MySQL primary/secondary replication requires a primary database and a secondary database. The binary logging feature based on the Change Data Capture (CDC) feature of PolarDB-X allows you to configure a PolarDB-X database as the primary database. The CDC feature of PolarDB-X provides the capabilities of the replication feature of MySQL. This allows you to configure a PolarDB-X database as the secondary database.
Usage notes
The configuration method of data replication from PolarDB-X to PolarDB-X is almost the same as that of data replication from PolarDB-X to MySQL. For more information, see Replicate data from PolarDB-X to MySQL.
The SQL statements for data replication provided by PolarDB-X are highly compatible with MySQL. For more information, see Replication.
Users cannot create replication links for PolarDB-X instances that are purchased in the PolarDB-X console due to network limits. In this case, the replication links mainly apply to self-managed databases.
Starting from version 5.4.12, PolarDB-X enables the RETURNING optimization for INSERT IGNORE statements on tables with global secondary indexes (GSIs) by default. However, the optimization may introduce a risk of data inconsistency during binlog consumption in PolarDB-X primary/secondary database replication scenarios. To mitigate this risk, you can disable the optimization by executing the
SET GLOBAL DML_USE_RETURNING = FALSEstatement. Disabling the optimization may reduce the performance ofINSERT IGNOREstatements on tables with GSIs, potentially affecting data import tasks. Evaluate your business requirements and workloads before deciding whether to disable the optimization.
Procedure
Create a primary/secondary replication link
Syntax
CHANGE MASTER TO option [, option] ... [ channel_option ] option: { MASTER_HOST = 'host_name' | MASTER_USER = 'user_name' | MASTER_PASSWORD = 'password' | MASTER_PORT = port_num | MASTER_LOG_FILE = 'source_log_name' | MASTER_LOG_POS = source_log_pos | MASTER_LOG_TIME_SECOND = source_log_time | SOURCE_HOST_TYPE = {RDS|POLARDBX|MYSQL} | STREAM_GROUP = 'stream_group_name' | WRITE_SERVER_ID = write_server_id | TRIGGER_AUTO_POSITION = {FALSE|TRUE} | WRITE_TYPE = {SPLIT|SERIAL|TRANSACTION} | MODE = {INCREMENTAL|IMAGE} | CONFLICT_STRATEGY = {OVERWRITE|INTERRUPT|IGNORE|DIRECT_OVERWRITE} | IGNORE_SERVER_IDS = (server_id_list) } channel_option: FOR CHANNEL channel server_id_list: [server_id [, server_id] ... ]Parameters
MASTER_HOST: the address of the primary instance.
MASTER_USER: the username that is used to connect to the primary instance.
MASTER_PASSWORD: the password that is used to connect to the primary instance.
MASTER_PORT: the port number that is used to connect to the primary instance.
MASTER_LOG_FILE: the name of the log file on the primary instance.
MASTER_LOG_POS: the offset from which the binlog replication starts in the log file on the primary instance.
MASTER_LOG_TIME_SECOND: the time offset of the primary instance. The value is a UNIX timestamp representing the number of seconds that have elapsed since January 1, 1970, 00:00:00 UTC. The MASTER_LOG_TIME_SECOND parameter is ignored if the MASTER_LOG_FILE and MASTER_LOG_POS parameters are configured to specify an exact offset.
SOURCE_HOST_TYPE: the type of the primary instance. Default value: MYSQL. If the primary instance is a PolarDB-X 2.0 instance, you must explicitly set this parameter to POLARDBX.
STREAM_GROUP: the name of the stream group if a multi-stream group is created. If the primary instance is a PolarDB-X 2.0 instance and you want to use the multi-stream binlog service of the primary instance, you must specify this parameter.
WRITE_SERVER_ID: the ID of the write server.
TRIGGER_AUTO_POSITION: specifies whether to automatically use the latest offset of the primary instance. Default value: FALSE.
WRITE_TYPE: the write mode. The default value is SPLIT, which indicates non-transactional parallel replication. A value of SERIAL indicates non-transactional serial replication, and a value of TRANSACTION indicates transactional serial replication.
MODE: the synchronization mode. A value of INCREMENTAL indicates incremental data synchronization, and a value of IMAGE indicates schema synchronization, full data synchronization, and incremental data synchronization.
CONFLICT_STRATEGY: the conflict policy. The default value is OVERWRITE, which indicates that the data with constraint violation is overwritten by executing the REPLACE INTO statement. A value of INTERRUPT indicates that the replication is interrupted, and a value of IGNORE indicates that the conflict is ignored.
IGNORE_SERVER_IDS: the ID of the server to ignore.
channel_option: the name of the link, which must be different from existing link names.
