This topic describes common issues and solutions for using ossfs. If you encounter an issue, first check your ossfs version. If you are using an older version, such as 1.80.x, upgrade to the latest version. The latest version includes new features and improved stability.
General description
Each ossfs error includes a message that you can use for troubleshooting. For example, if you encounter socket connection failures or receive HTTP 4xx or 5xx status codes, enable the debug log before you begin troubleshooting.
A 403 error indicates that access is denied due to insufficient permissions.
A 400 error indicates an incorrect user operation.
A 5xx error typically indicates network jitter or a client-side issue.
Keep the following characteristics of ossfs in mind:
ossfs mounts a remote OSS bucket to a local disk. If your business requires high file read and write performance, do not use ossfs.
Local file system operations are not atomic with remote OSS operations. A local action might appear to succeed even if the corresponding OSS operation fails.
If ossfs does not meet your business requirements, consider using ossutil.
Permission errors
A 403 error occurs when you touch a file after a successful mount
Cause: A 403 error is usually caused by insufficient access permissions. This error can occur when you use the touch command on a file in the following situations:
The file is an Archive Storage object. Running the touch command on this type of file returns a 403 error.
The AccessKey that you use does not have the required permissions to access the bucket.
Solution:
For Archive Storage objects, you must restore the object before you can access it. Alternatively, you can enable real-time access for Archive objects in the bucket where the object is stored.
For permission errors, grant the required permissions to the account that is associated with the AccessKey.
Why do I get an "Operation not permitted" error with the rm command?
Cause: When you run the rm command to delete a file, the DeleteObject API operation is called. If you mounted the bucket as a Resource Access Management (RAM) user, check whether the RAM user has permission to delete files.
Solution: Grant the required permissions to the RAM user. For more information, see RAM policies and Common examples of RAM policies.
Why do I get the "The bucket you are attempting to access must be addressed using the specified endpoint" error?
Cause: This message indicates that the Endpoint is incorrectly specified. This error can occur for the following two reasons:
The bucket and the Endpoint do not match.
The UID of the bucket owner is different from the UID of the account that is associated with the AccessKey.
Solution: Confirm that your configuration is correct and make changes if necessary.
Mounting errors
Does ossfs support custom domain names for mounting buckets?
No, it does not. ossfs does not support mounting buckets using custom domain names.
Why does mounting fail on CentOS 7.x over HTTPS with ossfs 1.91.5 or later?
Solution:
Add the
-ocurldbgoption when you mount the bucket. Check the logs forNSS error -8023 (SEC_ERROR_PKCS11_DEVICE_ERROR).If this error exists, check your local NSS version.
If the NSS version is 3.36, run the
yum update nsscommand to update NSS. Then, try to mount the bucket again.
Why does mounting fail with an ECS RAM role for ossfs 1.91.7 and later?
Solution:
Run the
curl http://100.100.100.200/latest/meta-data/ram/security-credentials/[your-ecs-ram-role]command to check for connectivity.If the curl command runs successfully, add the
-o disable_imdsv2option when you mount the bucket.
Mount error: "ossfs: unable to access MOUNTPOINT /tmp/ossfs: Transport endpoint is not connected"
Cause: This error occurs because the mount point directory does not exist.
Solution: Create the mount point directory before you mount the bucket.
Mounting error: "fusermount: failed to open current directory: Permission denied"
Cause: This is a bug in Filesystem in Userspace (FUSE). The current user must have read permissions on the current working directory, which is different from the mount directory.
Solution: Run the cd command to switch to a directory for which you have read permissions, and then run the ossfs command.
Mount error: "ossfs: Mountpoint directory /tmp/ossfs is not empty. if you are sure this is safe, can use the 'nonempty' mount option"
Cause: By default, ossfs can be mounted only to an empty directory. This error occurs when you try to mount a bucket to a non-empty directory.
Solution: Switch to an empty directory and mount the bucket again. If you must mount the bucket to the non-empty directory, add the -ononempty parameter to the mount command.
Mount error: "ops-nginx-12-32 s3fs[163588]: [tid-75593]curl.cpp:CurlProgress(532): timeout now: 1656407871, curl_times[curl]: 1656407810, readwrite_timeout: 60"
Cause: The ossfs mount operation timed out.
Solution: ossfs uses the readwrite_timeout option to specify the timeout period for read and write requests. The unit is seconds, and the default value is 60. You can increase this value as needed.
