ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL supports the creation of native replication instances. You can use these instances to build highly available, read-only secondary databases in the cloud for your self-managed MySQL databases. This topic describes how to create a native replication instance and configure a data replication link from a self-managed database to the RDS for MySQL native replication instance.
Prerequisites
An RDS instance that supports native replication is required. You can either create a new one or upgrade an existing one. The instance must meet the following conditions, which you can view on the Basic Information page for the instance:
Database version: MySQL 5.7 (minor version 20240930 or later) or 8.0 (minor version 20250531 or later)
Product series: Basic Edition
Billing methods: subscription and pay-as-you-go
NoteTo use a Serverless native replication instance, you must first create a pay-as-you-go instance, enable native replication, and then change the billing method to Serverless.
Supported regions: China (Shanghai), China (Beijing), China (Shenzhen), China (Guangzhou), and China (Chengdu)
ImportantApsaraDB RDS native replication is currently available only in the regions listed above. Support for other regions is being rolled out. If you need this feature in other regions, please submit a ticket.
You have created a privileged account for the RDS for MySQL instance.
You have established a network connection between the self-managed MySQL database and the RDS for MySQL instance. For more information, see Network configurations.
Workflow overview
The process of creating a cloud-based secondary database using RDS native replication involves three steps:
Perform a full backup of the self-managed MySQL database.
Import the full backup of the self-managed MySQL database into the RDS for MySQL native replication instance.
Use MySQL commands to set up the replication link from the self-managed MySQL database to the RDS for MySQL native replication instance.
Solution 1: XtraBackup stream backup, Object Storage Service, and data import to a native replication instance
Advantages
RDS for MySQL native replication instances are fully compatible with XtraBackup physical backups and support the following features:
Automatically detects the GTID in the backup file to align the offset for setting up the replication link.
You can upload backup files to Object Storage Service (OSS) and enable server-side encryption to ensure data security.
You can rebuild the native replication instance from a selected backup set, which helps resolve complex replication break issues.
Billing
You are charged instance fees when you create a new instance with native replication enabled. Upgrading an existing instance to a native replication instance does not incur extra fees.
If you import full data by uploading a backup of your self-managed database to Object Storage Service (OSS), OSS storage fees are incurred for storing the backup file in OSS.
Procedure
Install XtraBackup and perform a backup on the self-managed database
Install XtraBackup:
Install on CentOS
MySQL 5.7
wget https://downloads.percona.com/downloads/Percona-XtraBackup-2.4/Percona-XtraBackup-2.4.29/binary/redhat/8/x86_64/percona-xtrabackup-24-2.4.29-1.el8.x86_64.rpm yum localinstall percona-xtrabackup-24-2.4.29-1.el8.x86_64.rpmMySQL 8.0
wget https://downloads.percona.com/downloads/Percona-XtraBackup-8.0/Percona-XtraBackup-8.0.35-31/binary/redhat/8/x86_64/percona-xtrabackup-80-8.0.35-31.1.el8.x86_64.rpm yum localinstall percona-xtrabackup-80-8.0.35-31.1.el8.x86_64.rpm
Install on Ubuntu
Install XtraBackup
MySQL 5.7
wget https://downloads.percona.com/downloads/Percona-XtraBackup-2.4/Percona-XtraBackup-2.4.29/binary/redhat/8/x86_64/percona-xtrabackup-24-2.4.29-1.el8.x86_64.rpm yum localinstall percona-xtrabackup-24-2.4.29-1.el8.x86_64.rpmMySQL 8.0
wget https://downloads.percona.com/downloads/Percona-XtraBackup-8.0/Percona-XtraBackup-8.0.35-31/binary/redhat/8/x86_64/percona-xtrabackup-80-8.0.35-31.1.el8.x86_64.rpm yum localinstall percona-xtrabackup-80-8.0.35-31.1.el8.x86_64.rpm
Install qpress: Because XtraBackup installed on Ubuntu does not include qpress, you must install it separately.
