This topic describes how to resolve the "failed to obtain a metadata lock" error that occurs when you execute a DDL operation in PolarDB for MySQL.
Problem description
When you execute a DDL operation in a PolarDB for MySQL database, an error message is returned, indicating that a metadata lock cannot be obtained. The following error messages may be returned:
ERROR HY000: Fail to get MDL on replica during DDL synchronizeERROR HY000: Fail to get table lock on replica; you can 'set polar_support_mdl_sync_preemption = ON' and try restarting transactionCauses
This error occurs because a read-only node of the PolarDB for MySQL cluster has ongoing queries or uncommitted transactions.
Solutions
Choose one of the following solutions to resolve the issue:
Enable the preemptive DDL feature for the read-only node. For more information, see Preemptive DDL.
Commit or roll back the uncommitted transactions on the read-only node.
Enable the polar_slave_work_on_nonblock_mdl_mode parameter on the read-only node to prevent uncommitted long-running transactions from blocking DDL operations. For more information, see Prevent long-running transactions on read-only nodes from blocking DDL operations.
Log on to the PolarDB console. In the navigation pane on the left, choose . On the Session Manager tab, check for abnormal sessions. If abnormal sessions exist, click View Details in the anomaly section to view the session details. End the sessions that have long-running uncommitted transactions. For other abnormal sessions, you can optimize or end them as needed. For more information, see Session Manager.

