You must configure environment variables to run an application in the system. For example, the commands of a Java application can be run only after the Java_home and Path environment variables are configured. This topic describes how to configure environment variables, including custom environment variables and the environment variables that are imported from namespace configuration items, for an application in the Serverless App Engine (SAE) console.
Procedure
The procedure varies based on the scenario:
Create an application
Log on to the SAE console. In the left-side navigation pane, select . Select a destination region and a namespace, and click Create Application.
After configuring the parameters on the Basic Information section of the Create Application page, click Next: Advanced Settings.
Deploy an application
WarningAfter you redeploy an application, the application is restarted. To prevent unpredictable errors such as business interruptions, we recommend that you deploy applications during off-peak hours.
Log on to the SAE console. In the left-side navigation pane, select . Select a destination region and a namespace, and click the name of the application you want to manage.
On the Basic Information page of the destination application, click Deploy Application.
Modify application configurations
Log on to the SAE console. In the left-side navigation pane, select . Select a destination region and a namespace, and click the name of the application you want to manage.
On the Basic Information page of the destination application, click Modify Application Configurations.
Expand the Environment Variables section and configure environment variables as needed.
Configuration guide
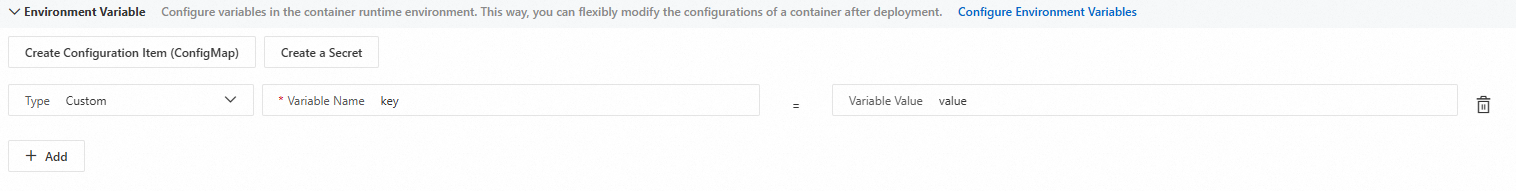
Add custom as environment variable
Select Custom from the Type drop-down list, and enter a Variable Name and a Variable Value.
Add reference configuration item as environment variable
Select Reference Configuration Item from the Type drop-down list, and enter a Variable Name. Select a desired configuration item name and key from the Configuration Item Name and Key drop-down list. You can configure either a single key or All Keys.
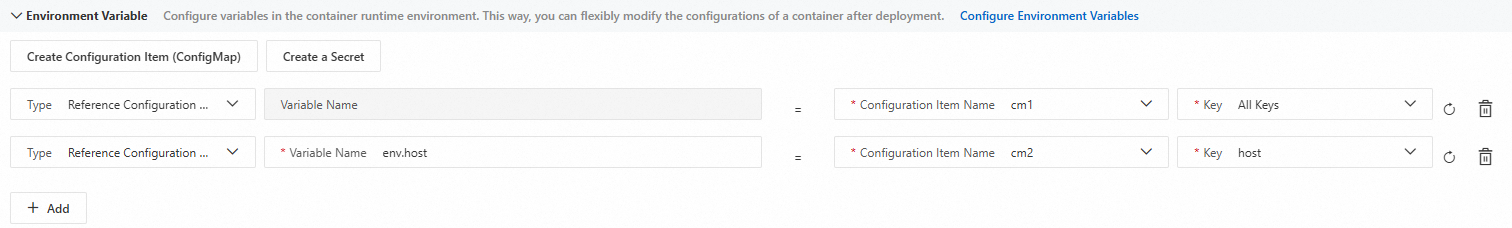
You can create configuration items in advance on the Namespace page, or click the Create Configuration Item (ConfigMap) in this section to create configuration items on the Create Kubernetes ConfigMap panel. For more information, see Manage and use a configuration item (Kubernetes ConfigMap).
When you select All Keys, the variable name for each key defaults to the key name of the selected configuration item and is not customizable.
We recommend that you set a variable name with a maximum length of 256 characters. SAE saves environment variables as properties during application deployment. You are allowed to add multiple environment variables.
Add a secret as environment variable
Select Reference the Secret from the Type drop-down list, and enter a Variable Name. Select a created secret name and a corresponding key from The Name of the Secret and Key drop-down box. You can configure either a single key or All Keys.
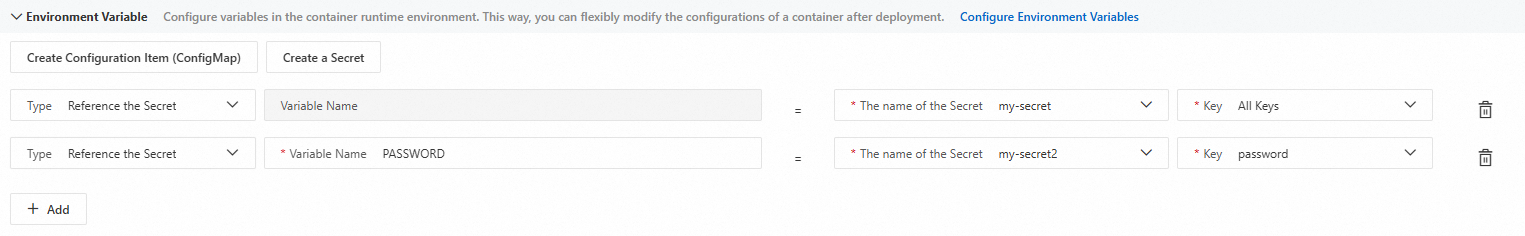
You can create Secrets in advance on the Namespace page, or click Create a Secret in this section to create a Secret on the Create a Secret panel. For more information, see Manage and use a configuration item (Kubernetes ConfigMap).
When you select All Keys, the variable name for each key defaults to the key name of the selected secret and is not customizable.
We recommend that you set a variable name with a maximum length of 256 characters. SAE saves environment variables as properties during application deployment. You are allowed to add multiple environment variables.
Sample
If you integrate MySQL into an application, you must configure the following necessary environment variables for MySQL operation:
Required: MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD: Allows you to specify a MySQL root password. If you left this parameter empty, the MySQL container will fail to start.
Optional: MYSQL_USER and MYSQL_PASSWORD: Allows you to create an account in addition to the root account and specify a password.
Optional: MYSQL_DATABASE: Allows you to specify the database that you want to create when the container is generated.