Data parsing plugins structure raw logs into key-value pairs or structured data.
Example of data parsing results
The following table shows the data structure of a raw log saved to Simple Log Service with and without a regular expression parsing plugin. Using a parsing plugin to structure the data simplifies subsequent queries.
Raw log | Without a parsing plugin | With a regular expression parsing plugin |
| Content: "127.0.0.1 - - [16/Aug/2024:14:37:52 +0800] "GET /wp-admin/admin-ajax.php?action=rest-nonce HTTP/1.1" 200 41 "http://www.example.com/wp-admin/post-new.php?post_type=page" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/127.0.0.0 Safari/537.36 Edg/127.0.0.0"" | Regular expression: |
Overview of data parsing plugins
Simple Log Service provides the following types of data parsing plugins. You can select a plugin based on your requirements.
Plugin | Type | Description |
Regular expression parsing | Native | Uses a regular expression to extract fields and convert them into key-value pairs. |
JSON parsing | Native | Parses JSON-formatted logs into key-value pairs. |
Separator-based parsing | Native | Structures logs based on a separator. |
Nginx-mode parsing | Native | Parses Nginx access logs. |
Apache-mode parsing | Native | Parses Apache access logs. |
IIS-mode parsing | Native | Parses IIS access logs. |
Entry point
If you want to use a Logtail plug-in to process logs, you can add a Logtail plug-in configuration when you create or modify a Logtail configuration. For more information, see Overview.
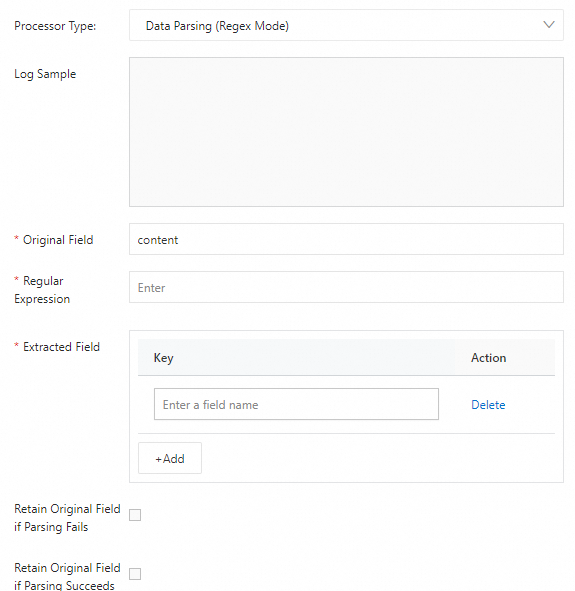
Regular expression parsing plugin
The regular expression parsing plugin extracts log fields using a regular expression and parses the log into key-value pairs.
Configuration description
Parameter | Description |
Source Field | The source field that contains the log content before parsing. The default value is content. |
Regular Expression | The regular expression used to match logs.
|
Extracted Log Fields | Set a key for each extracted log value. |
Keep Source Field On Parsing Failure | If you select Keep Source Field On Parsing Failure, the source field is retained even if parsing fails. |
Keep Source Field On Parsing Success | If you select Keep Source Field On Parsing Success, the source field is retained upon successful parsing. |
Renamed Source Field | After you select Keep Source Field On Parsing Failure or Keep Source Field On Parsing Success, you can rename the source field. |
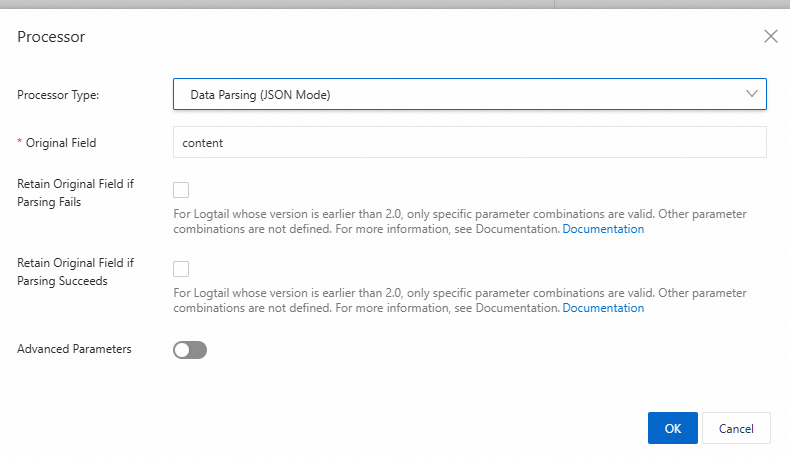
JSON parsing plugin
The JSON parsing plugin structures object-type JSON logs into key-value pairs.
