Security Token Service (STS) lets you grant time-limited access to data stored on Object Storage Service (OSS) by using temporary credentials. After the temporary credentials expire, they can no longer be used to access the data. This provides flexible, time-bound access control.
Use case
An e-commerce enterprise stores a large amount of its product data on OSS. A supplier of the enterprise needs to regularly upload data from its own business system to an OSS bucket of the enterprise.
The enterprise has the following information security and compliance requirements:
Data security: To prevent unauthorized access to its core business data, the enterprise does not want to expose its OSS AccessKey pair to the supplier.
Permission control: The enterprise requires granular permission control. Specifically, it wants to authorize the supplier for data uploads and can dynamically adjust these permissions as requirements change.
Permission management: The enterprise wants to flexibly generate access credentials for the supplier and future partners, without managing long-term credentials.
Time-limited access: The enterprise wants to grant time-limited access to the supplier. When the specified period of time elapses, the supplier is denied access to the data.
How it works
The enterprise authorizes the supplier to temporarily upload files to the OSS bucket.

The enterprise begins by creating a Resource Access Management (RAM) user and a RAM role, and then grants the necessary permissions. The supplier requests temporary credentials from the enterprise, which calls the AssumeRole operation to generate temporary credentials and returns the temporary credentials to the supplier. The supplier uses the temporary credentials to upload data to the OSS bucket owned by the enterprise.
Prerequisites
The enterprise has an existing OSS bucket. For more information, see Create buckets.
Step 1: Generation of temporary credentials by the enterprise
1. Create a RAM user
An Alibaba Cloud account owner or a RAM user with administrative privileges can create a RAM user.
Log on to the RAM console.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose Identities > Users.
On the Users page, click Create User.
Specify a Logon Name and Display Name.
In the Access Mode section, select Using permanent AccessKey to access and click OK.
Follow the on-screen instructions to complete security verification.
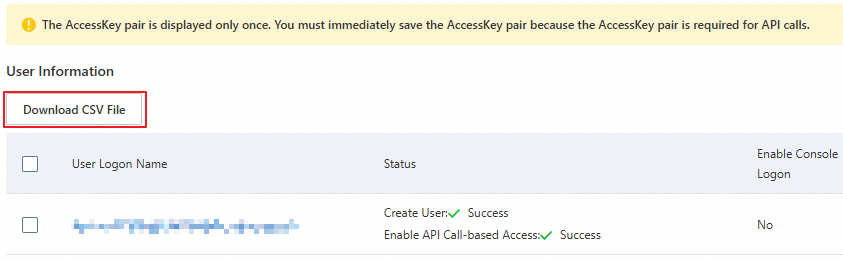
Copy the AccessKey pair (AccessKey ID and AccessKey secret) and paste it into a securely stored local file.
ImportantYou can obtain the AccessKey secret of a RAM user only when you create the RAM user. Download the CSV file that contains the AccessKey pair to a safe location on your device.
2. Authorize the RAM user to call the AssumeRole operation
The enterprise then uses the Alibaba Cloud account or RAM user that has RAM administration privileges to grant the created RAM user the permission to call the AssumeRole operation.
Log on to the RAM console.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose Identities > Users. Find the RAM user that you created earlier and click Add Permissions in the Actions column.
In the Policy section of the Grant Permission panel, select the AliyunSTSAssumeRoleAccess policy.
NoteThe AliyunSTSAssumeRoleAccess policy allows a RAM user to call the AssumeRole operation. The policy does not grant the permissions required by the RAM user to obtain temporary credentials from STS and initiate requests to OSS.
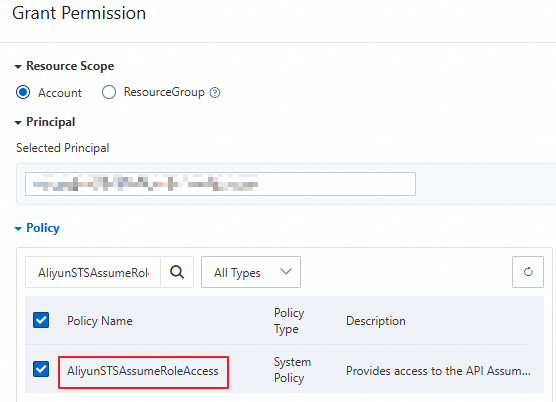
Click Grant permissions.
3. Create a RAM role
The enterprise uses its Alibaba Cloud account or a RAM user that has RAM administration privileges to create a RAM role by following the steps below:
Log on to the RAM console.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose Identities > Roles.
On the Roles page, click Create Role.
On the Create Role page, select Cloud Account for Principal Type, select Current Account for Principal Name, and click OK.