Mounting error: "ossfs: credentials file /etc/passwd-ossfs should not have others permissions"
Cause: The permissions for the /etc/passwd-ossfs file are incorrect.
Solution: The /etc/passwd-ossfs file stores access credentials. To protect these credentials, you must prevent other users from accessing this file. Run the chmod 640 /etc/passwd-ossfs command to modify the file's access permissions.
"Operation not permitted" error when running ls on a directory after a successful mount
Cause: This error can occur if your bucket contains objects whose names include invisible characters. File systems have strict limits on file and directory names.
Solution: Use another tool to rename these objects. After you rename them, the ls command can correctly display the directory content.
Error when mounting: "fuse: device not found, try 'modprobe fuse'"
Cause: The "fuse: device not found, try 'modprobe fuse'" error can occur when you try to mount with ossfs in a Docker container. This error is usually caused by the container lacking the permissions required to access or load the FUSE kernel module.
Solution: When you run ossfs in a Docker container, add the --privileged=true parameter to grant higher permissions to the container. This allows processes within the container to perform operations similar to those on the host, including using the FUSE file system. The following command is an example of how to start a container with the --privileged flag:
docker run --privileged=true -d your_imageError during mounting: "ossfs: error while loading shared libraries: libcrypto.so.1.1: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory"
Cause: The version of the installation package does not match the version of the operating system.
Solution: To resolve this issue, download the installation package that corresponds to your operating system.
Cost issues
Mounting OSS on ECS: How to avoid costs from background file scans
Cause: When a program scans a directory mounted by ossfs, the scan is converted into requests to OSS. Many requests can incur fees.
Solution: You can use the auditd tool to identify which processes are scanning the OSS mounted directory. The steps are as follows:
Install and start auditd.
sudo apt-get install auditd sudo service auditd startSet the OSS mounted directory as the directory to be watched. For example, if the mounted directory is /mnt/ossfs:
auditctl -w /mnt/ossfsCheck the audit log to identify which processes accessed this directory.
ausearch -i | grep /mnt/ossfsModify the program's parameters to skip the scan.
For example, if the audit log shows that updatedb scanned the mounted directory, you can modify /etc/updatedb.conf to skip the directory. To do this:
Add
fuse.ossfsafterRUNEFS =.Add the mounted directory to the
PRUNEPATHS =line.
Disk and memory issues
ossfs disconnects intermittently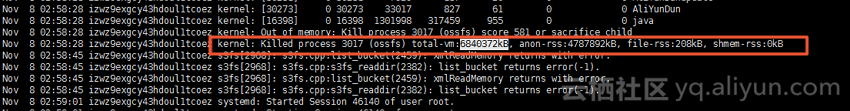
Analysis:
Enable the ossfs debug log by adding the -d -odbglevel=dbg parameters. ossfs writes logs to the default system log file.
On CentOS systems: Logs are written to
/var/log/message.On Ubuntu systems: Logs are written to
/var/log/syslog.
Analyze the logs. The logs might show that ossfs requested too much memory for listbucket and listobject operations, which triggered the system's out-of-memory (OOM) killer.
NoteThe listobject operation sends an HTTP request to OSS to retrieve object metadata. If there are many files, the ls command consumes a large amount of system memory to retrieve the metadata.
Solution:
Increase the size of the stat cache using the -omax_stat_cache_size=xxx parameter. The first ls operation will be slower, but subsequent ls operations will be faster because the object metadata is stored in the local cache. The default value is 1,000, which consumes about 4 MB of memory. Adjust this value based on your machine's memory size.
During read and write operations, ossfs uses disk space to write a large amount of temporary cache data, similar to how Nginx works. This may cause insufficient free disk space. When ossfs exits, it automatically cleans up these temporary files.
Use ossutil instead of ossfs. Use ossfs for non-production services that are not performance-sensitive. For services that require high reliability and stability, use ossutil.
Why does ossfs fill up the disk space?
Cause: To improve performance, ossfs uses as much disk space as possible by default to save temporary data for uploads and downloads. This can cause the disk to become full.
Solution: You can use the -oensure_diskfree option to specify the amount of disk space to reserve. For example, to reserve 20 GB of disk space, add the option to your mount command:
ossfs examplebucket /tmp/ossfs -o url=http://oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com -oensure_diskfree=20480After mounting with ossfs, why does the df command show a disk space of 256 TB?
The disk space shown by the df command is for display purposes only. It does not represent the actual capacity of the OSS bucket. The Size (total disk space) and Avail (free disk space) values are fixed at 256 TB. The Used (used disk space) value is fixed at 0 TB.
