If your data center has multiple gateways that have public IP addresses, you can use two of the gateways to establish IPsec-VPN connections to an Alibaba Cloud virtual private cloud (VPC). Each IPsec-VPN connection is associated with a different VPN gateway to implement load balancing on the connections between the data center and the VPC and improve availability.
Sample scenario
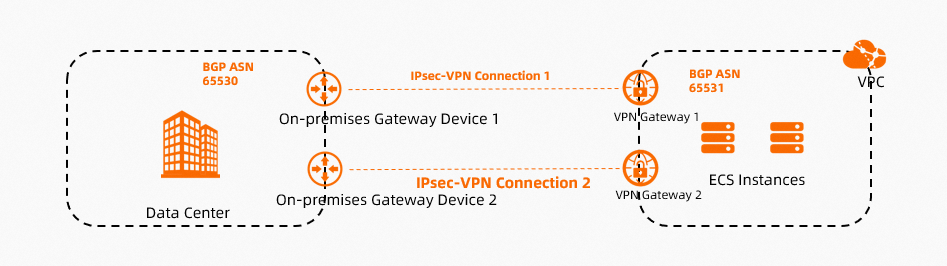
The following figure shows the scenario that is used in this topic. An enterprise owns a data center in Hangzhou and has a VPC deployed in the China (Hangzhou) region. Applications are deployed on Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instances in the VPC. The enterprise wants to enable the data center to access the VPC over multiple encrypted connections to ensure data security and network redundancy.
The enterprise deploys multiple on-premises gateways that have public IP addresses in the data center. The enterprise can use two of the on-premises gateways to establish IPsec-VPN connections to the VPC. Each IPsec-VPN connection is associated with a specific VPN gateway to implement load balancing on the connections between the data center and the VPC and enable encrypted access to the applications in the VPC. This ensures high availability and security.
The following section describes the data transfer in this example.
The data center learns VPC routes from the two VPN gateways. Then, the VPN gateways forward traffic from the data center to the VPC at the same time to implement load balancing. When one of the VPN gateways is unavailable, the other VPN gateway takes over to ensure the availability of services.
The VPC learns the routes of the data center from the two VPN gateways. By default, the VPC forwards traffic from the VPC to the data center through the VPN gateway whose ID is smaller. When the VPN gateway is unavailable, the other VPN gateway automatically takes over to implement load balancing and ensure the high availability of services.
Network design
Networking requirements
The following section describes the networking requirements in this scenario:
Two public VPN gateways are created and two IPsec-VPN connections are established between the data center and the VPC over the Internet.
Each IPsec-VPN connection is associated with a VPN gateway.
BGP route propagation is enabled for the VPN gateways. Each VPN gateway uses BGP dynamic routing to establish an IPsec-VPN connection to the on-premises gateway device. This simplifies routing configurations.
ImportantTo implement this scenario, the two IPsec-VPN connections must use BGP dynamic routing and the same autonomous system number (ASN). In addition, the two on-premises gateway devices must use the same ASN. Otherwise, failover cannot be performed.
Only VPN gateways that are deployed in some regions support BGP dynamic routing. For more information about the regions, see Regions that support BGP dynamic routing.
CIDR blocks
When you allocate CIDR blocks, make sure that the CIDR block of the data center and the CIDR block of the VPC do not overlap.
Item | CIDR block and IP address |
VPC | Primary CIDR block: 172.16.0.0/16
|
IPsec-VPN connections | BGP configurations:
|
On-premises gateway devices | Public IP addresses of the on-premises gateway devices:
|
BGP configurations of the on-premises gateway devices:
| |
Data center | CIDR block used to communicate with the VPC: 192.168.0.0/24 |
Preparations
Make sure that the following prerequisites are met before you start:
A VPC is deployed in the China (Hangzhou) region and applications are deployed on the ECS instances in VPC1. For more information, see Create a VPC with an IPv4 CIDR block.
The gateway device in the data center supports the IKEv1 and IKEv2 protocols. Gateway devices that support these protocols can connect to VPN gateways.
You have read and understand the security group rules that apply to the ECS instances in VPCs, and the security group rules allow gateway devices in the data center to access cloud resources. For more information, see View security group rules and Add a security group rule.
