You can add a custom HTTP response header to response messages from an accelerated domain name to enable cross-origin resource sharing (CORS). This topic describes how to configure a custom HTTP response header.
Background information
Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS), also known as cross-domain access, is a standard mechanism from HTML5. It allows web application servers to control cross-origin access and ensure secure data transmission.
When users request your business resources, you can configure response headers in the response message to enable cross-origin access. When CDN receives a cross-origin request, it reads the corresponding CORS rules and performs a permission check. CDN checks each rule in order and uses the first matching rule to allow the request and return the corresponding header. If no rules match, no CORS-related headers are added.
HTTP response header configuration is applied at the domain name level. After a configuration takes effect, it applies to the response messages for all resources under that domain name. Configuring an HTTP response header affects only the response behavior of clients, such as browsers, and does not affect the caching behavior of CDN nodes. Wildcard domain names do not support custom HTTP response headers.
Procedure
Log on to the ApsaraVideo VOD console.
In the navigation pane on the left, choose Configuration Management > CDN Configuration > Domain Names.
Find the domain name that you want to configure and click Configure.
In the navigation pane on the left for the specified domain name, click Cache.
Click the Custom HTTP Response Headers tab.
Click Add to configure a custom HTTP response header.
The following figure shows an example of how to add a custom HTTP response header.
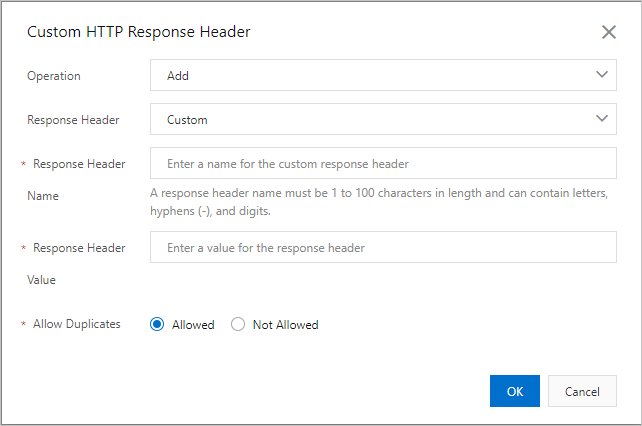
Parameter
Description
Operation
You can add, delete, change, or replace a specified response header.
Response Header
Select Customize or a standard response header parameter, such as Cache-Control, from the drop-down list. For more information, see Response header parameters.
Response Header Name
This parameter is required when you set Custom Response Header Parameter to Customize. The custom response header name must meet the following requirements:
Consists of letters, digits, and hyphens (-).
1 to 100 characters in length.
Response Header Value
Enter the value for the response header. For more information, see Response header parameters.
Allow Duplicates
Not Allowed: The header returned from the origin server is retained, and a new header with the same name is added.
Allowed: The header returned from the origin server is overwritten by the new header with the same name.
Click OK to complete the configuration.
After you configure a custom HTTP response header, you can change it by clicking Modify or Delete in the Actions column.
Response header parameters
All response header parameters support HTTP/2, except for custom parameters.
Response header parameter | Description | Example |
Custom | Lets you add a custom response header. The custom response header name must meet the following requirements:
| Test-Header |
Cache-Control | Specifies the cache policy that the client uses for requests and responses. | no-cache |
Content-Disposition | Specifies the default filename when the client program saves the requested content as a file. | examplefile.txt |
Content-Type | Specifies the content type of the response object for the client. Supported types include text, image, audio, video, and file. | image |
Pragma | The Pragma HTTP/1.0 general header is an implementation-specific header that may have various effects along the request-response chain. Pragma HTTP/1.0 is compatible with HTTP/1.1. | no-cache |
Access-Control-Allow-Origin | Specifies the origins that are allowed to make cross-origin requests. You can enter an asterisk (*) to allow all domain names, or enter a full domain name, such as Note
|
|
Access-Control-Allow-Methods | Specifies the allowed methods for cross-origin requests. You can set multiple methods, separated by commas (,). | POST,GET |
Access-Control-Allow-Headers | Specifies the allowed header fields for cross-origin requests. | X-Custom-Header |
Access-Control-Expose-Headers | Specifies the headers that can be exposed as part of the response. You can specify multiple headers, separated by commas (,). | Content-Length |
Access-Control-Allow-Credentials | Indicates whether the response to the request can be exposed to the page.
| true |
Access-Control-Max-Age | Specifies how long the results of a preflight request can be cached, in seconds. | 600 |