If your ApsaraDB RDS instance is overloaded, you can vertically split a database or table from the RDS instance into another RDS instance. This topic describes how to use the dual-write solution and simple splitting solution to perform vertical splitting on an RDS instance.
Background information
Assume that an RDS instance contains Database A and Database B. As your business grows, the bottlenecks of the RDS instance become increasingly evident. To reduce the load on the RDS instance, you can vertically split Database B to another RDS instance. For more information, see Dual-write solution and Simple splitting solution.
Precautions
You must create another RDS instance into which you want to split databases or tables of your RDS instance. Make sure that the permissions required for database accounts of the destination RDS instance and the source RDS instance are the same. For information about the supported destination instance types, see Overview of data migration solutions.
NoteWe recommend that you create a database account for the source and destination databases and grant permissions that are required for data migration to the database account. This facilitates session distinguishing and enhances data security.
You must add the endpoint of the destination RDS instance to your application.
Because the simple splitting solution requires you to temporarily pause your business and stop writing data to the database, we recommend that you perform the operations during off-peak hours. This reduces the impact on your business when you publish program changes and switch instances.
Dual-write solution
The dual-write solution helps implement phased switchover and reduce negative impacts on your service. Before you use the dual-write solution, you must modify your application and make sure that the application data can be written to Databases B of the source and destination RDS instances.
Configure a data migration task from the source RDS instance to the destination RDS instance. Select Database B as the object to be migrated. For more information about how to configure a data migration task, see Overview of data migration solutions.
NoteWhen you configure the data migration task, you must select Schema Migration, Full Data Migration, and Incremental Data Migration.
Wait until the data migration task enters the incremental data migration stage and the latency of incremental data migration becomes zero or less than 5 seconds.
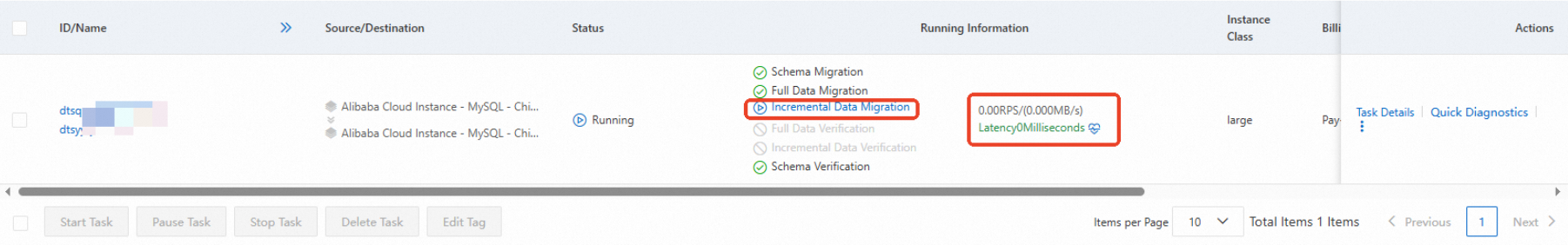
Verify that the data in Database B is consistent between the source and destination RDS instances.
If the data is consistent, complete the data migration task. For more information, see Complete a data migration task.
WarningThe database accounts that are used for data migration are granted the read and write permissions. After the data migration task is complete, you must delete the accounts or revoke the write permissions of the accounts to ensure data security.
Configure your application to write data to Database B of both the source and destination RDS instances.
Log on to Database B of the source and destination RDS instances. Run one of the following commands based on the database type to view session information. Make sure that new sessions are created to execute write operations.
MySQL
SHOW processlist;SQL Server
SELECT * FROM sys.dm_exec_connections;Oracle
SELECT sid,serial#,username,program,machine,status from v$session;PostgreSQL
SELECT * FROM pg_stat_activity;Redis
CLIENT LISTMongoDB
use admin db.runCommand({currentOp: 1, $all:[{"active" : true}]})NoteAfter you execute the required statement, the information that is returned includes the processes or sessions for DTS to connect to Database B of the source and destination RDS instances.
Make sure that your application can write data to Database B of both the source and destination RDS instances. Then, run your application for a business cycle or seven days.
Test all features that are related to your business and make sure that no issues occur. Then, you can unpublish Database B from the source RDS instance.
Simple splitting solution
If you use the simple splitting solution, you do not need to modify your application. However, a rollback failure may occur.
Configure a data migration task from the source RDS instance to the destination RDS instance. Select Database B as the object to be migrated. For more information about how to configure a data migration task, see Overview of data migration solutions.