Limits
JSON logs are built on two structures: object types (collections of key-value pairs) and array types (ordered lists of values). The JSON parsing plugin can parse object-type JSON logs by extracting the first-level keys and values. The plugin does not support parsing array-type JSON logs.
Parameters
Parameter | Description |
Source Field | The source field that contains the log content before parsing. The default value is content. |
Keep Source Field On Parsing Failure | If you select Keep Source Field On Parsing Failure, the source field is retained if parsing fails. |
Keep Source Field On Parsing Success | If you select Keep Source Field On Parsing Success, the source field is retained upon successful parsing. |
Renamed Source Field | After you select Keep Source Field On Parsing Failure or Keep Source Field On Parsing Success, you can rename the source field. |
Separator-based parsing plugin
The separator-based parsing plugin uses a separator to structure log content into multiple key-value pairs.
Parameters
Parameter | Description |
Source Field | The source field that contains the log content before parsing. The default value is content. |
Separator | The separator used to split log content, such as a VERTICAL LINE (|). Note When you specify an Invisible Character as the separator, you must find its corresponding hexadecimal value in the ASCII table. The input format is |
Quote | If a log field contains the separator, you must enclose the field with a quote character. Simple Log Service parses the content enclosed in quotes as a single field. The quote character must match your log format. Note When you specify an Invisible Character as the quote character, you must find its corresponding hexadecimal value in the ASCII table. The input format is |
Extracted Log Fields |
A key can contain only letters, digits, and underscores (_). It must start with a letter or an underscore (_). The maximum length is 128 bytes. |
Allow Partial Match | Specifies whether to upload a log to Simple Log Service if the number of extracted values is less than the number of keys. If you select Allow Partial Match, the log is uploaded. For example, the log is
|
Action On Extra Fields | The action to take when the number of extracted values is greater than the number of keys.
|
Keep Source Field On Parsing Failure | If you select Keep Source Field On Parsing Failure, the source field is retained when parsing fails. |
Keep Source Field On Parsing Success | If you select Keep Source Field On Parsing Success, the source field is retained after the parsing is successful. |
Renamed Source Field | After you select Keep Source Field On Parsing Failure or Keep Source Field On Parsing Success, you can rename the source field. |
Appendix
The separator-based parsing plugin supports single-character and multi-character separators.
Single character
The following is a sample log with a single-character separator.
05/May/2022:13:30:28,10.10.*.*,"POST /PutData?Category=YunOsAccountOpLog&AccessKeyId=****************&Date=Fri%2C%2028%20Jun%202013%2006%3A53%3A30%20GMT&Topic=raw&Signature=******************************** HTTP/1.1",200,18204,aliyun-sdk-java
05/May/2022:13:31:23,10.10.*.*,"POST /PutData?Category=YunOsAccountOpLog&AccessKeyId=****************&Date=Fri%2C%2028%20Jun%202013%2006%3A53%3A30%20GMT&Topic=raw&Signature=******************************** HTTP/1.1",401,23472,aliyun-sdk-javaIn single-character mode, you must specify a separator. You can also specify a quote character.
Separator: A single character used to split the log, such as a tab character (\t), a VERTICAL LINE (|), a space, a comma (,), a semicolon (;), or an invisible character. A double quotation mark (") cannot be used as a separator.
A double quotation mark (") can be used as a quote character at the field border or as part of the field content. If a double quotation mark (") is part of the field content, it must be escaped as
""in the log. Simple Log Service automatically restores""to"during parsing. For example, assume that the separator is a comma (,) and the quote character is a double quotation mark ("). If a log field contains both a double quotation mark (") and a comma (,), you must enclose the field in quote characters and escape the double quotation mark (") as"". For example, the log1999,Chevy,"Venture ""Extended Edition, Very Large""","",5000.00is parsed into five fields:1999,Chevy,Venture "Extended Edition, Very Large", an empty field, and 5000.00.Quote: If a log field contains the separator, you must enclose the field with a quote character. Simple Log Service then parses the content enclosed in quotes as a single field.