OSS provides unlimited bucket capacity. Your bucket's storage usage depends on your actual usage. For more information about how to query bucket usage, see Query bucket-level usage.
Error when copying data with the cp command: 'input/output error'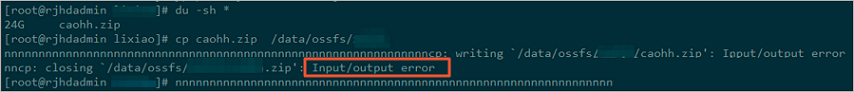
Cause: An input/output error is reported when a system disk error is detected. Check whether the disk is experiencing a high read/write load when the error occurs.
Solution: You can add sharding parameters to control file reads and writes. Run the ossfs -h command to view the available sharding parameters.
Rsync synchronization returns an "input/output error"
Cause: Using ossfs with rsync for synchronization can cause issues. In this case, a user ran the cp command on a 141 GB file. This put the disk in a high-load state for read and write operations, which caused the error.
Solution: If you want to download files from OSS to a local ECS instance or upload local files to an ECS instance, use the multipart upload or download feature of ossutil.
Why do I get a "there is no enough disk space for used as cache(or temporary)" error when uploading?
Cause
The available disk space is less than
multipart_size * parallel_count.multipart_size specifies the part size in MB, and parallel_count specifies the number of concurrent upload parts. The default value for parallel_count is 5.
Analysis
By default, ossfs uses multipart upload for large files. During the upload process, ossfs writes temporary cache files to the /tmp folder. Before writing a cache file, ossfs checks if the free space on the disk that contains the /tmp folder is less than
multipart_size * parallel_count. If the free disk space is greater thanmultipart_size * parallel_count, the cache file is written. If the free disk space is less thanmultipart_size * parallel_count, ossfs returns an error indicating insufficient local disk space.For example, assume the free disk space is 300 GB and the file to be uploaded is 200 GB. However, multipart_size is set to 100000 (which is 100 GB), and the number of concurrent upload parts is kept at the default value of 5. In this case, ossfs determines that the required upload space is 100 GB × 5 = 500 GB, which exceeds the available local disk space.
Solution
If the number of concurrent upload parts is kept at the default value of 5, set multipart_size to a reasonable value:
If the free disk space is 300 GB and the file to be uploaded is 200 GB, set multipart_size to 20.
If the free disk space is 300 GB and the file to be uploaded is 500 GB, set multipart_size to 50.
Dependency issues
Error during ossfs installation: "fuse: warning: library too old, some operations may not work"
Cause: This error occurs because the libfuse version used at compile-time for ossfs is higher than the libfuse version linked at runtime. This often happens when a user installs libfuse manually. In CentOS 5.x and CentOS 6.x systems, the ossfs installation package provided by Alibaba Cloud includes libfuse-2.8.4. If libfuse-2.8.3 is present in the runtime environment and ossfs is linked to the older version of FUSE, this error occurs.
Run the ldd $(which ossfs) | grep fuse command to confirm the FUSE version that ossfs links to at runtime. If the result is /lib64/libfuse.so.2, run the ls -l /lib64/libfuse* command to see the FUSE version.
Solution: Link ossfs to the correct version.
Run the rpm -ql ossfs | grep fuse command to find the libfuse directory.
If the result is /usr/lib/libfuse.so.2, run ossfs with the LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/usr/lib ossfs … command.
Error installing the fuse dependency library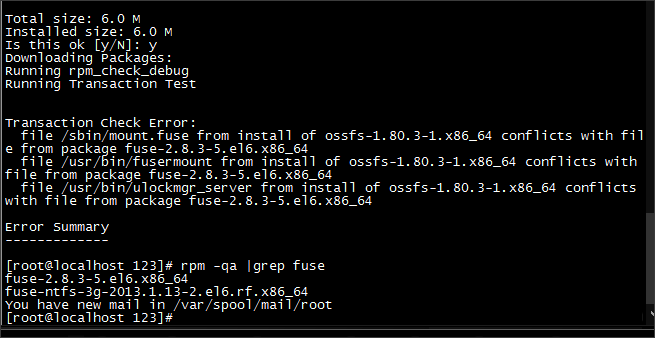
Cause: The FUSE version does not meet the requirements of ossfs.
Solution: Manually download and install the latest version of FUSE. Do not use yum for the installation. For more information, see fuse.
Why does ls cause an "Input/Output error"?