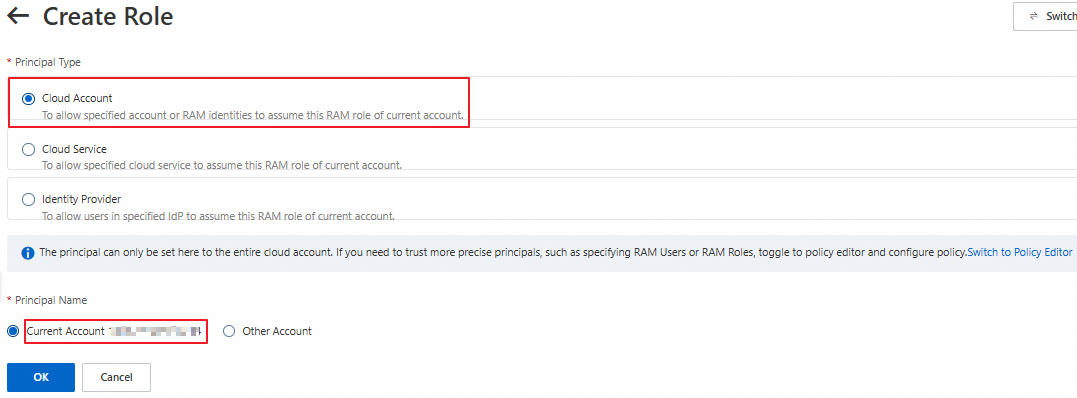
In the Create Role dialog box, specify a role name and click OK.
On the role details page that appears, click Copy next to the ARN field in the Basic Information section.

4. Grant the RAM role the permissions to upload objects to OSS
To grant the RAM role access to OSS, the enterprise needs to attach one or more policies to the RAM role by using the Alibaba Cloud account or as a RAM user that has RAM administration privileges. For example, the RAM role needs OSS write permissions to upload data to the specified bucket.
Create a custom policy to grant the role the permissions to upload objects.
Log on to the RAM console.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose Permissions > Policies.
On the Policies page, click Create Policy.
On the Create Policy page, click JSON. In the code editor, enter the permissions to upload data to the specified bucket. The following script provides an example policy:
WarningThe following example is provided for reference only. You need to configure fine-grained RAM policies based on your requirements to avoid granting excessive permissions. For more information about how to configure fine-grained RAM policies, see Example 9: Use RAM or STS to authorize users to access OSS resources.
{ "Version": "1", "Statement": [ { "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "oss:PutObject" ], "Resource": [ "acs:oss:*:*:examplebucket/*" ] } ] }NoteThe Action element specifies the permissions that you want to grant to the RAM role. For example, if you specify oss:PutObject, the RAM user that assumes the RAM role can upload objects to the specified bucket by using various upload methods, such as simple upload, form upload, append upload, multipart upload, and resumable upload. For more information, see Action element in RAM policies for OSS.
Click OK. In the Create Policy dialog box, specify a policy name in the Policy Name field (RamTestPolicy in this example), and click OK.
Attach the custom policy to the RamOssTest role to grant the permissions.
Log on to the RAM console.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose Identities > Roles.
On the Roles page, find the RamOssTest role.
Click Grant Permission in the Actions column.
In the Policy section of the Grant Permission page, select Custom Policy from the type drop-down list, and select the custom policy RamTestPolicy.
Click Grant permissions.
5. Use the RAM user to assume the RAM role to generate temporary credentials
Calling the STS API with an Alibaba Cloud account's AccessKey pair will fail. You must use a RAM user's AccessKey pair. The following sample code uses the AccessKey pair of a RAM user to request temporary credentials.
The RAM user that was created earlier assumes the RAM role to obtain temporary credentials. temporary credentials include an STS token (SecurityToken), temporary AccessKey pair (AccessKey ID and AccessKey secret), and validity period (Expiration). The following sample code generates temporary credentials that provide the
oss:PutObjectpermission required for simple uploads. For more information about how to use STS SDKs for other programming languages to generate temporary credentials, see STS SDK overview.The endpoint in the sample code specifies an STS endpoint. An STS endpoint located in the same region as or near to the application server can enhance STS response speeds. For information about STS endpoints, see Endpoints.
Java
import com.aliyuncs.DefaultAcsClient;
import com.aliyuncs.exceptions.ClientException;
import com.aliyuncs.http.MethodType;
import com.aliyuncs.profile.DefaultProfile;
import com.aliyuncs.profile.IClientProfile;
import com.aliyuncs.auth.sts.AssumeRoleRequest;
import com.aliyuncs.auth.sts.AssumeRoleResponse;
public class StsServiceSample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Specify an STS endpoint. Example: sts.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com. You can access STS over the Internet or a virtual private cloud (VPC).
String endpoint = "sts.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com";
// Obtain the AccessKey ID and AccessKey secret of the RAM user generated in Step 1.1 from environment variables.
String accessKeyId = System.getenv("ACCESS_KEY_ID");
String accessKeySecret = System.getenv("ACCESS_KEY_SECRET");
// Obtain the ARN of the RAM role generated in Step 1.3 from environment variables.
String roleArn = System.getenv("RAM_ROLE_ARN");
// Specify a custom role session name to distinguish different tokens. Example: SessionTest.
String roleSessionName = "yourRoleSessionName";
// Specify that the temporary credentials have all permissions of the RAM role.
String policy = null;
// Specify the validity period of the temporary credentials. Unit: seconds. The minimum validity period is 900 seconds. The maximum validity period is the same as the maximum session duration specified for the current role. The maximum session duration of the current role ranges from 3,600 to 43,200 seconds. The default maximum session duration of the current role is 3,600 seconds.