The quote character can be a single character, such as a tab character (\t), a VERTICAL LINE (|), a space, a comma (,), a semicolon (;), or an invisible character.
For example, if the separator is a comma (,) and the quote character is a double quotation mark ("), the log
1997,Ford,E350,"ac, abs, moon",3000.00is parsed into five fields:1997,Ford,E350,ac, abs, moon, and3000.00.
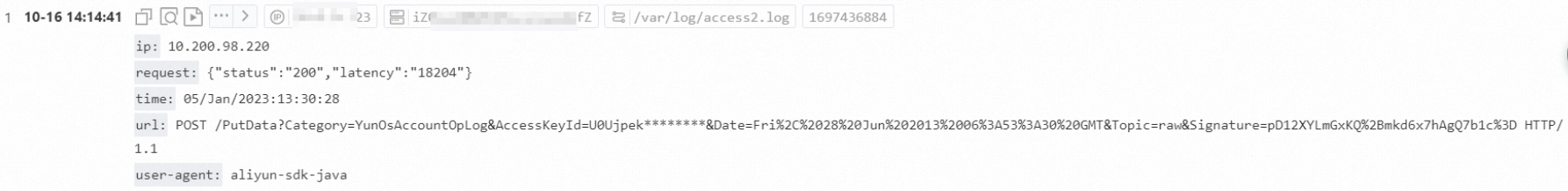
Multi-character
The following is a sample log with a multi-character separator.
05/May/2022:13:30:28&&10.200.**.**&&POST /PutData?Category=YunOsAccountOpLog&AccessKeyId=****************&Date=Fri%2C%2028%20Jun%202013%2006%3A53%3A30%20GMT&Topic=raw&Signature=******************************** HTTP/1.1&&200&&18204&&aliyun-sdk-java
05/May/2022:13:31:23&&10.200.**.**&&POST /PutData?Category=YunOsAccountOpLog&AccessKeyId=****************&Date=Fri%2C%2028%20Jun%202013%2006%3A53%3A30%20GMT&Topic=raw&Signature=******************************** HTTP/1.1&&401&&23472&&aliyun-sdk-javaIn multi-character mode, the separator consists of two or three characters, such as ||, &&&, or ^_^. Log parsing is based on matching the separator. You do not need to enclose log fields with quote characters.
Make sure that the full separator sequence does not appear within any log field content. Otherwise, fields may be split incorrectly.
For example, if the separator is &&, the log 1997&&Ford&&E350&&ac&abs&moon&&3000.00 is parsed into five fields: 1997, Ford, E350, ac&abs&moon, and 3000.00.
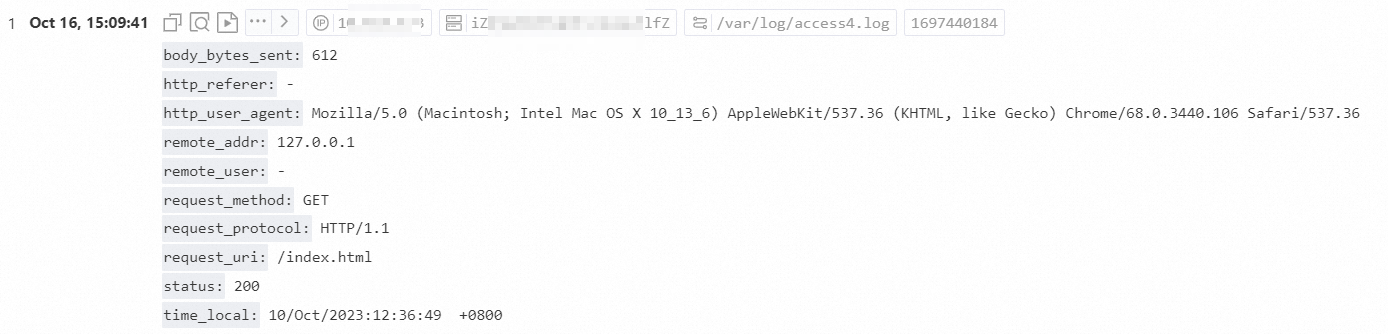
Nginx-mode parsing plugin
The Nginx-mode plugin structures log content into multiple key-value pairs based on the log_format definition.
