Optimize large language model (LLM) inference performance through intelligent traffic routing based on real-time resource metrics and scheduling policies. The LLM Intelligent Router dynamically distributes requests to balance computing resources and memory allocation across inference instances, improving cluster utilization and service reliability.
How it works
Architecture overview
The LLM Intelligent Router consists of three core components that work together to provide intelligent traffic distribution and management for backend LLM inference instance clusters:
LLM Gateway: Primary traffic entry point and request processor that supports HTTP/SSE and WebSocket protocols
LLM Scheduler: Central intelligence that aggregates real-time metrics and makes policy-based scheduling decisions
LLM Agent: Distributed monitoring probe deployed as sidecar container with each inference instance
The LLM Intelligent Router is a special EAS service that must be deployed in the same service group as the inference service to function properly.

The core workflow process:
Instance registration: After the inference service starts, the
LLM Agentwaits for the inference engine to become ready, then registers the instance with theLLM Schedulerand periodically reports health status and performance metrics.Traffic ingestion: User requests are first received by the
LLM Gateway.Scheduling decision: The
LLM Gatewaysends a scheduling request to theLLM Scheduler.Intelligent scheduling: The
LLM Schedulerselects the optimal backend instance based on the scheduling policy and real-time metrics reported by allLLM Agents.Request forwarding: The
LLM Schedulerreturns the decision to theLLM Gateway, which forwards the user's original request to the target instance.Request buffering: If all backend instances are under high load, new requests are temporarily buffered in the
LLM Gateway's queue, waiting for theLLM Schedulerto find a suitable forwarding opportunity to prevent request failures.
Core components
Component | Core responsibility |
LLM Gateway | Primary traffic entry point and request processor. Receives all user requests and forwards them to designated backend inference instances based on decisions from the
|
LLM Scheduler | Central intelligence for request distribution. Aggregates real-time metrics reported by all |
LLM Agent | Distributed monitoring and reporting probe. Deployed as a sidecar container with each inference instance, it collects performance metrics from the inference engine, maintains a heartbeat connection with the |
Failover mechanism
The system implements multiple layers of fault tolerance mechanisms to ensure service stability:
LLM Gateway (high availability): The LLM Gateway is a stateless traffic ingress layer. For high availability, you should deploy at least two instances. If one instance fails, traffic automatically switches to the healthy instances, which ensures continuous service availability.
LLM Scheduler (degraded fault tolerance): The LLM Scheduler is the request scheduling component and runs as a single instance to enable global scheduling. If the
LLM Schedulerfails, theLLM Gatewayautomatically enters a degraded mode after a heartbeat failure. In this mode, it uses a round-robin policy to forward requests directly to backend instances. This ensures service availability but sacrifices scheduling performance. After theLLM Schedulerrecovers, theLLM Gatewayautomatically resumes the intelligent scheduling mode.Inference instance or LLM Agent (automatic removal): If an inference instance or its associated
LLM Agentfails, the heartbeat between theLLM Agentand theLLM Scheduleris interrupted. TheLLM Schedulerthen immediately removes the instance from the list of available instances and stops assigning new traffic to it. After the instance recovers and re-establishes its heartbeat, it is automatically added back to the service list.
Multi-inference engine support
Because different LLM inference engines return different metric information through their /metrics endpoints, the LLM Agent collects these metrics and standardizes their format before reporting them. This means the LLM Scheduler does not need to understand the implementation details of a specific inference engine. It only needs to implement scheduling algorithms based on the standardized metrics. The currently supported LLM inference engines and their corresponding collected metrics are as follows:
LLM inference engine | Metric | Description |
vLLM | vllm:num_requests_running | Number of running requests. |
vllm:num_requests_waiting | Number of requests waiting in queue. | |
vllm:gpu_cache_usage_perc | GPU KV Cache usage percentage. | |
vllm:prompt_tokens_total | Total number of prompt tokens. | |
vllm:generation_tokens_total | Total number of generated tokens. | |
SGLang | sglang:num_running_reqs | Number of running requests. |
sglang:num_queue_reqs | Number of requests waiting in queue. | |
sglang:token_usage | KV Cache usage percentage. | |
sglang:prompt_tokens_total | Total number of prompt tokens. | |
sglang:gen_throughput | Number of tokens generated per second. |
Limitations
Cannot add during update: The LLM intelligent router feature can only be configured when you create a new service. You cannot add the intelligent routing feature to an existing inference service by performing an update service operation.
