PolarDB-X supports connections that use Data Management (DMS), the MySQL command line, third-party clients, and third-party application code that is compliant with the official MySQL protocol.
Preparations
Before you connect to a PolarDB-X database, perform the following steps:
Connect to a database
You can use various methods to connect to a database instance. The following sections provide examples of how to connect to a database instance using different methods.
Use DMS to connect to a database
DMS is a graphical data management tool provided by Alibaba Cloud. This integrated data management service provides features such as data management, schema management, user authorization, security audit, data trends, data tracking, BI charts, performance optimization, and server management. You can use DMS to manage your PolarDB-X instance without using other tools.
Go to the PolarDB for Distributed console. In the Instances list, click the ID of the target instance. On the instance details page, click Log On To Database in the upper-right corner.

In the dialog box, enter the Database Account and Database Password for your PolarDB-X instance and click Logon.
 Note
NoteBy default, the control mode is Flexible Management when you first log on to DMS. You can also modify the control mode after you log on. For more information, see Modify instance information and Control modes.
After you configure the logon parameters, click Test Connection in the lower-left corner. If the test connection fails, refer to the error message to check the instance information you entered, such as the account and password.
The system automatically adds the DMS server IP addresses to the whitelist of the ApsaraDB database. If the IP addresses are not automatically added, you must add them manually.
After you log on, you can view the PolarDB-X instance in the Instances Connected section of the navigation pane on the left and perform management operations.

Use a client to connect to a database
PolarDB-X supports connections from the following third-party clients. You can download these clients from their official websites.
MySQL Workbench (Recommended)
SQLyog
Sequel Pro
Navicat for MySQL
Third-party GUI clients can perform basic database operations, such as creating, retrieving, updating, and deleting data, and DDL operations. PolarDB-X may not support the advanced features of these clients.
The following example uses MySQL Workbench 8.0.29. The steps for other clients are similar.
Install MySQL Workbench. You can download it from the official download page.
Open MySQL Workbench and choose .
Enter the connection information and click OK.
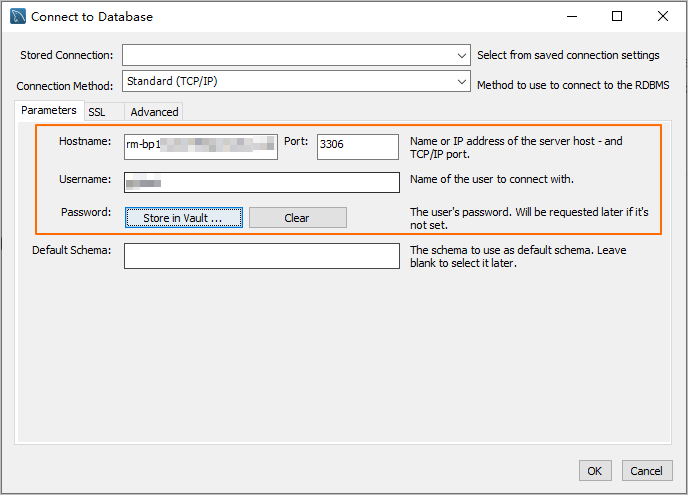
Parameter
Description
Example
Hostname
The database endpoint.
pxc-xxx.polarx.rds.aliyuncs.com
Port
The port number that corresponds to the database endpoint.
NoteThe default port is 3306.
3306
Username
The database account.
polardb_x_user
Password
The password of the database account.
Pass***233
Use the MySQL command line to connect to a database
If a MySQL client is installed on your server, you can run commands to connect to the PolarDB-X instance.
Syntax
mysql -h<endpoint> -P<port> -u<database_username> -p<database_user_password> -D<database_name>Example
mysql -hpxc-xxx.polarx.rds.aliyuncs.com -P3306 -upolardb_mysql_user -pPass***233 -Dtest_dbParameter | Description | Example |
-h | The database endpoint. | pxc-xxx.polarx.rds.aliyuncs.com |
-P | The port number that corresponds to the database endpoint. Note
| 3306 |
-u | The database account. | polardb_x_user |
-p | The password of the database account. Note This parameter is required.
| Pass***233 |
-D | The name of the database to which you want to log on. Note This parameter is optional. | test_db |
Use an application to connect to a database
Connecting to a PolarDB-X instance is similar to connecting to other MySQL databases. You only need to replace the database endpoint, port, account, and password. The following sections describe how to use applications in different programming languages to access a PolarDB database:
Java
This section uses a Maven project as an example to describe how to use a MySQL JDBC driver to connect to a PolarDB-X instance.