sudo apt-get install -y qpress
Perform a backup:
The following three compression methods are based on the
XtraBackupcommand and are suitable for instances that primarily use the InnoDB engine. If your database contains MyISAM tables, use theinnobackupexcommand.Method 1: Default qpress compression
xtrabackup --backup \ --host=127.0.0.1 \ --port=3306 \ --user=<user_of_self-managed_MySQL> \ --password=<password> \ --stream=xbstream \ --compress > ./<backup_file_name_such_as_backup_1206.xb>Method 2: QuickLZ compression
This method requires you to use XtraBackup version 8.0.34-29 or earlier. For more information, see the official Percona XtraBackup tutorial.
xtrabackup --backup \ --host=127.0.0.1 \ --port=3306 \ --user=<user_of_self-managed_MySQL> \ --password=<password> \ --stream=xbstream \ --compress > ./<backup_file_name_such_as_backup_1206_qp.xb>Method 3: External ZSTD compression
xtrabackup --backup \ --host=127.0.0.1 \ --port=3306 \ --user=<user_of_self-managed_MySQL> \ --password=<password> \ --stream=xbstream \ | zstd -q - > ./<backup_file_name_such_as_backup_1206.xb.zstd>
Upload the self-managed database backup to OSS
You can use different tools to upload backup files, such as ossutil or an OSS software development kit (SDK). This topic uses ossutil as an example.
ImportantEnsure that the target OSS Bucket is in the same region as the RDS MySQL instance. Otherwise, RDS cannot retrieve the OSS backup file during the upload.
Install ossutil.
yum install -y unzip sudo -v ; curl https://gosspublic.alicdn.com/ossutil/install.sh | sudo bash ossutil configUpload the backup data to OSS.
ossutil -e <OSS_Endpoint> -i <your_AccessKeyId> -k <your_AccessKeySecret> cp <backup_file_name> oss://<Bucket_name>/
Import the backup file from OSS to RDS and automatically set up the replication link
Go to the RDS Instances list, select a region, and click the ID of the target instance.
In the navigation pane on the left, click Native Replication.
On the Native Replication page, click Import Full Data, configure the parameters, and click OK.
Configuration Category
Parameter
Description
Backup Upload Method (Required)
MySQL Version
The system automatically displays 5.7 or 8.0. No configuration is required.
Import Method
Select Import from OSS.
OSS Bucket
Select the OSS Bucket where the backup file of the self-managed database is stored. For more information about OSS Buckets, see Upload files.
OSS File Name
Select the backup file for your self-built database from the OSS bucket. If the backup file is stored in a subdirectory of the OSS bucket, you must manually enter the full path to search. The following three backup file formats are supported:
An
xbstreamfile directly generated by XtraBackup.A
_qp.xbfile generated using the built-in quicklz compression of XtraBackup.An
xbstreamfile compressed with zstd (with the.xb.zstsuffix).
We recommend enabling automatic replication setup. The system will automatically set up the data replication link based on the following configuration. If you do not enable automatic replication setup, you must manually set up the replication link after importing the full data.
Automatic Replication Link Configuration (Optional)
Auto Replication Building
Turn on the switch to automatically set up the replication relationship from the self-managed MySQL database to the ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance.
Source IP Address
Enter the IP address of the source self-managed database.
Source Port
Enter the port number of the source self-managed database.
Source Account
Enter the account of the source self-managed database. The source account must have the
REPLICATION CLIENTandREPLICATION SLAVEpermissions.Account Password
Enter the password for the account of the source self-managed database.
View the replication status
Return to the Native Replication page for the RDS instance to view the data replication link information. When the replication status is Running, the data replication link is established.
Solution 2: XtraBackup stream backup, direct stream backup transfer, and data import to a native replication instance
Advantages
High usability with console-based operations and automatic replication link setup.
Billing
You are charged instance fees when you create a new instance with native replication enabled. Upgrading an existing instance to a native replication instance does not incur extra fees.
