This topic describes the design, process, and results of Sysbench tests in PolarDB-X of MySQL 5.7 and MySQL 8.0.
Background information
Sysbench is an open source and modular tool that can use multiple threads to test the performance of databases across different platforms, including the CPU, memory, thread, and I/O. This topic verifies the performance of PolarDB-X Sysbench tests in various scenarios.
Test design
Amount of test data
The results of the Sysbench test described in this topic are obtained based on 16 tables. Each table contains 10 million rows of data.
Instance specifications for the test
Instance specifications
Number of nodes
4C32G
2
4C32G
4
8C64G
2
8C64G
4
ECS instance type for stress testing
ecs.g7ne.8xlarge (32 vCPUs, 128 GB of memory)
Procedure
Create an Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance for stress testing.
Create an ECS instance that is used to prepare data and perform stress testing. To prevent performance bottlenecks when you test PolarDB-X instances with high specifications, we recommend that you create an ECS instance with 32 vCPUs and 128 GB of memory.
NoteThe ECS instance must be deployed in a virtual private cloud (VPC). Record the name and ID of the VPC for subsequent use. You must deploy all database instances that are described in subsequent steps in the VPC.
Create a PolarDB-X instance for stress testing.
Create a PolarDB-X instance. Select the MySQL 5.7 or MySQL 8.0 database engine based on your business requirements. For information about how to create a PolarDB-X instance, see Create a PolarDB-X instance.
NoteMake sure that the PolarDB-X instance and the ECS instance reside in the same VPC.
Create a database (the database name is sbtest in this example) in the instance. For more information, see Create a database.
CREATE DATABASE sbtest;
Modify instance parameters.
NoteTo achieve optimal performance in stress testing, modify specific parameters of the compute nodes of the PolarDB-X instance.
Set the ENABLE_COROUTINE parameter to true and the XPROTO_MAX_DN_CONCURRENT and XPROTO_MAX_DN_WAIT_CONNECTION parameters to 4000. For more information, see Parameter settings.
Connect to the PolarDB-X instance by using a command-line client. Then, execute the following SQL statements in the same session to disable logging and CPU statistical sampling:
set global RECORD_SQL=false; set global MPP_METRIC_LEVEL=0; set global ENABLE_CPU_PROFILE=false; set global ENABLE_TRANS_LOG=false;
Prepare data for stress testing.
Download the stress test tool package benchmarksql.tar.gz and run the following command to decompress it:
tar xzvf sysbench.tar.gz cd sysbench/Run the following commands to install and compile dependencies:
yum -y install make automake libtool pkgconfig libaio-devel mysql-devel ./autogen.sh ./configure make -j make installRun the
synben --versioncommand. Ifsysbench 1.1.0is returned, the stress test tool is installed.You can also download open source Sysbench from GitHub. For more information, see sysbench at GitHub.
Configure data for stress testing.
Create the configuration file sysb.conf and enter the PolarDB-X connection information in the configuration file. The following example shows the content of the configuration file. The parameters in the configuration file are described in this section after the example.
mysql-host='{HOST}' mysql-port='{PORT}' mysql-user='{USER}' mysql-password='{PASSWORD}' mysql-db='sbtest' db-driver='mysql' percentile='95' histogram='on' report-interval='1' time='60' rand-type='uniform'The parameters in the configuration file:
percentile: the percentile based on which the response time is sampled.
histogram: specifies whether to display the histogram of the response time distribution.
report-interval: the interval at which real-time results are displayed. Unit: seconds.
time: the duration of the stress test. Unit: seconds.
rand-type: the distribution type that is used to generate a random number.
Import the stress testing data.
sysbench --config-file='sysb.conf' --create-table-options='dbpartition by hash(id)' --tables='16' --table-size='10000000' --threads='16' --auto_inc='off' oltp_point_select prepareThe parameters in the command:
config-file: the common configuration file.
create-table-options: the mode used to create tables.
tables: the number of tables.
table-size: the amount of data that can be contained in a table.
threads: the number of concurrent threads that are used to import data.
auto_inc: specifies whether to use auto_increment.
Perform stress testing.
Run the following commands to perform the test in the six scenarios defined by Sysbench. We recommend that you increase the duration of the first stress test.
