Large Language Model (LLM) data processing algorithms allow you to edit, transform, filter, and deduplicate data samples. You can combine different algorithms to filter for suitable data and generate text that meets your requirements. This process prepares high-quality data for LLM training. This topic uses a small amount of data from the open source RedPajama arXiv dataset as an example. It demonstrates how to use the LLM data processing components in PAI to clean and process arXiv data.
Dataset description
The preset template 'LLM Data Processing-arXiv (Thesis Data)' in Machine Learning Designer uses a dataset of 5,000 samples. These samples are extracted from the raw data of the open source RedPajama project.
Create and run a pipeline
Go to the Machine Learning Designer page.
Log on to the PAI console.
In the upper-left corner, select a region.
In the navigation pane on the left, click Workspaces. Click the name of your workspace to open it.
In the navigation pane on the left, choose Model Training > Visualized Modeling (Designer) to open the Machine Learning Designer page.
Create a pipeline.
On the Preset Templates tab, choose Business Area > LLM. On the LLM Data Processing-arXiv (Thesis Data) template card, click Create.
Configure the pipeline parameters or keep the default settings, and click OK.
In the pipeline list, select the pipeline that you created and click Open.
Pipeline description:

The pipeline contains the following key algorithm components:
LLM-Sensitive Information Mask (MaxCompute)-1
Masks sensitive information in the "text" field. For example:
Replaces email addresses with
[EMAIL].Replaces mobile phone numbers with
[TELEPHONE]or[MOBILEPHONE].Replaces ID card numbers with
IDNUM.
LLM-Special Content Removal (MaxCompute)-1
Deletes URLs from the "text" field.
LLM-Text Normalization (MaxCompute)-1
Performs Unicode normalization on the text in the "text" field. It also converts Traditional Chinese characters to Simplified Chinese.
LLM-Count Filter (MaxCompute)-1
Removes samples from the "text" field that do not meet the specified count or ratio of alphanumeric characters. Most characters in the arXiv dataset are letters and numbers. This component can remove some dirty data.
LLM-Length Filter (MaxCompute)-1
Filters samples based on the average line length in the "text" field. The average length is calculated by splitting the sample by the line feed character (
\n).LLM-N-Gram Repetition Filter (MaxCompute)-1
Filters samples in the "text" field based on the character-level N-gram repetition rate. The component moves an N-character sliding window across the text to create a sequence of segments. Each segment is a gram. The component counts the occurrences of each gram. The repetition rate is calculated using the formula:
(Total frequency of grams that appear more than once) / (Total frequency of all grams). Samples are filtered based on this rate.LLM-Sensitive Words Filter (MaxCompute)-1
Uses the system-preset sensitive word file to filter samples in the "text" field that contain sensitive words.
LLM-Length Filter (MaxCompute)-2
Filters samples based on the maximum line length in the "text" field. The maximum line length is calculated by splitting the sample by the line feed character (
\n).LLM-Perplexity Filter (MaxCompute)-1
Calculates the perplexity of the text in the "text" field and filters samples based on the specified perplexity threshold.
LLM-Special Characters Ratio Filter (MaxCompute)-1
Removes samples from the "text" field that do not meet the specified ratio of special characters.
LLM-Length Filter (MaxCompute)-3
Filters samples based on the length of the "text" field.
LLM-Tokenization (MaxCompute)-1
Tokenizes the text in the "text" field and saves the result to a new column.
LLM-Length Filter (MaxCompute)-4
Splits samples in the "text" field into a list of words using the space character (
" ") as the separator. It then filters samples based on the length of the list, which is the word count.LLM-N-Gram Repetition Filter (MaxCompute)-2
Filters samples in the "text" field based on the word-level N-gram repetition rate. All words are converted to lowercase before the repetition rate is calculated. The component moves an N-word sliding window across the text to create a sequence of segments. Each segment is a gram. The component counts the occurrences of each gram. The repetition rate is calculated using the formula:
(Total frequency of grams that appear more than once) / (Total frequency of all grams). Samples are filtered based on this rate.LLM-MinHash Deduplicator (MaxCompute)-1
Removes similar samples based on the MinHash algorithm.
Run the pipeline.
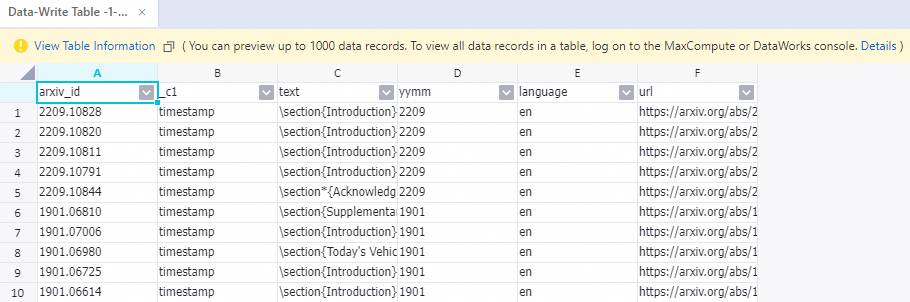
After the pipeline finishes running, right-click the Write To Data Table-1 component and choose View Data > Output to view the samples processed by the preceding components.
References
For more information about the LLM algorithm components, see LLM data processing (MaxCompute).