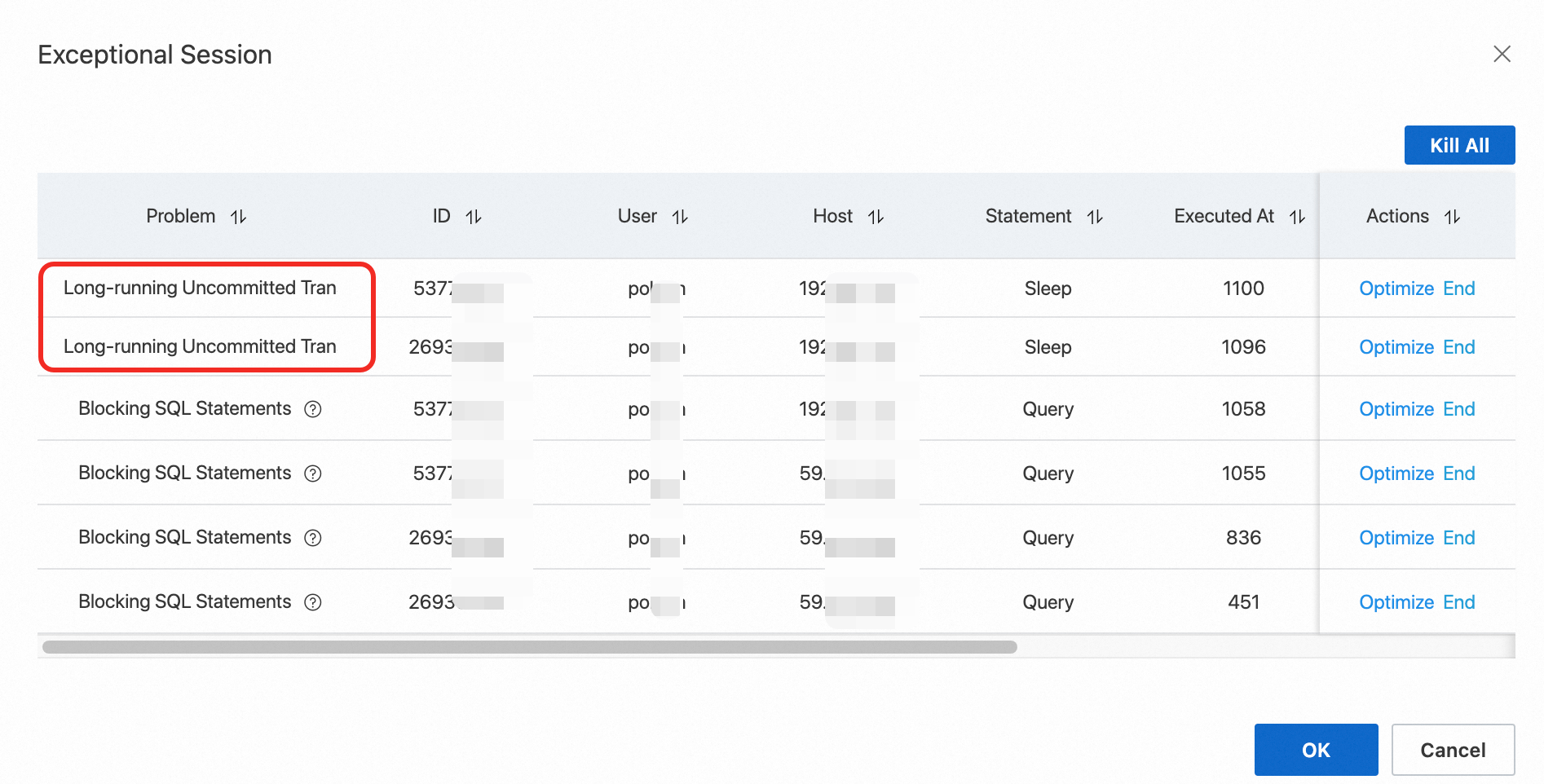
Use the Polar Performance Schema feature to query the metadata lock (MDL) status of the target table. Then, stop the threads related to uncommitted transactions on the read-only node. The steps are as follows:
Check the status of the Polar Performance Schema feature for the cluster. You can check the status in one of the following two ways:
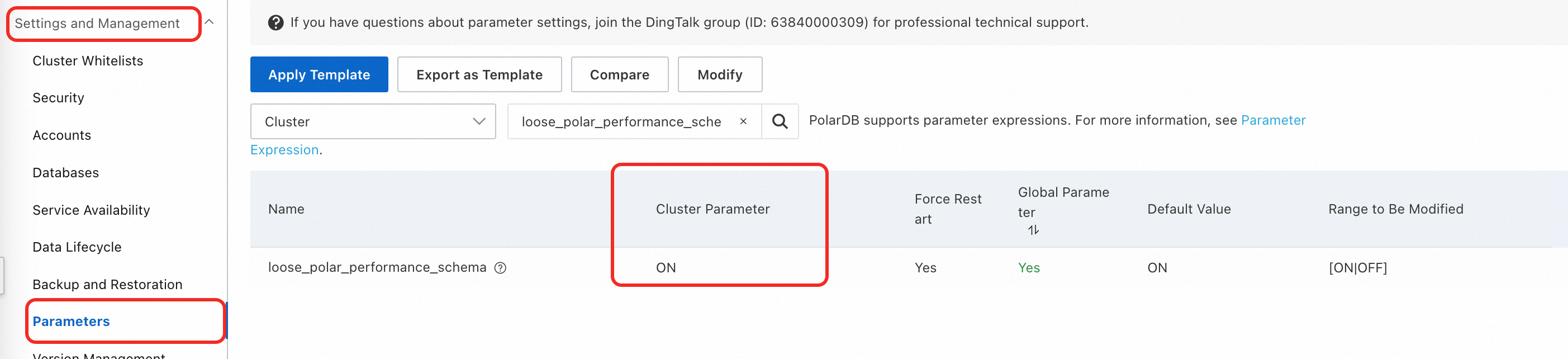
Log on to the PolarDB console. In the navigation pane on the left, choose to view the value of the
loose_polar_performance_schemaparameter.To ensure compatibility with MySQL configuration files, all cluster parameters in the console are prefixed with loose_.
Execute the following SQL statement:
SHOW VARIABLES LIKE 'polar_performance_schema';+--------------------------+-------+ | Variable_name | Value | +--------------------------+-------+ | polar_performance_schema | ON | +--------------------------+-------+
The procedure varies depending on whether the parameter is enabled or disabled.
Enabled (ON)
Query the
performance_schema.metadata_lockstable to check the MDL status on the target table and determine whether any transactions are uncommitted. Then, use thekillcommand to stop the threads for the uncommitted transactions.Use a hint to specify a read-only node and execute the following SQL statement to query the MDL status on the target table.