NoteThe parameters in the commands:
db-ps-mode: specifies whether to enable the prepare mode.
mysql-ignore-errors: the MySQL error codes to be ignored, such as some MySQL error codes caused by lock conflicts.
range-size: the range based on which range queries are performed.
oltp_point_select:
sysbench --config-file='sysb.conf' --db-ps-mode='disable' --mysql-ignore-errors='all' --tables='16' --table-size='10000000' --threads={Number of concurrent threads} oltp_point_select runoltp_read_only:
sysbench --config-file='sysb.conf' --db-ps-mode='disable' --mysql-ignore-errors='all' --tables='16' --table-size='10000000' --range-size=5 --threads={Number of concurrent threads} oltp_read_only runoltp_read_write:
sysbench --config-file='sysb.conf' --db-ps-mode='disable' --mysql-ignore-errors='all' --tables='16' --table-size='10000000' --range-size=5 --threads={Number of concurrent threads} oltp_read_write runoltp_update_index:
sysbench --config-file='sysb.conf' --db-ps-mode='disable' --mysql-ignore-errors='all' --tables='16' --table-size='10000000' --threads={Number of concurrent threads} oltp_update_index runoltp_update_non_index:
sysbench --config-file='sysb.conf' --db-ps-mode='disable' --mysql-ignore-errors='all' --tables='16' --table-size='10000000' --threads={Number of concurrent threads} oltp_update_non_index runoltp_write_only:
sysbench --config-file='sysb.conf' --db-ps-mode='disable' --mysql-ignore-errors='all' --tables='16' --table-size='10000000' --threads={Number of concurrent threads} oltp_write_only run
Test results
MySQL 5.7
PolarDB-X version: polardb-2.4.0_5.4.19-20240610_xcluster5.4.19-20240527. For more information, see Release notes.
