The network is the infrastructure of the digital world. Without network connectivity, information cannot be exchanged. Therefore, the design of network architecture, especially for high availability and disaster recovery, is crucial for application systems to achieve fast recovery and minimize business losses under abnormal circumstances.
Cloud Network Planning and Design
To meet the requirements of cloud network security, scalability, and high availability, the cloud network planning and design should adhere to the following principles:
Reserve IP address space for network scaling
In a single region, reserve IP address space for creating new VPCs;
In a single VPC, reserve IP address space for creating new subnets;
In a single subnet, pay attention to the remaining available IP addresses.
Plan IP address space for different regions, availability zones, and business systems
In a single region, plan different VPCs based on business needs, and each VPC uses an independent IP address space;
In a single VPC, plan subnets based on business needs, considering availability zones and IP address space;
Some cloud services may occupy a large number of IP addresses in a short time. In order to avoid insufficient IP address resources, it is advisable to consider targeted planning of switches.
Cloud Network Interconnection Design
Large enterprises usually have multiple departments, each consisting of multiple teams, such as development, testing, and operations. When different departments and teams use cloud services, they usually isolate their businesses using multiple VPCs. However, there are scenarios where different teams and departments need to access each other's services, which requires interconnectivity between VPCs, CEN can resolve this scenario.
Cloud Enterprise Network (CEN): All instances that need to communicate with each other, such as VPCs, VBRs, and VPNs, are connected to the Cloud Enterprise Network (CEN). The CEN acts as a hub connecting all instances. Any VPC that wants to communicate with another VPC must route through the CEN, reducing the complexity of network configuration. The CEN supports various routing policies and traffic control rules to better meet the networking requirements of large enterprises.
Internet Egress Design
When designing the internet egress for cloud environments, the following principles should be followed:
Avoid unnecessary exposure to the public network
When using static public IP or elastic public IP addresses for ECS instances, restrict the port exposure using security groups;
Provide public network access to ECS instances through network cloud services (such as Server Load Balancer and NAT Gateway) instead of directly using public IP addresses on ECS instances.
Properly use NAT Gateway for public network access
In scenarios with strict security access requirements, use Instance-level SNAT rules instead of subnet-level SNAT rules;
Ensure the consistent maximum bandwidth limit for each EIP in the same SNAT rule;
Different SNAT rules can be configured based on business requirements by using different Elastic IP (EIP) configurations;
Check whether the maximum number of concurrent connections provided by the EIPs in the SNAT rules meets the business requirements.
Properly use Shared Bandwidth to improve public network access capability
Different business models are recommended to use different shared bandwidth instances to configure different billing methods and reduce business costs;
Recommended for businesses that require resource isolation for public network bandwidth to configure dedicated shared bandwidth instances.
Hybrid Cloud Interconnection High Availability Design
As enterprises gradually migrate new businesses and deploy external business systems to the cloud, some enterprises that have their own on-premises IDCs need to connect the cloud and on-premises environments to form a hybrid cloud. In addition, some enterprises use resources from multiple cloud vendors to further improve business high availability. Therefore, interconnectivity between different cloud vendors is a necessary requirement for hybrid cloud deployment.
The high availability design of hybrid cloud interconnection should adhere to the following principles:
Link redundancy: In hybrid cloud interconnection, at least two links are required for redundancy or primary/backup load balancing. When one link is abnormal, traffic can be switched to the other link.
Link redundancy can be implemented in the following ways:
Dual dedicated lines redundancy: Connect to IDC/other clouds through two dedicated lines. If one link is interrupted, quickly switch to the other line. When accessing dedicated lines, it is recommended to choose two different access points to improve high availability. If it is necessary to meet the requirements of latency and other demands for business purposes, it is necessary to choose the same access point and ensure that the two dedicated lines are connected to two different access devices. This way, even if one device fails and causes one of the lines to become abnormal, the other line can still operate normally.
