This topic describes the architectural design and components of Platform for AI (PAI).
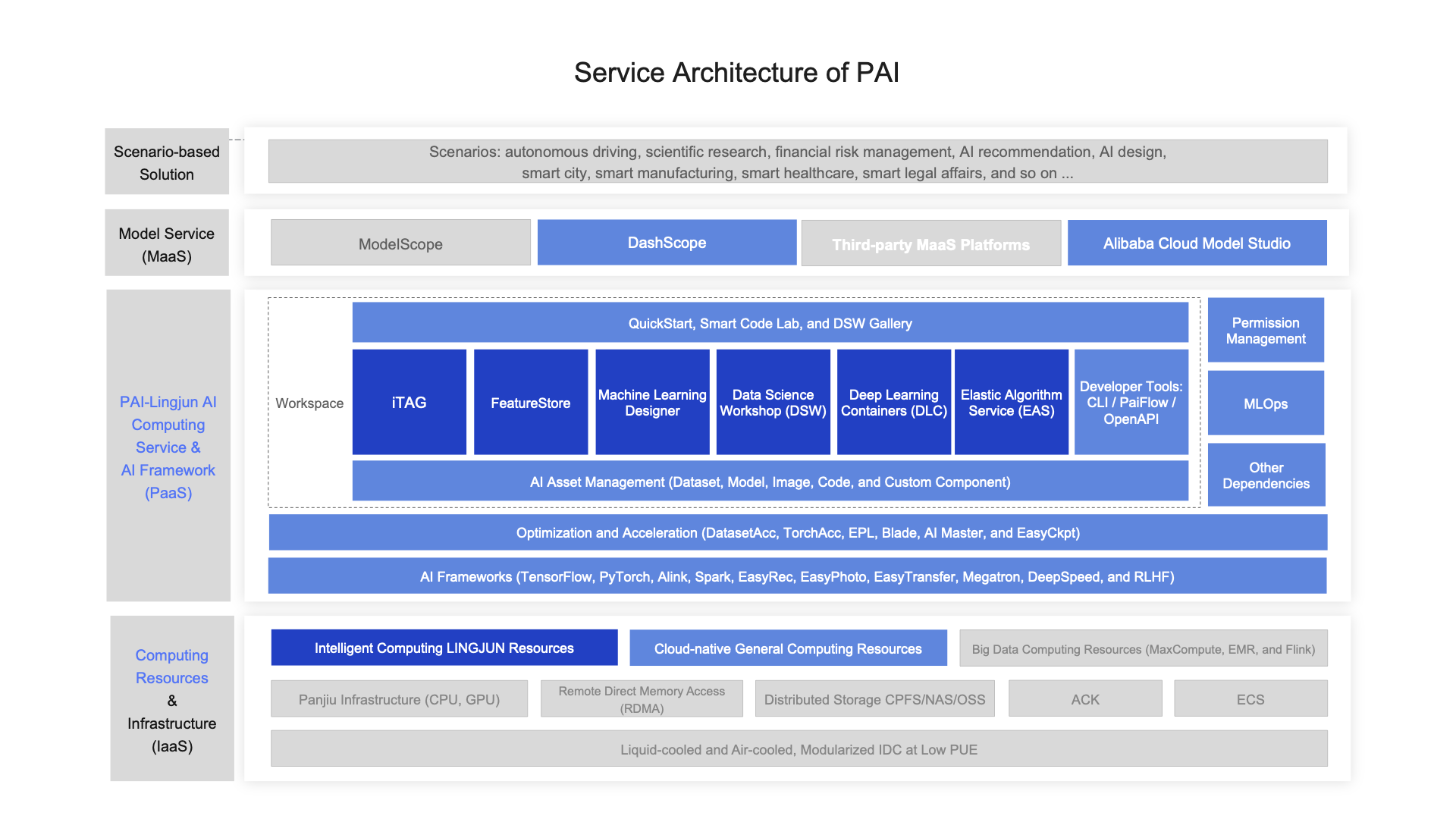
PAI uses a four-layer architecture that provides end-to-end capabilities for AI development and deployment:
-
Infrastructure layer (Computing resources and infrastructure)
This layer provides the foundational computing and networking resources:
-
Infrastructure: Includes CPUs, GPUs, high-speed Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA) networks, and Container Service for Kubernetes (ACK) for containerized workload orchestration.
-
Computing resources: Offers cloud-native computing resources (Lingjun specialized resources and general-purpose computing resources) alongside big data processing engines (MaxCompute and Flink).
-
-
Platform and tools layer (AI frameworks and acceleration)
This layer delivers core AI development capabilities through frameworks, optimization tools, and end-to-end machine learning workflows:
-
AI frameworks: Supports industry-standard frameworks including Alink, TensorFlow, PyTorch, Megatron, DeepSpeed, and Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF).
-
Optimization and acceleration: Provides specialized tools to accelerate AI workloads—Dataset Acceleration (DatasetAcc) for faster data loading, Training Acceleration (TorchAcc) for optimized training performance, Parallel Training (EPL) for distributed training, Inference Acceleration (BladeLLM) for efficient model serving, Automatic Fault-tolerant Training (AIMaster) for resilient training operations, and Training Snapshot (EasyCkpt) for checkpoint management.
-
End-to-end machine learning tools: Comprehensive workflow coverage from data preparation to model deployment.
-
Data preparation: Includes the iTAG data annotation service for labeling tasks and dataset management capabilities for organizing training data.
-
Model development and training: Offers multiple development environments including Machine Learning Designer for visual workflow creation, Data Science Workshop (DSW) for interactive notebook-based development, Deep Learning Containers (DLC) for scalable distributed training, and FeatureStore for centralized feature management and reuse.
-
Model deployment: Elastic Algorithm Service (EAS) enables production deployment of trained models as scalable, high-performance services.
-
-
-
Application layer (Model services and platforms)
This layer integrates PAI with model ecosystems and application platforms, enabling seamless access to pre-trained models and AI services through the ModelScope community, PAI-DashScope API service, third-party Model-as-a-Service (MaaS) platforms, and Alibaba Cloud Model Studio.
-
Business layer (Industry solutions)
This layer delivers domain-specific AI solutions for vertical industries including autonomous driving, AI for Science (AI4Science), financial risk management, and intelligent recommendation systems. For example, internal Alibaba Group systems leverage PAI for large-scale data mining tasks in search, recommendation, and financial service applications.