This topic describes the implementation and procedure to enable completely accurate mode for SQL, allowing efficient use of its core capabilities.
Limits
The following features are unavailable if you enable the completely accurate mode for SQL:
Implementation
The completely accurate mode ensures accurate and complete results by trading time for resources. By converting various resource constraints into the time dimension, query tasks run stably under safe load levels within the user-specified time range until the results are accurate or the execution times out. In technical implementation, multiple strategies are adopted, which include task allocation based on isolated resource pools, queue priority control for users, and load division based on task types, such as compute-intensive and IO-intensive. The strategies effectively achieve reasonable scheduling and efficient utilization of resources, ensuring the accuracy of final results.

Regular query tasks run in the on-demand computing resource pool. When a query task hits resource limits, the query task is automatically terminated and returns inaccurate results. If you enable the completely accurate mode for SQL, the query task runs in a dedicated accurate computing resource pool. The system ensures the query task runs stably under safe load levels until all data is loaded and accurate calculations are completed even if resource limits are hit.

Prerequisites
A Standard logstore is created. For more information, see Create a basic logstore.
Logs are collected. For more information, see Data collection overview.
Indexes are configured. For more information, see Configure indexes.
Procedure
Simple Log Service supports the enabled once method. After the completely accurate mode is enabled, only the query and analysis operations in the current Logstore can use the mode.
You can set the maximum timeout period for the completely accurate mode using APIs or SDKs, or in the Simple Log Service console. The maximum timeout period for analysis operations is 55 seconds.
Console
Log on to the Simple Log Service console.
In the Projects section, click the one you want.
On the tab, click the logstore you want.
Choose .
ImportantYou can configure the
query_max_run_timeparameter to modify the maximum timeout period.In this example, the
* | select count(*) as pvquery statement is specified. After you addset session query_max_run_time=10s;to the analytic statement, the query statement becomes* | set session query_max_run_time=10s; select count(*) as pv.
API
GetLogs (the query results are not compressed and are directly returned)
Parameter:
queryIn this example, the
* | select count(*) as pvquery statement is executed.Enable the completely accurate mode: Add
set session allow_incomplete=false;to the analytic statement, indicating that the completely accurate mode is used. The query statement becomes* | set session allow_incomplete=false; select count(*) as pv.Specify the maximum timeout period: Add
set session query_max_run_time=10s;to the analytic statement, indicating the maximum timeout period is10 seconds. The query statement becomes* | set session query_max_run_time=10s; select count(*) as pv.Enable the completely accurate mode and specify the maximum timeout period: The query statement becomes
* | set session allow_incomplete=false; set session query_max_run_time=10s;select count(*) as pv.
GetLogsV2 (the query results are compressed and then returned)
Parameter:
queryIn this example, the
* | select count(*) as pvquery statement is executed.Enable the completely accurate mode: Add
set session allow_incomplete=false;to the analytic statement, indicating that the completely accurate mode is used. The query statement becomes* | set session allow_incomplete=false; select count(*) as pv.Specify the maximum timeout period: Add
set session query_max_run_time=10s;to the analytic statement, indicating the maximum timeout period is10 seconds. The query statement becomes* | set session query_max_run_time=10s; select count(*) as pv.Enable the completely accurate mode and specify the maximum timeout period: The query statement becomes
* | set session allow_incomplete=false; set session query_max_run_time=10s;select count(*) as pv.
SDK
In this example, Simple Log Service SDK for Java is used.
Prerequisites
Simple Log Service SDK for Java is installed. For more information, see Install Simple Log Service SDK for Java.
GetLogs() method
Parameter:
queryIn this example, the
* | select count(*) as pvquery statement is executed.Enable the completely accurate mode: Add
set session allow_incomplete=false;to the analytic statement, indicating that the completely accurate mode is used. The query statement becomes* | set session allow_incomplete=false; select count(*) as pv.Specify the maximum timeout period: Add
set session query_max_run_time=10s;to the analytic statement, indicating the maximum timeout period is10 seconds. The query statement becomes* | set session query_max_run_time=10s; select count(*) as pv.Enable the completely accurate mode and specify the maximum timeout period: The query statement becomes
* | set session allow_incomplete=false; set session query_max_run_time=10s;select count(*) as pv.
