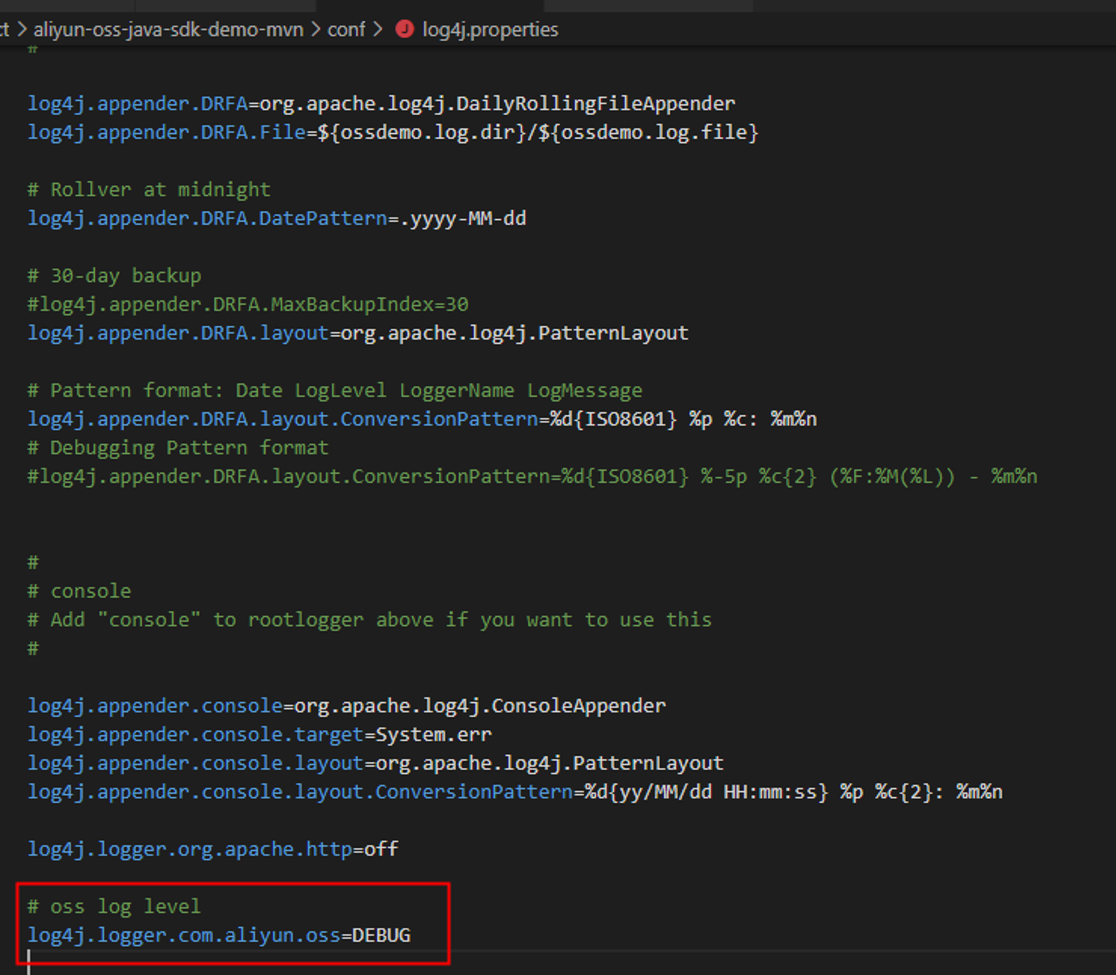
Quick integration
Follow these steps to quickly integrate OSS SDK for Java 1.0:

Environment preparation
You must install Java 7 or later. Run the java -version command to view your Java version. If Java is not installed or your version is earlier than Java 7, download Java.
Install the SDK
Choose an installation method based on your development environment. To ensure that the sample code runs as expected, use the latest version of OSS SDK for Java 1.0.
The following sections use the installation of OSS SDK for Java 1.0 3.17.4 as an example.
Add a Maven dependency (recommended)
To use OSS SDK for Java 1.0 in a Maven project, add the corresponding dependency to the pom.xml file.
<dependency>
<groupId>com.aliyun.oss</groupId>
<artifactId>aliyun-sdk-oss</artifactId>
<version>3.17.4</version>
</dependency>If you use Java 9 or later, add the following JAXB-related dependencies.
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.xml.bind</groupId>
<artifactId>jaxb-api</artifactId>
<version>2.3.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.activation</groupId>
<artifactId>activation</artifactId>
<version>1.1.1</version>
</dependency>
<!-- no more than 2.3.3-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.glassfish.jaxb</groupId>
<artifactId>jaxb-runtime</artifactId>
<version>2.3.3</version>
</dependency>Import JAR packages into an Eclipse project
Download OSS SDK for Java 1.0
Decompress the package.
Copy the aliyun-sdk-oss-3.17.4.jar file and all files from the lib folder of the decompressed package to your project.
In Eclipse, select your project, right-click it, and choose .
Select all the copied JAR files and import them into Libraries.
Import JAR packages into an IntelliJ IDEA project
Download OSS SDK for Java 1.0.
Decompress the package.
Copy the aliyun-sdk-oss-3.17.4.jar file and all JAR files from the lib folder of the decompressed package to your project.
In IntelliJ IDEA, select your project, right-click it, and choose .
Select all the copied JAR files and import them into External Libraries.
Configure access credentials
Configure access credentials using the AccessKey pair of a RAM user.
In the RAM console, create a RAM user that uses a Permanent AccessKey Pair for access. Save the AccessKey pair and grant the
AliyunOSSFullAccesspermission to the user.Use the AccessKey pair of the RAM user to configure environment variables.
Linux
Run the following commands in the command-line interface to append the environment variable settings to the
~/.bashrcfile.echo "export OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID='YOUR_ACCESS_KEY_ID'" >> ~/.bashrc echo "export OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET='YOUR_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET'" >> ~/.bashrcRun the following command to apply the changes.
source ~/.bashrcRun the following commands to verify that the environment variables are configured.
echo $OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID echo $OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET
macOS
Run the following command in the terminal to view the default shell type.
echo $SHELLPerform the following operations based on the default shell type.