Procedure
Install XtraBackup and perform a backup on the self-managed database
Install XtraBackup:
Install on CentOS
MySQL 5.7
wget https://downloads.percona.com/downloads/Percona-XtraBackup-2.4/Percona-XtraBackup-2.4.29/binary/redhat/8/x86_64/percona-xtrabackup-24-2.4.29-1.el8.x86_64.rpm yum localinstall percona-xtrabackup-24-2.4.29-1.el8.x86_64.rpmMySQL 8.0
wget https://downloads.percona.com/downloads/Percona-XtraBackup-8.0/Percona-XtraBackup-8.0.35-31/binary/redhat/8/x86_64/percona-xtrabackup-80-8.0.35-31.1.el8.x86_64.rpm yum localinstall percona-xtrabackup-80-8.0.35-31.1.el8.x86_64.rpm
Install on Ubuntu
Install XtraBackup
MySQL 5.7
wget https://downloads.percona.com/downloads/Percona-XtraBackup-2.4/Percona-XtraBackup-2.4.29/binary/redhat/8/x86_64/percona-xtrabackup-24-2.4.29-1.el8.x86_64.rpm yum localinstall percona-xtrabackup-24-2.4.29-1.el8.x86_64.rpmMySQL 8.0
wget https://downloads.percona.com/downloads/Percona-XtraBackup-8.0/Percona-XtraBackup-8.0.35-31/binary/redhat/8/x86_64/percona-xtrabackup-80-8.0.35-31.1.el8.x86_64.rpm yum localinstall percona-xtrabackup-80-8.0.35-31.1.el8.x86_64.rpm
Install qpress: Because XtraBackup installed on Ubuntu does not include qpress, you must install it separately.
sudo apt-get install -y qpress
Perform a backup:
The following three compression methods are based on the
XtraBackupcommand and are suitable for instances that primarily use the InnoDB engine. If your database contains MyISAM tables, use theinnobackupexcommand.Method 1: Default qpress compression
xtrabackup --backup \ --host=127.0.0.1 \ --port=3306 \ --user=<user_of_self-managed_MySQL> \ --password=<password> \ --stream=xbstream \ --compress > ./<backup_file_name_such_as_backup_1206.xb>Method 2: QuickLZ compression
This method requires you to use XtraBackup version 8.0.34-29 or earlier. For more information, see the official Percona XtraBackup tutorial.
xtrabackup --backup \ --host=127.0.0.1 \ --port=3306 \ --user=<user_of_self-managed_MySQL> \ --password=<password> \ --stream=xbstream \ --compress > ./<backup_file_name_such_as_backup_1206_qp.xb>Method 3: External ZSTD compression
xtrabackup --backup \ --host=127.0.0.1 \ --port=3306 \ --user=<user_of_self-managed_MySQL> \ --password=<password> \ --stream=xbstream \ | zstd -q - > ./<backup_file_name_such_as_backup_1206.xb.zstd>
Transfer the self-managed database backup to RDS
Install the backup-helper tool on the self-managed database and establish a backup transfer process
# Install the backup-helper tool wget -O backup-helper https://mysql-backup-helper.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/v1.0.0-alpha/backup-helper && chmod +x backup-helper # Establish a backup transfer process using the tool (Make sure MySQL is running in the environment and the corresponding version of XtraBackup is installed based on the self-managed database version) ./backup-helper --backup --mode=stream --host=<MySQL_IP> --port=<MySQL_port> --user=<MySQL_account> --password=<MySQL_password>Import data into RDS
Log on to the ApsaraDB RDS console, select a region at the top of the page, and click the instance ID.
In the navigation pane on the left, click Native Replication.
On the Native Replication page, click Import Full Data, configure the parameters, and click OK.
Configuration Category
Parameter
Description
Backup Upload Method (Required)
MySQL Version
The system automatically displays 5.7 or 8.0. No configuration is required.
Import Method
Select Direct Stream Backup.
Source Backup IP Address
Enter the IP address for the backup transfer.
Source Backup Por
Enter the port for the backup transfer. The default is 9999.
