The counting triangle algorithm is a graph analysis algorithm used to identify and count the number of triangles in a graph in which a triangle is a closed loop formed by three interconnected vertices. The algorithm is mainly applied in fields such as social network analysis, network clustering coefficient calculation, and community detection. You can assess the local density of a graph and the degree of tight connectivity between nodes by counting the number of triangles.
Configure the component
Method 1: Configure the component on the pipeline page
On the pipeline details page in Machine Learning Designer, add the Counting Triangle component to the pipeline and configure the parameters described in the following table.
Tab | Parameter | Description |
Fields Setting | Start Vertex | The start vertex column in the edge table. |
End Vertex | The end vertex column in the edge table. | |
Parameters Setting | Largest Vertex Degree | If the vertex degree is larger than the value of this parameter, sampling is required. Default value: 500. |
Tuning | Workers | The number of vertices for parallel job execution. The degree of parallelism and framework communication costs increase with the value of this parameter. |
Memory Size per Worker (MB) | The maximum size of memory that a single job can use. Unit: MB. Default value: 4096. If the size of used memory exceeds the value of this parameter, the | |
Data Split Size (MB) | The data split size. Unit: MB. Default value: 64. |
Method 2: Configure the component by using PAI commands
Configure the component parameters by using PAI commands. You can use the SQL Script component to call PAI commands. For more information, see Scenario 4: Execute PAI commands within the SQL script component.
PAI -name TriangleCount
-project algo_public
-DinputEdgeTableName=TriangleCount_func_test_edge
-DfromVertexCol=flow_out_id
-DtoVertexCol=flow_in_id
-DoutputTableName=TriangleCount_func_test_result;Parameter | Required | Default value | Description |
inputEdgeTableName | Yes | No default value | The name of the input edge table. |
inputEdgeTablePartitions | No | Full table | The partitions in the input edge table. |
fromVertexCol | Yes | No default value | The start vertex column in the input edge table. |
toVertexCol | Yes | No default value | The end vertex column in the input edge table. |
outputTableName | Yes | No default value | The name of the output table. |
outputTablePartitions | No | No default value | The partitions in the output table. |
lifecycle | No | No default value | The lifecycle of the output table. |
maxEdgeCnt | No | 500 | If the vertex degree is greater than the value of this parameter, sampling is required. |
workerNum | No | No default value | The number of vertices for parallel job execution. The degree of parallelism and framework communication costs increase with the value of this parameter. |
workerMem | No | 4096 | The maximum size of memory that a single job can use. Unit: MB. Default value: 4096. If the size of used memory exceeds the value of this parameter, the |
splitSize | No | 64 | The data split size. Unit: MB. |
Example
On the pipeline details page, add a SQL Script component to the pipeline and click the component. On the Parameters Setting tab, clear Use Script Mode and Whether the system adds a create table statement, and enter the following SQL statements in the SQL Script editor:
drop table if exists TriangleCount_func_test_edge; create table TriangleCount_func_test_edge as select * from ( select '1' as flow_out_id,'2' as flow_in_id union all select '1' as flow_out_id,'3' as flow_in_id union all select '1' as flow_out_id,'4' as flow_in_id union all select '1' as flow_out_id,'5' as flow_in_id union all select '1' as flow_out_id,'6' as flow_in_id union all select '2' as flow_out_id,'3' as flow_in_id union all select '3' as flow_out_id,'4' as flow_in_id union all select '4' as flow_out_id,'5' as flow_in_id union all select '5' as flow_out_id,'6' as flow_in_id union all select '5' as flow_out_id,'7' as flow_in_id union all select '6' as flow_out_id,'7' as flow_in_id )tmp; drop table if exists TriangleCount_func_test_result; create table TriangleCount_func_test_result ( node1 string, node2 string, node3 string );Data structure
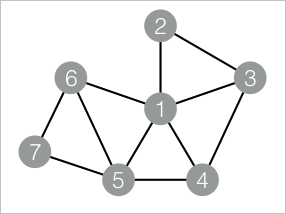
Add a SQL Script component to the pipeline and click the component. On the Parameters Setting tab, clear Use Script Mode and Whether the system adds a create table statement, and enter the following SQL statements in the SQL Script editor. Connect this component with the component added in Step 1.
drop table if exists ${o1}; PAI -name TriangleCount -project algo_public -DinputEdgeTableName=TriangleCount_func_test_edge -DfromVertexCol=flow_out_id -DtoVertexCol=flow_in_id -DoutputTableName=${o1};In the upper-left corner of the canvas, click
 to run the pipeline.
to run the pipeline.After the pipeline is run, right-click the component added in Step 2, click View data, and then select SQL Script Output.
| node1 | node2 | node3 | | ----- | ----- | ----- | | 1 | 2 | 3 | | 1 | 3 | 4 | | 1 | 4 | 5 | | 1 | 5 | 6 | | 5 | 6 | 7 |