Inference engine limitation: This feature currently supports only the vLLM or SGLang inference engines.
Deploy multiple inference instances: The LLM intelligent router is most effective when deployed with multiple inference instances.
Quick start: Use LLM intelligent router
Step 1: Deploy LLM intelligent router service
Log on to the PAI console and select the destination region at the top of the page.
In the navigation pane on the left, click Elastic Algorithm Service (EAS), select the target workspace, and go to the EAS page.
Click Deploy Service, and then choose Scenario-based Model Deployment > Deploy LLM gateway.
Configure the parameters:
Parameter
Description
Basic Information
Service Name
Customize a service name, such as
llm_gateway.Resource Information
Deployment Resources
Resource configuration for
LLM Gateway. To ensure high availability, the default Number of Replicas is 2. Keep this setting. Default CPU is 4 cores and memory is 8 GB.Scheduling configuration
Resource configuration for
LLM Scheduler. Default CPU is 2 cores and memory is 4 GB.Scheduling Policy
Select the load balancing policy for backend inference instances. Default is Prefix cache. For detailed comparisons and selection guidance, see Scheduling Policy Details and Selection.
Click Deploy. When the service status changes to Running, the deployment is successful.
After a successful deployment, the system automatically creates a service group named group_<LLM intelligent router service name>. You can go to the Elastic Algorithm Service (EAS) page and view the service group on the Canary Release tab. 
Because intelligent routing conflicts with service queues, they cannot coexist in the same service group.
Step 2: Deploy an LLM service
You must configure the LLM intelligent router feature when you deploy a new LLM service. You cannot add this feature by updating an existing LLM service.
The following steps show how to deploy Qwen3-8B:
You can click Deploy Service and select Scenario-based Model Deployment > LLM Deployment.
You can configure the following key parameters:
Parameter
Value
Basic Information
Model Settings
Select Public Model. Then, search for and select Qwen3-8B.
Inference Engine
Select vLLM (Recommended, compatible with the OpenAI API).
NoteIf you select the Prefix cache scheduling policy for the LLM intelligent router service, you must enable the prefix cache feature when you deploy an LLM service that uses vLLM as the inference engine.
Deployment Template
Select Standalone. The system automatically fills in recommended parameters, such as instance type and runtime image, based on the template.
Features
LLM Intelligent Router
Turn on the switch and select the LLM intelligent router service deployed in Step 1 from the drop-down list.
You can click Deploy. The service deployment takes about 5 minutes. When the service status changes to Running, the deployment is successful.
Step 3: Test the service
You must send all requests to the LLM intelligent router service endpoint, not to the endpoints of specific backend inference services.
Obtain access credentials.
Click the LLM intelligent router service to go to the Overview page. In the Basic Information section, click View Endpoint Information.
On the Endpoint Information page, copy the Internet Endpoint and Token from the Service-specific Traffic Entry section.

Construct the request URL and call the service.
URL structure:
<LLM intelligent router endpoint>/<LLM service API path>Example:
http://********.pai-eas.aliyuncs.com/api/predict/group_llm_gateway.llm_gateway/v1/chat/completions
Request example:
# Replace <YOUR_GATEWAY_URL> and <YOUR_TOKEN> with your actual values # Replace <model_name> with your actual model name curl -X POST "<YOUR_GATEWAY_URL>/v1/chat/completions" \ -H "Authorization: Bearer <YOUR_TOKEN>" \ -H "Content-Type: application/json" \ -N \ -d '{ "model": "<model_name>", "messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "Hello"}], "stream": true }'Sample response:
data: {"id":"chatcmpl-9a9f8299*****","object":"chat.completion.chunk","created":1762245102,"model":"Qwen3-8B","choices":[{"index":0,"delta":{"role":"assistant","content":""},"logprobs":null,"finish_reason":null}]} data: {"id":"chatcmpl-9a9f8299*****","object":"chat.completion.chunk","created":1762245102,"model":"Qwen3-8B","choices":[{"index":0,"delta":{"content":"<think>","tool_calls":[]}}]} ... data: [DONE]
Advanced Configuration
A JSON-based standalone deployment provides more flexible configuration options that allow you to specify resource specifications for the LLM Gateway and fine-tune request processing behavior.