// In large object upload or other time-consuming use cases, set a proper validity period to avoid having to repeatedly call the STS API operation to obtain temporary credentials before the task is complete.
Long durationSeconds = 3600L;
try {
// Specify the region of STS. Keep the default value. The default value is an empty string ("").
String regionId = "";
// Specify the endpoint. The following line applies to STS SDK for Java V3.12.0 and later.
DefaultProfile.addEndpoint(regionId, "Sts", endpoint);
// Specify the endpoint. The following line applies to STS SDK for Java versions earlier than V3.12.0.
// DefaultProfile.addEndpoint("",regionId, "Sts", endpoint);
// Create a default profile.
IClientProfile profile = DefaultProfile.getProfile(regionId, accessKeyId, accessKeySecret);
// Use the profile to create a client.
DefaultAcsClient client = new DefaultAcsClient(profile);
final AssumeRoleRequest request = new AssumeRoleRequest();
// The following line applies to STS SDK for Java V3.12.0 and later.
request.setSysMethod(MethodType.POST);
// The following line applies to STS SDK for Java versions earlier than V3.12.0.
// request.setMethod(MethodType.POST);
request.setRoleArn(roleArn);
request.setRoleSessionName(roleSessionName);
request.setPolicy(policy);
request.setDurationSeconds(durationSeconds);
final AssumeRoleResponse response = client.getAcsResponse(request);
System.out.println("Expiration: " + response.getCredentials().getExpiration());
System.out.println("Access Key Id: " + response.getCredentials().getAccessKeyId());
System.out.println("Access Key Secret: " + response.getCredentials().getAccessKeySecret());
System.out.println("Security Token: " + response.getCredentials().getSecurityToken());
System.out.println("RequestId: " + response.getRequestId());
} catch (ClientException e) {
System.out.println("Failed: ");
System.out.println("Error code: " + e.getErrCode());
System.out.println("Error message: " + e.getErrMsg());
System.out.println("RequestId: " + e.getRequestId());
}
}
}Python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from aliyunsdkcore import client
from aliyunsdkcore.request import CommonRequest
import json
import oss2
import os
# Obtain the AccessKey ID and AccessKey secret of the RAM user generated in Step 1.1 from environment variables.
access_key_id = os.getenv("ACCESS_KEY_ID")
access_key_secret = os.getenv("ACCESS_KEY_SECRET")
# Obtain the ARN of the RAM role generated in Step 1.3 from environment variables.
role_arn = os.getenv("RAM_ROLE_ARN")
# Create a policy.
clt = client.AcsClient(access_key_id, access_key_secret, 'cn-hangzhou')
request = CommonRequest(product="Sts", version='2015-04-01', action_name='AssumeRole')
request.set_method('POST')
request.set_protocol_type('https')
request.add_query_param('RoleArn', role_arn)
# Specify a custom role session name to distinguish different tokens. Example: sessiontest.
request.add_query_param('RoleSessionName', 'sessiontest')
# Set the validity period of temporary credentials to 3,600 seconds.
request.add_query_param('DurationSeconds', '3600')
request.set_accept_format('JSON')
body = clt.do_action_with_exception(request)
# Use the AccessKey pair of the RAM user to apply for temporary credentials from STS.
token = json.loads(oss2.to_unicode(body))
# Display the AccessKey ID, the AccessKey secret, the security token, and the expiration time of the temporary credentials returned by STS.
print('AccessKeyId: ' + token['Credentials']['AccessKeyId'])
print('AccessKeySecret: ' + token['Credentials']['AccessKeySecret'])
print('SecurityToken: ' + token['Credentials']['SecurityToken'])
print('Expiration: ' + token['Credentials']['Expiration'])Node.js
const { STS } = require('ali-oss');
const express = require("express");
const app = express();
app.get('/sts', (req, res) => {
let sts = new STS({
// Obtain the AccessKey ID and AccessKey secret of the RAM user generated in Step 1.1 from environment variables.
accessKeyId : process.env.ACCESS_KEY_ID,
accessKeySecret : process.env.ACCESS_KEY_SECRET
});
// Get the RAM Role ARN from environment variables (created in Step 1.3).
// Specify a custom policy to limit the permissions of the temporary credentials. If you do not specify a custom policy, the temporary credentials have full permissions of the specified RAM role.
// The permissions obtained by the temporary credentials are the intersection of the role permissions configured in Step 4 and the permissions specified by the custom RAM policy.
// Specify the validity period of the temporary credentials. Unit: seconds. The minimum validity period of the temporary credentials is 900 seconds. The maximum validity period of the temporary credentials is the maximum session duration specified for the current role. In this example, the validity period is set to 3,600 seconds.
