Cross-region replication (CRR) automatically and asynchronously replicates object operations, such as creation, updates, and deletions, from a source bucket in one region to a destination bucket in another region. The buckets can be in the same or different accounts. This process helps meet compliance requirements, reduce latency, and ensure security and availability.
Scenarios
The cross-region replication feature is designed for cross-region disaster recovery and data replication. Objects in the destination bucket are exact replicas of objects in the source bucket. They have the same object names, versioning information, metadata, and content, including the creation time, owner, user-defined metadata, and object access control lists (ACLs). You can configure cross-region replication rules for the following scenarios.
Compliance
Although OSS provides a data redundancy mechanism for every stored object, some compliance requirements mandate that data copies are stored a minimum distance apart. Cross-region replication lets you replicate data between distant OSS data centers to meet these compliance requirements.
Minimal latency
If you have customers in multiple geographical locations, you can minimize access latency by maintaining object replicas in OSS data centers that are geographically closer to them.
Data backup and disaster recovery
If you have high requirements for data security and availability, you can explicitly maintain a copy of all written data in another data center. This ensures that you can use the backup data from another OSS data center if one data center is destroyed by a major disaster, such as an earthquake or tsunami.
Data migration
You can use cross-region replication to migrate data from one OSS data center to another for business reasons.
Operational reasons
If you have compute clusters in two different data centers that analyze the same set of objects, you can maintain object replicas in both regions.
Features
Cross-region replication provides the following features:
Replication time control (RTC)
After you enable RTC, OSS replicates most of the objects that you upload to OSS within a few seconds and 99.99% of the objects within 10 minutes. RTC also provides real-time monitoring of data replication, allowing you to view various metrics of replication tasks.
Near real-time data replication
Operations such as object creation, deletion, and modification can be replicated to the destination bucket in near real-time.
Data consistency
By default, OSS ensures eventual consistency between the source and destination buckets. However, if you write a file with the same name to the destination bucket during the replication process, OSS cannot guarantee eventual consistency.
Historical data migration
You can replicate new data written to the source bucket after a replication rule is configured. You can also replicate historical data that existed in the bucket before the rule was configured.
Replication progress
You can view the most recent replication time for replicated data. For historical data migration, you can view the migration progress as a percentage.
Versioning
When both the source and destination buckets have versioning enabled, eventual consistency of data versions is guaranteed. If the replication rule is configured to sync write operations (additions and modifications), the deletion of a specific object version in the source bucket is not replicated. However, delete markers created in the source bucket are replicated to the destination bucket.
Transfer acceleration
You can use the transfer acceleration feature to increase the data transfer speed for cross-region replication between regions in the Chinese mainland and regions outside the Chinese mainland. For more information, see Access OSS using transfer acceleration.
Replicate encrypted data
You can replicate unencrypted objects and objects that are encrypted on the server side using SSE-KMS or SSE-OSS. For more information, see Cross-region replication with server-side encryption.
Configure event notifications
You can configure event notification rules by setting the event type to
ObjectReplication:ObjectCreated,ObjectReplication:ObjectRemoved, orObjectReplication:ObjectModified. This lets you receive notifications about changes to objects in the source and destination buckets during data replication, including object creation, updates, deletions, and overwrites. For more information, see Process OSS file changes in real time using event notifications.
Usage notes
Billing
For cross-region replication, OSS charges cross-region replication traffic fees based on the data transfer traffic. For more information, see Cross-region replication traffic fees.
For CRR across accounts, the cross-region replication traffic fees are charged to the account that owns the source bucket.
For each object that is successfully replicated, OSS counts the operation as one request and charges a request fee. For more information, see Request fees.
If you enable transfer acceleration, you are charged additional transfer acceleration fees for the destination bucket. These fees are charged to the account that owns the destination bucket. For more information, see Transfer acceleration fees.
If you enable replication time control (RTC), you are charged additional cross-region replication RTC fees. For more information, see Cross-region replication RTC fees.
When you use cross-region replication to copy Infrequent Access or Archive objects from a source bucket to a destination bucket, no data retrieval operations are performed and no data retrieval fees are charged.
Replication time
Cross-region data replication is an asynchronous (near real-time) process. The time required to transfer data from the source bucket to the destination bucket can range from a few minutes to several hours, depending on the amount of data. If replication takes an excessive amount of time, check whether the delay is caused by bandwidth limitations. If the delay is caused by bandwidth limitations, you can submit a ticket to request a bandwidth increase and improve replication efficiency.
In the OSS console, go to the tab. In the Used Bandwidth section, view the Cross-Region Replication Inbound data. This metric indicates the bandwidth used for data flowing into the destination bucket during cross-region replication. For more information, see Record the bandwidth usage of a bucket over different periods.
Risk of overwriting objects with the same name
If two buckets are in a replication relationship, you can perform operations on both buckets simultaneously. As a result, an object replicated from the source bucket might overwrite an object with the same name in the destination bucket.
Limits
Region restrictions
When you configure cross-region replication between a region in the Chinese mainland and a region outside the Chinese mainland, you must enable transfer acceleration.
Number of rules
Data in a source bucket can be replicated to multiple destination buckets. A single bucket can be associated with a maximum of 100 replication rules. In these rules, the bucket can serve as either a source bucket or a destination bucket.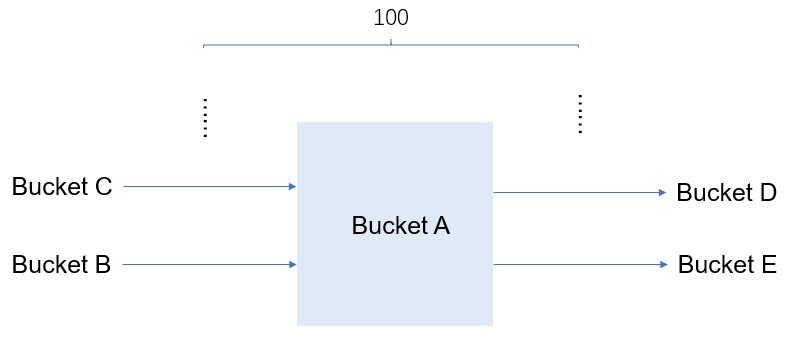
If your business scenario requires a larger number of replication rules, contact technical support.
Operation restrictions
The source and destination buckets must have the same versioning status. They must both be either unversioned or have versioning enabled. You cannot configure data replication rules for buckets with versioning suspended.
You cannot change the versioning status of two buckets that are in a replication relationship.
If two buckets are in a replication relationship, you can perform operations on both buckets simultaneously. As a result, an object replicated from the source bucket might overwrite an object with the same name in the destination bucket.
Data in a source bucket can be replicated to multiple destination buckets. A single bucket can be associated with a maximum of 100 replication rules. In these rules, the bucket can serve as either a source bucket or a destination bucket. If your business scenario requires a larger number of replication rules, contact technical support.
You cannot replicate Cold Archive or Deep Cold Archive objects from a source bucket to a destination bucket, regardless of whether the objects have been restored.
You cannot replicate appendable objects from a source bucket to a destination bucket whose storage class is Cold Archive or Deep Cold Archive.