Primary/backup for dedicated lines/VPN: In scenarios where physical dedicated lines, IPSec-VPN connections, and BGP dynamic routing protocols are all working properly, VPC instances can learn the local IDC's network segment through both physical dedicated lines and IPSec-VPN connections,. The system gives priority to routes learned through physical dedicated lines over routes learned through IPSec-VPN connections, so traffic between VPC instances and the local IDC is transmitted through physical dedicated lines by default. When the physical dedicated line is abnormal, the system automatically withdraws the learned routes through the physical dedicated line, and the routes learned through the IPSec-VPN connection take effect. The traffic between VPC instances and the local IDC is then transmitted through the IPSec-VPN connection. When the physical dedicated line is restored, the traffic between VPC instances and the local IDC is again transmitted through the physical dedicated line, and the IPSec-VPN connection becomes the backup link again. This solution can save costs compared to dual dedicated lines redundancy, as the cost of IPSec-VPN is lower than that of dedicated lines. However, IPSec-VPN typically has a maximum bandwidth limit of no more than 1 Gbps, which is suitable for businesses with small traffic.
VPN redundancy: If the local data center has multiple local gateway devices (each with a public IP address), you can use two local gateway devices to establish IPSec-VPN connections with the Alibaba Cloud Virtual Private Cloud (VPC). Each IPSec-VPN connection is associated with a different VPN gateway, achieving high availability of the link between the local data center and the VPC and load balancing of traffic. The local data center can learn the routes of the VPC from both VPN gateways, and the traffic from the local data center to the VPC can be transmitted through these two VPN gateways, achieving load balancing of traffic. When one VPN gateway is not available, the traffic of that VPN gateway will automatically be transmitted through the other VPN gateway, achieving high availability of the link. The VPC can learn the routes of the local data center from both VPN gateways, but the VPC only forwards traffic from the VPC to the local data center through one VPN gateway (the system selects the VPN gateway with the smaller instance ID by default). Only when the VPN gateway is not available does the traffic from the VPC to the local data center get forwarded through the other VPN gateway (automatic switching by the system). Therefore, traffic from the VPC to the local data center can achieve high availability through the two VPN gateways but does not support load balancing.
Bandwidth capacity design: When selecting a hybrid cloud interconnection solution, the bandwidth capacity requirements must be considered. Different bandwidths have different impacts on the solution selection. For example, large enterprises may have high traffic requirements for hybrid cloud, reaching several Gbps or even hundreds of Gbps. In this case, a primary/backup dedicated line solution is required, and it is necessary to ensure that the bandwidth threshold of the primary/backup dedicated lines is below 50%. If it reaches or approaches 50%, it needs to be expanded in a timely manner. When there is an abnormal link, all traffic will be directed to the other line, causing the bandwidth threshold of the other line to reach 100%, which cannot handle all the traffic, resulting in business disruption.
Fast link switchover: If the enterprise has achieved redundant links in the IDC, it also needs to achieve fast switchover through technical solutions in the event of an anomaly.
Dual dedicated line redundancy: For dedicated line scenarios, BGP can be used for IDC interconnection, or static routing can be used. If BGP is used, it is recommended to use BFD protocol for redundancy switching. When a link is abnormal, BFD can detect the link abnormality at the millisecond level, quickly withdraw the abnormal routes, and redirect the traffic to the normal link. If static routing is used for interconnection with IDC, you need to enable health checks in the cloud to detect the quality of the dedicated line in real time. If the detection fails, switch the line to the normal line immediately.
Primary/backup for dedicated lines/VPN: Under dedicated line and VPN scenarios, redundancy cannot be achieved, and only the primary dedicated line/VPN backup solution can be implemented because dedicated lines generally have higher availability than VPNs. Dedicated lines and VPNs use the BGP protocol to learn IDC routes. When the line is abnormal, the BGP routes of the dedicated line are withdrawn, and the routes are forwarded through the VPN.
VPN redundancy: The VPN redundancy solution is similar to the dedicated line solution. It uses the BGP route withdrawal method to quickly switch the route to the normal link when the VPN link is abnormal.
High Availability Design for Business Services
In the present era, enterprises have higher requirements for business availability, but physical device failures, application anomalies, network fluctuations, etc. cannot be avoided. To deal with abnormal situations, service high availability needs to be designed. If the business only uses a single ECS server to provide services, any issues with that ECS instance will affect the business and the recovery time is often unpredictable. However, if multiple servers are configured to provide external access, the business needs to resolve multiple ECS public IP addresses to the domain name, which becomes difficult to manage when there are many ECS instances. It also hinders elastic scaling.