Introduction to Nginx logs
An Nginx server outputs Nginx access logs based on the log_format and access_log configurations. The following are the default values for log_format and access_log.
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$request_time $request_length '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent"';
access_log /var/logs/nginx/access.log mainThe following table describes the log fields.
Field Name | Description |
remote_addr | The client IP address. |
remote_user | The client username. |
time_local | The server time. It must be enclosed in square brackets ([]). |
request | The request URI and HTTP protocol. |
request_time | The total time of the request, in seconds. |
request_length | The length of the request, including the request line, request header, and request body. |
status | The request status. |
body_bytes_sent | The number of bytes sent to the client, excluding the size of the response header. |
http_referer | The URL of the referrer. |
http_user_agent | Information about the client browser. |
Configuration description
Parameter | Description |
NGINX Log Configuration | The log configuration section in the Nginx configuration file. It starts with log_format. Example: |
Source Field | The source field that contains the log content before parsing. The default value is content. |
Extracted Log Fields | The log keys are automatically extracted based on the NGINX Log Configuration. |
Keep Source Field On Parsing Failure | If you select Keep Source Field On Parsing Failure, the source field is retained if parsing fails. |
Keep Source Field On Parsing Success | If you select Keep Source Field On Parsing Success, the source field is retained upon successful parsing. |
Renamed Source Field | After you select Keep Source Field On Parsing Failure or Keep Source Field On Parsing Success, you can rename the source field. |
Apache-mode parsing plugin
The Apache-mode parsing plugin structures log content into multiple key-value pairs based on the definitions in the Apache log configuration file.
Introduction to Apache logs
An Apache server outputs Apache logs based on the log format, path, and name specified in the Apache log configuration file. For example, CustomLog "/var/log/apache2/access_log" combined indicates that the combined format is used for logging and that the log file path is /var/log/apache2/access_log.
Apache log formats
combined format
LogFormat "%h %l %u %t \"%r\" %>s %b \"%{Referer}i\" \"%{User-Agent}i\"" combinedcommon format
LogFormat "%h %l %u %t \"%r\" %>s %b"Custom format
LogFormat "%h %l %u %t \"%r\" %>s %b \"%{Referer}i\" \"%{User-Agent}i\" %D %f %k %p %q %R %T %I %O" customized
The following table describes the related fields. For more information, see mod_log_config.
Format String
Field Name
Description
%a
client_addr
The client IP address.
%A
local_addr
The local IP address.
%b
response_size_bytes
The size of the response in bytes. A hyphen (-) is displayed for empty values.
%B
response_bytes
The size of the response in bytes. A 0 is displayed for empty values.
%D
request_time_msec
The time taken to serve the request, in microseconds.
%f
filename
The filename.
%h
remote_addr
The remote hostname.
%H
request_protocol_supple
The request protocol.
%I
bytes_received
The number of bytes received by the server. The mod_logio module must be enabled.
%k
keep_alive
The number of keep-alive requests handled on this connection.
%l
remote_ident
The remote host's identification information.
%m
request_method_supple
The request method.
%O
bytes_sent
The number of bytes sent by the server. The mod_logio module must be enabled.
%p
remote_port
The server port number.
%P
child_process
The child process ID.
%q
request_query
The query string. If no query string exists, this is an empty string.
%r
request
The request line, including the method, URI, and HTTP protocol.
%R
response_handler
The handler on the server that generated the response.
%s
status
The HTTP status of the response (initial status).
%>s
status
The HTTP status of the response (final status).
%t
time_local
The server time.
%T
request_time_sec
The time taken to serve the request, in seconds.
%u
remote_user
The client username.
%U
request_uri_supple
The URL path requested, not including any query string.
%v
server_name
The server name.
%V
server_name_canonical
The canonical server name set by the UseCanonicalName directive.
“%{User-Agent}i”
http_user_agent
The client information.
“%{Referer}i”
http_referer
The referrer page.
