ApsaraDB RDS for SQL Server allows you to manage read-only ApsaraDB RDS for SQL Server instances in your database system and provides the read-only routing endpoint for your database system. You can add the endpoint of the primary RDS instance and the read-only routing endpoint to your application to implement read/write splitting. Read/write splitting helps improve the performance and scalability of your database system and offload read requests from your primary RDS instance. This helps achieve efficient read/write splitting in applications.
Overview
After you create read-only RDS instances, you can enable the read-only routing endpoint to implement read/write splitting and add the endpoint of the primary RDS instance and the read-only routing endpoint to your application. This way, write requests are forwarded to the primary RDS instance and read requests are forwarded to the read-only routing endpoint. Then, the read-only routing endpoint distributes the read requests to the read-only RDS instances based on the read weights of the read-only RDS instances.

Benefits
Unified read-only routing endpoint to facilitate maintenance
The read-only routing endpoint is provided and used to distribute read requests to read-only RDS instances, which reduces maintenance costs. You can create read-only RDS instances to increase the read capability of your database system without the need to modify the application configuration.
Configurable read weights to meet various requirements
You can specify read weights for read-only RDS instances to meet the business requirements in different scenarios.
Instance-level health checks to ensure high availability
Read/write splitting proactively checks the health status of read-only RDS instances. If a read-only RDS instance fails or its data replication latency exceeds the specified threshold, the system stops forwarding read requests to the read-only RDS instance and redirects these read requests to other healthy read-only RDS instances. Instance-level health checks ensure service availability in the event of faults on a single read-only RDS instance. After the faulty read-only RDS instance recovers, the system resumes forwarding read requests to the read-only RDS instance.
NoteTo mitigate the impacts of single points of failure (SPOFs), we recommend that you create at least two read-only RDS instances.
Introduction to read-only routing endpoint and the internal and public endpoints
A read-only routing endpoint is added to an application to implement read/write splitting. The read requests from your application are forwarded to the read-only routing endpoint and then are distributed to the involved secondary RDS instance or read-only RDS instances based on the read weights of these instances.
If only the internal or public endpoint of the primary RDS instance is added to your application, all requests are forwarded to the primary RDS instance.
Prerequisites
A read-only RDS instance is created. For more information, see Create a read-only ApsaraDB RDS for SQL Server instance.
Usage notes
The read-only routing endpoint is fixed and does not change even if you enable or disable the read-only routing endpoint multiple times. You cannot manually modify the read-only routing endpoint. You do not need to update the configuration on your application. This reduces maintenance costs.
The read-only routing endpoint is free of charge. However, you still need to pay for the read-only RDS instances that you use. For more information, see Overview of read-only ApsaraDB RDS for SQL Server instances.
The read-only routing endpoint is not supported in the classic network.
Enable read/write splitting
After you enable the read-only routing endpoint and configure read weights for your read-only RDS instances, the system processes read requests based on the read weights that you configure.
Log on to the ApsaraDB RDS console and go to the Instances page. In the top navigation bar, select the region in which the RDS instance resides. Then, find the RDS instance and click the instance ID.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Cluster Management. On the page that appears, click Enable now..
In the dialog box that appears, configure the type of the read-only routing endpoint and the read weight of each RDS instance, such as the primary RDS instance, secondary RDS instance, and read-only RDS instances. Then, click OK.
In RDS Cluster Edition for ApsaraDB RDS for SQL Server, a primary RDS instance and a secondary RDS instance are provisioned in your database system. You can manually create read-only RDS instances. For more information, see RDS Cluster Edition.
Parameter
Description
Network Type
Internal (VPC): This type of read/write splitting endpoint can only be used to connect your RDS instance to an instance that resides in the same virtual private cloud (VPC), such as Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance, over an internal network.
Internet Address: This type of read/write splitting endpoint is used to connect your application that resides in a different VPC or on an on-premises device to your RDS instance over the Internet. If you want to use this type of read/write splitting endpoint, you must apply for a public endpoint in advance. For more information, see Apply for or release a public endpoint.
NoteWe recommend that you use the internal read/write splitting endpoint to connect to RDS instances because connections over the Internet are prone to fluctuations. For more information, see Internal and public endpoints.
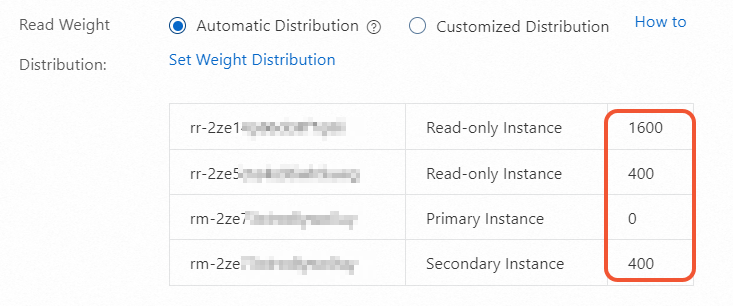
Read Weight Distribution
The read weight of each RDS instance, such as the primary RDS instance, secondary RDS instance, and read-only RDS instances. The read weights of read-only RDS instances are displayed only if read-only RDS instances are created. A higher read weight indicates more read requests to process. For example, if the primary RDS instance has three read-only RDS instances whose read weights are 100, 200, and 200, the read-only RDS instances process read requests at a ratio of 1:2:2.