// Specify a custom role session name to distinguish different tokens. Example: sessiontest.
sts.assumeRole('process.env.RAM_ROLE_ARN', ``, '3600', 'sessiontest').then((result) => {
console.log(result);
res.set('Access-Control-Allow-Origin', '*');
res.set('Access-Control-Allow-METHOD', 'GET');
res.json({
AccessKeyId: result.credentials.AccessKeyId,
AccessKeySecret: result.credentials.AccessKeySecret,
SecurityToken: result.credentials.SecurityToken,
Expiration: result.credentials.Expiration
});
}).catch((err) => {
console.log(err);
res.status(400).json(err.message);
});
});
app.listen(8000,()=>{
console.log("server listen on:8000")
})Go
package main
import (
"fmt"
"os"
openapi "github.com/alibabacloud-go/darabonba-openapi/v2/client"
sts20150401 "github.com/alibabacloud-go/sts-20150401/v2/client"
util "github.com/alibabacloud-go/tea-utils/v2/service"
"github.com/alibabacloud-go/tea/tea"
)
func main() {
// Obtain the AccessKey ID and AccessKey secret of the RAM user generated in Step 1.1 from environment variables.
accessKeyId := os.Getenv("ACCESS_KEY_ID")
accessKeySecret := os.Getenv("ACCESS_KEY_SECRET")
// Obtain the ARN of the RAM role generated in Step 1.3 from environment variables.
roleArn := os.Getenv("RAM_ROLE_ARN")
// Create a client.
config := &openapi.Config{
// Provide the AccessKey ID obtained in Step 1.1.
AccessKeyId: tea.String(accessKeyId),
// Provide the AccessKey secret obtained in Step 1.1.
AccessKeySecret: tea.String(accessKeySecret),
}
// Specify the endpoint of the region in which the bucket is located. For more information, visit https://api.alibabacloud.com/product/Sts.
config.Endpoint = tea.String("sts.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com")
client, err := sts20150401.NewClient(config)
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Failed to create client: %v\n", err)
return
}
// Use the AccessKey pair of the RAM user to apply for temporary credentials from STS.
request := &sts20150401.AssumeRoleRequest{
// Set the validity period of temporary credentials to 3,600 seconds.
DurationSeconds: tea.Int64(3600),
// Obtain the ARN of the RAM role generated in Step 1.3 from environment variables.
RoleArn: tea.String(roleArn),
// Specify a custom session name.
RoleSessionName: tea.String("examplename"),
}
response, err := client.AssumeRoleWithOptions(request, &util.RuntimeOptions{})
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Failed to assume role: %v\n", err)
return
}
// Display the AccessKey ID, the AccessKey secret, the security token, and the expiration time of the temporary credentials returned by STS.
credentials := response.Body.Credentials
fmt.Println("AccessKeyId: " + tea.StringValue(credentials.AccessKeyId))
fmt.Println("AccessKeySecret: " + tea.StringValue(credentials.AccessKeySecret))
fmt.Println("SecurityToken: " + tea.StringValue(credentials.SecurityToken))
fmt.Println("Expiration: " + tea.StringValue(credentials.Expiration))
}php
<?php
require __DIR__ . '/vendor/autoload.php';
use AlibabaCloud\Client\AlibabaCloud;
use AlibabaCloud\Client\Exception\ClientException;
use AlibabaCloud\Client\Exception\ServerException;
use AlibabaCloud\Sts\Sts;
// Obtain the AccessKey ID and AccessKey secret of the RAM user generated in Step 1.1 from environment variables.
$accessKeyId = getenv("ACCESS_KEY_ID");
$accessKeySecret = getenv("ACCESS_KEY_SECRET");
// Obtain the ARN of the RAM role generated in Step 1.3 from environment variables.
$roleArn = getenv("RAM_ROLE_ARN");
// Initialize the Alibaba Cloud client.
AlibabaCloud::accessKeyClient($accessKeyId, $accessKeySecret)
->regionId('cn-hangzhou')
->asDefaultClient();
try {
// Create a request to obtain temporary credentials from STS.
$result = Sts::v20150401()
->assumeRole()
// Specify the role ARN.
->withRoleArn($roleArn)
// Specify a custom session name for the role to distinguish different tokens.
->withRoleSessionName('sessiontest')
// Set the validity period of temporary credentials to 3,600 seconds.
->withDurationSeconds(3600)
->request();
// Display the credential information in the response.
$credentials = $result['Credentials'];
// Display the AccessKey ID, the AccessKey secret, the security token, and the expiration time of the temporary credentials returned by STS.
echo 'AccessKeyId: ' . $credentials['AccessKeyId'] . PHP_EOL;
echo 'AccessKeySecret: ' . $credentials['AccessKeySecret'] . PHP_EOL;
echo 'SecurityToken: ' . $credentials['SecurityToken'] . PHP_EOL;
echo 'Expiration: ' . $credentials['Expiration'] . PHP_EOL;
} catch (ClientException $e) {
// Handle client exceptions.
echo $e->getErrorMessage() . PHP_EOL;
} catch (ServerException $e) {
// Handle server exceptions.
