You can use the real-time log query feature of Simple Log Service (SLS) to analyze OSS access logs and hourly metering logs. This lets you monitor and optimize OSS usage, identify and analyze issues, and improve storage and access efficiency. This topic provides common examples of real-time log queries.
Analyze outbound traffic over Internet for files in an OSS folder
OSS usage queries cannot be scoped to a specific folder. To calculate the outbound traffic over the Internet for files in a folder, you can analyze the OSS access logs. In the logs, filter by the public endpoint using the host field, exclude CDN origin requests using the sync_request field, and match files using the object field prefix. Finally, sum the values in the response_body_length field to obtain the total traffic.
Query statement
Calculate the total outbound traffic over the Internet for all files in the exampledir folder of the examplebucket bucket.
* and __topic__ : oss_access_log and bucket: examplebucket and host : "examplebucket.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com" not sync_request : cdn | select
SUM(response_body_length) AS total_traffic_out_byte
WHERE
url_decode(object) LIKE 'exampledir/%'Query results
The host field in a request can be forged, so the query results are only estimates. Refer to your bill for the actual costs of outbound traffic over the Internet from OSS.
The total outbound traffic over the Internet for all files in the exampledir folder of the examplebucket bucket is 11749 bytes.

Analyze file size changes in an OSS folder
OSS usage queries show the size changes for all files in a bucket, but not for a specific folder. To analyze file size changes in a specific folder, you can match the object field prefix in OSS access logs to identify the files in the folder. Then, you can calculate the sum of the values in the delta_data_size field to obtain the total size change for all files in that folder.
Query statement
Calculate the file size changes in the exampledir folder of the examplebucket bucket.
* and __topic__ : oss_access_log and bucket: examplebucket | select
SUM(delta_data_size) AS total_delta_data_size
WHERE
url_decode(object) LIKE 'exampledir/%'Query results
The file size in the exampledir folder of the examplebucket bucket increased by 941 bytes.

Analyze OSS internet requests that are not accelerated by CDN
After you enable CDN acceleration, a significant number of OSS Internet requests may still occur. This indicates that resource URLs in your application still point to the OSS source instead of the CDN-accelerated domain name. To identify these non-accelerated requests, you can analyze the OSS access logs. Use the host field to filter for OSS public endpoints and the sync_request field to exclude CDN origin requests. You can also use the referer field to determine the source webpage or application of these requests.
Query statement
Analyze the OSS Internet requests for the examplebucket bucket that are not accelerated by CDN.
* and __topic__: oss_access_log and bucket: examplebucket and host : "examplebucket.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com" not sync_request: cdn | select
referer,
host,
count(*) as request_count
group by
referer,
host
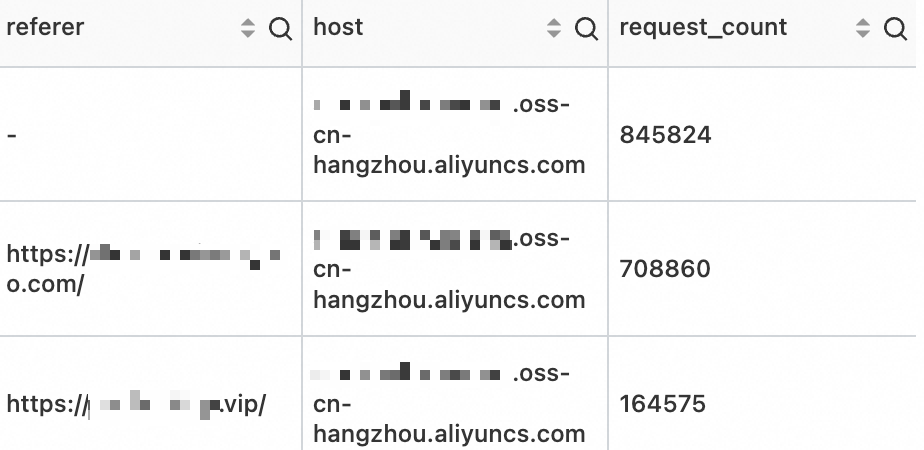
order by request_count descQuery results
The host field in a request can be forged, so the query results are only estimates. Refer to your bill for the actual costs of outbound traffic over the Internet from OSS.
The results for non-accelerated OSS Internet requests for the examplebucket bucket show the top three sources of traffic. The sources include requests with an empty `Referer` field, which may occur when users enter the URL directly in a browser, and requests from websites with domain names that end in .com and .vip.
Query batch delete records for files
You can query records of batch file deletions in OSS using real-time log queries. The information about the deleted files is stored in the HTTP request body. You can use the Request ID to query for the associated records.
Method 1: Known Request ID
To run the query, replace bucketname and request_id in the following SQL statement:
* and __topic__: oss_batch_delete_log and operation : DeleteObjects and bucket: bucketname | select from_unixtime( __time__) as Time,url_decode(object) as objectname,user_agent where request_id = '68xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx'
Method 2: Unknown Request ID
If you do not have the Request ID, follow these steps to query:
Locate the Request ID using information such as the file name or the time of the batch deletion. For example, to run the query, replace
bucketnameand the file name in the following SQL statement:* and __topic__: oss_batch_delete_log and bucket: bucketname | select request_id where url_decode(object) = 'test/001.bin'
After you obtain the Request ID, you can use the SQL statement from Method 1 to query the complete batch deletion records.