8 | Integer.parseInt(ips[i]); } return ip2long; } public static long getIp2long2(String ip) { ip = ip.trim(); String[] ips = ip.split("\\."); long ip1 = Integer.parseInt(ips[0]); long ip2 = Integer.parseInt(ips[1]); long ip3 = Integer.parseInt(ips[2]); long ip4 = Integer.parseInt(ips[3]); long ip2long = 1L * ip1 * 256 * 256 * 256 + ip2 * 256 * 256 + ip3 * 256 + ip4; return ip2long; } public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(StringToLong("2002:7af3:f3be:ffff:ffff:ffff:ffff:ffff")); System.out.println(StringToLong("54.38.72.63")); } private class Invalid{ private Invalid() { } } }IpV4Obj
package com.aliyun.odps.udf.objects; public class IpV4Obj { public long startIp ; public long endIp ; public String city; public String province; public IpV4Obj(long startIp, long endIp, String city, String province) { this.startIp = startIp; this.endIp = endIp; this.city = city; this.province = province; } @Override public String toString() { return "IpV4Obj{" + "startIp=" + startIp + ", endIp=" + endIp + ", city='" + city + '\'' + ", province='" + province + '\'' + '}'; } public void setStartIp(long startIp) { this.startIp = startIp; } public void setEndIp(long endIp) { this.endIp = endIp; } public void setCity(String city) { this.city = city; } public void setProvince(String province) { this.province = province; } public long getStartIp() { return startIp; } public long getEndIp() { return endIp; } public String getCity() { return city; } public String getProvince() { return province; } }IpV6Obj
package com.aliyun.odps.udf.objects; public class IpV6Obj { public String startIp ; public String endIp ; public String city; public String province; public String getStartIp() { return startIp; } @Override public String toString() { return "IpV6Obj{" + "startIp='" + startIp + '\'' + ", endIp='" + endIp + '\'' + ", city='" + city + '\'' + ", province='" + province + '\'' + '}'; } public IpV6Obj(String startIp, String endIp, String city, String province) { this.startIp = startIp; this.endIp = endIp; this.city = city; this.province = province; } public void setStartIp(String startIp) { this.startIp = startIp; } public String getEndIp() { return endIp; } public void setEndIp(String endIp) { this.endIp = endIp; } public String getCity() { return city; } public void setCity(String city) { this.city = city; } public String getProvince() { return province; } public void setProvince(String province) { this.province = province; } }
MaxCompute UDFの書き込み
[Project] タブの左側のナビゲーションウィンドウで、 を選択し、[java] を右クリックして、 を選択します。
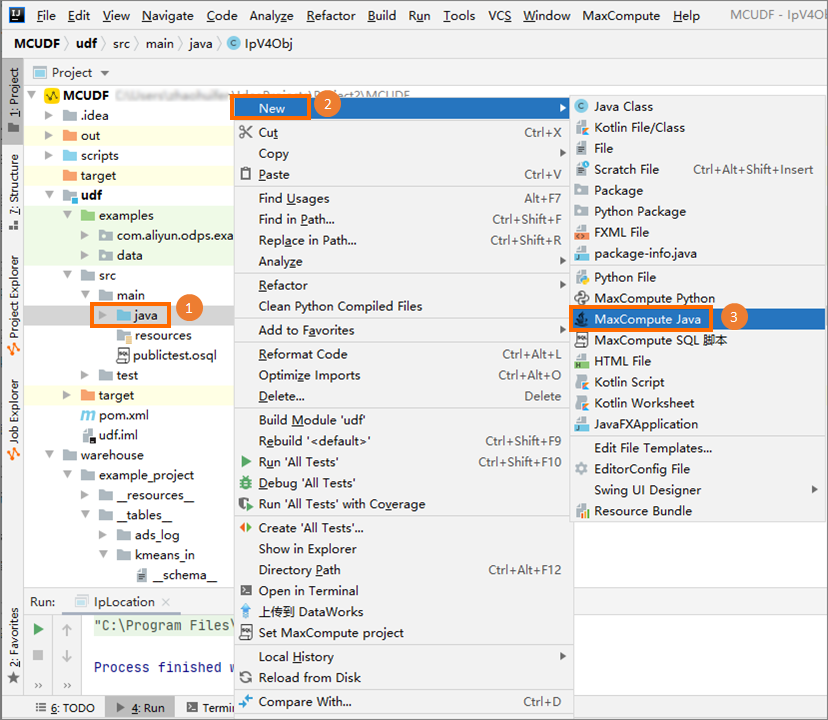
[新しいMaxCompute javaクラスの作成] ダイアログボックスで、[UDF] をクリックし、[名前] フィールドにクラス名を入力します。 次に、Enterキーを押して、コードエディターにコードを入力します。
 次のコードは、IpLocationという名前のJavaクラスに基づいてUDFを記述する方法を示しています。 コードを変更せずに再利用できます。
次のコードは、IpLocationという名前のJavaクラスに基づいてUDFを記述する方法を示しています。 コードを変更せずに再利用できます。 package com.aliyun.odps.udf.udfFunction; import com.aliyun.odps.udf.ExecutionContext; import com.aliyun.odps.udf.UDF; import com.aliyun.odps.udf.UDFException; import com.aliyun.odps.udf.utils.IpUtils; import com.aliyun.odps.udf.objects.IpV4Obj; import com.aliyun.odps.udf.objects.IpV6Obj; import java.io.*; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Comparator; import java.util.List; import java.util.stream.Collectors; public class IpLocation extends UDF { public static IpV4Obj[] ipV4ObjsArray; public static IpV6Obj[] ipV6ObjsArray; public IpLocation() { super(); } @Override public void setup(ExecutionContext ctx) throws UDFException, IOException { //IPV4 if(ipV4ObjsArray==null) { BufferedInputStream bufferedInputStream = ctx.readResourceFileAsStream("ipv4.txt"); BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(bufferedInputStream)); ArrayList<IpV4Obj> ipV4ObjArrayList=new ArrayList<>(); String line = null; while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) { String[] f = line.split("\\|", -1); if(f.length>=5) { long startIp = IpUtils.StringToLong(f[0]); long endIp = IpUtils.StringToLong(f[1]); String city=f[3]; String province=f[4]; IpV4Obj ipV4Obj = new IpV4Obj(startIp, endIp, city, province); ipV4ObjArrayList.add(ipV4Obj); } } br.close(); List<IpV4Obj> collect = ipV4ObjArrayList.