echo $e->getErrorMessage() . PHP_EOL;
}Ruby
require 'sinatra'
require 'base64'
require 'open-uri'
require 'cgi'
require 'openssl'
require 'json'
require 'sinatra/reloader'
require 'sinatra/content_for'
require 'aliyunsdkcore'
# Set the path of the public-folder folder to the templates subfolder within the current folder.
set :public_folder, File.dirname(__FILE__) + '/templates'
def get_sts_token_for_oss_upload()
client = RPCClient.new(
# Obtain the AccessKey ID and AccessKey secret of the RAM user generated in Step 1.1 from environment variables.
access_key_id: ENV['ACCESS_KEY_ID'],
access_key_secret: ENV['ACCESS_KEY_SECRET'],
endpoint: 'https://sts.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com',
api_version: '2015-04-01'
)
response = client.request(
action: 'AssumeRole',
params: {
# Obtain the ARN of the RAM role generated in Step 1.3 from environment variables.
"RoleArn": ENV['RAM_ROLE_ARN'],
# Set the validity period of temporary credentials to 3,600 seconds.
"DurationSeconds": 3600,
# Specify a custom role session name, which is used to distinguish different tokens. Example: sessiontest.
"RoleSessionName": "sessiontest"
},
opts: {
method: 'POST',
format_params: true
}
)
end
if ARGV.length == 1
$server_port = ARGV[0]
elsif ARGV.length == 2
$server_ip = ARGV[0]
$server_port = ARGV[1]
end
$server_ip = "127.0.0.1" # To listen to another IP address, such as 0.0.0.0, implement your authentication mechanism on the server side.
$server_port = 8000
puts "App server is running on: http://#{$server_ip}:#{$server_port}"
set :bind, $server_ip
set :port, $server_port
get '/get_sts_token_for_oss_upload' do
token = get_sts_token_for_oss_upload()
response = {
"AccessKeyId" => token["Credentials"]["AccessKeyId"],
"AccessKeySecret" => token["Credentials"]["AccessKeySecret"],
"SecurityToken" => token["Credentials"]["SecurityToken"],
"Expiration" => token["Credentials"]["Expiration"]
}
response.to_json
end
get '/*' do
puts "********************* GET "
send_file File.join(settings.public_folder, 'index.html')
endExamples of temporary credentials
NoteAn Alibaba Cloud account, along with its RAM users and RAM roles, can send up to 100 requests per second (RPS) to STS to request temporary credentials. Reuse temporary credentials in high concurrency use cases.
The temporary credential's expiration time is in UTC format. For example, if the expiration time is 2024-04-18T11:33:40Z, the temporary credentials expire on April 18, 2024, at 19:33:40 (UTC+8).
{ "AccessKeyId": "STS.****************", "AccessKeySecret": "3dZn*******************************************", "SecurityToken": "CAIS*****************************************************************************************************************************************", "Expiration": "2024-**-*****:**:50Z" }
Fine-grained permissions for temporary credentials
After temporary credentials obtain permissions from a RAM role, you can further limit the permissions of the temporary credentials. For example, if the temporary credentials have the permissions to upload objects to the examplebucket bucket, specify that the access credentials can be used to upload data only to a specific directory in the bucket. The following sample code limits the permissions of the temporary credentials.
// The following policy specifies that the temporary credentials can be used to upload objects only to the src directory of the examplebucket bucket. // The final permissions granted to the temporary credentials are the intersection of the role permissions that are specified in Step 4 and the permissions that are specified in the policy. This allows data uploads only to the src directory in the examplebucket bucket. String policy = "{\n" + " \"Version\": \"1\", \n" + " \"Statement\": [\n" + " {\n" + " \"Action\": [\n" + " \"oss:PutObject\"\n" + " ], \n" + " \"Resource\": [\n" + " \"acs:oss:*:*:examplebucket/src/*\" \n" + " ], \n" + " \"Effect\": \"Allow\"\n" + " }\n" + " ]\n" + "}";
Step 2: Data upload by the supplier using the temporary credentials
Due to a policy change to improve compliance and security, starting March 20, 2025, new OSS users must use a custom domain name (CNAME) to perform data API operations on OSS buckets located in Chinese mainland regions. Default public endpoints are restricted for these operations. Refer to the official announcement for a complete list of the affected operations. If you access your data via HTTPS, you must bind a valid SSL Certificate to your custom domain. This is mandatory for OSS Console access, as the console enforces HTTPS.
The following sample code shows how to upload data using the temporary credentials. For information about how to upload data to OSS based on temporary credentials by using OSS SDKs for other programming languages, see Overview.
Java
import com.aliyun.oss.*;
import com.aliyun.oss.common.auth.CredentialsProvider;
import com.aliyun.oss.common.auth.DefaultCredentialProvider;
import com.aliyun.oss.common.comm.SignVersion;
import com.aliyun.oss.model.PutObjectRequest;
import com.aliyun.oss.model.PutObjectResult;
import java.io.File;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// Specify the temporary AccessKey ID, AccessKey secret and STS token generated in step 1.5. Do not use the credentials of a RAM user.
// Take note that the AccessKey ID provided by STS starts with STS.
String accessKeyId = "yourSTSAccessKeyID";
String accessKeySecret = "yourSTSAccessKeySecret";
// Specify the security token obtained from STS.
String stsToken= "yourSecurityToken";
// Pass the AccessKey ID and secret to DefaultCredentialProvider to initialize the credential provider.
CredentialsProvider credentialsProvider = new DefaultCredentialProvider(accessKeyId, accessKeySecret, stsToken);
// Use credentialsProvider to initialize the client.
ClientBuilderConfiguration clientBuilderConfiguration = new ClientBuilderConfiguration();
// Explicitly declare the use of the V4 signature algorithm.
clientBuilderConfiguration.setSignatureVersion(SignVersion.V4);
// Create an OSSClient instance.
