The partition-wise join feature supported by PolarDB for PostgreSQL (Compatible with Oracle) can dramatically reduce unnecessary joins during execution of queries that involve join operations.
Overview
The partion-wise join feature improves the performance of queries that are between partitioned tables by reducing overheads caused by unnecessary joins.
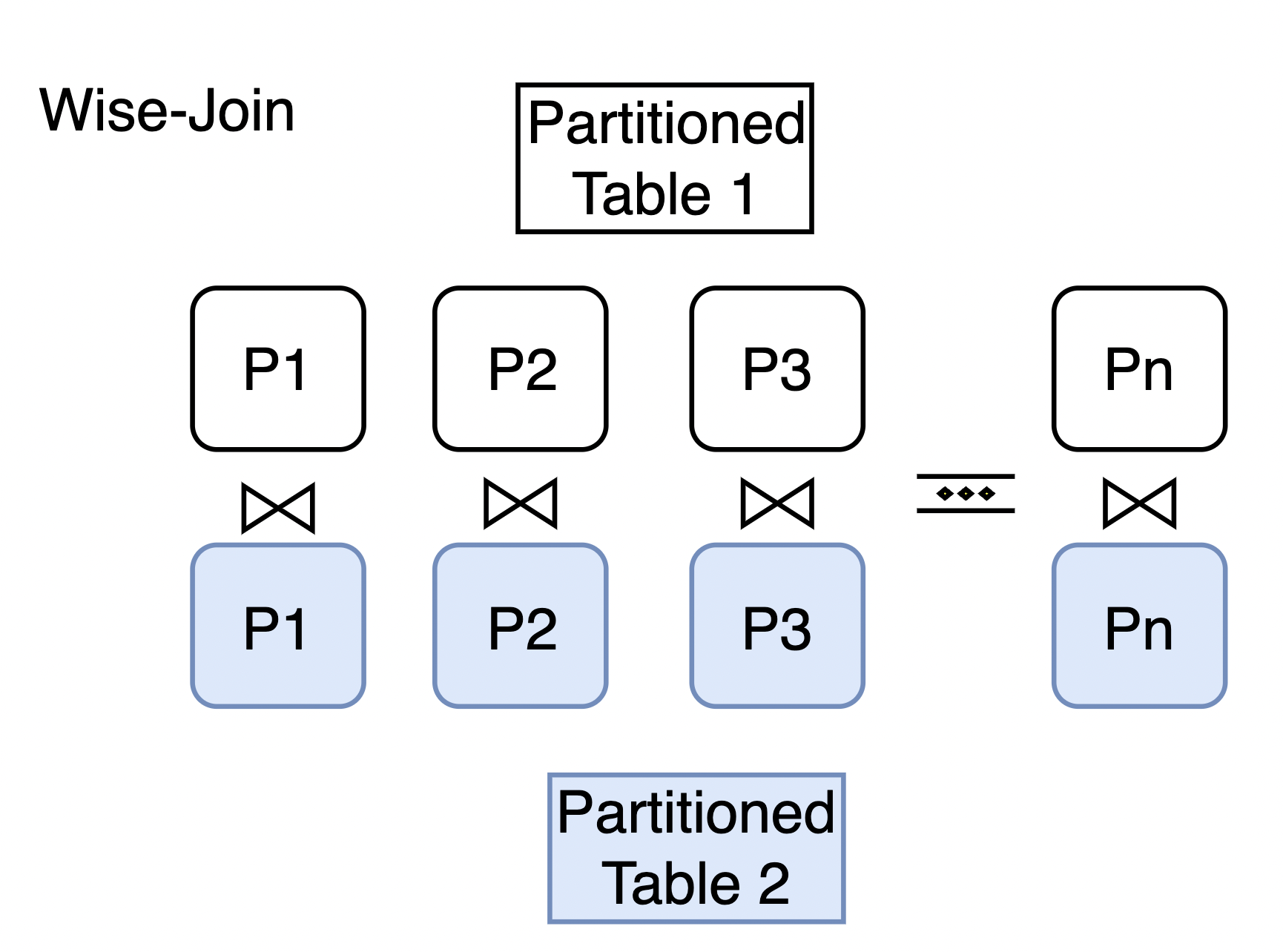
Usage notes
You can enable partition-wise joins by executing the following statement.
SET enable_partitionwise_join to ON;Examples
Two tables are used in this example. One is named measurement, and the other is named sales.
CREATE TABLE measurement(
city_id int not null,
logdate date not null,
peaktemp int,
unitsales int
) PARTITION BY RANGE (logdate);
CREATE TABLE measurement_y2023q1 PARTITION OF measurement
FOR VALUES FROM ('2023-01-01') TO ('2023-04-01');
CREATE TABLE measurement_y2023q2 PARTITION OF measurement
FOR VALUES FROM ('2023-04-01') TO ('2023-07-01');
CREATE TABLE measurement_y2023q3 PARTITION OF measurement
FOR VALUES FROM ('2023-07-01') TO ('2023-10-01');
CREATE TABLE measurement_y2023q4 PARTITION OF measurement
FOR VALUES FROM ('2023-10-01') TO ('2024-04-01');
CREATE TABLE sales (
dept_no number,
part_no varchar2,
country varchar2(20),
date date,
amount number
) PARTITION BY RANGE (date);
CREATE TABLE sales_y2023q1 PARTITION OF sales
FOR VALUES FROM ('2023-01-01') TO ('2023-04-01');
CREATE TABLE sales_y2023q2 PARTITION OF sales
FOR VALUES FROM ('2023-04-01') TO ('2023-07-01');
CREATE TABLE sales_y2023q3 PARTITION OF sales
FOR VALUES FROM ('2023-07-01') TO ('2023-10-01');
CREATE TABLE sales_y2023q4 PARTITION OF sales
FOR VALUES FROM ('2023-10-01') TO ('2024-04-01');As is shown in the preceding statement:
The
measurementtable has four partitions:measurement_y2023q1,measurement_y2023q2,measurement_y2023q3, andmeasurement_y2023q4, each of which contains data of the corresponding quarter in 2023.The
salestable also has four partitions:sales_y2023q1,sales_y2023q2,sales_y2023q3, andsales_y2023q4, each of which also contains data of the corresponding quarter in 2023.
