If you are familiar with Kubernetes and want to perform specific operations before application containers are started or stopped, you can configure application lifecycle management. For example, you want to deploy resources before the containers run, or gracefully shut down an application before the containers are stopped. This topic describes how to configure PostStart, PreStop, and TerminationGracePeriodSeconds in Serverless App Engine (SAE).
Overview
Pod hook (container hook) is a mechanism implemented by the kubelet component managed by Kubernete. It is used to execute custom tasks at critical stages of the container lifecycle, including before the container process starts (preStart) and stops (preStop). Hooks allow Kubernetes to manage the container lifecycle with greater flexibility and precision. For more information, see Container Lifecycle Hooks.
PostStart Setting: The hook is immediately triggered after a container is created. The hook notifies Kubernetes that the container is created. The hook does not pass parameters to the corresponding hook handler. If the corresponding hook handler fails to be executed, the container is stopped, and the restart policy of the container is used to determine whether to restart the container.
PreStop Setting: The hook is triggered before a container is deleted, often used for cleanup operations or to gracefully shut down services. The corresponding hook handler must be completely executed before the request to delete the container is sent to the Docker daemon. The Docker daemon sends an SGTERN semaphore to itself to delete the container, regardless of the execution result of the corresponding hook handler.
Timeout Duration Settings of Graceful Shutdown (TerminationGracePeriodSeconds): This setting provides a time buffer for the graceful shutdown, ensuring that necessary cleanup and shutdown tasks complete before applications are forcibly stopped. This improves system stability and reliability and prevents issues like data loss, request failure, and service unavailability caused by forced termination. Combined with the PreStop hook, it facilitates a complete graceful shutdown process.
Preparation
The procedure varies in different scenarios:
Create an application
Log on to the SAE console. In the left-side navigation pane, choose . On the page that appears, select a region in the top navigation bar and a namespace from the Namespace drop-down list, and click Create Application.
In the Basic Information section of the Create Application page, configure the required parameters and click Next: Advanced Settings.
On the page that appears, find and expand the Application Lifecycle Management section.
Modify a running application
After you redeploy an application, the application is restarted. To prevent unpredictable errors such as business interruptions, we recommend that you deploy applications during off-peak hours.
Log on to the SAE console. In the left-side navigation pane, choose . On the page that appears, select a region in the top navigation bar and a namespace from the Namespace drop-down list, and click the target application name.
On the Basic Information page of the target application, click Deploy Application.
On the Deploy Application page, find and expand the Application Lifecycle Management section.
Modify a stopped application
Log on to the SAE console. In the left-side navigation pane, choose . On the page that appears, select a region in the top navigation bar and a namespace from the Namespace drop-down list, and click the target application name.
On the Basic Information page of the target application, click Modify Application Configurations.
On the Modify Application Configurations page, find and expand the Application Lifecycle Management section.
Procedure
In the Application Lifecycle Management section, configure PostStart Settings, PreStop Settings, and Timeout Duration Settings of Graceful Shutdown as needed.
We recommend that you configure all three to achieve a complete lifecycle management for the container, ensuring smooth service startup and shutdown, orderly resource release, and zero business interruption.
PostStart settings
Configure PostStart on the PostStart Settings tab in the Application Lifecycle Management section.
SAE provides two shell interpreters:
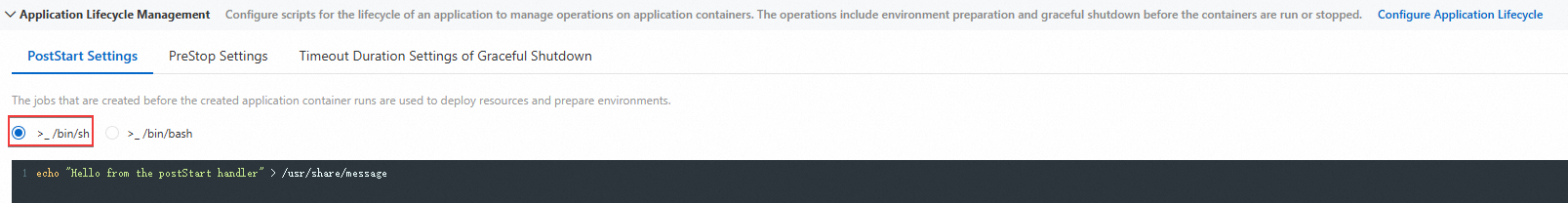
>_ /bin/sh
>_ /bin/bash
In this example, write Hello from the postStart handler in the script /usr/share/message before you start an application.
In a production environment, configure the parameter based on your business requirements. The example provided in this section is for minimal verification of feature availability and should not be used in a production environment.
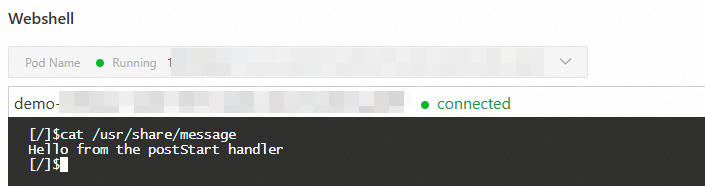
Verification:
After the application is created or redeployed, use Webshell to check whether the /usr/share/message script contains the expected content.