Procedure: On the Inference Service page, click Deploy Service. Then, in the Custom Model Deployment section, click JSON Deployment.
Configuration example:
{ "cloud": { "computing": { "instance_type": "ecs.c7.large" } }, "llm_gateway": { "max_queue_size": 128, "retry_count": 2, "wait_schedule_timeout": 5000, "wait_schedule_try_period": 500 }, "llm_scheduler": { "cpu": 2, "memory": 4000, "policy": "prefix-cache" }, "metadata": { "group": "group_llm_gateway", "instance": 2, "name": "llm_gateway", "type": "LLMGatewayService" } }Parameters:
Parameter
Description
metadata
type
Required. Fixed as
LLMGatewayService, indicating deployment of an LLM intelligent router service.instance
Required. Number of replicas for
LLM Gateway. Set to at least 2 to avoid single point of failure.cpu
CPU cores per replica for
LLM Gateway.memory
Memory (GB) for
LLM Gateway.group
Service group to which the LLM intelligent router service belongs.
cloud.computing.instance_type
Specify the resource specification for
LLM Gateway. In this case, do not configuremetadata.cpuandmetadata.memory.llm_gateway
max_queue_size
Maximum length of the
LLM Gatewaybuffer queue. Default is 512.When backend inference frameworks exceed processing capacity, excess requests are buffered in this queue, waiting for scheduling.
retry_count
Number of retry attempts. Default is 2. When a backend inference instance fails, the request is retried and forwarded to a different instance.
wait_schedule_timeout
When backend engines are at full capacity, requests attempt scheduling at intervals. This parameter specifies the total scheduling attempt duration. Default is 10 seconds.
wait_schedule_try_period
Interval between each scheduling attempt. Default is 1 second.
llm_scheduler
cpu
CPU cores for
LLM Scheduler. Default is 4 cores.memory
Memory (GB) for
LLM Scheduler. Default is 4 GB.policy
Scheduling policy. Default value is
prefix-cache. For available values and descriptions, see Scheduling Policy Details and Selection.prefill_policy
When policy is set to pd-split, specify separate scheduling policies for Prefill and Decode phases. Valid values: prefix-cache, llm-metric-based, least-request, least-token.
decode_policy
Scheduling policy details and selection
Selecting the right scheduling policy is crucial for maximizing the effectiveness of the LLM intelligent router. The following table compares the logic, applicable scenarios, advantages, and considerations for each policy to help you choose the most suitable one.
Policy Name | JSON Value | Core Logic | Applicable Scenario | Advantages | Considerations |
Prefix cache | prefix-cache | (Recommended) This is a comprehensive policy that prioritizes sending requests with an identical historical context (prompt) to instances that have already cached the corresponding KV Cache. | Multi-turn conversation bots and Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems that use fixed system prompts. | Significantly reduces Time to First Token (TTFT), which improves multi-turn conversation performance and throughput. | The inference engine must have prefix caching enabled. |
LLM Metrics | llm-metric-based | Intelligently schedules requests based on comprehensive backend instance load metrics, including the number of queued requests, running requests, and KV Cache usage. | General LLM workloads that have diverse request patterns and no clear conversational characteristics. | Effectively balances the load across instances and improves resource utilization. | The scheduling logic is relatively complex and may not deliver optimal results in specific scenarios when compared to the prefix cache policy. |
Minimum Requests | least-request | Sends new requests to the instance that is currently handling the fewest requests. | Scenarios where the computational complexity of requests, such as token length and generation length, is relatively uniform. | Simple and efficient. Quickly balances the number of requests across instances. | Does not perceive the actual request load. This can potentially leave instances that handle short requests idle while instances that handle long requests become overloaded. |
Minimum tokens | least-token | Sends new requests to the instance that is currently processing the fewest total tokens (input and output). | Scenarios where the token count is a reasonable reflection of the request processing cost. | Reflects the actual instance load more accurately than the 'Least Request' policy. | Relies on token count estimation. Not all engines report this metric. |
Static PD Disaggregation | pd-split | Requires you to pre-divide instances into Prefill and Decode groups and specify a separate scheduling policy for each group. | Scenarios where the Prefill and Decode phases have vastly different computing and memory characteristics, and a separated deployment provides significant benefits. | Maximizes hardware utilization through deep optimization. | Complex configuration: This policy requires a deep understanding of the models and business logic, in addition to the independent deployment of Prefill and Decode services. |
Dynamic PD Disaggregation | dynamic-pd-split | Instances do not require predefined roles. The scheduler dynamically assigns the Prefill or Decode phases of requests to the most suitable instances based on the real-time load. | Same as the static separation policy, but suitable for scenarios with dynamically changing loads. | More flexible than static separation. Adapts automatically to load changes. | Extremely complex configuration: This policy has higher requirements for the scheduler and the engine. |
View service monitoring metrics
After you deploy the service, you can view core performance metrics in the EAS console to evaluate the effectiveness of the intelligent routing.
