Collation naming conventions
The name of a collation must start with the name of the character set that corresponds to the collation and end with _ci, _cs, or _bin. _ci indicates that characters are not case-sensitive. _cs indicates that characters are case-sensitive. _bin indicates that characters are sorted based on code values and are case-sensitive.
For example, if collation_connection of a session is set to utf8_general_ci, Character a and Character A are equivalent. If collation_connection of the session is set to utf8_bin, Character a and Character A are not equivalent.
Example: 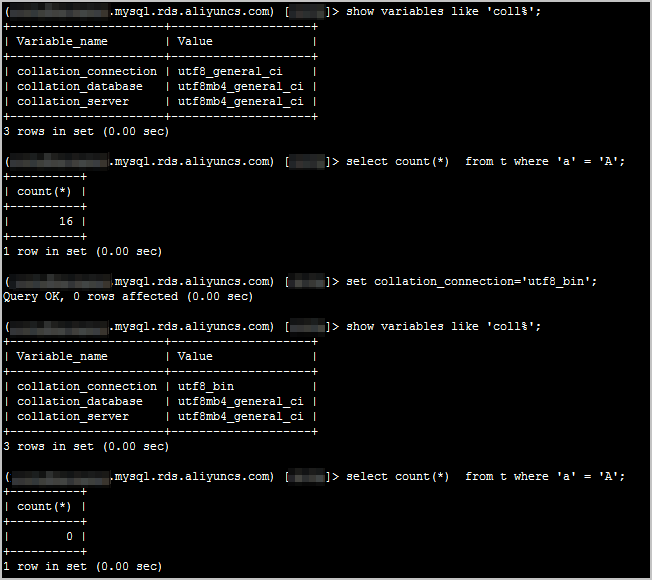
MySQL statements related to character sets
show global variables like '%char%'; #Queries the settings of parameters that are related to character sets of an RDS instance.
show global variables like 'coll%'; #Queries the settings of parameters that are related to character sets of the current session.
show character set; #Queries the character sets that are supported by an RDS instance.
show collation; #Queries the collations that are supported by an RDS instance.
show create table table_name \G #Queries the character set settings of a table.
show create database database_name \G #Queries the character set settings of a database.
show create procedure procedure_name \G #Queries the character set settings of a stored procedure.
show procedure status \G #Queries the character set settings of a stored procedure.
alter database db_name default charset utf8; #Changes the character set of a database.
create database db_name character set utf8; #Specifies a character set for a database during database creation.
alter table tab_name default charset utf8 collate utf8_general_ci; #Changes the character set and collation of a table.Example: 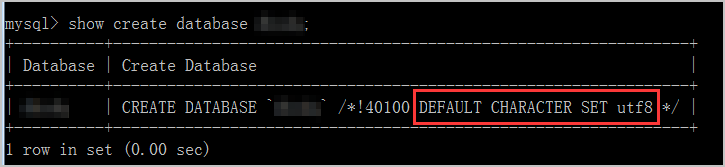
Modify the character_set_server parameter in the ApsaraDB RDS console
If you modify the character_set_server parameter of your RDS instance, you must restart the instance for the modification to take effect. We recommend that you modify the parameter during off-peak hours.
Procedure
Log on to the ApsaraDB RDS console.
In the top navigation bar, select the region in which the RDS instance resides.
Find the RDS instance and click the instance ID.
In the left-side navigation pane of the page that appears, click Parameters.
On the Editable Parameters tab of the page that appears, find the character_set_server parameter and click the
 icon in the Running Parameter Value column. In the dialog box that appears, enter a new value and click OK.
icon in the Running Parameter Value column. In the dialog box that appears, enter a new value and click OK. Click Apply Changes. In the dialog box that appears, click OK and wait for the RDS instance to restart.
NoteThe modification takes effect only for databases that are created after an privileged account is created for the RDS instance.
Change the character set by using SQL statements
Syntax:
If you want to change the character set of a database, execute the ALTER DATABASE <Database name> CHARACTER SET <Character set name> COLLATE <Collation name>; statement.
If you want to change the character set of a table, execute the ALTER TABLE <Table name> CONVERT TO CHARACTER SET <Character set name> COLLATE <Collation name>; statement.
If you want to change the character set of a column in a table, execute the ALTER TABLE <Table name> MODIFY <Column name> <Field type> CHARACTER SET <Character set name> COLLATE <Collation name>;statement.
Example: Execute the following SQL statements to change the character sets of the dbsdq database, the tt2 table, and the c2 column in the tt2 table to utf8mb4:
alter database dbsdq character set utf8mb4 collate utf8mb4_unicode_ci;
use dbsdq;
alter table tt2 convert to character set utf8mb4 collate utf8mb4_unicode_ci;
alter table tt2 modify c2 varchar(10) character set utf8mb4 collate utf8mb4_unicode_ci;When you change the character set of a column, the new character set immediately takes effect on all rows of the column.
The ALTER TABLE statement creates a metadata lock on a table.
If you want to specify a character set for an object, you must separately change the character set of the object. Otherwise, the server-level character set is globally used by default. You can specify character sets for servers, databases, tables, and fields. Server-level, database-level, and table-level character sets use the default settings. We recommend that you execute the
SHOW CREATE TABLE tableName;orSHOW FULL FIELDS FROM tableName;statement to query the character set settings of fields in a table.