We recommend enabling automatic replication setup. The system will automatically set up the data replication link based on the following configuration. If you do not enable automatic replication setup, you must manually set up the replication link after importing the full data.
Automatic Replication Link Configuration (Optional)
Auto Replication Building
Turn on the switch to automatically set up the replication relationship from the self-managed MySQL database to the ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance.
Source IP Address
Enter the IP address of the source self-managed database.
Source Port
Enter the port number of the source self-managed database.
Source Account
Enter the account of the source self-managed database. The source account must have the
REPLICATION CLIENTandREPLICATION SLAVEpermissions.Account Password
Enter the password for the account of the source self-managed database.
View the replication status
Return to the Native Replication page for the RDS instance to view the data replication link information. When the replication status is Running, the data replication link is established.
Solution 3: mysqldump logical backup, DMS data import, and SQL-based replication link setup
Advantages
High usability with console-based operations.
Billing
Creating a new RDS for MySQL instance incurs RDS instance fees and storage fees.
Procedure
Use mysqldump to perform a logical backup of the self-managed MySQL database and obtain the SQL file. The command is as follows:
mysqldump --all-databases \ --single-transaction \ --order-by-primary \ --set-gtid-purged=off \ --master-data=2 \ -u local_user \ -p local_password \ -h 127.0.0.1 -P 3306 > data.sqlBecause RDS for MySQL does not grant permissions to modify
SET GTID_PURGED, enabling this parameter will cause SQL playback errors. Therefore, you must setset-gtid-purged=offin the command.When you use
mysqldumpto set up a secondary database, add the--master-data=2option. This option automatically generates a comment that contains theCHANGE MASTER TOstatement. This makes it easy to retrieve the binary logging file name and position from the primary database without manually querying and entering the replication offset. For example: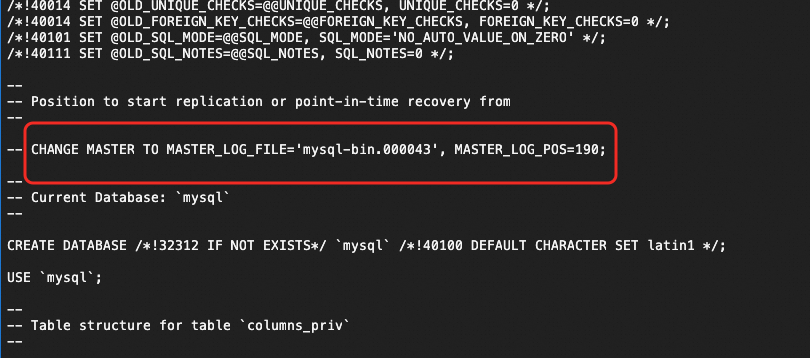
Import the logical backup using DMS.
Log on to the RDS for MySQL database using DMS (use a privileged account).
Click the
 icon in the upper-left corner of the DMS console and choose .Note
icon in the upper-left corner of the DMS console and choose .NoteIf you are using the console in non-streamlined mode, choose from the top menu bar.
On the Ticket Application page, select Large Data Import, specify the target RDS for MySQL database, and upload the logical backup SQL file. For more information about other configuration parameters, see Data Import.
Run commands in DMS to set up the replication link.
ImportantImporting a logical backup using DMS generates a separate binary log and GTID on the cloud-based secondary database. If you switch this secondary database to a primary node, these extra GTIDs might be replicated to other nodes and cause replication to break. To avoid this issue, take one of the following measures:
Before setting up replication, disable and then re-enable native replication. This operation runs
RESET MASTER.Insert empty transactions on other nodes in the replication topology to overwrite the redundant GTIDs. This acts as a placeholder.
# Set up replication CHANGE MASTER TO MASTER_HOST = '<source_host_IP>', MASTER_USER = '<replication_user>',MASTER_PASSWORD ='<replication_password>', MASTER_PORT = 3306,MASTER_LOG_FILE = '<binlog_file_name>',MASTER_LOG_POS = 190; # Start replication START SLAVE; # Check replication status SHOW SLAVE STATUS\G