Wait until the data migration task enters the incremental data migration stage and the latency of incremental data migration becomes zero or less than 5 seconds.
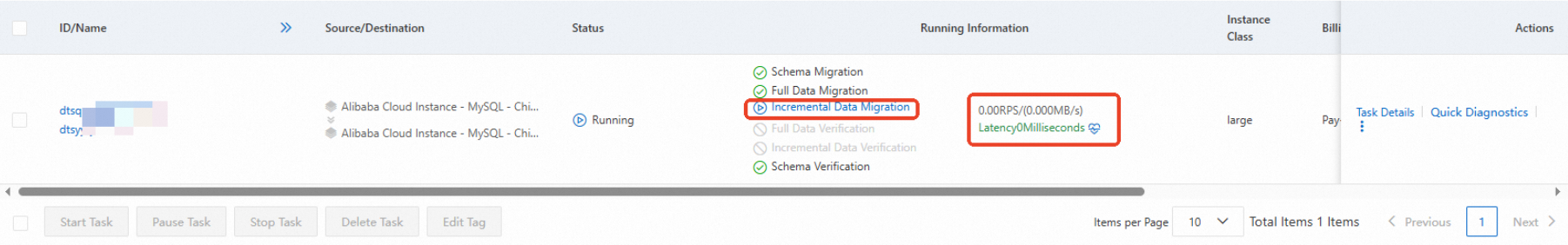 Note
NoteIf you do not select Incremental Data Migration when you configure the data migration task, the progress bar does not show the incremental data migration stage. After the data migration task is complete, the task automatically ends. In this case, you must stop your business and stop writing data to the source database before you start the data migration task. Then, skip to Step 6.
Verify that the data in Database B is consistent between the source and destination RDS instances.
If the data is consistent, complete the data migration task. For more information, see Complete a data migration task.
WarningThe database accounts that are used for data migration are granted the read and write permissions. After the data migration task is complete, you must delete the accounts or revoke the write permissions of the accounts to ensure data security.
Disconnect your application from Database B of the source RDS instance.
NoteAfter the application is disconnected from Database B of the source RDS instance, if the services and features that are related to Database A of the source RDS instance are affected, you must disconnect the application from the source RDS instance.
Log on to Database B of the source RDS instance. Run one of the following commands based on the database type to view session information. Make sure that no new sessions are created to execute write operations.
MySQL
SHOW processlist;SQL Server
SELECT * FROM sys.dm_exec_connections;Oracle
SELECT sid,serial#,username,program,machine,status from v$session;PostgreSQL
SELECT * FROM pg_stat_activity;Redis
CLIENT LISTMongoDB
use admin db.runCommand({currentOp: 1, $all:[{"active" : true}]})NoteAfter you execute the required statement, the information that is returned includes the processes or sessions for DTS to connect to Database B of the source RDS instance.
Create and start a reverse data migration task to migrate incremental data from Database B of the destination RDS instance to Database B of the source RDS instance.
The migration task that is created in this step is used for data rollback. After your service is resumed, if an error occurs, you can switch workloads to the source database.
WarningWhen you configure the preceding data migration task, you can select only "Incremental Data Migration" in the "Configure Migration Types and Objects" step. Then, you can select the database or table that you want to migrate back to the source database.
Keep your application disconnected from Database B of the source RDS instance. After you verify that the data in Database B is consistent between the source and destination RDS instances, switch the database service of your application to Database B of the destination RDS instance and resume your business.
Log on to Database B of the destination RDS instance. Run one of the following commands based on the database type to view session information. Make sure that new sessions are created to execute write operations.
MySQL
SHOW processlist;SQL Server
SELECT * FROM sys.dm_exec_connections;Oracle
SELECT sid,serial#,username,program,machine,status from v$session;PostgreSQL
SELECT * FROM pg_stat_activity;Redis
CLIENT LISTMongoDB
use admin db.runCommand({currentOp: 1, $all:[{"active" : true}]})NoteAfter you execute the required statement, the information that is returned includes the processes or sessions for DTS to connect to Database B of the source RDS instance.
After your business is switched to the destination database, run your business for a business cycle or seven days.
Test all features that are related to your business and make sure that no issues occur. Then, you can unpublish Database B from the source RDS instance and complete the reverse data migration task. For more information, see Complete a data migration task.
WarningThe database accounts that are used for data migration are granted the read and write permissions. After the data migration task is complete, you must delete the accounts or revoke the write permissions of the accounts to ensure data security.