ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL is developed based on PostgreSQL, which is an advanced open source relational database. ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL is highly compatible with SQL syntax and supports multiple data types and various community extensions. This topic provides examples on how to design table schemas and create databases and tables on an ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instance. In this topic, a course selection system is used.
Description
To facilitate online course selection and score statistics collection, a school plans to establish a course selection system. The backend of the system uses an RDS instance. In this scenario, table schemas need to be designed, and information about the identities, courses, and scores of students need to be stored in the tables.
Design table schemas
Design the schemas for the students, courses, and enrollments tables based on your business requirements. The following figure shows the Entity Relationship (ER) Diagram.
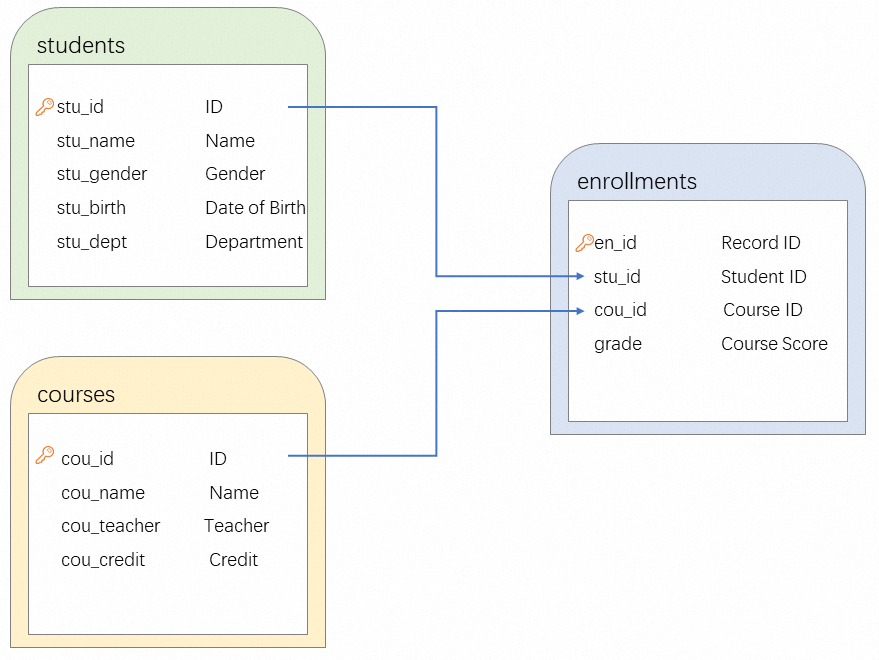
This section describes the table schemas.
students table
The table stores the identity information about students. In this table, a record is stored for each student, and the stu_id column is used to match a student with the course score.
Field
Field type
Description
stu_id
SERIAL
The ID of the student.
stu_name
VARCHAR(50)
The name of the student.
stu_gender
VARCHAR(10)
The gender of the student.
stu_birth
DATE
The date of birth of the student.
stu_dept
VARCHAR(50)
The department of the student.
courses table
The table stores the course information about students. In this table, a record is stored for each course. Each course has a unique ID that is specified by the cou_id field.
Field
Field type
Description
cou_id
SERIAL
The ID of the course.
cou_name
VARCHAR(100)
The name of the course.
cou_teacher
VARCHAR(50)
The teacher of the course.
cou_credit
INTEGER
The score of the course.
enrollments table
Field
Field type
Description
en_id
SERIAL
The ID of the course selection record.
stu_id
INTEGER
The ID of the student, which is used to match the stu_id field in the students table.
cou_id
INTEGER
The ID of the course, which is used to match the cou_id field in the courses table.
grade
VARCHAR(2)
The score.
Create tables on the RDS instance
Create an RDS instance. For more information, see Create an ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instance.
Create a database and an account. For more information, see Create a database and an account on an ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instance.
Configure a whitelist. For more information, see Configure an IP address whitelist.
Connect to the RDS instance. For more information, see Connect to an ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instance.