Zsh
Run the following commands to append the environment variable settings to the
~/.zshrcfile.echo "export OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID='YOUR_ACCESS_KEY_ID'" >> ~/.zshrc echo "export OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET='YOUR_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET'" >> ~/.zshrcRun the following command to apply the changes.
source ~/.zshrcRun the following commands to verify that the environment variables are configured.
echo $OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID echo $OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET
Bash
Run the following commands to append the environment variable settings to the
~/.bash_profilefile.echo "export OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID='YOUR_ACCESS_KEY_ID'" >> ~/.bash_profile echo "export OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET='YOUR_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET'" >> ~/.bash_profileRun the following command to apply the changes.
source ~/.bash_profileRun the following commands to verify that the environment variables are configured.
echo $OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID echo $OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET
Windows
CMD
Run the following commands in CMD.
setx OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID "YOUR_ACCESS_KEY_ID" setx OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET "YOUR_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET"Run the following commands to verify that the environment variables are configured.
echo %OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID% echo %OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET%
PowerShell
Run the following commands in PowerShell.
[Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable("OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID", "YOUR_ACCESS_KEY_ID", [EnvironmentVariableTarget]::User) [Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable("OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET", "YOUR_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET", [EnvironmentVariableTarget]::User)Run the following commands to verify that the environment variables are configured.
[Environment]::GetEnvironmentVariable("OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID", [EnvironmentVariableTarget]::User) [Environment]::GetEnvironmentVariable("OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET", [EnvironmentVariableTarget]::User)
Initialize the client
The following sample code uses the public endpoint of the China (Hangzhou) region to initialize the client and lists the buckets in that region for verification. For a complete list of regions and endpoints, see Regions and endpoints.
import com.aliyun.oss.*;
import com.aliyun.oss.common.auth.*;
import com.aliyun.oss.common.comm.SignVersion;
import com.aliyun.oss.model.Bucket;
import java.util.List;
/**
* OSS SDK quick integration example
* Shows how to initialize an OSS client and list all buckets
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Obtain access credentials from environment variables
String accessKeyId = System.getenv("OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID");
String accessKeySecret = System.getenv("OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET");
// Set the OSS region and endpoint
String region = "cn-hangzhou";
String endpoint = "oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com";
// Create a credential provider
DefaultCredentialProvider provider = new DefaultCredentialProvider(accessKeyId, accessKeySecret);
// Configure client parameters
ClientBuilderConfiguration clientBuilderConfiguration = new ClientBuilderConfiguration();
// Explicitly declare the use of the V4 signature algorithm
clientBuilderConfiguration.setSignatureVersion(SignVersion.V4);
// Initialize the OSS client
OSS ossClient = OSSClientBuilder.create()
.credentialsProvider(provider)
.clientConfiguration(clientBuilderConfiguration)
.region(region)
.endpoint(endpoint)
.build();
// List all buckets of the current user
List<Bucket> buckets = ossClient.listBuckets();
System.out.println("Successfully connected to OSS. Buckets under the current account:");
if (buckets.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("No buckets found under the current account.");
} else {
for (Bucket bucket : buckets) {
System.out.println("- " + bucket.getName());
}
}
// Release resources
ossClient.shutdown();
System.out.println("OSS client has been shut down.");
}
}After you run the code, the buckets of the current account in all regions are displayed:
Successfully connected to OSS. Buckets under the current account:
- example-bucket
OSS client has been shut down.Client configuration
Use the ClientConfiguration class to configure parameters for OSSClient, such as timeout periods, retries, and proxy servers.
Use a custom domain name
When you use the default OSS domain name, you might encounter issues such as access denial or preview failures because of OSS security policies. By binding a custom domain name to access OSS, you can bypass these access restrictions to enable direct file previews. You can also integrate with CDN for global content acceleration to improve the user experience.
ClientBuilderConfiguration clientBuilderConfiguration = new ClientBuilderConfiguration();
// Enable the CNAME option to support access through a custom domain name
clientBuilderConfiguration.setSupportCname(true);
OSS ossClient = new OSSClientBuilder()
// Other configurations...
.clientConfiguration(clientBuilderConfiguration)
// Use your custom domain name as the endpoint, such as https://static.example.com
.endpoint("https://static.example.com")
.build();Use an internal endpoint
When your application is deployed on Alibaba Cloud services, such as ECS or Container Service, use an internal endpoint. This provides free internal data transfer, faster speeds, and better network stability. Internal access is ideal for large file uploads, batch data processing, and high-frequency access scenarios. It effectively reduces costs and improves performance. For a complete list of regions and internal endpoints, see Regions and endpoints.
ClientBuilderConfiguration clientBuilderConfiguration = new ClientBuilderConfiguration();
OSS ossClient = new OSSClientBuilder()
// Other configurations...
.clientConfiguration(clientBuilderConfiguration)
// Use an internal endpoint. The China (Hangzhou) region is used as an example. For other regions, specify the actual endpoint.
.endpoint("oss-cn-hangzhou-internal.aliyuncs.com")
.build();Timeout control
Configure timeout parameters based on your business scenario. For large file transfers or unstable network environments, increase the timeout period. For high-concurrency, lightweight operations, set a shorter timeout period to quickly release resources.
ClientBuilderConfiguration clientBuilderConfiguration = new ClientBuilderConfiguration();
// Set the maximum number of allowed open HTTP connections. The default is 1024.
clientBuilderConfiguration.setMaxConnections(1024)
// Set the timeout period for data transfers at the socket layer, in milliseconds. The default is 50000 ms.
.setSocketTimeout(50000)
// Set the timeout period for establishing a connection, in milliseconds. The default is 50000 ms.