In the following test results, QPS values are used to measure the database performance.
point_select
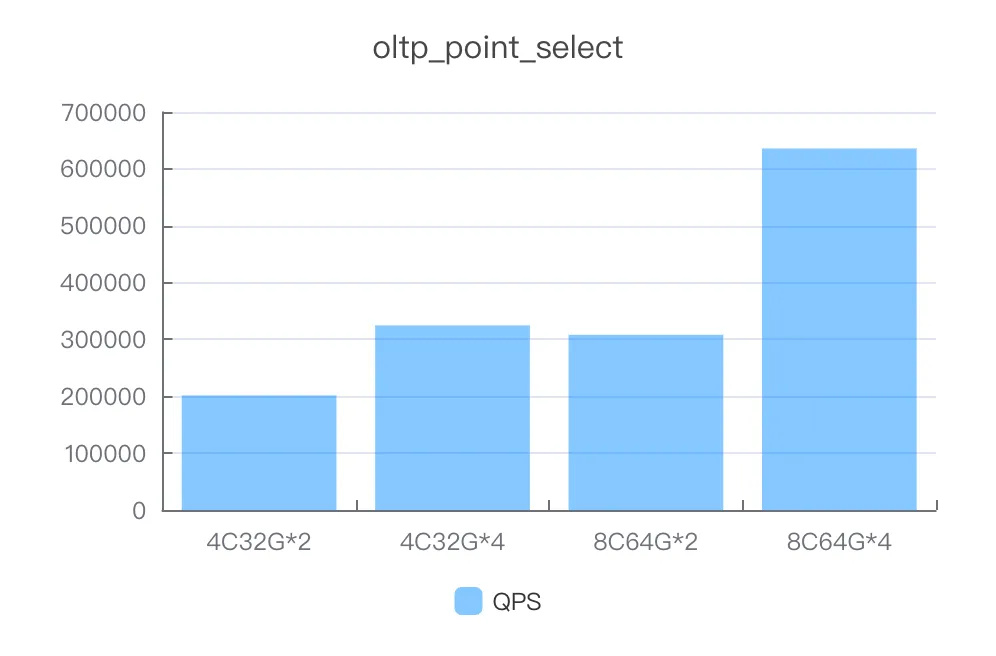
Instance specifications | Number of concurrent threads | QPS |
4C32G*2 | 1000 | 201462.73 |
4C32G*4 | 1000 | 324683.03 |
8C64G*2 | 1000 | 308174.91 |
8C64G*4 | 2000 | 635865.65 |
read_only
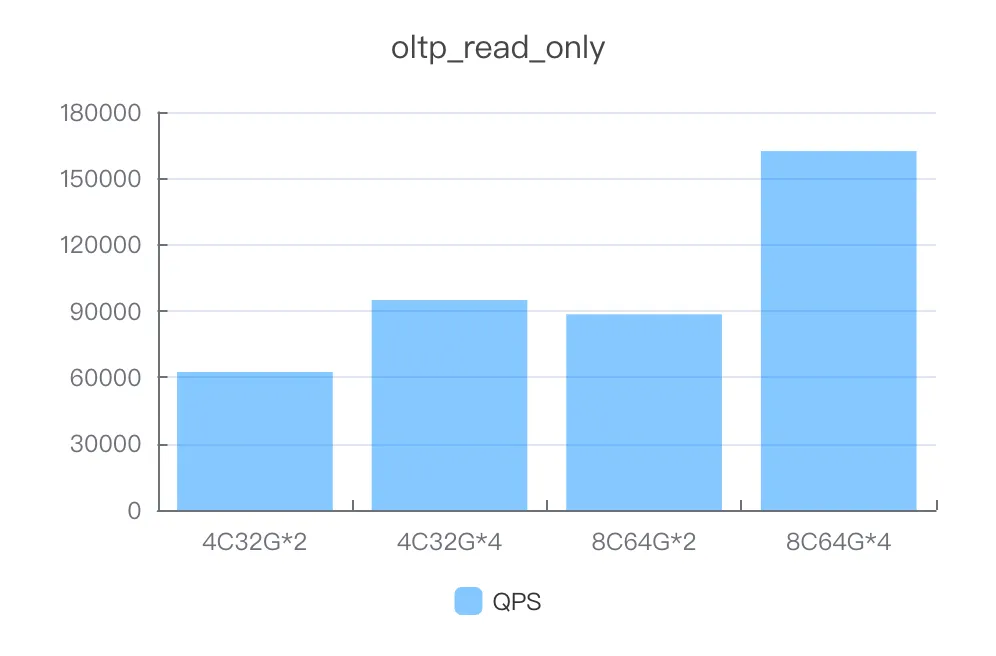
Instance specifications | Number of concurrent threads | QPS |
4C32G*2 | 600 | 62446.59 |
4C32G*4 | 1000 | 94930.57 |
8C64G*2 | 1000 | 88487.24 |
8C64G*4 | 2000 | 162330.95 |
read_write
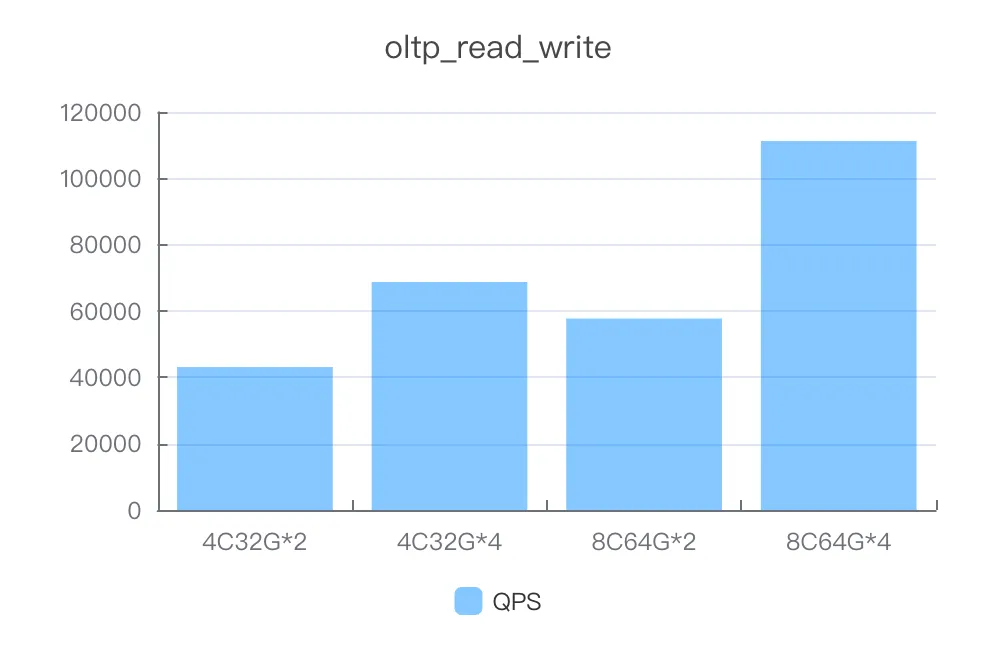
Instance specifications | Number of concurrent threads | QPS |
4C32G*2 | 600 | 43098.16 |
4C32G*4 | 600 | 68750.24 |
8C64G*2 | 600 | 57730.62 |
8C64G*4 | 600 | 111261.22 |
update_index
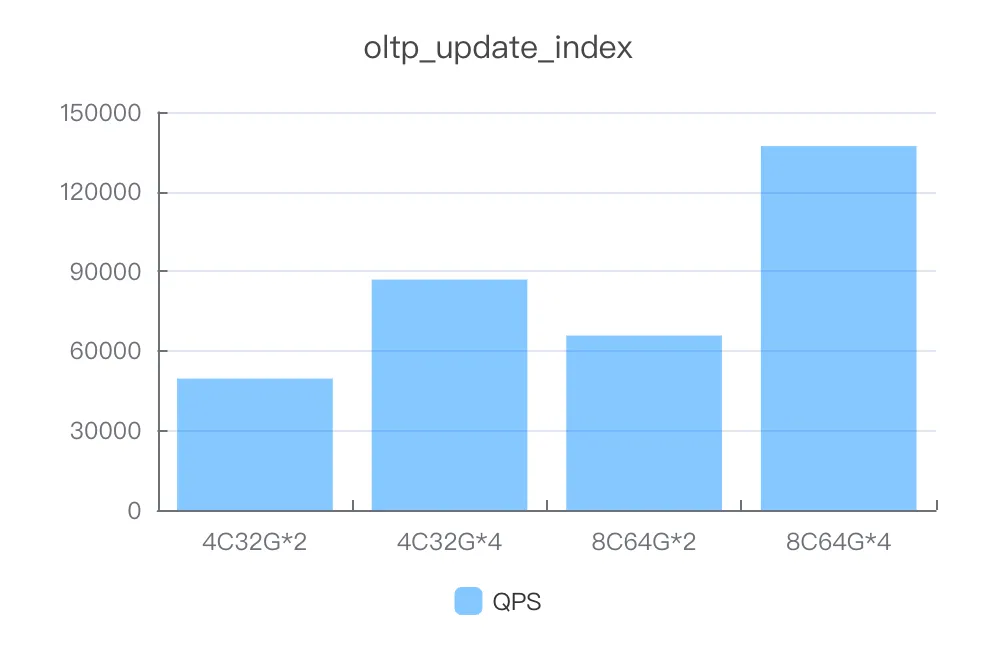