Create tables based on the designed table schemas.
students table
CREATE TABLE students ( stu_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY, stu_name VARCHAR(50), stu_gender VARCHAR(10), stu_birth DATE, stu_dept VARCHAR(50) );courses table
CREATE TABLE courses ( cou_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY, cou_name VARCHAR(100), cou_teacher VARCHAR(50), cou_credit INTEGER );enrollments table
CREATE TABLE enrollments ( en_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY, stu_id INTEGER, cou_id INTEGER, grade VARCHAR(2), FOREIGN KEY (stu_id) REFERENCES students(stu_id), FOREIGN KEY (cou_id) REFERENCES courses(cou_id) );
Assume that students select courses from the frontend program, the teacher enters the stores of the students, and the relevant data is sent back to the backend database. Insert test data into the database.
-- Insert test data into the students table. INSERT INTO students (stu_name, stu_gender, stu_birth, stu_dept) VALUES ('Zhangsan', 'Female', '2000-01-01', 'Computer Science'), ('Lisi', 'Male', '1999-05-10', 'Mathematics'), ('Wangwu', 'Male', '2001-08-20', 'Physics'), ('Zhaoliu', 'Female', '1998-03-15', 'Chemistry'), ('Sunqi', 'Female', '2002-11-30', 'Biology'); -- Insert test data into the courses table. INSERT INTO courses (cou_name, cou_teacher, cou_credit) VALUES ('Database Systems', 'Professor Zhang', 3), ('Calculus', 'Professor Wang', 4), ('Computer Network', 'Professor Li', 4), ('Organic Chemistry', 'Professor Wang', 4), ('Biology Basics', 'Professor Zhang', 2); -- Insert test data into the enrollments table. INSERT INTO enrollments (stu_id, cou_id, grade) VALUES (1, 1,'A'),(1, 3,'B+'),(1, 5,'C'), (2, 1,'B+'),(2, 2,'A'),(2, 3,'B-'), (3, 2,'A-'),(3, 4,'A'),(3, 5,'B+'), (4, 3,'B'),(4, 4,'B-'), (5, 4,'C');
Examples
At the end of a semester, the student named
Zhangsanneeds to query the score of each course in the course selection system.SELECT courses.cou_name, enrollments.grade FROM students JOIN enrollments ON students.stu_id = enrollments.stu_id JOIN courses ON enrollments.cou_id = courses.cou_id WHERE students.stu_name = 'Zhangsan';The following code shows the sample output.
cou_name | grade ------------------+------- Database Systems | A Computer Network | B+ Biology Basics | C (3 rows)NoteIn the query statement, a JOIN clause is used to join the
students,enrollments, andcoursestables. The stu_id and cou_id fields are used to join the enrollments table. The WHERE clause is used to filter the records of the student namedZhangsan.The teacher named
Professor Zhangneeds to query the scores of all students he teaches in the course selection system.SELECT students.stu_name, courses.cou_name, enrollments.grade FROM students JOIN enrollments ON students.stu_id = enrollments.stu_id JOIN courses ON enrollments.cou_id = courses.cou_id WHERE courses.cou_teacher = 'Professor Zhang';The following code shows the sample output.
stu_name | cou_name | grade ----------+------------------+------- Zhangsan | Database Systems | A Zhangsan | Biology Basics | C Lisi | Database Systems | B+ Wangwu | Biology Basics | B+ (4 rows)NoteIn the query statement, a JOIN clause is used to join the
students,enrollments, andcoursestables. The stu_id and cou_id fields are used to join the enrollments table. The WHERE clause is used to filter the records of the teacher namedProfessor Zhang.The school needs to rank the course credits of all students to choose outstanding students. The top 3 students will be honored outstanding students.
SELECT students.stu_name, SUM( CASE WHEN enrollments.grade = 'C' THEN 0 ELSE courses.cou_credit END ) AS total_credits FROM students JOIN enrollments ON students.stu_id = enrollments.stu_id JOIN courses ON enrollments.cou_id = courses.cou_id GROUP BY students.stu_name ORDER BY total_credits DESC LIMIT 3;The following code shows the sample output.
stu_name | total_credits ----------+--------------- Lisi | 11 Wangwu | 10 Zhaoliu | 8 (3 rows)NoteIn the query statement, a JOIN clause is used to join the
students,enrollments, andcoursestables. The stu_id and cou_id fields are used to join the enrollments table. The GROUP BY clause is used to group students by student name, the SUM function is used to calculate the total course credits of each student, and the ORDER BY clause is used to sort the total course credits in descending order. If a student gets C for one course, the student fails to obtain the course credit of the course. TheLIMIT 3clause is used to return the top 3 students by course credit.