.setConnectionTimeout(50000)
// Set the timeout period for obtaining a connection from the connection pool, in milliseconds. By default, there is no timeout limit.
.setConnectionRequestTimeout(60 * 60 * 24 * 1000)
// Set the idle timeout period for a connection, in milliseconds. If a connection is idle for longer than this period, it is closed. The default is 60000 ms.
.setIdleConnectionTime(60000);
OSS ossClient = new OSSClientBuilder()
// Other configurations...
.clientConfiguration(clientBuilderConfiguration)
.build();Maximum error retries
By default, the OSS client retries a request three times to improve the success rate. In high-concurrency or unstable network environments, use setMaxErrorRetry to increase the number of retries. This can significantly improve service availability. Adjust the number of retries based on your business's tolerance for latency and the quality of your network environment.
ClientBuilderConfiguration clientBuilderConfiguration = new ClientBuilderConfiguration();
// Set the maximum number of retries for a failed request. Adjust this based on your network environment and business needs.
clientBuilderConfiguration.setMaxErrorRetry(5);
OSS ossClient = new OSSClientBuilder()
// Other configurations...
.clientConfiguration(clientBuilderConfiguration)
.build();Retry policy
Do not use setRetryStrategy to set a custom retry policy because a custom policy may cause unexpected behavior and affect service stability. The OSS client uses proven retry policies for different request types:
POST requests: These are not retried by default to avoid data inconsistency from repeated submissions.
Non-POST requests: These are retried up to three times if the following conditions are met.
A
ClientExceptionoccurs with one of the following error codes:ConnectionTimeout,SocketTimeout,ConnectionRefused,UnknownHost, orSocketException.An
OSSExceptionoccurs with an error code other thanInvalidResponse.A temporary server-side error occurs with an HTTP status code of 500, 502, or 503.
Proxy server
Corporate network environments often use proxy servers to access external resources for security purposes. After you configure a proxy server, the OSS client forwards all HTTP requests through the specified proxy for secure access to OSS.
ClientBuilderConfiguration clientBuilderConfiguration = new ClientBuilderConfiguration();
// Set the user agent, which is the User-Agent header in HTTP. The default value is aliyun-sdk-java.
clientBuilderConfiguration.setUserAgent("aliyun-sdk-java");
// Set the IP address of the proxy server. Replace "" with the actual IP address of the proxy server, such as "196.128.xxx.xxx".
clientBuilderConfiguration.setProxyHost("");
// Set the port of the proxy server, such as 8080.
clientBuilderConfiguration.setProxyPort(8080);
// Set the username for proxy server authentication. Replace "" with the actual username, such as "admin".
clientBuilderConfiguration.setProxyUsername("");
// Set the password for proxy server authentication. Replace "" with the corresponding password.
clientBuilderConfiguration.setProxyPassword("");
OSS ossClient = new OSSClientBuilder()
// Other configurations...
.clientConfiguration(clientBuilderConfiguration)
.build();HTTP/HTTPS protocol
Use setProtocol to set the communication protocol between the client and the OSS server. The default is HTTP. We recommend that you use HTTPS in production environments to ensure secure data transfer and prevent man-in-the-middle attacks and data breaches.
ClientBuilderConfiguration clientBuilderConfiguration = new ClientBuilderConfiguration();
// Set the communication protocol to HTTPS to ensure secure data transfer.
clientBuilderConfiguration.setProtocol(Protocol.HTTPS);
OSS ossClient = new OSSClientBuilder()
// Other configurations...
.clientConfiguration(clientBuilderConfiguration)
.build();Signature version
Alibaba Cloud Object Storage Service Signature 1.0 will be phased out according to the following schedule. We recommend that you upgrade to Signature V4 as soon as possible to ensure your services are not affected.
Starting from March 1, 2025, new users will not be able to use Signature 1.0.
Starting from September 1, 2025, Signature 1.0 will no longer be updated or maintained, and new buckets will not be able to use Signature V1.
Use setSignatureVersion to configure the signature algorithm version. When you use Signature V4, you must use the region parameter to specify the correct region ID. The V4 signature algorithm provides higher security. OSS SDK for Java 1.0 3.15.0 and later support Signature V4.
ClientBuilderConfiguration clientBuilderConfiguration = new ClientBuilderConfiguration();
// Set the signature algorithm version to V4 for higher security.
clientBuilderConfiguration.setSignatureVersion(SignVersion.V4);
OSS ossClient = new OSSClientBuilder()
// Other configurations...
// You must specify the region ID when using Signature V4.
.region("cn-hangzhou")
.clientConfiguration(clientBuilderConfiguration)
.build();Use an IP address
Using an IP address as an endpoint is primarily for internal network access and special network environments. After you establish a network connection using CEN, Express Connect, a leased line, or a VPN, use an IP address to directly access OSS. This bypasses the DNS resolution process and improves access efficiency. For specific routing configurations, see Internal endpoints and VIP CIDR blocks for OSS.
ClientBuilderConfiguration clientBuilderConfiguration = new ClientBuilderConfiguration();
// Enable access to OSS through a second-level domain. This feature is disabled by default.
// This value must be set for OSS Java SDK 1.0 2.1.2 and earlier.
// Versions 2.1.2 and later automatically detect the IP address, so this value is no longer required.
clientBuilderConfiguration.setSLDEnabled(true);
OSS ossClient = new OSSClientBuilder()
// Other configurations...
.clientConfiguration(clientBuilderConfiguration)
// When you access OSS using an IP address, use the HTTP protocol to avoid SSL certificate verification issues.
.endpoint("http://10.10.10.10")
.build();CRC check
OSS enables cyclic redundancy check (CRC) data checks by default to ensure data transfer integrity. Although this slightly increases transfer time, we recommend that you keep it enabled in production environments to ensure data consistency. Consider disabling CRC checks to improve performance in specific scenarios, such as live preview streams, real-time data from IoT devices, low-quality surveillance videos where minor data loss is tolerable, or batch data transfers in highly reliable internal networks. Before you disable CRC checks, you must fully assess the data consistency risks and perform complete tests.