Cause: This issue mainly occurs in CentOS environments. The log reports an NSS error -8023. An issue occurs when ossfs uses libcurl for HTTPS communication. This may be because the version of the Network Security Services (NSS) library that libcurl depends on is too low.
Solution: Run the following command to upgrade the NSS library to the latest version.
yum update nssError when installing ossfs with yum/apt-get: "conflicts with file from package fuse-devel"
Cause: An old version of FUSE exists in the system, which conflicts with the dependency version in ossfs.
Solution: You can use the relevant package manager to uninstall FUSE, and then reinstall ossfs.
Other issues
How can I improve performance when dealing with many files or high concurrency?
ossfs 1.0 is not recommended for high-concurrency scenarios. If you must use it in such scenarios, consider the following solutions:
Solution 1: Mount with ossfs 2.0. Compared to ossfs 1.0, ossfs 2.0 provides significant performance improvements for sequential reads and writes, and for reading small files with high concurrency. For more information about the performance of ossfs 2.0, see the Performance improvements section.
Solution 2: Use Mount OSS using Cloud Storage Gateway for better performance. The ossfs 1.0 tool is not recommended for high-concurrency uploads and downloads of large files. It is better suited for daily operations on small files.
Content-Type for ossfs uploads to OSS is always application/octet-stream
Cause: When uploading a file, ossfs sets the Content-Type of the file by querying the content of /etc/mime.types. If this file does not exist, the Content-Type is set to application/octet-stream by default.
Solution: Check whether this file exists. If it does not exist, you must add it.
Automatically add the mime.types file using a command
Ubuntu systems
Run the sudo apt-get install mime-support command to add the file.
CentOS systems
Run the sudo yum install mailcap command to add the file.
Manually add the mime.types file
Create the mime.types file.
vi /etc/mime.typesAdd the required formats. Each format should be on a new line, in the format
application/javascript js.
After you add the file, you must remount the OSS bucket.
Why does ossfs identify a folder as a regular file?
Scenario 1:
Cause: When you create a folder object (an object whose name ends with
/) and specify the content-type as text/plain, ossfs identifies this object as a regular file.Solution: Add the -ocomplement_stat parameter during mounting. If the size of the folder object is 0 or 1, ossfs identifies it as a folder.
Scenario 2:
Cause: Run the
ossutil stat folder_object (ends with '/')command (for example,ossutil stat oss://[bucket]/folder/). After you run the command:Check the Content-Length field of the object, which is the object size. If the object size is not 0, the object is identified as a file.
Solution: If you no longer need the content of the folder object, run the
ossutil rm oss://[bucket]/folder/command to delete the object. This does not affect the files under the folder. Alternatively, upload a zero-byte object with the same name to overwrite it.If the object size is 0, check the Content-Type field, which is the object attribute. If the Content-Type is not
application/x-directory,httpd/unix-directory,binary/octet-stream, orapplication/octet-stream, the object is also identified as a file.Solution: Run the
ossutil rm oss://[bucket]/folder/command to delete the object. This does not affect the files under the folder.
Ossfs mv operation fails
Cause: The mv operation in ossfs may fail because the source file is an Archive, Cold Archive, or Deep Cold Archive object.
Solution: Before you run the mv command on an Archive, Cold Archive, or Deep Cold Archive object, you must restore the object. For more information, see Restore objects.
Does ossfs support mounting buckets in a Windows environment?
No. You can use Rclone to mount a bucket in Windows. For more information, see Rclone.
Does ossfs support mounting an OSS bucket to multiple Linux ECS servers?
Yes. You can mount a bucket to multiple Linux ECS servers. For more information, see Mount a bucket.
Why is the file information (such as size) seen in ossfs inconsistent with what is seen in other tools?
Cause: By default, ossfs caches file metadata, including size and permissions. This cache speeds up ls operations because it avoids sending a request to OSS each time. If a user modifies a file using another program, such as an SDK, the OSS console, or ossutil, ossfs does not immediately update its cache. This causes the file information to be inconsistent with the information displayed in other tools.
Solution: Add the -omax_stat_cache_size=0 parameter during mounting to disable the metadata cache feature. When the cache is disabled, each time you run ls, a request is sent to OSS to retrieve the latest file information.
Why does mounting become slow after versioning is enabled for a bucket?
Cause: By default, ossfs lists files by calling the ListObjects (GetBucket) operation. If versioning is enabled for a bucket and the bucket contains one or more previous versions of objects and many expired delete markers, the response speed of the ListObjects (GetBucket) operation decreases when listing current object versions. This slows down the ossfs mount operation.