// Call the shutdown method to release resources when the OSSClient is no longer in use.
OSS ossClient = OSSClientBuilder.create()
// Specify the endpoint of the region in which the bucket is located. For example, if the bucket is located in the China (Hangzhou) region, set the endpoint to https://oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com.
.endpoint("endpoint")
.credentialsProvider(credentialsProvider)
.clientConfiguration(clientBuilderConfiguration)
// Specify the region ID. Example: cn-hangzhou.
.region("region")
.build();
try {
// Create a PutObjectRequest object. Upload the local file exampletest.txt to examplebucket.
PutObjectRequest putObjectRequest = new PutObjectRequest("examplebucket", "exampletest.txt", new File("D:\\localpath\\exampletest.txt"));
// Optional. Specify the storage class and ACL of the object.
// ObjectMetadata metadata = new ObjectMetadata();
// metadata.setHeader(OSSHeaders.OSS_STORAGE_CLASS, StorageClass.Standard.toString());
// metadata.setObjectAcl(CannedAccessControlList.Private);
// putObjectRequest.setMetadata(metadata);
// Upload the object.
PutObjectResult result = ossClient.putObject(putObjectRequest);
} catch (OSSException oe) {
System.out.println("Caught an OSSException, which means your request made it to OSS, "
+ "but was rejected with an error response for some reason.");
System.out.println("Error Message:" + oe.getErrorMessage());
System.out.println("Error Code:" + oe.getErrorCode());
System.out.println("Request ID:" + oe.getRequestId());
System.out.println("Host ID:" + oe.getHostId());
} catch (ClientException ce) {
System.out.println("Caught an ClientException, which means the client encountered "
+ "a serious internal problem while trying to communicate with OSS, "
+ "such as not being able to access the network.");
System.out.println("Error Message:" + ce.getMessage());
} finally {
if (ossClient != null) {
ossClient.shutdown();
}
}
}
}
Python
OSS SDK for Python is available in 2 versions, 2.0 and 1.0. OSS SDK for Python 2.0 is a complete refactoring of 1.0, streamlining core operations such as authentication, request retries, and error handling. It offers more flexible parameter configurations and introduces new advanced features. The following examples are provided to help you implement OSS SDK for Python based on your actual requirements.
OSS SDK for Python 2.0
import alibabacloud_oss_v2 as oss
def main():
# Specify the temporary AccessKey ID, AccessKey secret and STS token generated in step 1.5. Do not use the credentials of a RAM user.
# Take note that the AccessKey ID provided by STS starts with STS.
sts_access_key_id = 'yourSTSAccessKeyID'
sts_access_key_secret = 'yourSTSAccessKeySecret'
# Specify the STS token obtained from STS.
sts_security_token = 'yourSecurityToken'
# Create a static credential provider and explicitly specify the AccessKey ID, AccessKey secret, and STS token provided by STS.
credentials_provider = oss.credentials.StaticCredentialsProvider(
access_key_id=sts_access_key_id,
access_key_secret=sts_access_key_secret,
security_token=sts_security_token,
)
# Load the default configuration of the SDK and specify the credential provider.
cfg = oss.config.load_default()
cfg.credentials_provider = credentials_provider
# Specify the region in which the bucket is located. For example, if the bucket is located in the China (Hangzhou) region, set the region to cn-hangzhou.
cfg.region = 'cn-hangzhou'
# Use the preceding configurations to create an OSSClient instance.
client = oss.Client(cfg)
# Specify the full path of the local object that you want to upload. Example: D:\\localpath\\exampletest.txt.
local_file_path = 'D:\\localpath\\exampletest.txt'
with open(local_file_path, 'rb') as file:
data = file.read()
# Execute the request to upload exampletest.txt to examplebucket.
result = client.put_object(oss.PutObjectRequest(
# Name of the bucket.
bucket='examplebucket',
# Name of the object to upload.
key='exampletest.txt',
body=data,
))
# Display the HTTP status code, request ID, MD5 hash, ETag, CRC-64 value, and object version ID to check whether the request is successful.
print(f'status code: {result.status_code},'
f' request id: {result.request_id},'
f' content md5: {result.content_md5},'
f' etag: {result.etag},'
f' hash crc64: {result.hash_crc64},'
f' version id: {result.version_id},'
)
# Call the main function when the script is directly run.
if __name__ == "__main__":
main() # The entry point of the script. When the script is directly run, the main function is called.OSS SDK for Python 1.0
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import oss2
# Specify the endpoint of the region in which the bucket is located. For example, if the bucket is located in the China (Hangzhou) region, set the endpoint to https://oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com.
endpoint = 'https://oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com'
# Specify the temporary AccessKey ID and AccessKey secret that were generated in step 1.5. Do not use the AccessKey ID and AccessKey secret of an Alibaba Cloud account.
sts_access_key_id = 'yourAccessKeyId'
sts_access_key_secret = 'yourAccessKeySecret'
# Specify the name of the bucket.
bucket_name = 'examplebucket'
# Specify the full path of the object by using a string. Do not include the bucket name in the full path.
object_name = 'examplebt.txt'
# Enter the STS token generated in Step 1.5.
security_token = 'yourSecurityToken'
# Initialize the StsAuth instance by using the temporary credentials.
auth = oss2.StsAuth(sts_access_key_id,
sts_access_key_secret,
security_token)
# Initialize the bucket by using the StsAuth instance.
bucket = oss2.Bucket(auth, endpoint, bucket_name)
# Upload the object.
result = bucket.put_object(object_name, "hello world")
print(result.status)Go
OSS SDK for Go is available in 2 versions, 2.0 and 1.0. OSS SDK for Go 2.0 is a complete refactoring of 1.0, streamlining core operations such as authentication, request retries, and error handling. It offers more flexible parameter configurations and introduces new advanced features. The following examples are provided to help you implement OSS SDK for Go based on your actual requirements.