Instance specifications | Number of concurrent threads | QPS |
4C32G*2 | 600 | 49530.87 |
4C32G*4 | 600 | 86850.17 |
8C64G*2 | 600 | 65750.01 |
8C64G*4 | 1000 | 137154.16 |
update_non_index
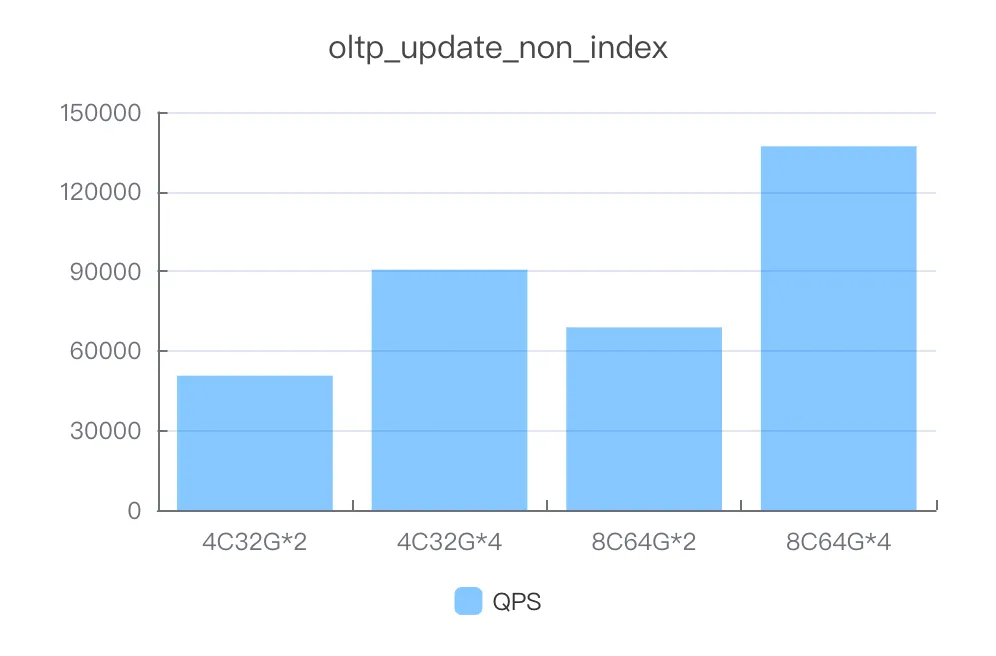
Instance specifications | Number of concurrent threads | QPS |
4C32G*2 | 400 | 50627.05 |
4C32G*4 | 1000 | 90555.72 |
8C64G*2 | 1000 | 68838.02 |
8C64G*4 | 1000 | 137071.73 |
write_only
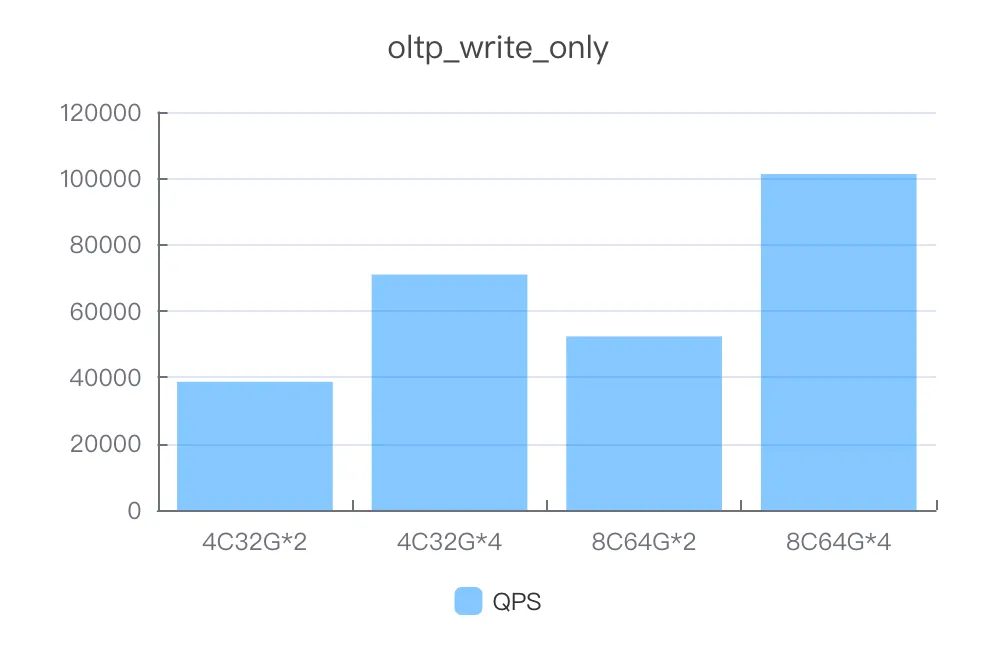
Instance specifications | Number of concurrent threads | QPS |
4C32G*2 | 400 | 38636.02 |
4C32G*4 | 600 | 70974.3 |
8C64G*2 | 600 | 52344.94 |
8C64G*4 | 600 | 101282.38 |
MySQL 8.0
PolarDB-X version: polardb-2.4.0_5.4.19-20240610_xcluster8.4.19-20240523. For more information, see Release notes.
In the following test results, QPS values are used to measure the database performance.