/*force_node='pi-bp10k7631d6k3****'*/ SELECT t.PROCESSLIST_ID, m.OBJECT_TYPE, m.OBJECT_SCHEMA, m.OBJECT_NAME, m.LOCK_TYPE, m.LOCK_DURATION, m.LOCK_STATUS FROM performance_schema.metadata_locks m LEFT JOIN performance_schema.threads t ON m.owner_thread_id=t.thread_id;Sample result:
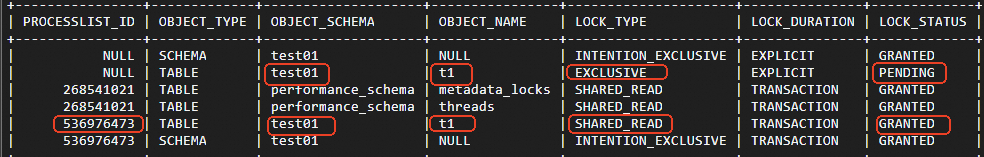
The preceding figure shows that the
test01/t1table holds a lock withLOCK_TYPEset toSHARED_READdue to a large query or an uncommitted transaction. Thetest/t1table also holds a lock in thePENDINGstate withLOCK_TYPEset toEXCLUSIVE.Use a hint to specify a read-only node and execute the
killcommand to stop the thread that corresponds to the connection.NoteIf the uncommitted transaction on the read-only node is important, do not use the
killcommand to stop it directly. Wait for the transaction to complete before you execute the DDL operation.If you cannot stop the thread using the
killcommand, the thread ID does not exist, or the following error occurs, contact us for assistance.ERROR 1094 (HY000): Unknown thread id: xxx
/*force_node='pi-bp10k7631d6k3****'*/ kill 536976473;
Disabled (OFF)
Query the
information_schema.innodb_trxtable to check the MDL status on the target table and determine whether any transactions are uncommitted. Then, use thekillcommand to stop the threads for the uncommitted transactions.Use a hint to specify a read-only node and execute the following SQL statement to query the
information_schema.innodb_trxtable./*force_node='pi-bp10k7631d6k3****'*/ SELECT * FROM information_schema.innodb_trx\GCheck the result to determine whether the issue is caused by a large query or a large transaction:
DDL execution failed due to a large query. Sample result:
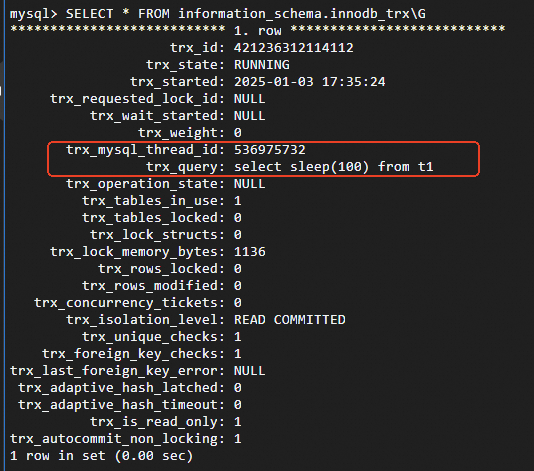
The preceding figure shows that a large query exists on the
t1table. This indicates that the current connection holds the MDL on thet1table.DDL execution failed due to a large transaction. Sample result:

The preceding figure shows that transaction 537247177 is uncommitted. Because the
trx_queryfield is empty, you cannot determine whether this transaction holds the MDL on the current table. In this case, check thetrx_startedfield. If the time in thetrx_startedfield is much earlier than the current time, it is highly likely that transaction 537247177 holds the MDL.
Use a hint to specify a read-only node and execute the
killcommand to stop thetrx_mysql_thread_idthread that corresponds to the connection./*force_node='pi-bp10k7631d6k3****'*/ kill 537247177
Contact us
If you have any questions about DDL operations, please contact technical support.
More information
The DDL operation process in the cloud-native database PolarDB is as follows:
During a DDL operation, if the table schema needs to be changed, the primary node first obtains an MDL and then writes a redo log entry before the change.
When a read-only node parses this redo log entry, it attempts to obtain the MDL on the same table. One of the following two situations occurs:
The retrieval was successful. You can now proceed to the next step.
The lock cannot be obtained. The read-only node sends feedback to the primary node.
The primary node waits for all read-only nodes to synchronize with the latest replication offset. Within a specific period, the primary node determines whether all read-only nodes have parsed the redo log entry and successfully obtained the lock. One of the following two situations occurs:
All read-only nodes synchronize with the latest replication offset. The DDL operation succeeds.
Some read-only nodes fail to synchronize with the latest replication offset. The DDL operation is rolled back and an error is reported. Two types of errors can be reported: a synchronization timeout error or the lock acquisition failure error described in this topic. Lock acquisition fails on a read-only node primarily because of ongoing queries or uncommitted transactions.