Automatic Distribution: The system automatically assigns a read weight to each RDS instance in your database system based on the specifications of the RDS instance.
After you create a read-only RDS instance, the system automatically assigns a read weight to the created read-only RDS instance. You do not need to manually specify a read weight for the created read-only RDS instance. For more information, see Rules of weight allocation by the system.
Customized Distribution: You must manually specify a read weight for each read-only RDS instance. Valid values: 0 to 10000.
After you create a read-only RDS instance, the system sets the read weight of the read-only RDS instance to 0. You must manually modify the read weight of the created read-only RDS instance.
ImportantIf a read-only RDS instance is released, the system automatically removes the read weight of the read-only RDS instance.
View cluster information
On the Cluster Management page, you can view the basic information about and configurations of your RDS cluster. An RDS cluster refers to an ApsaraDB RDS for SQL Server instance that runs RDS Cluster Edition.
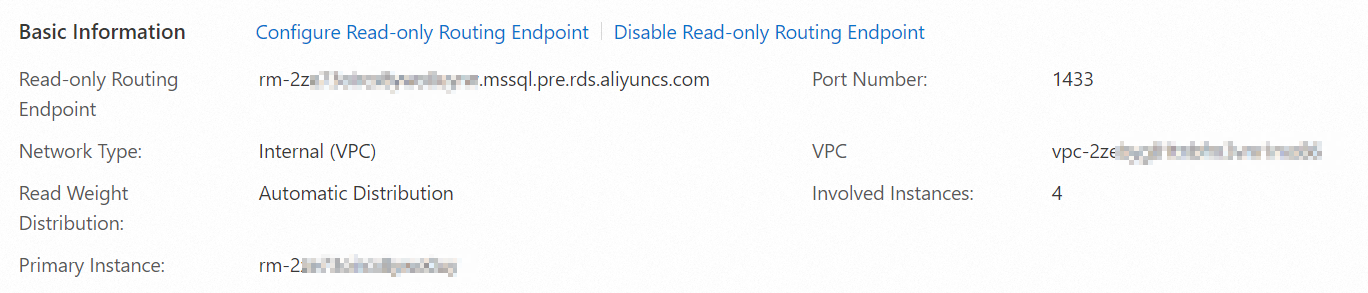
Basic information
In the Basic Information section, you can view the read-only routing endpoint, port number, network type, read weight distribution, and number of involved instances.
Configurations
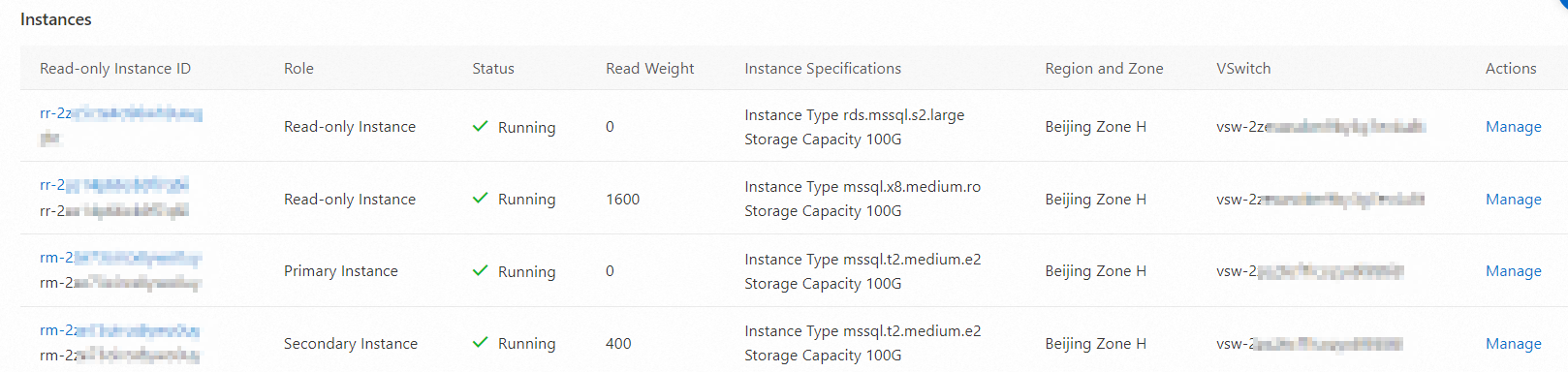
In the Instances section, you can view all involved instances in the RDS cluster and the status, roles, and read weights of the instances. You can also view and manage the instances of different roles in the instance list.
Related operations
You can modify the read weights of the read-only RDS instances based on your business requirements. The read-only routing endpoint distributes read requests to the secondary RDS instance and read-only RDS instances based on the new read weights. For more information, see Modify read weights.
If your RDS instance no longer requires read/write splitting, you can disable read/write splitting by disabling the read-only routing endpoint. For more information, see Disable read/write splitting by disabling the read-only routing endpoint.