point_select
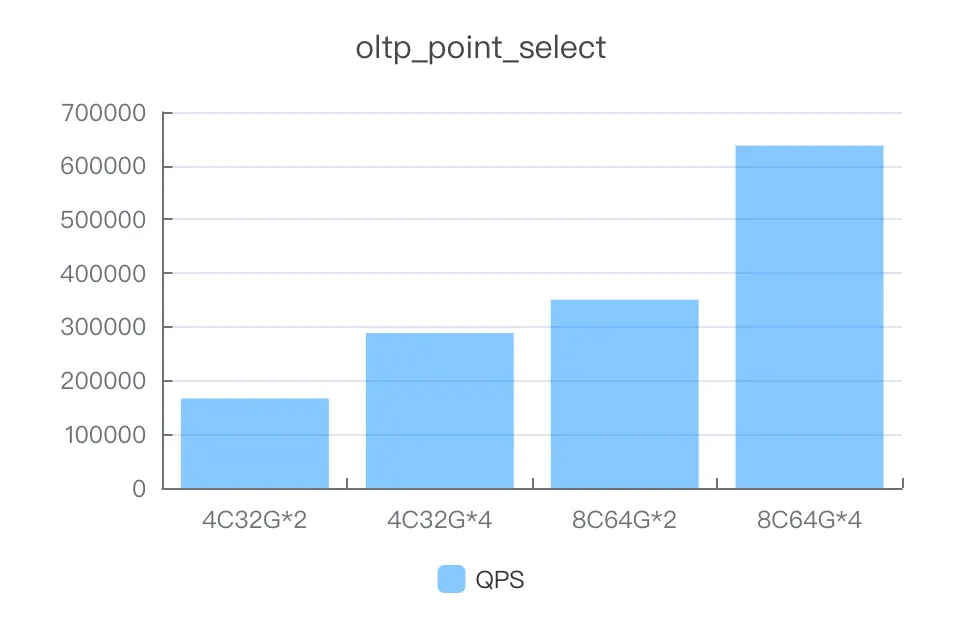
Instance specifications | Number of concurrent threads | QPS |
4C32G*2 | 1000 | 166590.48 |
4C32G*4 | 1000 | 288516.53 |
8C64G*2 | 1000 | 350510.72 |
8C64G*4 | 2000 | 637414.68 |
read_only
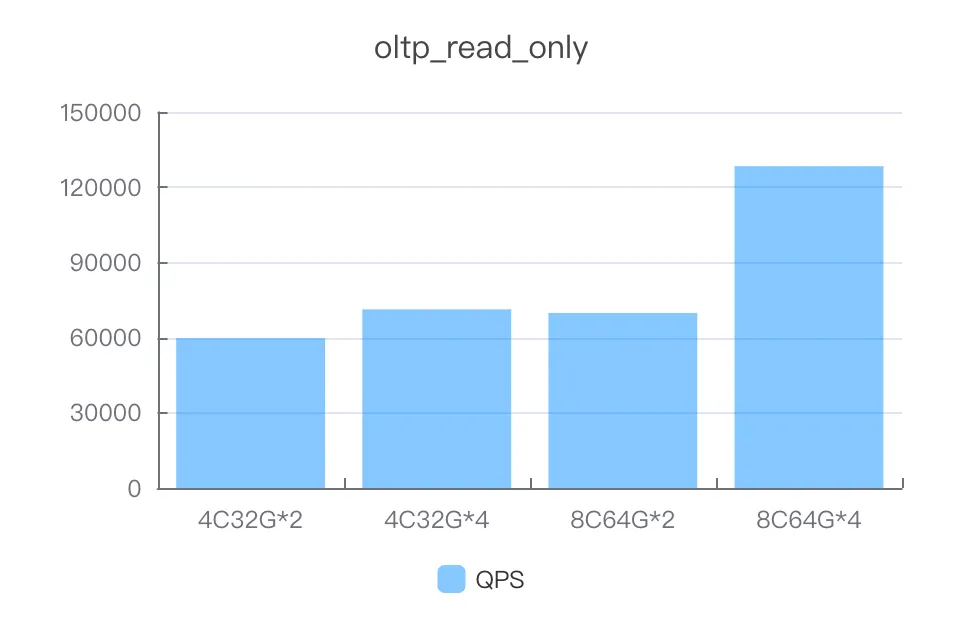
Instance specifications | Number of concurrent threads | QPS |
4C32G*2 | 600 | 59770.01 |
4C32G*4 | 1000 | 71259.87 |
8C64G*2 | 1000 | 69829.69 |
8C64G*4 | 2000 | 128366.39 |