Parameter:
sessionEnable the completely accurate mode:
request.SetSession("allow_incomplete=false");.Specify the maximum timeout period:
request.SetSession("query_max_run_time=10s");.Enable the completely accurate mode and specify the maximum timeout period:
request.SetSession("allow_incomplete=false;query_max_run_time=10s").
import com.aliyun.openservices.log.Client; import com.aliyun.openservices.log.exception.LogException; import com.aliyun.openservices.log.request.GetLogsRequest; import com.aliyun.openservices.log.response.GetLogsResponse; public class CrearteLogStore { public static void main(String[] args) throws LogException { // Configure environment variables. In this example, the AccessKey ID and AccessKey secret are obtained from environment variables. String accessId = System.getenv("ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID"); String accessKey = System.getenv("ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET"); // The Simple Log Service endpoint. In this example, the Simple Log Service endpoint for the China (Hangzhou) region is used. Replace the parameter value with the actual endpoint. String host = "https://cn-beijing.log.aliyuncs.com"; // Create a Simple Log Service client. Client client = new Client(host, accessId, accessKey); // The project name. String projectName = "aliyun-test-project"; // The logstore name. String logstore = "request_log"; String query = "* | SELECT count(0)"; int from = (int)(System.currentTimeMillis()/1000) - 60; int to = (int)(System.currentTimeMillis()/1000); GetLogsRequest request = new GetLogsRequest(projectName, logstore, from, to, "", query); request.SetSession("allow_incomplete=false;query_max_run_time=10s"); GetLogsResponse response = client.GetLogs(request); System.out.println(response.getCpuSec()); } }
FAQs
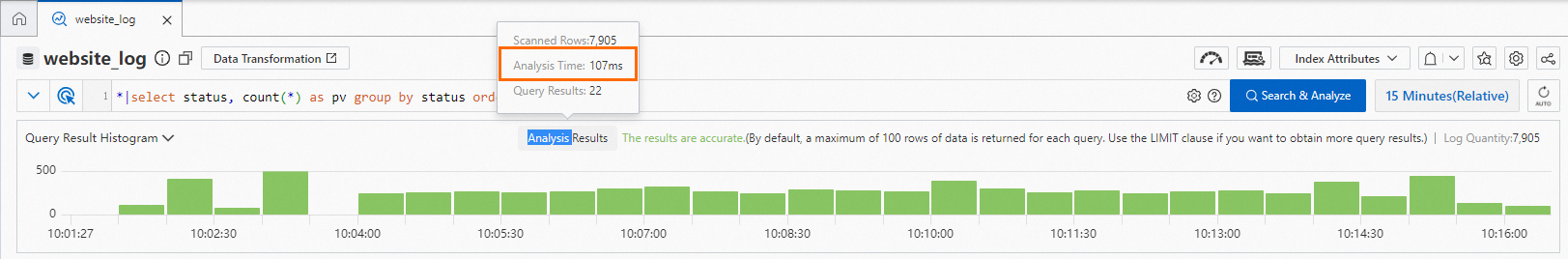
How do I obtain the amount of CPU time that I use?
After performing analysis and query operations, move the pointer over Analysis Results to view the amount of CPU time you use. The following figure shows an example.
What are the fees of the Dedicated SQL feature when I execute a query statement once?
The fees of the Dedicated SQL feature vary based on the amount of data on which you execute query statements. The following table provides examples.
Query statement
Amount of data (rows)
Average cost per execution (USD)
* | select avg(double_0) from stress_s1_mil14 billion
0.004435
* | select avg(double_0), sum(double_0),), min(double_0), count(double_0) from stress_s1_mil14 billion
0.006504
* | select avg(double_0), sum(double_1), max(double_2), min(double_3), count(double_4) from stress_s1_mil14 billion
0.013600
* | select key_0 , avg(double_0) as pv from stress_s1_mil1 group by key_0 order by pv desc limit 10004 billion
0.011826
* | select long_0, avg(double_0) as pv from stress_s1_mil1 group by long_0 order by pv desc limit 10004 billion
0.011087
* | select long_0, long_1, avg(double_0) as pv from stress_s1_mil1 group by long_0,long_1 order by pv desc limit 10000.3 billion
0.010791
* | select avg(double_0) from stress_s1_mil1 where key_0='key_987'4 billion
0.00007
 > Completely Accurate
> Completely Accurate