To achieve the goal of high availability for services, Alibaba Cloud's Server Load Balancer (SLB) can be used. SLB acts as a proxy to distribute traffic to multiple backend servers, while the real servers are not exposed to external access and do not require configuration of public IP addresses. When a backend server becomes abnormal, SLB can automatically isolate it, redirecting the traffic to the healthy servers to continue providing services, achieving high availability of the business.
The SLB instance is deployed in a cluster to implement session synchronization, eliminating single points of failure and improving redundancy to ensure service stability. Layer 4 load balancing is implemented using LVS (Linux Virtual Server) + Keepalived, and layer 7 load balancing is implemented using Tengine, which is based on Nginx but optimized for high-traffic websites.
Requests from the public network reach the LVS cluster through Equal-Cost Multipath Routing (ECMP). Each LVS broadcasts session information to other LVS machines in the cluster, achieving session synchronization between the LVS machines in the cluster. Meanwhile, the LVS cluster performs health checks on the Tengine cluster. If an abnormality is detected, the LVS cluster removes it from the Tengine cluster to ensure the availability of layer 7 load balancing.
High Availability of a Single CLB Instance
To provide more stable and reliable load balancing services to users, Alibaba Classic Server Load Balancer (CLB) has deployed multiple availability zones in most regions to achieve cross-data center disaster recovery within the same region. When the primary availability zone fails or becomes unavailable, CLB can switch to the backup availability zone and restore the service within a very short time (about 30 seconds). When the primary availability zone is restored, CLB will automatically switch back to the primary availability zone to provide services.
To make better use of the primary/backup availability zone mechanism in load balancing, it is recommended to create a load balancer instance in a region that supports primary/backup availability zones. This means selecting a region with multi-zone support when purchasing a load balancer instance.
When selecting the primary and backup availability zones for CLB, it is recommended to consider the distribution of ECS instances across availability zones. Choose the availability zone where the majority of ECS instances are located as the primary availability zone for CLB to minimize access latency. However, it is not advisable to deploy all ECS instances in the same availability zone. It is recommended to deploy a small number of ECS instances in the backup availability zone of CLB to ensure that, in extreme cases where the primary availability zone becomes completely unavailable, the load balancing requests can still be processed smoothly after switching to the backup availability zone.
High Availability of Multiple CLB Instances
If high availability is required for the business, the availability guarantee mechanism of a single load balancer instance may not be sufficient to meet the high availability requirements. For example, if a load balancer instance becomes unavailable due to network attacks or configuration errors, it will not trigger an availability zone switch as long as there is no availability zone-level failure. In such cases, it is recommended to create multiple CLB instances and use cloud DNS to schedule access or implement cross-region disaster recovery backup through a global load balancing solution. Deploy load balancer instances and backend ECS instances across multiple availability zones within a region or across multiple regions, and then use cloud DNS to schedule access.
High Availability of Backend ECS Instances
Load balancing uses health checks to determine the availability of backend ECS instances. The health check mechanism improves the overall availability of front-end services, preventing the impact of abnormal backend ECS instances on the overall service.
After enabling the health check feature, when a backend ECS instance fails the health check, the load balancer will automatically distribute new requests to other ECS instances that pass the health check. Once the problematic ECS instance recovers and passes the health check, the load balancer will automatically restore it to the load balancing service. To ensure the proper functioning of the health check feature, it is necessary to enable and correctly configure the health check settings.
Traffic Redirection for Disaster Recovery
With the rapid development of the Internet, to ensure the continuous high availability of business, same-city active-active and cross-region active-active have become the preferred choices for enterprises. Setting up multiple centers and distributing traffic across different addresses within a center is a common practice for most enterprises. In such cases, effectively controlling traffic to achieve the best user access efficiency and quickly switching business continuity to other regions when a certain region experiences anomalies becomes particularly important. Here are a few typical scenarios:
The business needs to provide services to users nearest to the service center to reduce network latency.
How to achieve load balancing or weighted round-robin across multiple IP addresses in a service center, and ensure the stability of the overall load.
When an IP address in a service center fails, how to quickly detect and isolate the failure, and automatically add the address back to the resolution list after it recovers, without any manual intervention.
