Each cluster in a global database network (GDN), including the primary and secondary clusters, has its own cluster endpoint. You can connect your application to the nearest cluster endpoint based on its region. The GDN automatically handles read/write splitting. Read requests are routed to the local cluster, and write requests are forwarded to the primary cluster.
Read/write splitting and request routing
In a GDN, the routing of read/write requests to clusters (the primary cluster and secondary clusters) is determined by the database proxy configuration of each cluster. Your application requires no code modifications. You only need to connect to the endpoint of the corresponding cluster, and read/write requests are automatically routed based on the following logic:
Write requests, such as
INSERT,UPDATE, andDELETE, and all requests within a transaction are automatically forwarded to the primary node of the primary cluster for processing.By default, read requests are routed to the read-only nodes of the local secondary cluster for low-latency access. If session consistency is enabled, some read requests may also be routed to the primary node of the primary cluster to ensure data consistency.
Only cluster endpoints or custom endpoints with the Read/Write Mode set to Read/Write (Automatic Read/Write Splitting) support the GDN read/write splitting service.
The Primary Endpoint and custom endpoints with the Read/Write Mode set to Read-only do not support the GDN read/write splitting service.
To reduce the potential impact of replication delay between the primary and secondary clusters on your business, when you configure a custom cluster endpoint on a secondary cluster, set Primary Node Accepts Read Requests to No and set Consistency Level to Eventual Consistency (Weak).
View a cluster endpoint
Log on to the PolarDB console. In the navigation pane on the left, click Global Database Network (GDN).
On the Global Database Network (GDN) page, find the target GDN and click the Global Database Network ID to go to the GDN details page.
In the Cluster List section, find the target secondary cluster and click View in the Cluster Endpoint column. You can then view the cluster endpoint details in the dialog box that appears.
 Note
NoteYou can only view the endpoint information for the default cluster, including the VPC and Internet addresses.
To view more endpoint details, click View Or Manage More Endpoints. You are redirected to the details page of the target cluster, where you can view more endpoints in the Database Connection section.
Connect to a global database cluster
Applications in different regions can connect to the nearest cluster endpoint to access the GDN, which automatically handles read/write splitting. You can connect to a database cluster in several ways. Choose the method that best suits your needs. The following sections provide examples:
Use DMS to connect to a cluster
Data Management (DMS) is a graphical data management tool provided by Alibaba Cloud. It provides various data management services, including data management, schema management, user management, security audit, data trends, data tracking, business intelligence (BI) charts, performance optimization, and server management. You can manage your PolarDB cluster directly by using DMS without using other tools.
Log on to the PolarDB console. In the cluster list, click the ID of the cluster that you want to connect to go to its Basic Information page. In the upper-right corner of the page, click Log On To Database.
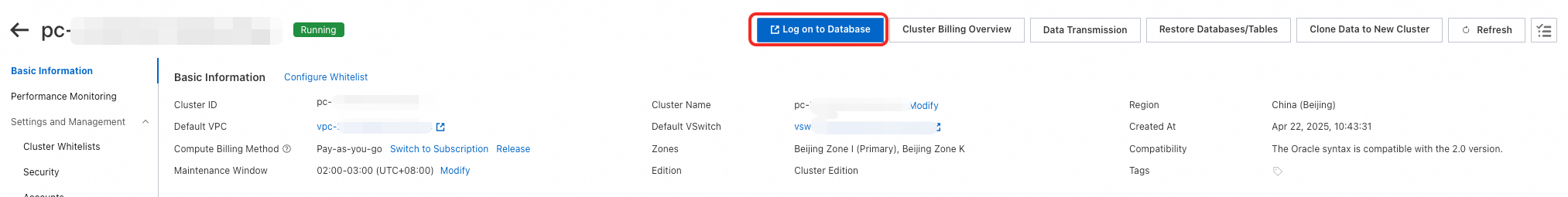
In the dialog box that appears, enter the database account and password that you created for the cluster, and click Login.
After you log on to the cluster, choose in the left-side navigation pane to manage the cluster.

Use a client to connect to a cluster
You can use a client to connect to a PolarDB cluster. The following procedure uses the pgAdmin 4 v9.0 client to connect to a cluster.
Download and install the pgAdmin 4 client.
Open the pgAdmin 4 client, right-click Servers, and select .

On the General tab, set the connection name. On the Connection tab, configure the cluster connection information, and click Save.