ClientBuilderConfiguration clientBuilderConfiguration = new ClientBuilderConfiguration();
// Disable the CRC data check feature. Use this with caution and fully assess the risks.
clientBuilderConfiguration.setCrcCheckEnabled(false);
OSS ossClient = new OSSClientBuilder()
// Other configurations...
.clientConfiguration(clientBuilderConfiguration)
.build();Singleton pattern
When you use OSS SDK for Java 1.0, use the singleton pattern to create and use OSSClient instances.
OSSClient is thread-safe, which allows multiple threads to access the same instance. You can use the singleton pattern to create and reuse an OSSClient instance based on your business needs. This avoids the overhead of frequently creating and destroying instances.
An OSSClient instance maintains a connection pool internally. When an OSSClient instance is no longer needed, you must call the shutdown method to close it and prevent resource exhaustion from creating too many instances.
import com.aliyun.oss.ClientBuilderConfiguration;
import com.aliyun.oss.OSS;
import com.aliyun.oss.*;
import com.aliyun.oss.OSSClientBuilder;
import com.aliyun.oss.common.auth.CredentialsProvider;
import com.aliyun.oss.common.auth.CredentialsProviderFactory;
import com.aliyun.oss.common.comm.SignVersion;
import com.aliyun.oss.internal.OSSHeaders;
import com.aliyun.oss.model.*;
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
public class OssClientSingleton {
private OssClientSingleton() {}
// Implement singleton with a static inner class (thread-safe)
private static class SingletonHolder {
private static final OSS INSTANCE = create();
private static OSS create() {
try {
// The China (Hangzhou) region is used as an example. For other regions, specify the actual endpoint.
String endpoint = "https://oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com";
// Enter the region where the bucket is located. The China (Hangzhou) region is used as an example. Set the region to cn-hangzhou.
String region = "cn-hangzhou";
ClientBuilderConfiguration config = new ClientBuilderConfiguration();
// Explicitly declare the use of the V4 signature algorithm.
config.setSignatureVersion(SignVersion.V4);
// Obtain access credentials from environment variables. Before running this sample code, make sure the OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID and OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET environment variables are set.
CredentialsProvider credentialsProvider = CredentialsProviderFactory.newEnvironmentVariableCredentialsProvider();
// Build the OSS client.
return OSSClientBuilder.create()
.endpoint(endpoint)
.credentialsProvider(credentialsProvider)
.clientConfiguration(config)
.region(region)
.build();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to initialize OSS client", e);
}
}
}
// Get the singleton instance.
public static OSS getInstance() {
return SingletonHolder.INSTANCE;
}
// Test the PutObject operation in the main function.
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Get the singleton OSS client.
OSS ossClient = OssClientSingleton.getInstance();
// Enter the bucket name, such as examplebucket.
String bucketName = "examplebucket";
// Enter the full path of the object, excluding the bucket name, such as testfolder/exampleobject.txt.
String objectKey = "testfolder/exampleobject.txt";
try {
// Enter the string.
String content = "Hello OSS";
// Create a PutObjectRequest object.
PutObjectRequest putObjectRequest = new PutObjectRequest(bucketName, objectKey, new ByteArrayInputStream(content.getBytes()));
// To set the storage class and access permissions during upload, see the following sample code.
ObjectMetadata metadata = new ObjectMetadata();
metadata.setHeader(OSSHeaders.OSS_STORAGE_CLASS, StorageClass.Standard.toString());
metadata.setObjectAcl(CannedAccessControlList.Private);
putObjectRequest.setMetadata(metadata);
// Upload the string.
PutObjectResult result = ossClient.putObject(putObjectRequest);
// Print the upload result.
System.out.println("File uploaded successfully!");
System.out.println("ETag: " + result.getETag());
System.out.println("Request ID: " + result.getRequestId());
} catch (OSSException oe) {
System.out.println("Caught an OSSException, which means your request made it to OSS, "
+ "but was rejected with an error response for some reason.");
System.out.println("Error Message:" + oe.getErrorMessage());
System.out.println("Error Code:" + oe.getErrorCode());
System.out.println("Request ID:" + oe.getRequestId());
System.out.println("Host ID:" + oe.getHostId());
} catch (ClientException ce) {
System.out.println("Caught an ClientException, which means the client encountered "
+ "a serious internal problem while trying to communicate with OSS, "
+ "such as not being able to access the network.");
System.out.println("Error Message:" + ce.getMessage());
} finally {
// In singleton mode, do not close the client after each operation (to reuse the connection), as this may affect subsequent use.
// When the OSSClient instance is no longer needed (for example, before the application exits), call the shutdown method once to release resources.
// ossClient.shutdown();
}
}
}
Exception handling
OSS SDK for Java 1.0 includes two types of exceptions: ClientException and OSSException. Both inherit from RuntimeException.
Client exceptions (ClientException)
Client exceptions occur during request construction, sending, or data transfer. Common scenarios include the following:
The network connection is unavailable, which prevents the request from being sent to the server.
An IO exception occurs during file upload.
Underlying network exceptions occur, such as request timeout or certificate verification failure.
A ClientException indicates that the request was not successfully sent to the OSS server or that an error occurred during client-side processing. This usually requires checking the network connection status, client configuration, or retry mechanism.
Server exceptions (OSSException)
Server exceptions are returned by the OSS server. This means the request was successfully sent and received by the server but could not be processed for some reason. OSS server exceptions have the following characteristics:
They include detailed error codes and error messages for precise problem identification.
Common errors include SignatureDoesNotMatch, AccessDenied, and NoSuchKey.
Handling these exceptions based on the error code can significantly improve program robustness and user experience.
We recommend that you catch these two types of exceptions separately during development to more accurately identify the source of the problem and create a corresponding handling strategy.
// Create client operation...
try {
// Perform OSS operations, such as uploading a file, downloading a file, or listing objects.
// These operations may throw OSS-related exceptions.
ossClient.putObject(...);
} catch (OSSException oe) {
// Catch exceptions returned by the OSS server.