Add the dependency for the MySQL JDBC driver to the
pom.xmlfile. The following code provides an example:<dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <version>8.0.27</version> </dependency>Connect to the instance. Replace the
<HOST>, port number,<USER>,<PASSWORD>,<DATABASE>,<YOUR_TABLE_NAME>, and<YOUR_TABLE_COLUMN_NAME>parameters with your actual values.import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.DriverManager; import java.sql.ResultSet; import java.sql.Statement; public class DatabaseConnection { public DatabaseConnection() { } public static void main(String[] args) { // The endpoint, port, and name of the database to which you want to connect. String url = "jdbc:mysql://<HOST>:3306/<DATABASE>?useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC"; // The database account. String user = "<USER>"; // The password of the database account. String password = "<PASSWORD>"; try { Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"); Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password); Statement stmt = conn.createStatement(); // The name of the table from which you want to retrieve data. ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery("SELECT * FROM `<YOUR_TABLE_NAME>`"); while(rs.next()) { // The name of the column from which you want to retrieve data. System.out.println(rs.getString("<YOUR_TABLE_COLUMN_NAME>")); } rs.close(); stmt.close(); conn.close(); } catch (Exception var7) { var7.printStackTrace(); } } }
Python
This section uses Python 3 as an example to describe how to use the PyMySQL library to connect to a PolarDB-X instance.
Install the PyMySQL library by running the following command:
pip3 install PyMySQLConnect to the instance. Replace the
<HOST>, port number,<USER>,<PASSWORD>,<DATABASE>, and<YOUR_TABLE_NAME>parameters with your actual values.import pymysql # Database connection parameters. host = '<HOST>' # The endpoint of the PolarDB-X instance. port = 3306 # The default port is 3306. user = '<USER>' # The database account. password = '<PASSWORD>' # The password of the database account. database = '<DATABASE>' # The name of the database to which you want to connect. try: # Create a database connection. connection = pymysql.connect( host=host, port=port, user=user, passwd=password, db=database ) # Get the cursor. with connection.cursor() as cursor: # Execute an SQL query. sql = "SELECT * FROM `<YOUR_TABLE_NAME>`" # The name of the table from which you want to retrieve data. cursor.execute(sql) # Get the query results. results = cursor.fetchall() for row in results: print(row) finally: # Close the database connection. if 'connection' in locals() and connection.open: connection.close()
Go
This section uses Go 1.23.0 as an example to describe how to use the database/sql package and the go-sql-driver/mysql driver to connect to a PolarDB-X instance.
Install the
go-sql-driver/mysqldriver by running the following command:go get -u github.com/go-sql-driver/mysqlConnect to the instance. Replace the
<HOST>, port number,<USER>,<PASSWORD>,<DATABASE>, and<YOUR_TABLE_NAME>parameters with your actual values.package main import ( "database/sql" "fmt" "log" _ "github.com/go-sql-driver/mysql" ) func main() { // Database connection parameters. dbHost := "<HOST>" // The endpoint of the PolarDB-X instance. dbPort := "3306" // The default port is 3306. dbUser := "<USER>" // The database account. dbPass := "<PASSWORD>" // The password of the database account. dbName := "<DATABASE>" // The name of the database to which you want to connect. // Build the Data Source Name (DSN). dsn := fmt.Sprintf("%s:%s@tcp(%s:%s)/%s?charset=utf8mb4&parseTime=True&loc=Local", dbUser, dbPass, dbHost, dbPort, dbName) // Open the database connection. db, err := sql.Open("mysql", dsn) if err != nil { log.Fatalf("Failed to connect to database: %v", err) } defer db.Close() // Test the connection. err = db.Ping() if err != nil { log.Fatalf("Failed to ping database: %v", err) } // Query the database version. var result string err = db.QueryRow("SELECT VERSION()").Scan(&result) if err != nil { log.Fatalf("Failed to execute query: %v", err) } // Print the database version. fmt.Printf("Connected to database, version: %s\n", result) // Execute an SQL query. rows, err := db.Query("SELECT * FROM `<YOUR_TABLE_NAME>`") // The name of the table from which you want to retrieve data. if err != nil { log.Fatalf("Failed to execute query: %v", err) } defer rows.Close() // Process the query results. for rows.Next() { var id int var name string if err := rows.Scan(&id, &name); err != nil { log.Fatalf("Failed to scan row: %v", err) } fmt.Printf("ID: %d, Name: %s\n", id, name) } // Check for errors during iteration. if err := rows.Err(); err != nil { log.Fatalf("Error during iteration: %v", err) } }