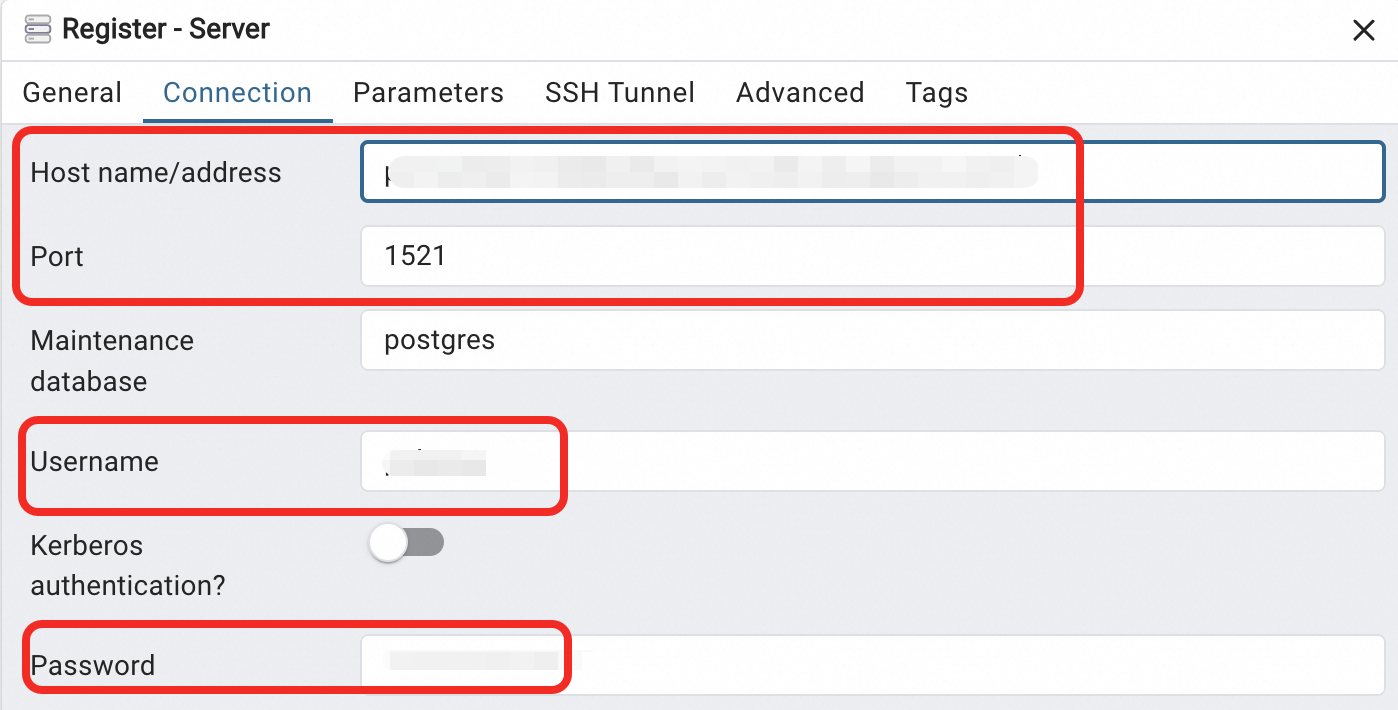
Parameter
Description
Host name/address
The endpoint and port of the PolarDB cluster.
To access the PolarDB cluster from an ECS instance, and the ECS instance is in the same VPC as the PolarDB cluster, specify the Private endpoint and port.
To access the PolarDB cluster from your on-premises environment, specify the Public endpoint and port.
The default port number is 1521.
Port
Username
The database account and password of the PolarDB cluster.
Password
View the connection result. If the connection information is correct, the following interface appears, indicating a successful connection.
 Note
Notepostgresis the default system database. Do not perform any operations on this database.
Use psql to connect to a cluster
You can download psql from PostgreSQL Downloads to connect to a PolarDB cluster. You can also use psql in the PolarDB-Tools to connect to a PolarDB cluster.
Th cluster connection method by using psql is the same for Windows and Linux systems.
For more information about how to use psql, see psql.