Procedure
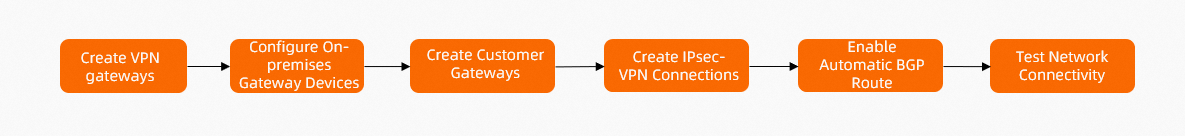
Step 1: Create VPN gateways
Before you create IPsec-VPN connections, you must create two VPN gateways and enable the IPsec-VPN feature for the VPN gateways.
Log on to the VPN Gateway console.
In the top navigation bar, select the region where you want to create VPN gateways.
The VPN gateways must be deployed in the same region as the VPC with which you want to associate the VPN gateways. China (Hangzhou) is selected in this example.
On the VPN Gateways page, click Create VPN Gateway.
On the buy page, configure the following parameters, click Buy Now, and then complete the payment.
Create two VPN gateways in the China (Hangzhou) region based on the following table.
Parameter
Description
VPN Gateway 1
VPN Gateway 2
Name
Enter a name for the VPN gateway.
In this example, VPN Gateway 1 is used.
In this example, VPN Gateway 2 is used.
Region
Select the region where you want to deploy the VPN gateway.
China (Hangzhou) is selected in this example.
China (Hangzhou) is selected in this example.
Gateway Type
Select the type of the VPN gateway.
In this example, Standard is selected.
In this example, Standard is selected.
Network Type
Select the network type of the VPN gateway.
In this example, Public is selected.
In this example, Public is selected.
Tunnels
The supported tunnel modes are automatically displayed.
In this example, the default value is used.
In this example, the default value is used.
VPC
Select the VPC with which you want to associate the VPN gateway.
In this example, the VPC that is created in the Preparations section is selected.
In this example, the VPC that is created in the Preparations section is selected.
VSwitch
Select a vSwitch from the selected VPC.
- If you select Single-tunnel, you need to specify one vSwitch.
- If you select Dual-tunnel, you need to specify two vSwitches.
Note- The system selects a vSwitch by default. You can change or use the default vSwitch.
- After you create a VPN gateway, you cannot change the vSwitch associated with the VPN gateway. You can view the associated vSwitch and the zone of the vSwitch on the details page of the VPN gateway.
Select a vSwitch from the selected VPC.
Select a vSwitch from the selected VPC.
vSwitch 2
Select another vSwitch from the selected VPC.
Ignore this parameter if you select Single-tunnel.
Select another vSwitch from the selected VPC.
Select another vSwitch from the selected VPC.
Maximum Bandwidth
Select a maximum bandwidth value for the VPN gateway. Unit: Mbit/s.
Select the maximum bandwidth based on your business requirements.
Select the maximum bandwidth based on your business requirements.
Traffic
Select a billing method for the VPN gateway. Default value: Pay-by-data-transfer.
For more information, see Billing.
In this example, the default value is used.
In this example, the default value is used.
IPsec-VPN
Specify whether to enable the IPsec-VPN feature.
In this example, the default value Enable is selected.
In this example, the default value Enable is selected.
SSL-VPN
Specify whether to enable the SSL-VPN feature.
In this example, the default value Disable is selected.
In this example, the default value Disable is selected.
Duration
Select a billing cycle. Default value: By Hour.
Use the default value.
Use the default value.
Service-linked Role
A VPN gateway can assume the service-linked role AliyunServiceRoleForVpn to access other cloud resources. For more information, see AliyunServiceRoleForVpn.
Click Create Service-linked Role. Then, the system automatically creates the service-linked role AliyunServiceRoleForVpn.
If Created is displayed, the service-linked role is created and you do not need to create it again.
Click Create Service-linked Role. Then, the system automatically creates the service-linked role AliyunServiceRoleForVpn.
If Created is displayed, the service-linked role is created and you do not need to create it again.
Return to the VPN Gateways page to view the VPN gateway.
After you create a VPN gateway, it is in the Preparing state. After 1 to 5 minutes, the VPN gateway changes to the Normal state. After the status changes to Normal, the VPN gateway is ready for use.
VPN gateway name
Public IP address of the VPN gateway
VPN Gateway 1
47.XX.XX.48
VPN Gateway 2
47.XX.XX.224
Step 2: Create customer gateways
You must create customer gateways and register the gateway information on Alibaba Cloud before you can create IPsec-VPN connections.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
In the top navigation bar, select the region where you want to create the customer gateways.
NoteThe customer gateways must be deployed in the same region as the VPN gateways created in Step 1: Create VPN gateways.
On the Customer Gateway page, click Create Customer Gateway.
In the Create Customer Gateway panel, configure the following parameters and click OK.