PreStop settings
Configure PreStop on the PreStop Settings tab in the Application Lifecycle Management section.
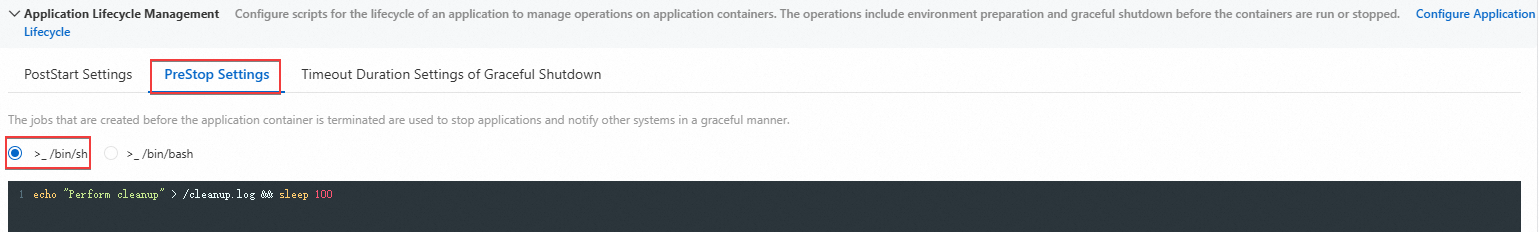
SAE provides two shell interpreters:
>_ /bin/sh
>_ /bin/bash
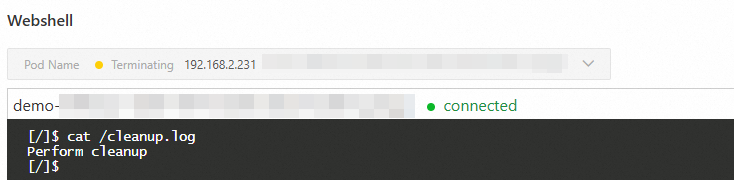
In this example, run the Perform cleanup command and write Perform cleanup in the script /cleanup.log. Wait for 100 seconds before you perform verification.
In a production environment, configure the parameter based on your business requirements. The example provided in this section is for minimal verification of feature availability and should not be used in a production environment.
Verification:
On the Basic Information page of the application, click Stop Application, and then use Webshell to check whether the /cleanup.log file contains the expected content.
Timeout Duration Settings of Graceful Shutdown (TerminationGracePeriodSeconds)
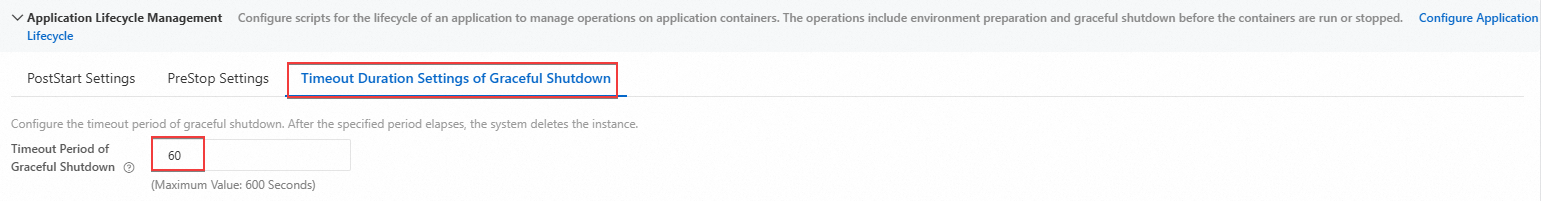
Configure the timeout duration of graceful shutdown on the Timeout Duration Settings of Graceful Shutdown tab in the Application Lifecycle Management section.
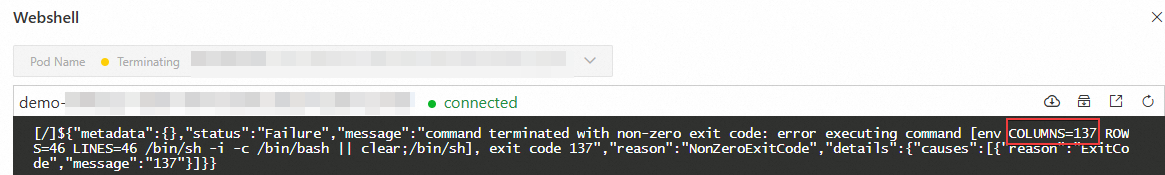
If the timeout duration of graceful shutdown you set is less than the graceful shutdown period (including the time for PreStop hook execution and the time for the container processes SIGTERM signal), the container will be forcibly terminated (signal name: SIGKILL, exit code: 137) when the timeout expires, interrupting the graceful shutdown process. For instance, if the stop period of container's graceful termination time is 100 seconds and the the timeout period of graceful shutdown is set to 60 seconds, the container will be killed before the graceful termination completes.
Verification:
In this example, the timeout duration of graceful shutdown is set to be shorter than the graceful shutdown period for verification purpose.
On the Basic Information page of the application, click Stop Application, and then use Webshell to check whether the 137 exit code appears in the container.
During graceful shutdown, the container will remain in the Terminating state until the timeout period is exceeded.