Solution: You can use the -olistobjectsV2 option to configure ossfs to use the ListObjectsV2 (GetBucketV2) operation to improve file listing performance.
How do I mount a bucket over HTTPS?
ossfs supports mounting over HTTPS. The following command is an example for the China (Hangzhou) region:
ossfs examplebucket /tmp/ossfs -o url=https://oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.comWhy is the ls command slow in directories with many files?
Cause: If a directory contains N files, the ls command for that directory requires at least N HTTP requests to OSS. When a directory contains a very large number of files, this can cause serious performance issues.
Solution: Increase the size of the stat cache using the -omax_stat_cache_size=xxx parameter. The first ls operation will be slower, but subsequent ls operations will be faster because the object metadata is stored in the local cache. Before version 1.91.1, the default value was 1,000. Starting from version 1.91.1, the default value is 100,000, which uses several tens of megabytes of memory. Adjust this value based on your machine's memory.
Error during unmounting: "fusermount: failed to unmount /mnt/ossfs-bucket: Device or resource busy"
Cause: A process is accessing a file in the mounted directory /mnt/ossfs-bucket, which prevents the directory from being unmounted.
Solution:
Run
lsof /mnt/ossfs-bucketto find the process that is accessing the directory.Run the kill command to force the process to close.
Run
fusermount -u /mnt/ossfs-bucketto unmount the bucket.
Excessive 404 logs are generated by ossfs 1.0
Background: When you use ossfs 1.0, it is common to see 404 Not Found records in the logs. This is expected behavior, not an error. ossfs sends probe requests (such as HeadObject) to check if a file or directory exists before performing an operation. If the object does not exist, OSS returns a 404, which ossfs correctly interprets.
Before operating on a file, the operating system checks whether the target object exists. This process can cause many probe requests to be sent to OSS. If the object does not exist, OSS returns a 404 status code.
The complete process that ossfs 1.0 uses to check for an object's existence is as follows:
Sends a HeadObject request to query whether the specified path, such as
object, exists as an actual object.If the object exists, OSS returns the object metadata. If the object does not exist, OSS returns a 404 error and ossfs proceeds to the next step.
After receiving the 404 error, ossfs sends a HeadObject request to query whether the
object/object exists.If the object exists, OSS returns the object metadata. If the object does not exist, OSS returns a 404 error and ossfs proceeds to the next step.
After receiving the 404 error, ossfs sends a HeadObject request to query whether the
object_$folder$object exists.If the object exists, OSS returns the object metadata. If the object does not exist, OSS returns a 404 error and ossfs proceeds to the next step.
After receiving the 404 error, ossfs sends a ListObjects request to determine whether the specified path is a "directory" by querying for objects with the prefix
object/.If the result is empty, the path is determined not to exist. If the result is not empty, the directory exists, and the system lists the directory's contents.
Analysis:
When you use commands such as stat to access a file that does not exist, OSS returns a 404 error, which is mapped to the local file system's "No such file or directory" error.
Before creating files or directories in a batch, the operating system first checks whether the target file exists. It sends a create request only if the file does not exist. The 404 error generated during this check is expected behavior, not a system exception.
Solution: Although the 404 error is normal behavior, frequent probe requests can affect performance in high-concurrency or batch operation scenarios. Optimize the configuration in the following ways:
After you configure these options, ossfs 1.0 cannot detect changes made to files on OSS until the local cache expires.
Increase the metadata cache duration and the number of cached entries by increasing the values of
-o stat_cache_expireand-o max_stat_cache_size.Querying a file or directory before its metadata expires avoids repeated OSS requests.
-o stat_cache_expire: The expiration time of the metadata cache in seconds. The default value is 900.-o max_stat_cache_size: The number of entries in the metadata cache. The default value is 100,000.
If you are using a version of ossfs earlier than 1.91.6, enable the negative cache by configuring
-o enable_noobj_cache. The negative cache is enabled by default in ossfs 1.91.6 and later.When a file is queried for the first time and does not exist, the result is cached in memory. Subsequent queries for the file before the cache expires directly query the local negative cache instead of sending an OSS request.
NoteThe file negative cache of ossfs 1.0 is part of the metadata cache. The expiration time is controlled by the
-o stat_cache_expireparameter, and the maximum number of cached entries is controlled by the-o max_stat_cache_sizeparameter.