// This exception is thrown when a request successfully reaches the OSS server, but the server rejects the request.
// Common causes: insufficient permissions, incorrect parameters, resource does not exist, etc.
System.out.println("Caught an OSSException, which means your request made it to OSS, "
+ "but was rejected with an error response for some reason.");
// Output detailed error information for problem location and debugging.
System.out.println("Error Message: " + oe.getErrorMessage());
System.out.println("Error Code: " + oe.getErrorCode());
System.out.println("Request ID: " + oe.getRequestId());
System.out.println("Host ID: " + oe.getHostId());
} catch (ClientException ce) {
// Catch client exceptions.
// This exception is thrown when the client encounters a serious internal problem while communicating with OSS.
// Common causes: network connection issues, SSL certificate issues, DNS resolution failure, etc.
System.out.println("Caught an ClientException, which means the client encountered "
+ "a serious internal problem while trying to communicate with OSS, "
+ "such as not being able to access the network.");
// Output detailed information about the client exception.
System.out.println("Error Message: " + ce.getMessage());
} finally {
// Release client resources regardless of whether the operation succeeded or failed.
// This is a best practice to avoid resource leaks and connection pool exhaustion.
if (ossClient != null) {
ossClient.shutdown(); // Close the client to release network connections and other resources.
}
}Sample code
OSS SDK for Java 1.0 provides a rich set of sample code that covers core features such as bucket management, file operations, access control, and encrypted transfer for your reference or direct use. The sample code includes the following:
Sample file | Sample content |
Note The implementation of PostObject does not depend on the Java SDK. | |
Access credential configuration
OSS provides multiple ways to initialize credentials. Choose an initialization method based on your authentication and authorization needs.
Use the AccessKey pair of a RAM user
This method is for applications that are deployed in a secure and stable environment, are not vulnerable to external attacks, require long-term access to OSS, and cannot have their credentials frequently rotated. You can initialize the credential provider with the AccessKey pair (AccessKey ID and AccessKey secret) of an Alibaba Cloud account or a RAM user. This method requires you to manually maintain an AccessKey pair, which increases security risks and maintenance complexity.
An Alibaba Cloud account has full permissions on its resources. If the AccessKey pair is leaked, it poses a significant risk to your system. We do not recommend using the AccessKey pair of an Alibaba Cloud account. Instead, use the AccessKey pair of a RAM user with the minimum required permissions.
To create an AccessKey pair for a RAM user, see Create an AccessKey pair. The AccessKey ID and AccessKey secret of a RAM user are displayed only when the AccessKey pair is created. If you forget them, you must create a new AccessKey pair to replace the old one.
Environment variables
Use the AccessKey pair of a RAM user to configure environment variables.
Linux
Run the following commands in the command-line interface to append the environment variable settings to the
~/.bashrcfile.echo "export OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID='YOUR_ACCESS_KEY_ID'" >> ~/.bashrc echo "export OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET='YOUR_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET'" >> ~/.bashrcRun the following command to apply the changes.
source ~/.bashrcRun the following commands to verify that the environment variables are configured.
echo $OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID echo $OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET
macOS
Run the following command in the terminal to view the default shell type.
echo $SHELLPerform the following operations based on the default shell type.
Zsh
Run the following commands to append the environment variable settings to the
~/.zshrcfile.echo "export OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID='YOUR_ACCESS_KEY_ID'" >> ~/.zshrc echo "export OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET='YOUR_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET'" >> ~/.zshrcRun the following command to apply the changes.
source ~/.zshrcRun the following commands to verify that the environment variables are configured.
echo $OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID echo $OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET
Bash
Run the following commands to append the environment variable settings to the
~/.bash_profilefile.echo "export OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID='YOUR_ACCESS_KEY_ID'" >> ~/.bash_profile echo "export OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET='YOUR_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET'" >> ~/.bash_profileRun the following command to apply the changes.
source ~/.bash_profileRun the following commands to verify that the environment variables are configured.
echo $OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID echo $OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET
Windows
CMD
Run the following commands in CMD.
setx OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID "YOUR_ACCESS_KEY_ID" setx OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET "YOUR_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET"Run the following commands to verify that the environment variables are configured.
echo %OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID% echo %OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET%
PowerShell
Run the following commands in PowerShell.
[Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable("OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID", "YOUR_ACCESS_KEY_ID", [EnvironmentVariableTarget]::User) [Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable("OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET", "YOUR_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET", [EnvironmentVariableTarget]::User)Run the following commands to verify that the environment variables are configured.
[Environment]::GetEnvironmentVariable("OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID", [EnvironmentVariableTarget]::User) [Environment]::GetEnvironmentVariable("OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET", [EnvironmentVariableTarget]::User)
After you modify the system environment variables, restart or refresh your development environment, including your IDE, command-line interface, other desktop applications, and backend services, to ensure the latest system environment variables are loaded successfully.
Use environment variables to pass credential information.
import com.aliyun.oss.ClientBuilderConfiguration; import com.aliyun.oss.OSS; import com.aliyun.oss.OSSClientBuilder; import com.aliyun.oss.common.auth.CredentialsProviderFactory; import com.aliyun.oss.common.auth.EnvironmentVariableCredentialsProvider; import com.aliyun.oss.common.comm.SignVersion; public class AkDemoTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { // Obtain credentials from environment variables. EnvironmentVariableCredentialsProvider credentialsProvider = CredentialsProviderFactory.newEnvironmentVariableCredentialsProvider(); // Use credentialsProvider for subsequent operations... ClientBuilderConfiguration clientBuilderConfiguration = new ClientBuilderConfiguration(); clientBuilderConfiguration.setSignatureVersion(SignVersion.V4); // Create an OSSClient instance. // When the OSSClient instance is no longer needed, call the shutdown method to release resources. OSS ossClient = OSSClientBuilder.create() .endpoint("endpoint") .credentialsProvider(credentialsProvider) .clientConfiguration(clientBuilderConfiguration) .region("region") .build(); ossClient.shutdown(); } }
Static credentials
The following sample code shows how to hard-code access credentials and explicitly set the AccessKey pair to use.