OSS SDK for Go 2.0
package main
import (
"context"
"log"
"github.com/aliyun/alibabacloud-oss-go-sdk-v2/oss"
"github.com/aliyun/alibabacloud-oss-go-sdk-v2/oss/credentials"
)
func main() {
// Specify the region in which the bucket is located. For example, if the bucket is located in the China (Hangzhou) region, set the region to cn-hangzhou.
region := "cn-hangzhou"
// Specify the temporary AccessKey ID, AccessKey secret and STS token generated in step 1.5. Do not use the credentials of a RAM user.
// Take note that the AccessKey ID provided by STS starts with STS.
accessKeyID := "yourSTSAccessKeyID"
accessKeySecret := "yourSTSAccessKeySecret"
// Specify the STS token obtained from STS.
stsToken := "yourSecurityToken"
// Use the NewStaticCredentialsProvider method to specify the AccessKey ID, AccessKey secret and STS Token.
provider := credentials.NewStaticCredentialsProvider(accessKeyID, accessKeySecret, stsToken)
// Load the default configuration of the SDK and specify the credential provider and region.
cfg := oss.LoadDefaultConfig().
WithCredentialsProvider(provider).
WithRegion(region)
// Create an OSS client.
client := oss.NewClient(cfg)
// Specify the path of the local file that you want to upload. Example: D:\\localpath\\exampletest.txt.
localFile := "D:\\localpath\\exampletest.txt"
// Create a request to upload an object.
putRequest := &oss.PutObjectRequest{
Bucket: oss.Ptr("examplebucket"), // Name of the bucket.
Key: oss.Ptr("exampletest.txt"), // name of the obejct to upload.
StorageClass: oss.StorageClassStandard, // Set the storage class of the object to Standard.
Acl: oss.ObjectACLPrivate, // Set the ACL of the object to private.
Metadata: map[string]string{
"yourMetadataKey1": "yourMetadataValue1", // Configure the metadata of the object.
},
}
// Execute the request to upload exampletest.txt to examplebucket.
result, err := client.PutObjectFromFile(context.TODO(), putRequest, localFile)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("failed to put object from file %v", err)
}
// Display the result of the object upload.
log.Printf("put object from file result:%#v\n", result)
}OSS SDK for Go 1.0
package main
import (
"fmt""github.com/aliyun/aliyun-oss-go-sdk/oss""os"
)
func main() {
// Obtain the temporary credentials from the environment variables. Before you run the sample code, make sure that the OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID, OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET, and OSS_SESSION_TOKEN environment variables are configured.
provider, err := oss.NewEnvironmentVariableCredentialsProvider()
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error:", err)
os.Exit(-1)
}
// Create an OSSClient instance. // Specify the endpoint of the region in which the bucket is located. For example, if the bucket is located in the China (Hangzhou) region, set the endpoint to https://oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com. Specify your actual endpoint.
client, err := oss.New("yourEndpoint", "", "", oss.SetCredentialsProvider(&provider))
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error:", err)
os.Exit(-1)
}
// Specify the name of the bucket. Example: examplebucket.
bucketName := "examplebucket"// Specify the full path of the object. Do not include the bucket name in the full path. Example: exampledir/exampleobject.txt.
objectName := "exampledir/exampleobject.txt"// Specify the full path of the local object. Example: D:\\localpath\\examplefile.txt.
filepath := "D:\\localpath\\examplefile.txt"
bucket,err := client.Bucket(bucketName)
// Upload the local file by using the temporary credentials.
err = bucket.PutObjectFromFile(objectName,filepath)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error:", err)
os.Exit(-1)
}
fmt.Println("upload success")
}Node.js
This sample code requires Axios.
const axios = require("axios");
const OSS = require("ali-oss");
// Use the temporary credentials to initialize an OSSClient instance. The instance is used to authorize temporary access to OSS resources.
const getToken = async () => {
// Specify the address that is used by the client to obtain the temporary credentials.
await axios.get("http://localhost:8000/sts").then((token) => {
const client = new OSS({
// Specify the region in which the bucket is located. For example, if the bucket is located in the China (Hangzhou) region, set the region to oss-cn-hangzhou.
region: 'oss-cn-hangzhou',
// Specify the temporary AccessKey ID, AccessKey secret and STS token generated in step 1.5. Do not use the credentials of a RAM user.
accessKeyId: token.data.AccessKeyId,
accessKeySecret: token.data.AccessKeySecret,
// Enter the STS token generated in Step 1.5.
stsToken: token.data.SecurityToken,
authorizationV4: true,
// Specify the name of the bucket.
bucket: "examplebucket",
// Refresh the temporary credentials.
refreshSTSToken: async () => {
const refreshToken = await axios.get("http://localhost:8000/sts");
return {
accessKeyId: refreshToken.data.AccessKeyId,
accessKeySecret: refreshToken.data.AccessKeySecret,
stsToken: refreshToken.data.SecurityToken,
};
},
});
// Use the temporary credentials to upload an object.