Create two customer gateways and configure different public IP addresses for them based on the following table.
Parameter
Description
Customer Gateway 1
Customer Gateway 2
Parameter
Enter a name for the customer gateway.
In this example, Customer Gateway 1 is used.
In this example, Customer Gateway 2 is used.
IP Address
Enter the public IP address of the customer gateway.
In this example, the public IP address (118.XX.XX.20) of the on-premises gateway device is entered.
In this example, the public IP address (120.XX.XX.40) of the on-premises gateway device is entered.
ASN
Enter the ASN of the on-premises gateway device.
In this example, 65530 is used. This is the ASN of On-premises Gateway Device 1.
In this example, 65530 is used. This is the ASN of On-premises Gateway Device 2.
Step 3: Create IPsec-VPN connections
After you create customer gateways, you must create IPsec-VPN connections to connect the on-premises gateway devices to the VPN gateways.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
In the top navigation bar, select the region where you want to create the IPsec-VPN connections.
NoteThe IPsec-VPN connections must be deployed in the same region as the VPN gateways created in Step 1: Create VPN gateways.
On the IPsec Connections page, click Create IPsec-VPN Connection.
On the Create IPsec-VPN Connection page, configure the parameters and click OK.
Create two IPsec-VPN connections and associate them with different VPN gateways and customer gateways based on the following table. Parameters not listed in the following table use the default values. For more information, see Create and manage IPsec-VPN connections in single-tunnel mode.
Parameter
Description
IPsec-VPN Connection 1
IPsec-VPN Connection 2
Parameter
Enter a name for the IPsec-VPN connection.
In this example, IPsec-VPN Connection 1 is used.
In this example, IPsec-VPN Connection 2 is used.
Associate Resource
Select the type of network resource to be associated with the IPsec-VPN connection.
In this example, VPN Gateway is selected.
VPN Gateway
Select the VPN gateway that you created.
In this example, VPN Gateway 1 is selected.
In this example, VPN Gateway 2 is selected.
Customer Gateway
Select the customer gateway that you created.
In this example, Customer Gateway 1 is selected.
In this example, Customer Gateway 2 is selected.
Routing Mode
Select a routing mode.
In this example, Destination Routing Mode is selected.
Effective Immediately
Specify whether to immediately start IPsec negotiations. Valid values:
Yes: starts negotiations when the configuration is complete.
No: starts connection negotiations when traffic is received.
In this example, No is selected.
Pre-Shared Key
Enter a pre-shared key that is used to authenticate the on-premises gateway devices.
The pre-shared key must be 1 to 100 characters in length, and can contain digits, letters, and the following characters:
~`!@#$%^&*()_-+={}[]\|;:',.<>/?.If you do not specify a pre-shared key, the system generates a random 16-bit string as the pre-shared key. After you create an IPsec-VPN connection, you can click Edit to view the pre-shared key that is generated by the system. For more information, see Modify an IPsec-VPN connection.
ImportantThe IPsec-VPN connection and the peer gateway device must use the same pre-shared key. Otherwise, the system cannot establish an IPsec-VPN connection.
fddsFF123****
fddsFF456****
Encryption Configuration
Configure IKE and IPsec settings based on your business requirements.
In this example, ikev2 is selected for the Version parameter in the IKE Configurations section. The default values are used for the other parameters.
BGP Configuration
Specify whether to enable BGP.
In this example, BGP is enabled.
Tunnel CIDR Block
Specify the CIDR block that is used for IPsec tunneling.
The CIDR block must fall within 169.254.0.0/16. The subnet mask of the CIDR block must be 30 bits in length.
In this example, 169.254.10.0/30 is used.
In this example, 169.254.11.0/30 is used.
Local BGP IP address
Enter a BGP IP address for each IPsec-VPN connection.
This IP address must fall within the CIDR block for IPsec tunneling.
In this example, 169.254.10.1 is used.
In this example, 169.254.11.1 is used.
Local ASN
Enter the ASN of the IPsec-VPN connection.
In this example, 65531 is used.
In this example, 65531 is used.
Health Check
Specify whether to enable the health check feature.
In this example, the default value is used. The health check feature is disabled.
In the Created message, click OK.
Return to the IPsec Connections page, find the IPsec-VPN connection that you want to manage and click Generate Peer Configuration in the Actions column.
Save the peer configurations of IPsec-VPN Connection 1 and IPsec-VPN Connection 2 to your on-premises machine. The peer configurations will be used in subsequent steps when you configure the on-premises gateway device.