When a failure occurs in a region, how to quickly switch traffic to another region to reduce interruption time.
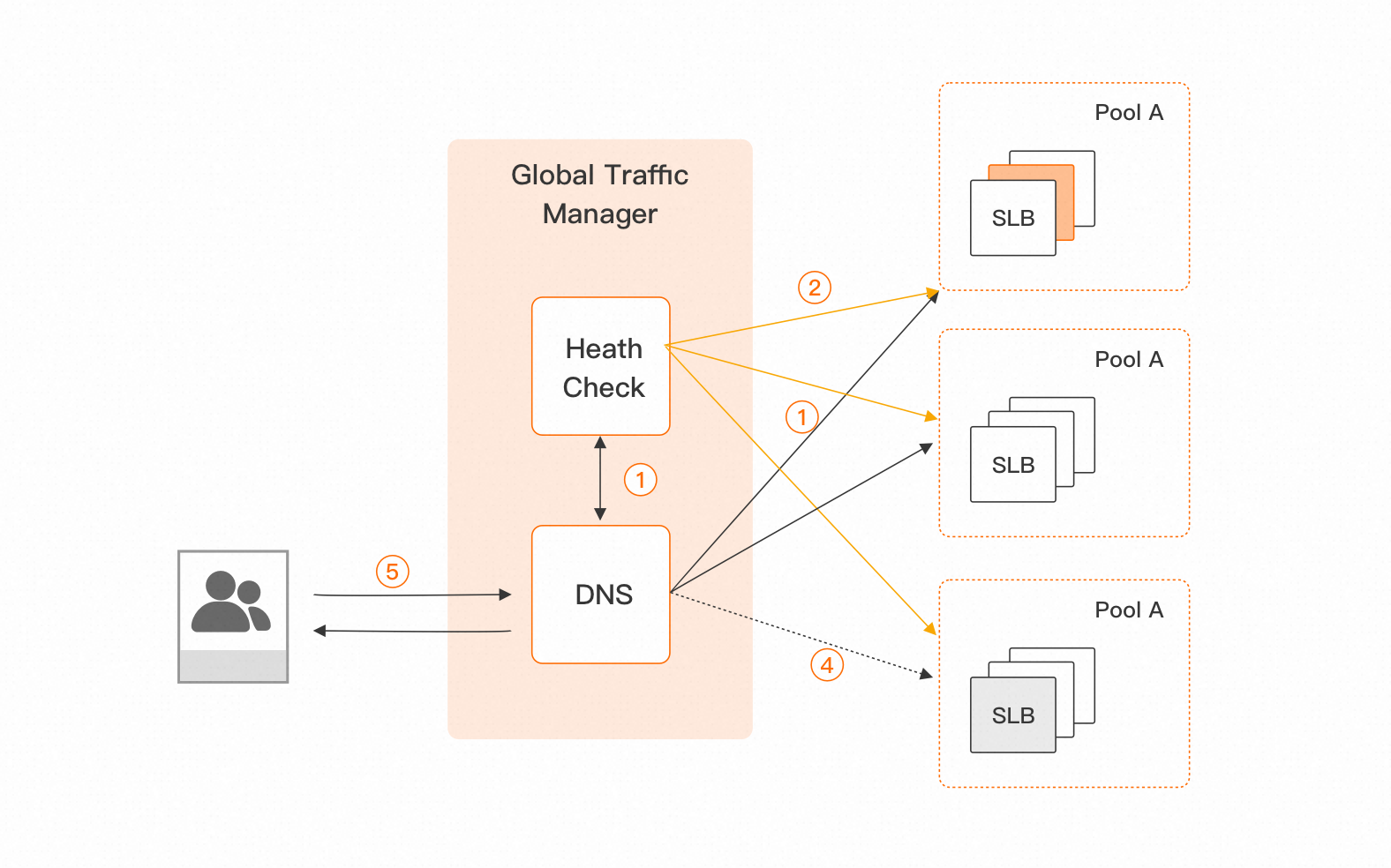
Alibaba Cloud's Global Traffic Manager (GTM) can perfectly solve these scenarios. Based on Alibaba Cloud's DNS entry scheduling and distributed cloud monitoring, GTM helps enterprises achieve users' closest access to the application services, high-concurrency load balancing, health checks for application services, and fault isolation or traffic switching based on the health check results, facilitating the flexible and fast construction of same-city active-active and cross-region disaster recovery services.