Do not embed access credentials in applications in a production environment. This method is for testing purposes only.
import com.aliyun.oss.ClientBuilderConfiguration;
import com.aliyun.oss.OSS;
import com.aliyun.oss.OSSClientBuilder;
import com.aliyun.oss.common.auth.CredentialsProvider;
import com.aliyun.oss.common.auth.DefaultCredentialProvider;
import com.aliyun.oss.common.comm.SignVersion;
public class AkDemoTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// Enter the AccessKey ID and AccessKey secret of the RAM user.
String accessKeyId = "yourAccessKeyID";
String accessKeySecret = "yourAccessKeySecret";
// Use the DefaultCredentialProvider method to directly set the AccessKey ID and AccessKey secret.
CredentialsProvider credentialsProvider = new DefaultCredentialProvider(accessKeyId, accessKeySecret);
// Use credentialsProvider to initialize the client.
ClientBuilderConfiguration clientBuilderConfiguration = new ClientBuilderConfiguration();
// Explicitly declare the use of the V4 signature algorithm.
clientBuilderConfiguration.setSignatureVersion(SignVersion.V4);
// Create an OSSClient instance.
// When the OSSClient instance is no longer needed, call the shutdown method to release resources.
OSS ossClient = OSSClientBuilder.create()
.endpoint("endpoint")
.credentialsProvider(credentialsProvider)
.clientConfiguration(clientBuilderConfiguration)
.region("region")
.build();
ossClient.shutdown();
}
}Use an STS token
This method is for applications that require temporary access to OSS. Initialize the credential provider with temporary identity credentials (AccessKey ID, AccessKey secret, and security token) that you obtain from Security Token Service (STS). This method requires you to manually maintain an STS token, which increases security risks and maintenance complexity. To temporarily access OSS multiple times, you must manually refresh the STS token.
To quickly obtain an STS token through an OpenAPI, see AssumeRole - Obtain temporary identity credentials for a RAM role.
To obtain an STS token using an SDK, see Use an STS token to access OSS.
You must specify an expiration time when you generate an STS token. The token becomes invalid and cannot be used after it expires.
For a list of STS service endpoints, see Service endpoints.
Environment variables
Use temporary identity credentials to set environment variables.
Mac OS/Linux/Unix
ImportantNote that the temporary identity credentials (AccessKey ID, AccessKey secret, and security token) obtained from the STS service are used here, not the AccessKey pair of a RAM user.
Note that the AccessKey ID obtained from the STS service starts with "STS", such as "STS.****************".
export OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID=<STS_ACCESS_KEY_ID> export OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET=<STS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET> export OSS_SESSION_TOKEN=<STS_SECURITY_TOKEN>Windows
ImportantNote that the temporary identity credentials (AccessKey ID, AccessKey secret, and security token) obtained from the STS service are used here, not the AccessKey pair (AccessKey ID and AccessKey secret) of a RAM user.
Note that the AccessKey ID obtained from the STS service starts with "STS", such as "STS.****************".
set OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID=<STS_ACCESS_KEY_ID> set OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET=<STS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET> set OSS_SESSION_TOKEN=<STS_SECURITY_TOKEN>Pass credential information through environment variables.
import com.aliyun.oss.ClientBuilderConfiguration; import com.aliyun.oss.OSS; import com.aliyun.oss.OSSClientBuilder; import com.aliyun.oss.common.auth.CredentialsProviderFactory; import com.aliyun.oss.common.auth.EnvironmentVariableCredentialsProvider; import com.aliyun.oss.common.comm.SignVersion; public class StsDemoTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { // Obtain credentials from environment variables. EnvironmentVariableCredentialsProvider credentialsProvider = CredentialsProviderFactory.newEnvironmentVariableCredentialsProvider(); // Use credentialsProvider to initialize the client. ClientBuilderConfiguration clientBuilderConfiguration = new ClientBuilderConfiguration(); // Explicitly declare the use of the V4 signature algorithm. clientBuilderConfiguration.setSignatureVersion(SignVersion.V4); // Create an OSSClient instance. // When the OSSClient instance is no longer needed, call the shutdown method to release resources. OSS ossClient = OSSClientBuilder.create() .endpoint("endpoint") .credentialsProvider(credentialsProvider) .clientConfiguration(clientBuilderConfiguration) .region("region") .build(); ossClient.shutdown(); } }
Static credentials
Hard-code credentials in your application and explicitly set the temporary access key to use.
import com.aliyun.oss.ClientBuilderConfiguration;
import com.aliyun.oss.OSS;
import com.aliyun.oss.OSSClientBuilder;
import com.aliyun.oss.common.auth.CredentialsProvider;
import com.aliyun.oss.common.auth.DefaultCredentialProvider;
import com.aliyun.oss.common.comm.SignVersion;
public class StsDemoTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// Set this to the temporary AccessKey ID, AccessKey secret, and security token obtained from the STS service, not the credential information of a RAM user.
// Note that the AccessKey ID obtained from the STS service starts with "STS", as shown below.
String accessKeyId = "STS.****************";
String accessKeySecret = "yourAccessKeySecret";
String stsToken= "yourSecurityToken";
// Use the DefaultCredentialProvider method to directly set the AccessKey ID and AccessKey secret.
CredentialsProvider credentialsProvider = new DefaultCredentialProvider(accessKeyId, accessKeySecret, stsToken);
// Use credentialsProvider to initialize the client.
ClientBuilderConfiguration clientBuilderConfiguration = new ClientBuilderConfiguration();
// Explicitly declare the use of the V4 signature algorithm.
clientBuilderConfiguration.setSignatureVersion(SignVersion.V4);
// Create an OSSClient instance.
// When the OSSClient instance is no longer needed, call the shutdown method to release resources.