// Specify the full path of the object. Do not include the bucket name in the full path. Example: exampleobject.jpg.
// Specify the full path of the local object. Example: D:\\example.jpg.
client.put('exampleobject.jpg', 'D:\\example.jpg').then((res)=>{console.log(res)}).catch(e=>console.log(e))
});
};
getToken()php
<?php
if (is_file(__DIR__ . 'autoload.php')) {
require_once __DIR__ . 'autoload.php';
}
if (is_file(__DIR__ . '/vendor/autoload.php')) {
require_once __DIR__ . '/vendor/autoload.php';
}
use OSS\Credentials\StaticCredentialsProvider;
use OSS\OssClient;
use OSS\Core\OssException;
try {
// Specify the temporary AccessKey ID, AccessKey secret and STS token generated in step 1.5. Do not use the credentials of a RAM user.
// Take note that the AccessKey ID provided by STS starts with STS.
$accessKeyId = 'yourSTSAccessKeyID';
$accessKeySecret = 'yourSTSAccessKeySecret';
// Specify the STS token obtained from STS.
$securityToken = 'yourSecurityToken';
// Create a credential provider by using StaticCredentialsProvider.
$provider = new StaticCredentialsProvider($accessKeyId, $accessKeySecret, $securityToken);
// Specify the endpoint of the region in which the bucket is located. For example, if the bucket is located in the China (Hangzhou) region, set the endpoint to https://oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com.
$endpoint = "https://oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com";
// Specify the name of the bucket. Example: examplebucket.
$bucket= "examplebucket";
// Specify the name of the object to upload.
$object = "exampletest.txt";
// Specify the full path of the local object that you want to upload. Example: D:\\localpath\\exampletest.txt.
$localFilePath = "D:\\localpath\\exampletest.txt";
// Configure headers in upload requests to specify information about the uploaded string. For example, set the object ACL to private and configure the user metadata of the object.
$options = array(
OssClient::OSS_HEADERS => array(
'x-oss-object-acl' => 'private',
'x-oss-meta-info' => 'yourinfo'
),
);
$config = array(
"provider" => $provider,
"endpoint" => $endpoint,
"signatureVersion" => OssClient::OSS_SIGNATURE_VERSION_V4,
// Specify the region in which the bucket is located. For example, if your bucket is located in the China (Hangzhou) region, set the region to cn-hangzhou.
"region" => "cn-hangzhou"
);
// Use the preceding configurations to create an OSSClient instance.
$ossClient = new OssClient($config);
// Send the request to upload the local file named exampletest.txt to examplebucket.
$ossClient->putObject($bucket, $object, $localFilePath, $options);
} catch (OssException $e) {
printf($e->getMessage() . "\n");
return;
}Ruby
require 'aliyun/sts'
require 'aliyun/oss'
client = Aliyun::OSS::Client.new(
# In this example, the endpoint of the China (Hangzhou) region is used. Specify your actual endpoint.
endpoint: 'https://oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com',
# Specify the temporary AccessKey ID and AccessKey secret that were generated in step 1.5. Do not use the AccessKey ID and AccessKey secret of an Alibaba Cloud account.
access_key_id: 'token.access_key_id',
access_key_secret: 'token.access_key_secret',
# Enter the STS token generated in Step 1.5.
sts_token: 'token.security_token'
)
# Specify the name of the bucket. Example: examplebucket.
bucket = client.get_bucket('examplebucket')
# Upload the object.
bucket.put_object('exampleobject.txt', :file => 'D:\test.txt')FAQ
How do I fix the error "You are not authorized to do this action. You should be authorized by RAM"?
How do I fix the error "The Min/Max value of DurationSeconds is 15min/1hr"?
How do I fix the error "The security token you provided is invalid"?
How do I fix the error "The OSS Access Key Id you provided does not exist in our records"?
How do I fix the error "AccessDenied: Anonymous access is forbidden for this operation"?
How do I fix the error NoSuchBucket?
How do I fix the error "You have no right to access this object because of bucket acl" when I attempt to use the temporary credentials to access OSS resources?
How do I fix the error "Access denied by authorizer's policy" when I use the temporary credentials obtained from STS to perform operations on OSS resources?
How do I fix the error "The bucket you are attempting to access must be addressed using the specified endpoint"?
Can I obtain multiple sets of temporary credentials at the same time?
How do I fix the time format error?
How do I fix the 0003-0000301 error?
References
Use temporary credentials to upload data to OSS directly from your client and specify upload conditions, such as the file size, file types, and destination directories. For more information, see Direct client uploads.
Use presigned URLs to share objects that are uploaded by using temporary credentials. For more information, see Using presigned URLs to download or preview files.