Parameters
Parameter | Description |
Log Format | The log format defined in your Apache log configuration file. Options include common, combined, and custom. |
APACHE Configuration Field | The log configuration section in the Apache configuration file. It usually starts with LogFormat.
|
Source Field | The source field that contains the log content before parsing. The default value is content. |
Regular Expression | The regular expression used to extract Apache logs. Simple Log Service automatically generates this regular expression based on the content in the APACHE Configuration Field. |
Extracted Log Fields | The log keys are automatically generated based on the content in the APACHE Configuration Field. |
Keep Source Field On Parsing Failure | If you select Keep Source Field On Parsing Failure, the source field is retained if parsing fails. |
Keep Source Field On Parsing Success | If you select Keep Source Field On Parsing Success, the source field is retained upon successful parsing. |
Renamed Source Field | After you select Keep Source Field On Parsing Failure or Keep Source Field On Parsing Success, you can rename the source field. |
IIS-mode parsing plugin
The IIS-mode plugin structures log content into multiple key-value pairs based on the IIS log format definition.
Introduction to IIS logs
A Windows server generates IIS logs based on the log format you select (IIS, NCSA, or W3C).
Log format
#Fields: date time s-sitename s-ip cs-method cs-uri-stem cs-uri-query s-port cs-username c-ip cs(User-Agent) sc-status sc-substatus sc-win32-status sc-bytes cs-bytes time-takenField prefix descriptions
Prefix
Description
s-
Server action.
c-
Client action.
cs-
Client-to-server action.
sc-
Server-to-client action.
Field descriptions
Field
Description
date
The date on which the client made the request.
time
The time at which the client made the request.
s-sitename
The Internet service and instance number of the site that the client accessed.
s-computername
The name of the server on which the log entry was generated.
s-ip
The IP address of the server on which the log entry was generated.
cs-method
The request method, such as GET or POST.
cs-uri-stem
The URI resource, which is the target of the action.
cs-uri-query
The query string that the client requested. It is the information that follows the question mark (?).
s-port
The server port number.
cs-username
The domain or username that was authenticated.
For authenticated users, the format is
Domain\Username.For anonymous users, a hyphen (-) is displayed.
c-ip
The originating IP address of the client that accessed the server.
cs-version
The protocol version, such as HTTP 1.0 or HTTP 1.1.
cs(User-Agent)
The browser that the client used.
Cookie
The content of the cookie sent or received. If no cookie is present, a hyphen (-) is displayed.
referer
The site that the user last visited.
cs-host
The host information.
sc-status
The HTTP protocol return status.
sc-substatus
The HTTP subprotocol status.
sc-win32-status
The status of the operation in Windows terms.
sc-bytes
The number of bytes sent by the server.
cs-bytes
The number of bytes received by the server.
time-taken
The time taken for the request to be processed, in milliseconds.
Parameters
Parameter | Description |
Log Format | The log format used by your IIS server.
|
IIS Configuration Field | The IIS configuration field.
|
Source Field | The source field that contains the log content before parsing. The default value is content. |
Regular Expression | The regular expression used to extract IIS logs. Simple Log Service automatically generates this regular expression based on the content in the IIS Configuration Field. |
Extracted Log Fields | The log keys are automatically generated based on the content in the IIS Configuration Field. |
Keep Source Field On Parsing Failure | If you select Keep Source Field On Parsing Failure, the source field is retained when parsing fails. |
Keep Source Field On Parsing Success | If you select Keep Source Field On Parsing Success, the source field is retained after successful parsing. |
Renamed Source Field | After you select Keep Source Field On Parsing Failure or Keep Source Field On Parsing Success, you can rename the source field. |
References
Configure a Logtail pipeline by calling API operations:
GetLogtailPipelineConfig - Get a Logtail pipeline configuration
ListLogtailPipelineConfig - List Logtail pipeline configurations
CreateLogtailPipelineConfig - Create a Logtail pipeline configuration
DeleteLogtailPipelineConfig - Delete a Logtail pipeline configuration
UpdateLogtailPipelineConfig - Update a Logtail pipeline configuration
Configure a processing plugin in the console:
Use Kubernetes CRD to collect container logs (stdout and files) from a cluster