OSS ossClient = OSSClientBuilder.create()
.endpoint("endpoint")
.credentialsProvider(credentialsProvider)
.clientConfiguration(clientBuilderConfiguration)
.region("region")
.build();
ossClient.shutdown();
}
}Use a RAMRoleARN
This method is for applications that require authorized access to OSS, such as for cross-account access. Initialize the credential provider by specifying the Alibaba Cloud Resource Name (ARN) of a RAM role. The underlying implementation is based on an STS token. The Credentials tool obtains an STS token from the STS service and calls the AssumeRole API operation to request a new STS token before the current one expires. You can also assign a value to the policy parameter to restrict the RAM role to a smaller set of permissions.
An Alibaba Cloud account has full permissions on its resources. If the AccessKey pair is leaked, it poses a significant risk to your system. We do not recommend using the AccessKey pair of an Alibaba Cloud account. Instead, use the AccessKey pair of a RAM user with the minimum required permissions.
To create an AccessKey pair for a RAM user, see Create an AccessKey pair. The AccessKey ID and AccessKey secret of a RAM user are displayed only when the AccessKey pair is created. You must save them promptly. If you forget them, you must create a new AccessKey pair to replace the old one.
To obtain a RAMRoleARN, see CreateRole - Create a RAM role.
Add the credentials dependency.
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.aliyun/credentials-java --> <dependency> <groupId>com.aliyun</groupId> <artifactId>credentials-java</artifactId> <version>LATEST</version> </dependency>Configure the AccessKey pair and RAMRoleARN as access credentials.
import com.aliyun.credentials.models.CredentialModel; import com.aliyun.oss.ClientBuilderConfiguration; import com.aliyun.oss.OSS; import com.aliyun.oss.OSSClientBuilder; import com.aliyun.oss.common.auth.Credentials; import com.aliyun.oss.common.auth.CredentialsProvider; import com.aliyun.oss.common.auth.DefaultCredentials; import com.aliyun.oss.common.comm.SignVersion; public class RamRoleArnAkDemoTest { public static void main(String[] args) { com.aliyun.credentials.models.Config config = new com.aliyun.credentials.models.Config(); // Type of access credential. Set to ram_role_arn. config.setType("ram_role_arn"); // The ARN of the RAM role to assume. Example: acs:ram::123456789012****:role/adminrole. You can set RoleArn through the ALIBABA_CLOUD_ROLE_ARN environment variable. config.setRoleArn("<RoleArn>"); // Obtain the AccessKey ID from the environment variable. config.setAccessKeyId(System.getenv().get("ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID")); // Obtain the AccessKey secret from the environment variable. config.setAccessKeySecret(System.getenv().get("ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET")); // The name of the role session. You can set RoleSessionName through the ALIBABA_CLOUD_ROLE_SESSION_NAME environment variable. config.setRoleName("<RoleSessionName>"); // Set a smaller permission policy. This is optional. Example: {"Statement": [{"Action": ["*"],"Effect": "Allow","Resource": ["*"]}],"Version":"1"} config.setPolicy("<Policy>"); // Set the validity period of the role session. This is optional. config.setRoleSessionExpiration(3600); final com.aliyun.credentials.Client credentialsClient = new com.aliyun.credentials.Client(config); CredentialsProvider credentialsProvider = new CredentialsProvider(){ @Override public void setCredentials(Credentials credentials) { } @Override public Credentials getCredentials() { CredentialModel credential = credentialsClient.getCredential(); return new DefaultCredentials(credential.getAccessKeyId(), credential.getAccessKeySecret(), credential.getSecurityToken()); } }; // Use credentialsProvider to initialize the client. ClientBuilderConfiguration clientBuilderConfiguration = new ClientBuilderConfiguration(); // Explicitly declare the use of the V4 signature algorithm. clientBuilderConfiguration.setSignatureVersion(SignVersion.V4); // Create an OSSClient instance. // When the OSSClient instance is no longer needed, call the shutdown method to release resources. OSS ossClient = OSSClientBuilder.create() .endpoint("endpoint") .credentialsProvider(credentialsProvider) .clientConfiguration(clientBuilderConfiguration) .region("region") .build(); ossClient.shutdown(); } }
Use an ECSRAMRole
This method is for applications that run on ECS instances, ECI instances, or worker nodes of Container Service for Kubernetes (CSK). We recommend that you initialize the credential provider with an ECSRAMRole. The underlying implementation is based on an STS token. ECSRAMRole lets you attach a role to an ECS instance, an ECI instance, or a worker node of CSK, which enables automatic refreshing of the STS token within the instance. This method eliminates the risk of manually maintaining an AccessKey pair or an STS token because you do not need to provide one. To obtain an ECSRAMRole, see CreateRole - Create a RAM role. To attach a role to an ECS instance, see Instance RAM roles.
Add the credentials dependency.
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.aliyun/credentials-java --> <dependency> <groupId>com.aliyun</groupId> <artifactId>credentials-java</artifactId> <version>LATEST</version> </dependency>Configure the ECSRAMRole as the access credential.