Step 4: Configure on-premises gateway devices
After the IPsec-VPN connections are created, perform the following steps to add the VPN and BGP configurations in the IPsec-VPN connection configurations that you downloaded to the two on-premises gateway devices. This way, the data center can communicate with the VPC over the IPsec-VPN connections.
The following configurations are used for reference only. The commands may vary based on the network device vendor. Contact the vendor to obtain the information about specific commands.
Open the command-line interface (CLI) of the gateway device.
Run the following commands to configure an IKEv2 proposal and policy:
//Add the following configuration to On-premises Gateway Device 1 and On-premises Gateway Device 2 in the data center: crypto ikev2 proposal alicloud encryption aes-cbc-128 //Configure the encryption algorithm. In this example, aes-cbc-128 is used. integrity sha1 //Configure the authentication algorithm. In this example, sha1 is used. group 2 //Configure the Diffie-Hellman group. In this example, group 2 is used. exit ! crypto ikev2 policy Pureport_Pol_ikev2 proposal alicloud exit !Run the following command to configure an IKEv2 keyring:
//Add the following configurations to On-premises Gateway Device 1 in the data center: crypto ikev2 keyring alicloud peer alicloud address 47.XX.XX.48 //Specify the public IP address of VPN Gateway 1. In this example, 47.XX.XX.48 is used. pre-shared-key fddsFF123**** //Configure the pre-shared key. In this example, fddsFF123**** is used. exit ! //Add the following configuration to On-premises Gateway Device 2: crypto ikev2 keyring alicloud peer alicloud address 47.XX.XX.224 //Specify the public IP address of VPN Gateway 2. In this example, 47.XX.XX.224 is used. pre-shared-key fddsFF456**** //Configure the pre-shared key. In this example, fddsFF456**** is used. exit !Run the following command to configure an IKEv2 profile:
// Add the following configuration to On-premises Gateway Device 1 in the data center: crypto ikev2 profile alicloud match identity remote address 47.XX.XX.48 255.255.255.255 //Match the public IP address of VPN Gateway 1. In this example, 47.XX.XX.48 is matched. identity local address 118.XX.XX.20 //Specify the public IP address of On-premises Gateway Device 1. In this example, 118.XX.XX.20 is used. authentication remote pre-share //Set the authentication mode of the VPC to PSK. authentication local pre-share //Set the authentication mode of the data center to PSK. keyring local alicloud //Use the IKEv2 keyring. exit ! //Add the following configuration to On-premises Gateway Device 2: crypto ikev2 profile alicloud match identity remote address 47.XX.XX.224 255.255.255.255 //Match the public IP address of VPN Gateway 1. In this example, 47.XX.XX.224 is matched. identity local address 120.XX.XX.40 //Specify the public IP address of On-premises Gateway Device 2. In this example, 120.XX.XX.40 is used. authentication remote pre-share //Set the authentication mode of the VPC to PSK. authentication local pre-share //Set the authentication mode of the data center to PSK. keyring local alicloud //Use the IKEv2 keyring. exit !Run the following command to configure a transform set:
//Add the following configuration to On-premises Gateway Device 1 and On-premises Gateway Device 2 in the data center: crypto ipsec transform-set TSET esp-aes esp-sha-hmac mode tunnel exit !Run the following command to configure an IPsec profile, and invoke the transform set, Perfect Forward Secrecy (PSF), and the IKEv2 profile:
//Add the following configuration to On-premises Gateway Device 1 and On-premises Gateway Device 2 in the data center: crypto ipsec profile alicloud set transform-set TSET set pfs group2 set ikev2-profile alicloud exit !Run the following commands to configure the IPsec tunnel:
//Add the following configuration to On-premises Gateway Device 1 in the data center: interface Tunnel100 ip address 169.254.10.2 255.255.255.252 //Specify the IP address of the tunnel on the On-premises Gateway Device 1 side. In this example, 169.254.10.2 is used. tunnel source GigabitEthernet1 tunnel mode ipsec ipv4 tunnel destination 47.XX.XX.48 //Specify the IP address of the tunnel on the VPN Gateway 1 side. In this example, 47.XX.XX.48 is used. tunnel protection ipsec profile alicloud no shutdown exit ! interface GigabitEthernet1 //Configure the IP address of the interface that is used to connect to VPN Gateway 1. ip address 118.XX.XX.20 255.255.255.0 negotiation auto ! //Add the following configuration to On-premises Gateway Device 2: interface Tunnel100 ip address 169.254.11.2 255.255.255.252 //Specify the IP address of the tunnel on the On-premises Gateway Device 2 side. In this example, 169.254.11.2 is used. tunnel source GigabitEthernet1 tunnel mode ipsec ipv4 tunnel destination 47.XX.XX.224 //Specify the IP address of the tunnel on the VPN Gateway 2 side. In this example, 47.XX.XX.224 is used. tunnel protection ipsec profile alicloud no shutdown exit ! interface GigabitEthernet1 //Configure the IP address of the interface that is used to connect to VPN Gateway 2. ip address 120.XX.XX.40 255.255.255.0 negotiation auto !Run the following command to configure BGP:
//Add the following configuration to On-premises Gateway Device 1 in the data center: router bgp 65530 //Enable BGP and configure the BGP ASN of the data center. In this example, 65530 is used. bgp router-id 169.254.10.2 //Specify the ID of the BGP router. In this example, 169.254.10.2 is used. bgp log-neighbor-changes neighbor 169.254.10.1 remote-as 65531 //Configure the ASN of the BGP peer. In this example, the BGP ASN of IPsec-VPN Connection 1 is used, which is 65531. neighbor 169.254.10.1 ebgp-multihop 10 //Set the eBGP hop-count to 10. ! address-family ipv4 network 192.168.0.0 mask 255.255.255.0 //Advertise the CIDR block of the data center. In this example, 192.168.0.0/24 is advertised. neighbor 169.254.10.1 activate //Activate the BGP peer. exit-address-family ! //Add the following configuration to On-premises Gateway Device 2: router bgp 65530 //Enable BGP and configure the BGP ASN of the data center. In this example, 65530 is used. bgp router-id 169.254.11.2 //Specify the ID of the BGP router. In this example, 169.254.11.2 is used. bgp log-neighbor-changes neighbor 169.254.11.1 remote-as 65531 //Configure the ASN of the BGP peer. In this example, the BGP ASN of IPsec-VPN Connection 2 is used, which is 65531. neighbor 169.254.11.1 ebgp-multihop 10 //Set the eBGP hop-count to 10. ! address-family ipv4 network 192.168.0.0 mask 255.255.255.0 //Advertise the CIDR block of the data center. In this example, 192.168.0.0/24 is advertised. neighbor 169.254.11.1 activate //Activate the BGP peer. exit-address-family !ImportantAfter you configure the on-premises gateway devices, they can learn the routes that point to the VPC from the IPsec-VPN connections. To implement load balancing through the IPsec-VPN connections for traffic from the data center to the VPC, make sure that the clients or devices that need to access the VPC can learn the routes that point to the VPC from the on-premises gateway devices. Contact the device supplier to obtain the specific commands.
Step 5: Enable automatic BGP route propagation
If you enable automatic BGP route propagation for a VPN gateway, the VPN gateway automatically advertises the learned BGP routes to the route table of the associated VPC. For more information about automatic BGP route propagation, see How BGP dynamic routes are advertised.
Perform the following steps to enable the automatic BGP route propagation feature for VPN Gateway 1 and VPN Gateway 2.
Log on to the VPN Gateway console.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
In the top navigation bar, select the region of the VPN gateway.
On the VPN Gateways page, find the VPN gateway that you created and choose in the Actions column.
In the Enable Automatic BGP Propagation message, click OK.
After you enable automatic BGP route propagation for VPN Gateway 1 and VPN Gateway 2, the VPC learns the routes of the data center from the VPN gateways.
Step 6: Test network connectivity
After you enable automatic BGP route propagation, the data center and the VPC can communicate with each other through IPsec-VPN connections. This section describes how to test network connectivity and how to check whether load balancing is achieved over the two IPsec-VPN connections.
Tests the network connectivity.
Log on to an ECS instance in the VPC. For more information, see Connect to an ECS instance.
Run the ping command on the ECS instance to ping a client in the data center.
ping <The IP address of a client in the data center>If the ECS instance receives echo reply messages, the data center can communicate with the VPC.
Check whether loads are balanced.
Use multiple clients in the data center or iPerf3 to continuously send requests to the ECS instance in the VPC. Then, navigate to the details pages of the two IPsec-VPN connections to view the traffic monitoring data. If all details pages display traffic monitoring data, load balancing is implemented over the two IPsec-VPN connections. For more information about how to install and use Iperf3, see Test the performance of an Express Connect circuit.
Log on to the VPN Gateway console.
In the top navigation bar, select the region in which the IPsec-VPN connection is created.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the IPsec Connections page, click the ID of the IPsec-VPN connection that you want to manage.
Go to the details page of the IPsec-VPN connection to view the monitoring data of data transfer on the Monitor tab.