On the Elastic Algorithm Service (EAS) page, click the name of the deployed LLM intelligent router service to go to the service details page. On the Monitoring tab, you can monitor the following core metrics:
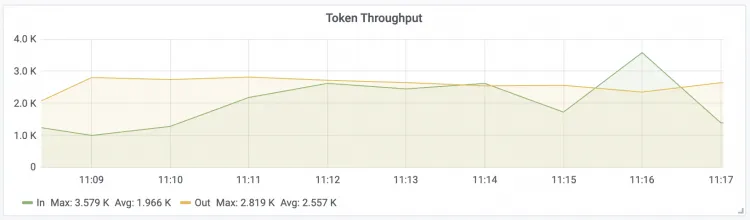
Token Throughput The throughput of input and output tokens for the LLM.
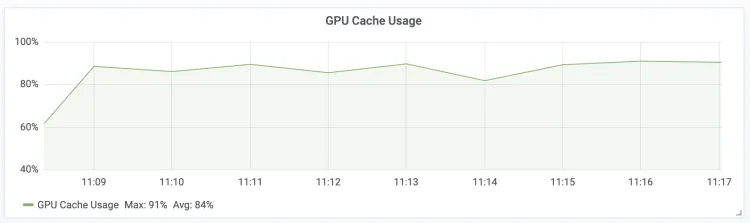
| GPU Cache Usage The GPU KV Cache usage percentage for the LLM Engine.
|
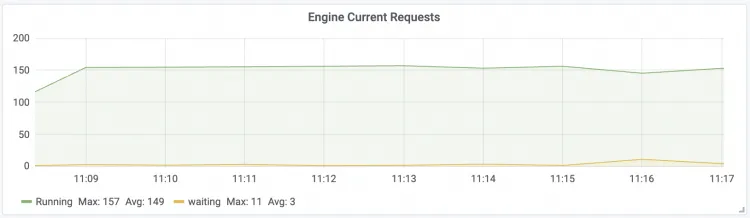
Engine Current Requests The number of real-time concurrent requests for the LLM Engine.
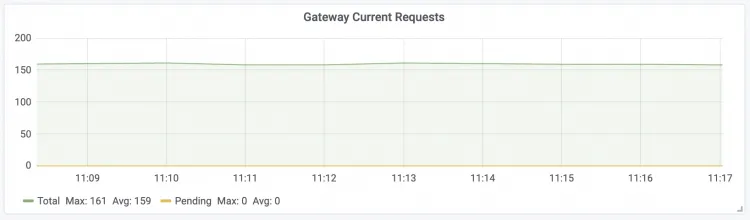
| Gateway Current Requests The number of real-time requests for the LLM intelligent router.
|
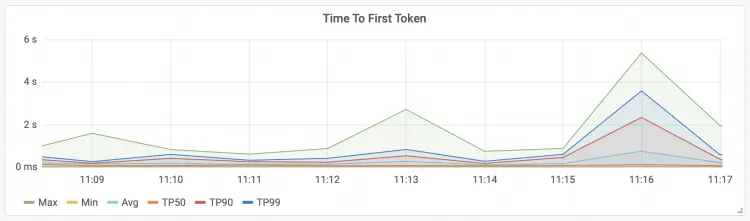
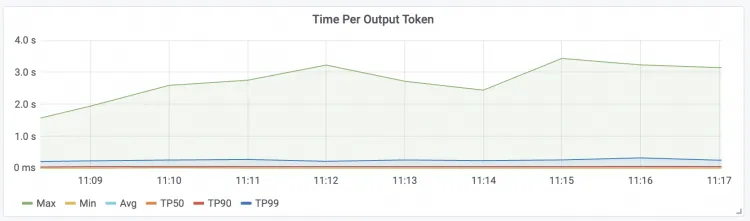
Time To First Token The latency of the first token for requests.
| Time Per Output Token Request latency per package
|
Appendix: Using Claude Code
Set the BASE URL and TOKEN that are provided by the EAS intelligent router service for Claude Code.