Syntax
psql -h <host> -p <port> -U <username> -d <dbname>Parameter | Description |
| The cluster endpoint and port of the PolarDB cluster.
|
| |
| The database account of the PolarDB cluster. |
| The database name. |
Example
psql -h pc-xxx.rwlb.rds.aliyuncs.com -p 1521 -U testusername -d postgresConnect to a cluster in a programming language
Connecting to a PolarDB for PostgreSQL (Compatible with Oracle) cluster is similar to connect a regular PostgreSQL database. You only need to change the connection parameters, including the endpoint, port, account, and password. Below are examples of how to connect to a PolarDB cluster in specific programming languages.
Java
This example describes how to connect to a PolarDB for PostgreSQL (Compatible with Oracle) cluster by using the PostgreSQL JDBC driver in a Maven-based Java project.
Add the PostgreSQL JDBC driver dependency to your pom.xml file. Sample code:
<dependency> <groupId>org.postgresql</groupId> <artifactId>postgresql</artifactId> <version>42.2.18</version> </dependency>Connect to the cluster. Replace the
<HOST>,<PORT>,<USER>,<PASSWORD>,<DATABASE>,<YOUR_TABLE_NAME>, and<YOUR_TABLE_COLUMN_NAME>placeholders with the actual cluster connection parameters.import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.DriverManager; import java.sql.ResultSet; import java.sql.Statement; public class PolarDBConnection { public static void main(String[] args) { // Database URL, username, and password. String url = "jdbc:postgresql://<HOST>:<PORT>/<DATABASE>"; String user = "<USER>"; String password = "<PASSWORD>"; try { // Load the PostgreSQL JDBC driver. Class.forName("org.postgresql.Driver"); // Establish the connection. Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password); // Create a Statement object. Statement stmt = conn.createStatement(); // Execute an SQL query. ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery("SELECT * FROM <YOUR_TABLE_NAME>"); // Process the result set. while (rs.next()) { System.out.println(rs.getString("<YOUR_TABLE_COLUMN_NAME>")); } // Close resources. rs.close(); stmt.close(); conn.close(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
Python
This example describes how to connect to a PolarDB for PostgreSQL (Compatible with Oracle) cluster by using the psycopg2 library in Python 3.
Install the psycopg2 library.
pip3 install psycopg2-binaryConnect to the cluster. Replace the
<HOST>,<PORT>,<USER>,<PASSWORD>,<DATABASE>, and<YOUR_TABLE_NAME>placeholders with the actual cluster connection parameters.import psycopg2 try: # Connection parameters conn = psycopg2.connect( host="<HOST>", # The cluster endpoint. database="<DATABASE>", # The database name. user="<USER>", # The username. password="<PASSWORD>", # The password. port="<PORT>" # The port number. ) # Create a cursor object. cursor = conn.cursor() # Execute a query. cursor.execute("SELECT * FROM <YOUR_TABLE_NAME>") # Get all results. records = cursor.fetchall() for record in records: print(record) except Exception as e: print("Error:", e) finally: # Close the connection. if 'cursor' in locals(): cursor.close() if 'conn' in locals(): conn.close()
Go
This example describes how to connect to a PolarDB for PostgreSQL (Compatible with Oracle) cluster by using the database/sql package and the lib/pq driver in Go 1.23.0.
Install the
lib/pqdriver.go get -u github.com/lib/pqConnect to the cluster. Replace the
<HOST>,<PORT>,<USER>,<PASSWORD>,<DATABASE>, and<YOUR_TABLE_NAME>placeholders with the actual cluster connection parameters.package main import ( "database/sql" "fmt" "log" _ "github.com/lib/pq" // Initialize the PostgreSQL driver. ) func main() { // The connection string format. connStr := "user=<USER> password=<PASSWORD> dbname=<DATABASE> host=<HOST> port=<PORT> sslmode=disable" // Open a database connection. db, err := sql.Open("postgres", connStr) if err != nil { log.Fatal(err) } defer db.Close() // Close the connection when the program exits. // Test the connection. err = db.Ping() if err != nil { log.Fatal(err) } fmt.Println("Connected to PostgreSQL!") // Execute a query. rows, err := db.Query("SELECT * FROM <YOUR_TABLE_NAME>") if err != nil { log.Fatal(err) } defer rows.Close() }
Related API operations
API | Description |
Queries the endpoint information of a PolarDB cluster. | |
Modifies the properties of a PolarDB cluster endpoint, including the read/write mode, whether to automatically add new nodes to the endpoint, the consistency level, transaction splitting, whether the primary node accepts read requests, and the connection pool. |