Compared with traditional DNS resolution, GTM has the following features:
Address Pool: Traditional DNS resolution maps to a single address, while GTM introduces the concept of address pools. As shown in Pool A/B/C in the figure, an address pool represents a set of IP addresses or domain addresses that provide the same application service, that is, IP addresses or domain addresses with the same operator or geographical attributes. Address pools can be used to uniformly manage the IP addresses of application services. They can direct end-user access to application service address pools, achieving load balancing high traffic and custom traffic distribution. When an address pool becomes completely unavailable, it can act as a backup.
Health Check: Based on the powerful distributed monitoring function of CloudMonitor, GTM introduces the HealthCheck module. As shown in the GTM architecture diagram, health checks are performed on multiple application service IP addresses in an address pool from different regions. Currently supported health check methods include HTTP/HTTPS, TCP, and ICMP (ping). When an IP address in the address pool becomes faulty, the HealthCheck module can accurately detect the abnormality, interact with DNS, and remove the faulty address. When the address recovers, it is automatically added back to the resolution list.
Access Policy: The access policy is designed to address the issue of address pool switching based on the request source and address pool health. It can perform intelligent resolution at the address pool level and achieve automatic failover. When the address pool encounters a failure, GTM can switch between the default address pool and the backup address pool within minutes based on user-defined policies. When the address pool recovers, GTM switches back.
Cross-region Disaster Recovery
Take cross-region active-active as an example to illustrate how to use GTM to quickly switch disaster recovery. As shown in the figure below, the users of a service are mainly divided into overseas users and domestic users, and the backend service adopts a unified deployment plan. Through GTM, requests from different regions are intelligently scheduled to different access service points. For example, overseas users access the Singapore center (Singapore), and domestic users access the Hangzhou center (CN-Hangzhou). When a site experiences a failure or disaster, each access site has its own backup, ultimately achieving high availability of the business.
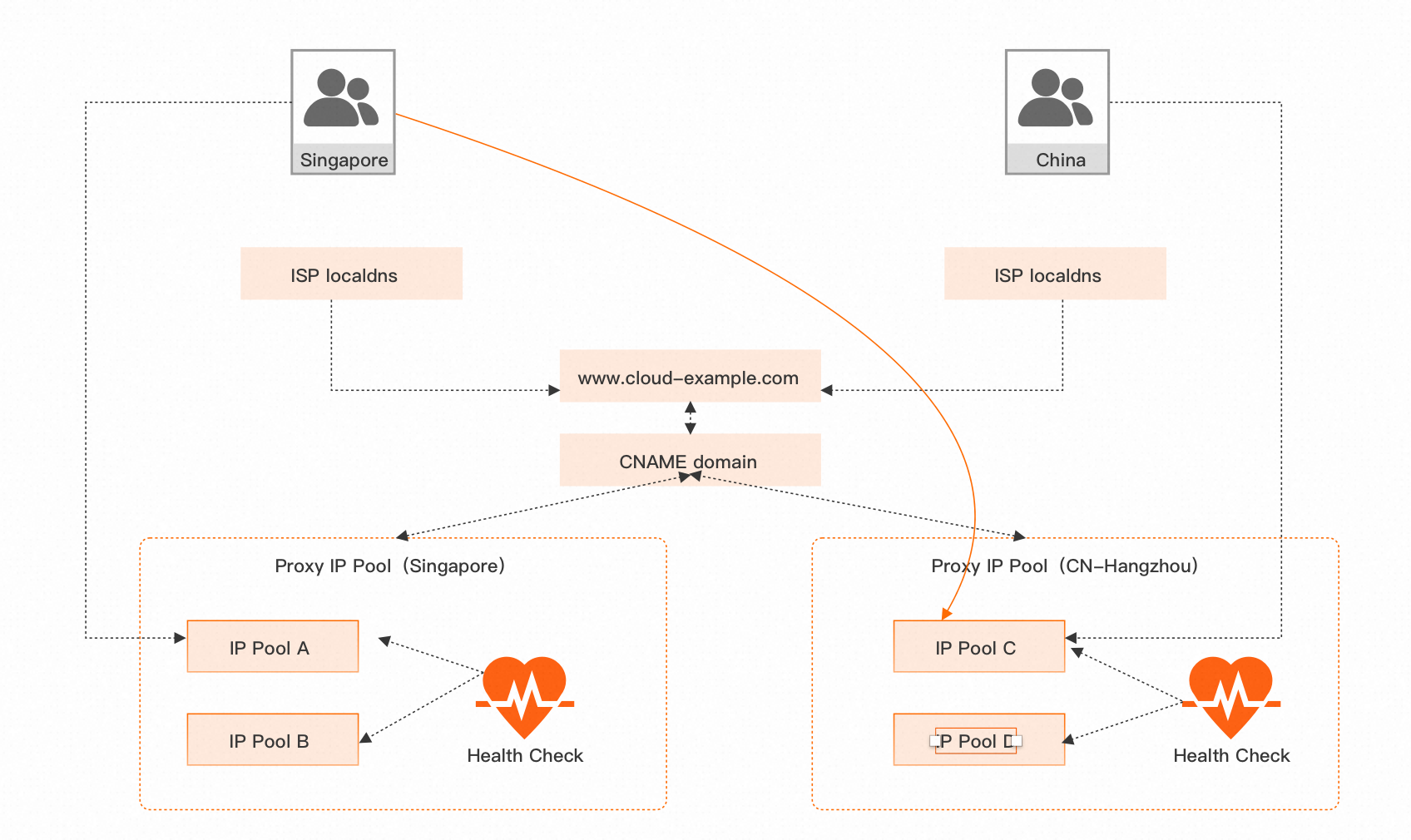
To implement disaster recovery across different regions using GTM, follow these 5 steps:
1. Global Configuration: Basic configuration, mainly configuring load balancing policies, global TTL, alarming notification groups, and other related information.