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(IpV4Obj::getStartIp)).collect(Collectors.toList()); ArrayList<IpV4Obj> basicIpV4DataList=(ArrayList)collect; IpV4Obj[] ipV4Objs = new IpV4Obj[basicIpV4DataList.size()]; ipV4ObjsArray = basicIpV4DataList.toArray(ipV4Objs); } //IPV6 if(ipV6ObjsArray==null) { BufferedInputStream bufferedInputStream = ctx.readResourceFileAsStream("ipv6.txt"); BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(bufferedInputStream)); ArrayList<IpV6Obj> ipV6ObjArrayList=new ArrayList<>(); String line = null; while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) { String[] f = line.split("\\|", -1); if(f.length>=5) { String startIp = IpUtils.StringToBigIntString(f[0]); String endIp = IpUtils.StringToBigIntString(f[1]); String city=f[3]; String province=f[4]; IpV6Obj ipV6Obj = new IpV6Obj(startIp, endIp, city, province); ipV6ObjArrayList.add(ipV6Obj); } } br.close(); List<IpV6Obj> collect = ipV6ObjArrayList.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(IpV6Obj::getStartIp)).collect(Collectors.toList()); ArrayList<IpV6Obj> basicIpV6DataList=(ArrayList)collect; IpV6Obj[] ipV6Objs = new IpV6Obj[basicIpV6DataList.size()]; ipV6ObjsArray = basicIpV6DataList.toArray(ipV6Objs); } } public String evaluate(String ip){ if(ip==null||ip.trim().isEmpty()||!(ip.contains(".")||ip.contains(":"))) { return null; } int ipV4OrV6=0; try { ipV4OrV6= IpUtils.isIpV4OrV6(ip); } catch (Exception e) { return null; } // IPv4 addresses are used. if(ipV4OrV6==4) { int i = binarySearch(ipV4ObjsArray, IpUtils.StringToLong(ip)); if(i>=0) { IpV4Obj ipV4Obj = ipV4ObjsArray[i]; return ipV4Obj.city+","+ipV4Obj.province; }else{ return null; } } else if(ipV4OrV6==6)// IPv6 addresses are used. { int i = binarySearchIPV6(ipV6ObjsArray, IpUtils.StringToBigIntString(ip)); if(i>=0) { IpV6Obj ipV6Obj = ipV6ObjsArray[i]; return ipV6Obj.city+","+ipV6Obj.province; }else{ return null; } } else{// IP addresses are invalid. return null; } } @Override public void close() throws UDFException, IOException { super.close(); } private static int binarySearch(IpV4Obj[] array,long ip){ int low=0; int hight=array.length-1; while (low<=hight) { int