Example 1
Execute the following statement to create a replication link and start synchronization from 1713159938 (2024-04-15 13:45:38) in the log file:
CHANGE MASTER TO MASTER_HOST='pxc-YOURENDPOINT.com', MASTER_PORT=3306, MASTER_USER='polardbx', MASTER_PASSWORD='123456', SOURCE_HOST_TYPE=polardbx, MASTER_LOG_TIME_SECOND=1713159938, write_server_id=1944903859 FOR CHANNEL 'pxc-bjrcsnbyagcdxh';Example 2
Execute the following statement to create a replication link and start synchronization from Offset 4 in the binlog.000001 file on the primary instance:
CHANGE MASTER TO MASTER_HOST='pxc-YOURENDPOINT.com', MASTER_PORT=3306, MASTER_USER='polardbx', MASTER_PASSWORD='123456', SOURCE_HOST_TYPE=polardbx, MASTER_LOG_FILE='binlog.000001', MASTER_LOG_POS=4, write_server_id=1944903859 FOR CHANNEL 'pxc-bjrcsnbyagcdxh';
For more information, see CHANGE MASTER TO.
Modify the filter configurations of a primary/secondary replication link
Syntax
CHANGE REPLICATION FILTER option [, option] ... [ channel_option ] option: { REPLICATE_DO_DB = (do_db_list) | REPLICATE_IGNORE_DB = (ignore_db_list) | REPLICATE_DO_TABLE = (do_table_list) | REPLICATE_IGNORE_TABLE = (ignore_table_list) | REPLICATE_WILD_DO_TABLE = (wild_do_table_list) | REPLICATE_WILD_IGNORE_TABLE = (wile_ignore_table_list) | REPLICATE_SKIP_TSO = 'tso_num' | REPLICATE_SKIP_UNTIL_TSO = 'tso_num' | REPLICATE_ENABLE_DDL = {TRUE|FALSE} } channel_option: FOR CHANNEL channelParameters
REPLICATE_SKIP_TSO: the Timestamp Oracle (TSO) at which the binlog event is skipped. For more information about TSO, see Distributed transactions.
REPLICATE_SKIP_UNTIL_TSO: the TSO before which all binlog events are skipped.
REPLICATE_ENABLE_DDL: specifies whether to synchronize DDL statements. Default value: TRUE.
For more information about the following parameters, see CHANGE REPLICATION FILTER.
REPLICATE_DO_DB
REPLICATE_IGNORE_DB
REPLICATE_DO_TABLE
REPLICATE_IGNORE_TABLE
REPLICATE_WILD_DO_TABLE
REPLICATE_WILD_IGNORE_TABLE
Example 1
Execute the following statement to modify replication links to synchronize only the changes in the TEST database:
CHANGE REPLICATION FILTER REPLICATE_DO_DB=(TEST);Example 2
Obtain TSOs
Execute the SHOW BINLOGS EVENTS statement to obtain the TSOs of binlog events. The following figure shows a sample response.
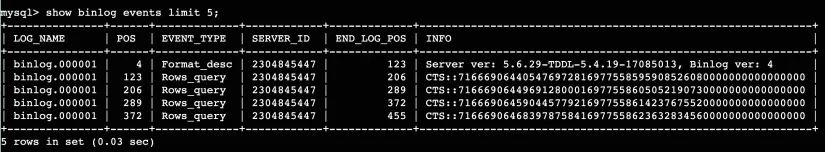
The numeric string that follows CTS:: in the INFO column is the TSO of an event.
Skip the event corresponding to a TSO
Execute the following statement to modify replication links to skip the bin event corresponding to the following TSO: 716669064683978758416977558623632834560000000000000000. In this case, the binlog event whose value in the POS column is 372 is skipped.
CHANGE REPLICATION FILTER REPLICATE_SKIP_TSO='716669064683978758416977558623632834560000000000000000';For more information, see CHANGE REPLICATION FILTER.
For more information, see CHANGE REPLICATION FILTER.
Start a primary/secondary replication link
Syntax
START SLAVE [ channel_option ] channel_option: FOR CHANNEL channelExample 1
Execute the following statement to enable all the primary/secondary replication links that are created by executing the CHANGE MASTER TO statement:
START SLAVE;Example 2
Execute the following statement to enable the primary/secondary replication link whose name is TEST:
START SLAVE for channel 'TEST';
For more information, see START SLAVE.
Stop a primary/secondary replication link
Syntax
STOP SLAVE [ channel_option ] channel_option: FOR CHANNEL channelExample 1
Execute the following statement to disable all the primary/secondary replication links that are created by executing the CHANGE MASTER TO statement:
STOP SLAVE;Example 2
Execute the following statement to disable the primary/secondary replication link whose name is TEST:
STOP SLAVE for channel 'TEST';
For more information, see STOP SLAVE.
Delete a primary/secondary replication link
Stop the data replication process before you delete a primary/secondary replication link.
Syntax
RESET SLAVE ALL [ channel_option ] channel_option: FOR CHANNEL channelExample 1
Execute the following statement to remove all primary/secondary replication links established by executing the CHANGE MASTER TO statement.
RESET SLAVE ALL;Example 2
Execute the following statement to remove the primary/secondary replication link with the channel named TEST.
RESET SLAVE ALL for channel 'TEST';
For more information, see RESET SLAVE ALL.