2. Address Pool Configuration: Create address pools for Singapore and CN-Hangzhou. Configure multiple service IPs in each address pool, which belong to the same region and have the same operator or geographical attributes. When the number of available addresses in an address pool is less than the quantity of the address pool, the address pool is considered unavailable. In addition, traffic distribution is automatically achieved based on the load balancing policy configured in the global configuration.
3. Enable Health Checks: Configure health checks for the IP addresses in the address pool, enabling real-time monitoring of the availability status of the addresses. When an address in the address pool becomes faulty, the HealthCheck module accurately detects the abnormality, interacts with DNS, removes the faulty address, and notifies the corresponding alarming group. When the address recovers, it is automatically added back to the resolution list. Furthermore, if the entire address pool encounters problems, it triggers automatic switching between the default address pool and the backup address pool. The entire process can be completed within 5 minutes, with 90% of the traffic switched.
4. Configure Access Policies: Set which address pool is selected for final user access based on the request source and policy configuration. For example, if overseas users want to access the Singapore address pool, an access policy needs to be set, with the request source set to overseas regions, the default address pool set to Singapore, and the backup address pool set to CN-Hangzhou. During normal requests, overseas users will access the Singapore center by default. If a failure occurs, the traffic will be quickly switched to the CN-Hangzhou center.
5. CNAME Access Configuration: The main domain name of user access needs to be CNAME to the instance domain name of GTM to achieve disaster recovery and intelligent access to application services. In other words, the domain name www.cloud-example.com should be CNAME to the provided instance domain name.
After the configuration is completed, we will detect the addresses in the address pool in real-time based on the health configuration. When an address triggers an alarm, it will automatically switch to a backup address. When the default address pool (Singapore) is available, the address will be removed from the resolution list. If the default address pool becomes completely unavailable, it will switch to the backup address pool (CN-Hangzhou) automatically. The switching process will be completed automatically and the time required will be reduced to minutes, ensuring efficient disaster recovery switching for different locations.
Disaster Recovery plan drills
In addition, the newly-added Disaster Recovery Plan feature in GTM can help users perform routine disaster recovery drills or quickly switch traffic in the event of a failure of the application service. The Disaster Recovery Plan supports batch simulation and rollback of address pool failures and helps users verify whether the switching strategy meets expectations.