Execute the following statement to view the execution plan of the query where measurement and sales are joined.
explain SELECT a.* FROM sales a JOIN measurement b ON a.date = b.logdate WHERE b.unitsales > 10;When partition-wise join is disabled, the execution plan looks like this:
QUERY PLAN
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Aggregate (cost=871.75..871.76 rows=1 width=8)
-> Merge Join (cost=448.58..812.79 rows=23587 width=32)
Merge Cond: (a.date = b.logdate)
-> Sort (cost=185.83..191.03 rows=2080 width=40)
Sort Key: a.date
-> Append (cost=0.00..71.20 rows=2080 width=40)
-> Seq Scan on sales_y2023q1 a (cost=0.00..15.20 rows=520 width=40)
-> Seq Scan on sales_y2023q2 a_1 (cost=0.00..15.20 rows=520 width=40)
-> Seq Scan on sales_y2023q3 a_2 (cost=0.00..15.20 rows=520 width=40)
-> Seq Scan on sales_y2023q4 a_3 (cost=0.00..15.20 rows=520 width=40)
-> Sort (cost=262.75..268.42 rows=2268 width=8)
Sort Key: b.logdate
-> Append (cost=0.00..136.34 rows=2268 width=8)
-> Seq Scan on measurement_y2023q1 b (cost=0.00..31.25 rows=567 width=8)
Filter: (unitsales > 10)
-> Seq Scan on measurement_y2023q2 b_1 (cost=0.00..31.25 rows=567 width=8)
Filter: (unitsales > 10)
-> Seq Scan on measurement_y2023q3 b_2 (cost=0.00..31.25 rows=567 width=8)
Filter: (unitsales > 10)
-> Seq Scan on measurement_y2023q4 b_3 (cost=0.00..31.25 rows=567 width=8)
Filter: (unitsales > 10)
(21 rows)In this execution plan, the join is performed on all the data of measurement and sales. However, there are unnecessary joins. For example, the join between sales_y2023q1 and measurement_y2023q3 can only be empty because the connection condition is that the partition key values are the same, while the partition keys of sales_y2023q1 and measurement_y2023q3 are different.
Enable the partition-wise join feature.
SET enable_partitionwise_join to ON;When partition-wise join is enabled, the execution plan for the query looks like this.
explain SELECT a.* FROM sales a JOIN measurement b ON a.date = b.logdate WHERE b.unitsales > 10;
QUERY PLAN
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Append (cost=21.70..453.33 rows=5896 width=128)
-> Hash Join (cost=21.70..105.96 rows=1474 width=128)
Hash Cond: (b.logdate = a.date)
-> Seq Scan on measurement_y2023q1 b (cost=0.00..31.25 rows=567 width=8)
Filter: (unitsales > 10)
-> Hash (cost=15.20..15.20 rows=520 width=128)
-> Seq Scan on sales_y2023q1 a (cost=0.00..15.20 rows=520 width=128)
-> Hash Join (cost=21.70..105.96 rows=1474 width=128)
Hash Cond: (b_1.logdate = a_1.date)
-> Seq Scan on measurement_y2023q2 b_1 (cost=0.00..31.25 rows=567 width=8)
Filter: (unitsales > 10)
-> Hash (cost=15.20..15.20 rows=520 width=128)
-> Seq Scan on sales_y2023q2 a_1 (cost=0.00..15.20 rows=520 width=128)
-> Hash Join (cost=21.70..105.96 rows=1474 width=128)
Hash Cond: (b_2.logdate = a_2.date)
-> Seq Scan on measurement_y2023q3 b_2 (cost=0.00..31.25 rows=567 width=8)
Filter: (unitsales > 10)
-> Hash (cost=15.20..15.20 rows=520 width=128)
-> Seq Scan on sales_y2023q3 a_2 (cost=0.00..15.20 rows=520 width=128)
-> Hash Join (cost=21.70..105.96 rows=1474 width=128)
Hash Cond: (b_3.logdate = a_3.date)
-> Seq Scan on measurement_y2023q4 b_3 (cost=0.00..31.25 rows=567 width=8)
Filter: (unitsales > 10)
-> Hash (cost=15.20..15.20 rows=520 width=128)
-> Seq Scan on sales_y2023q4 a_3 (cost=0.00..15.20 rows=520 width=128)
(25 rows)The performance is significantly improved, as unnecessary joins are reduced. sales_y2023q2, sales_y2023q3, and sales_y2023q4 only need to be joined with measurement_y2023q2, measurement_y2023q3, and measurement_y2023q4 respectively.