middle=(low+hight)/2; if((ip>=array[middle].startIp)&&(ip<=array[middle].endIp)) { return middle; } if (ip < array[middle].startIp) hight = middle - 1; else { low = middle + 1; } } return -1; } private static int binarySearchIPV6(IpV6Obj[] array,String ip){ int low=0; int hight=array.length-1; while (low<=hight) { int middle=(low+hight)/2; if((ip.compareTo(array[middle].startIp)>=0)&&(ip.compareTo(array[middle].endIp)<=0)) { return middle; } if (ip.compareTo(array[middle].startIp) < 0) hight = middle - 1; else { low = middle + 1; } } return -1; } private class Invalid{ private Invalid() { } } }
ローカルデバッグ用のテストデータを準備します。
ローカルプロジェクトの
warehouse/example_project/__tables__/wc_in2/p1=2/p2=1/ディレクトリで、dataファイルを開きます。データファイルの最後の列にipv4.txtファイルに含まれているIPアドレスを入力し、変更を保存します。 3つのIPアドレスを入力できます。
MaxCompute UDFをデバッグして、コードが期待どおりに実行されているかどうかを確認します。
UDAFをデバッグする方法の詳細については、「UDFをデバッグするためのローカル実行の実行」をご参照ください。
作成したMaxCompute UDFスクリプトを右クリックし、[Run] を選択します。
[実行 /デバッグ設定] ダイアログボックスで、必要なパラメーターを設定し、[OK] をクリックします。 以下の図は一例です。
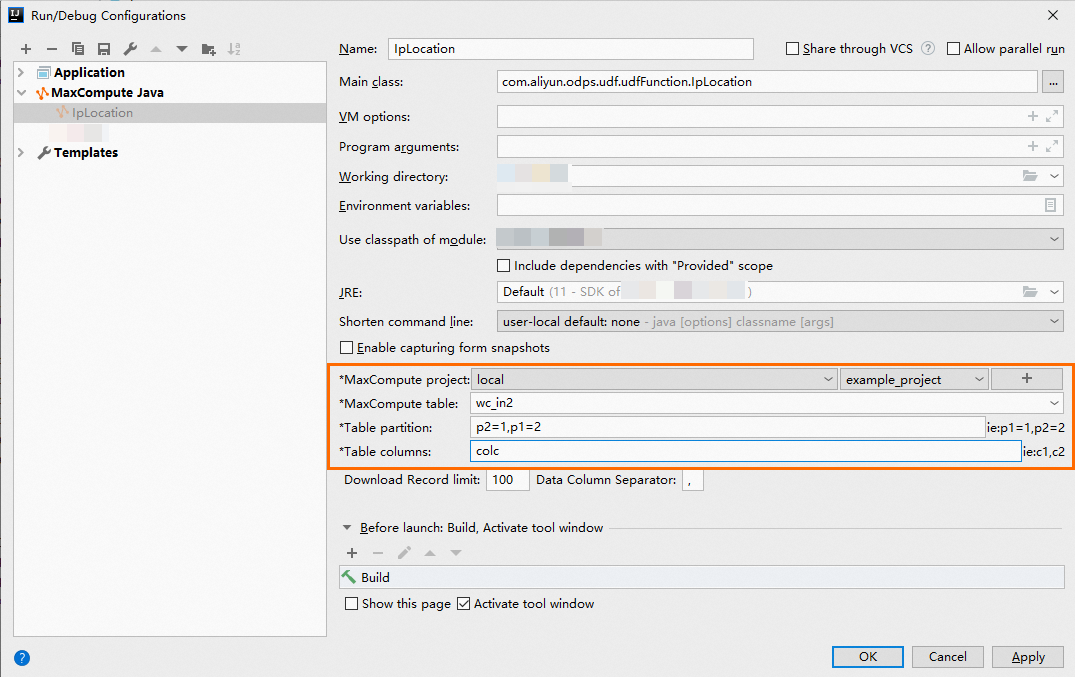 エラーが返されない場合、コードは正常に実行されます。 次の手順に進むことができます。 エラーが報告された場合は、IntelliJ IDEAに表示されたエラー情報に基づいてトラブルシューティングを実行できます。 説明
エラーが返されない場合、コードは正常に実行されます。 次の手順に進むことができます。 エラーが報告された場合は、IntelliJ IDEAに表示されたエラー情報に基づいてトラブルシューティングを実行できます。 説明前の図のパラメーター設定は参考用です。
ステップ4: MaxCompute UDFの作成
コンパイルしたMaxCompute UDFスクリプトを右クリックし、[サーバーにデプロイ] を選択します。
[jarのパッケージ化、リソースの送信、機能の登録] ダイアログボックスで、パラメーターを設定します。
パラメーターの詳細については、「Javaプログラムのパッケージ化、パッケージのアップロード、MaxCompute UDFの作成」をご参照ください。
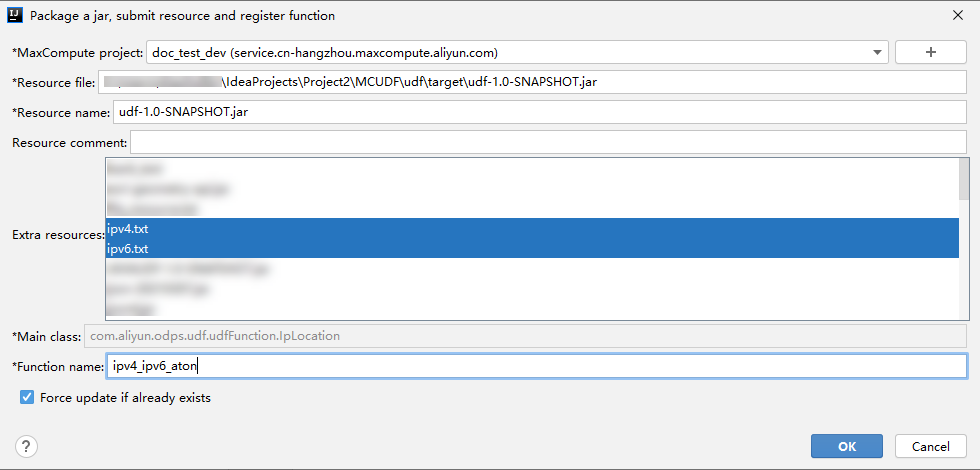 Extra resources: ステップ1でアップロードしたIPアドレスライブラリファイルipv4.txtおよびipv6.txtを選択する必要があります。 このトピックでは、作成される関数の名前はipv4_ipv6_atonです。
Extra resources: ステップ1でアップロードしたIPアドレスライブラリファイルipv4.txtおよびipv6.txtを選択する必要があります。 このトピックでは、作成される関数の名前はipv4_ipv6_atonです。
ステップ5: MaxCompute UDFを呼び出してIPアドレスをジオロケーションに変換する
SQL SELECTステートメントを実行してMaxCompute UDFを呼び出し、IPv4またはIPv6アドレスをジオロケーションに変換できます。
サンプル文:
IPv4アドレスをジオロケーションに変換する
select ipv4_ipv6_aton('116.11.XX.XX');次の応答が返されます。
Beihai, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous RegionIPv6アドレスをジオロケーションに変換する
select ipv4_ipv6_aton('2001:0250:080b:0:0:0:0:0');次の応答が返されます。
Baoding, Hebei Province