# Replace <YOUR_GATEWAY_URL> and <YOUR_TOKEN> with your actual values export ANTHROPIC_BASE_URL=<YOUR_GATEWAY_URL> export ANTHROPIC_AUTH_TOKEN=<YOUR_TOKEN>Run the Claude Code tool directly.
claude "Write a Python Hello World"
Appendix: Performance test comparison
Tests on the Distill-Qwen-7B, QwQ-32B, and Qwen2.5-72B models show that the LLM intelligent router significantly improves the speed and throughput of inference services. The test environment and results are as follows.
The following test results are for reference only. Actual performance may vary based on your specific tests.
Test environment
Scheduling Policy: prefix-cache
Test dataset: ShareGPT_V3_unfiltered_cleaned_split.json (multi-turn conversation dataset)
Inference engine: vLLM (0.7.3)
Number of backend instances: 5
Test results
Test Model | Distill-Qwen-7B | QwQ-32B | Qwen2.5-72b | ||||||
Card Type | ml.gu8tf.8.40xlarge | ml.gu8tf.8.40xlarge | ml.gu7xf.8xlarge-gu108 | ||||||
Concurrency | 500 | 100 | 100 | ||||||
Metric | Without LLM Intelligent Router | Use the LLM intelligent router | Improvement | Without LLM Intelligent Router | With LLM Intelligent Router | Improvement | Without LLM Intelligent Router | Using the LLM intelligent router | Improvement |
Successful requests | 3698 | 3612 | - | 1194 | 1194 | - | 1194 | 1194 | - |
Benchmark duration | 460.79 s | 435.70 s | - | 1418.54 s | 1339.04 s | - | 479.53 s | 456.69 s | - |
Total input tokens | 6605953 | 6426637 | - | 2646701 | 2645010 | - | 1336301 | 1337015 | - |
Total generated tokens | 4898730 | 4750113 | - | 1908956 | 1902894 | - | 924856 | 925208 | - |
Request throughput | 8.03 req/s | 8.29 req/s | +3.2% | 0.84 req/s | 0.89 req/s | +5.95% | 2.49 req/s | 2.61 req/s | +4.8% |
Output token throughput | 10631.17 tok/s | 10902.30 tok/s | +2.5% | 1345.72 tok/s | 1421.08 tok/s | +5.6% | 1928.66 tok/s | 2025.92 tok/s | +5.0% |
Total Token throughput | 24967.33 tok/s | 25652.51 tok/s | +2.7% | 3211.52 tok/s | 3396.38 tok/s | +5.8% | 4715.34 tok/s | 4953.56 tok/s | +5.0% |
Mean TTFT | 532.79 ms | 508.90 ms | +4.5% | 1144.62 ms | 859.42 ms | +25.0% | 508.55 ms | 389.66 ms | +23.4% |
Median TTFT | 274.23 ms | 246.30 ms | - | 749.39 ms | 565.61 ms | - | 325.33 ms | 190.04 ms | - |
P99 TTFT | 3841.49 ms | 3526.62 ms | - | 5339.61 ms | 5027.39 ms | - | 2802.26 ms | 2678.70 ms | - |
Mean TPOT | 40.65 ms | 39.20 ms | +3.5% | 68.78 ms | 65.73 ms | +4.4% | 46.83 ms | 43.97 ms | +4.4% |
Median TPOT | 41.14 ms | 39.61 ms | - | 69.19 ms | 66.33 ms | - | 45.37 ms | 43.30 ms | - |
P99 TPOT | 62.57 ms | 58.71 ms | - | 100.35 ms | 95.55 ms | - | 62.29 ms | 54.79 ms | - |