read_write
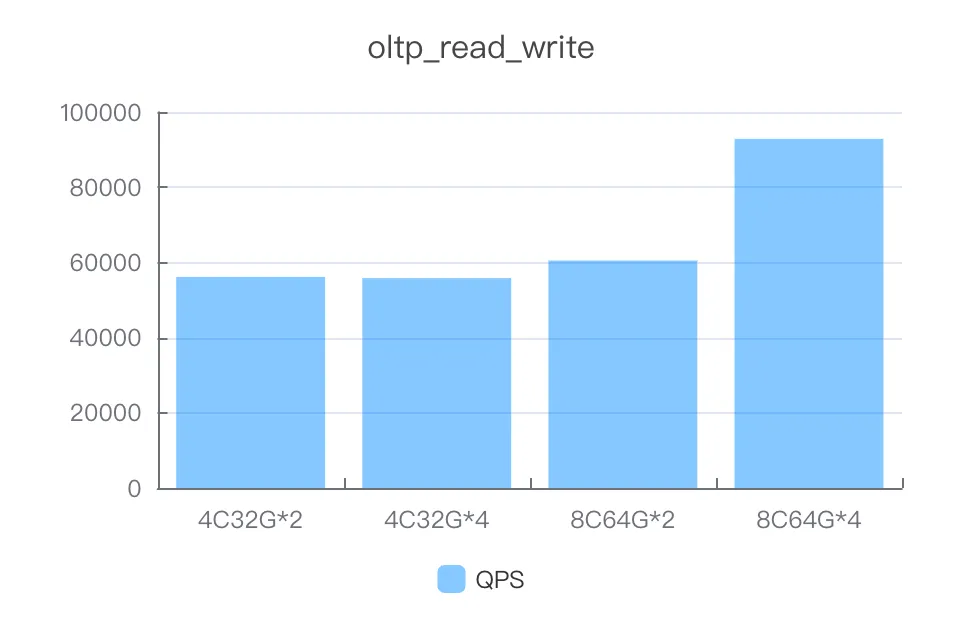
Instance specifications | Number of concurrent threads | QPS |
4C32G*2 | 600 | 56134.05 |
4C32G*4 | 600 | 55817.45 |
8C64G*2 | 600 | 60482.86 |
8C64G*4 | 600 | 92855.15 |
update_index
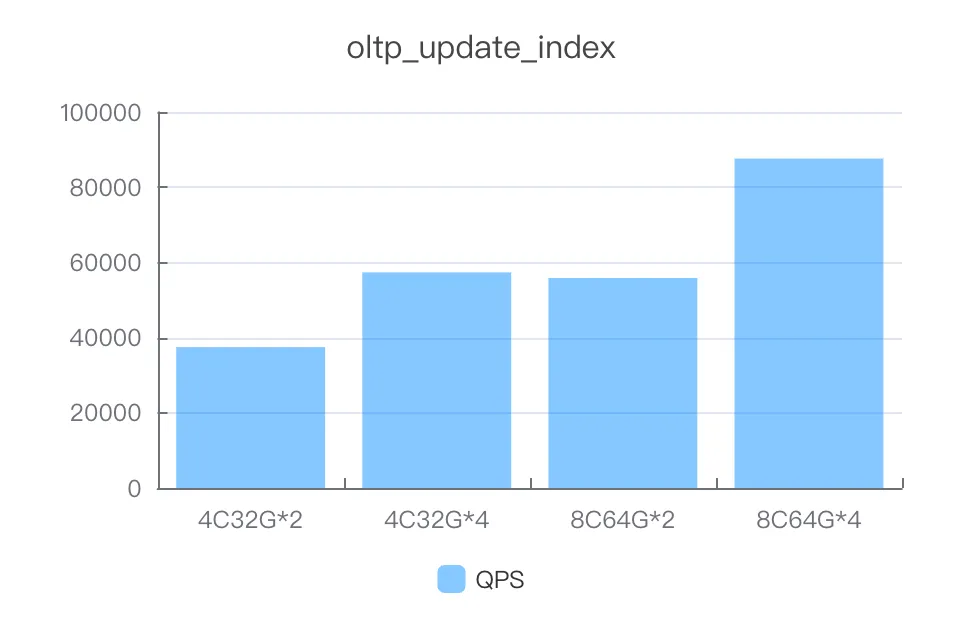
Instance specifications | Number of concurrent threads | QPS |
4C32G*2 | 600 | 37474.15 |
4C32G*4 | 600 | 57344.42 |
8C64G*2 | 600 | 55856.94 |
8C64G*4 | 1000 | 87618.81 |
update_non_index
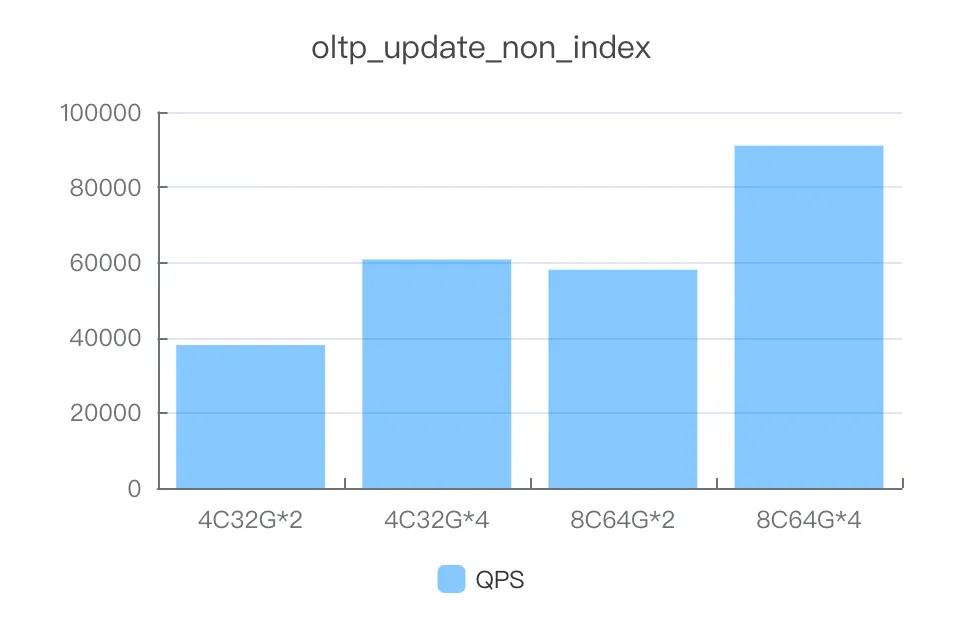
Instance specifications | Number of concurrent threads | QPS |
4C32G*2 | 400 | 38017.57 |
4C32G*4 | 1000 | 60779.25 |
8C64G*2 | 1000 | 58065.02 |
8C64G*4 | 1000 | 91060.65 |
write_only
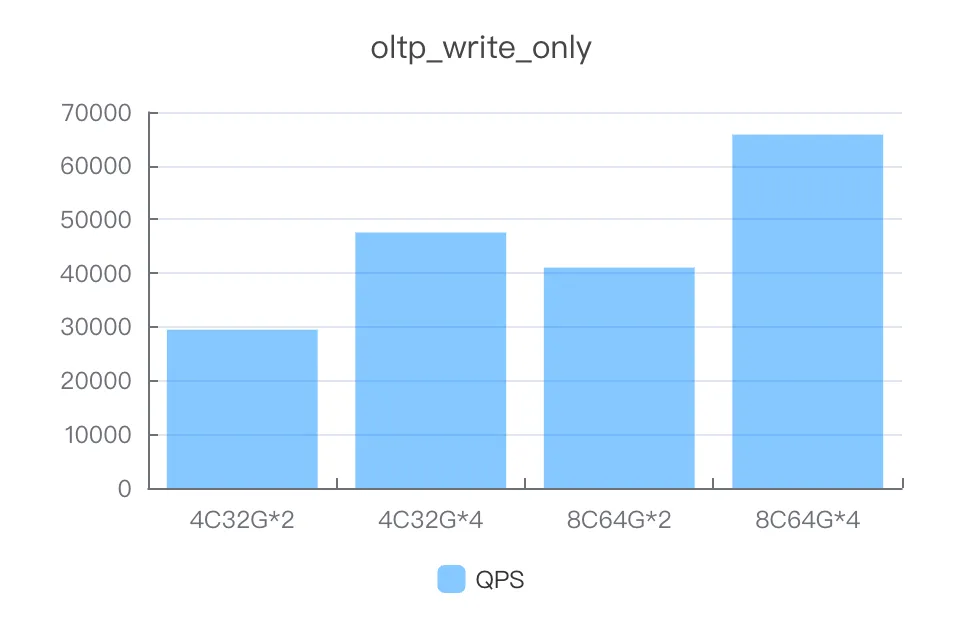
Instance specifications | Number of concurrent threads | QPS |
4C32G*2 | 400 | 29476.72 |
4C32G*4 | 600 | 47558.73 |
8C64G*2 | 600 | 41032.61 |
8C64G*4 | 600 | 65794.57 |