import com.aliyun.credentials.models.CredentialModel; import com.aliyun.oss.ClientBuilderConfiguration; import com.aliyun.oss.OSS; import com.aliyun.oss.OSSClientBuilder; import com.aliyun.oss.common.auth.Credentials; import com.aliyun.oss.common.auth.CredentialsProvider; import com.aliyun.oss.common.auth.DefaultCredentials; import com.aliyun.oss.common.comm.SignVersion; public class EcsRamRoleDemoTest { public static void main(String[] args) { com.aliyun.credentials.models.Config config = new com.aliyun.credentials.models.Config(); // Type of access credential. Set to ecs_ram_role. config.setType("ecs_ram_role"); // The name of the RAM role assigned to the ECS instance. config.setRoleName("<RoleName>"); final com.aliyun.credentials.Client credentialsClient = new com.aliyun.credentials.Client(config); CredentialsProvider credentialsProvider = new CredentialsProvider(){ @Override public void setCredentials(Credentials credentials) { } @Override public Credentials getCredentials() { CredentialModel credential = credentialsClient.getCredential(); return new DefaultCredentials(credential.getAccessKeyId(), credential.getAccessKeySecret(), credential.getSecurityToken()); } }; // Use credentialsProvider to initialize the client. ClientBuilderConfiguration clientBuilderConfiguration = new ClientBuilderConfiguration(); // Explicitly declare the use of the V4 signature algorithm. clientBuilderConfiguration.setSignatureVersion(SignVersion.V4); // Create an OSSClient instance. // When the OSSClient instance is no longer needed, call the shutdown method to release resources. OSS ossClient = OSSClientBuilder.create() .endpoint("endpoint") .credentialsProvider(credentialsProvider) .clientConfiguration(clientBuilderConfiguration) .region("region") .build(); ossClient.shutdown(); } }
Use an OIDCRoleARN
After you configure a worker node RAM role in Container Service for Kubernetes (CSK), applications in pods on the corresponding node can obtain the STS token of the attached role through the Metadata Server, just like applications deployed on ECS. However, if untrusted applications are deployed on the container cluster (for example, applications submitted by your customers with code that is not open to you), you may not want them to obtain the STS token of the worker node's attached instance RAM role through the Metadata Server. To avoid affecting the security of your cloud resources while allowing these untrusted applications to securely obtain the required STS tokens and achieve application-level permission minimization, use the RAM Roles for Service Accounts (RRSA) feature. The underlying implementation of this method is based on an STS token. The Alibaba Cloud container cluster creates and mounts the corresponding service account OpenID Connect (OIDC) token file for different application pods and injects the relevant configuration information into environment variables. The Credentials tool obtains the STS token of the bound role by calling the AssumeRoleWithOIDC API operation of the STS service using the configuration information from the environment variables. This method eliminates the risk of manually maintaining an AccessKey pair or an STS token because you do not need to provide one. For more information, see Configure RAM permissions for a ServiceAccount through RRSA to achieve pod permission isolation.
Add the credentials dependency.
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.aliyun/credentials-java --> <dependency> <groupId>com.aliyun</groupId> <artifactId>credentials-java</artifactId> <version>LATEST</version> </dependency>Configure the OIDC RAM role as the access credential.
import com.aliyun.credentials.models.CredentialModel; import com.aliyun.oss.ClientBuilderConfiguration; import com.aliyun.oss.OSS; import com.aliyun.oss.OSSClientBuilder; import com.aliyun.oss.common.auth.Credentials; import com.aliyun.oss.common.auth.CredentialsProvider; import com.aliyun.oss.common.auth.DefaultCredentials; import com.aliyun.oss.common.comm.SignVersion; public class OidcRoleArnDemoTest { public static void main(String[] args) { com.aliyun.credentials.models.Config config = new com.aliyun.credentials.models.Config(); // Specify the Credential type. Set to oidc_role_arn. config.setType("oidc_role_arn"); // The ARN of the RAM role. You can set RoleArn through the ALIBABA_CLOUD_ROLE_ARN environment variable. config.setRoleArn("<RoleArn>"); // The ARN of the OIDC provider. You can set OidcProviderArn through the ALIBABA_CLOUD_OIDC_PROVIDER_ARN environment variable. config.setOidcProviderArn("<OidcProviderArn>"); // The path to the OIDC token file. You can set OidcTokenFilePath through the ALIBABA_CLOUD_OIDC_TOKEN_FILE environment variable. config.setOidcTokenFilePath("<OidcTokenFilePath>"); // The name of the role session. You can set RoleSessionName through the ALIBABA_CLOUD_ROLE_SESSION_NAME environment variable. config.setRoleSessionName("<RoleSessionName>"); // Set a smaller permission policy. This is optional. Example: {"Statement": [{"Action": ["*"],"Effect": "Allow","Resource": ["*"]}],"Version":"1"} config.setPolicy("<Policy>"); // Set the session expiration time. config.setRoleSessionExpiration(3600); final com.aliyun.credentials.Client credentialsClient = new com.aliyun.credentials.Client(config); CredentialsProvider credentialsProvider = new CredentialsProvider(){ @Override public void setCredentials(Credentials credentials) { } @Override public Credentials getCredentials() { CredentialModel credential = credentialsClient.getCredential(); return new DefaultCredentials(credential.getAccessKeyId(), credential.getAccessKeySecret(), credential.getSecurityToken()); } }; // Use credentialsProvider to initialize the client. ClientBuilderConfiguration clientBuilderConfiguration = new ClientBuilderConfiguration(); // Explicitly declare the use of the V4 signature algorithm. clientBuilderConfiguration.setSignatureVersion(SignVersion.V4); // Create an OSSClient instance. // When the OSSClient instance is no longer needed, call the shutdown method to release resources. OSS ossClient = OSSClientBuilder.create() .endpoint("endpoint") .credentialsProvider(credentialsProvider) .clientConfiguration(clientBuilderConfiguration) .region("region") .build(); ossClient.shutdown(); } }
Use credentials from the Function Compute context
This method is for functions of applications deployed in Function Compute. Initialize the credential provider with credentials from the Function Compute context. The underlying implementation is based on an STS token. Function Compute obtains an STS token by assuming the service role configured for the function and then passes the STS token to your application through the Credentials parameter in the context. This STS token is valid for 36 hours and cannot be modified. The maximum execution time of a function is 24 hours, so the STS token will not expire during function execution, and you do not need to consider refreshing it. This method eliminates the risk of manually maintaining an AccessKey pair or an STS token because you do not need to provide one. To grant Function Compute permissions to access OSS, see Use a function role to grant Function Compute permissions to access other Alibaba Cloud services.
Add the Function Compute context dependency.
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.aliyun.fc.runtime/fc-java-core --> <dependency> <groupId>com.aliyun.fc.runtime</groupId> <artifactId>fc-java-core</artifactId> <version>1.4.1</version> </dependency>Initialize the credential provider with credentials from the Function Compute context.
import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.io.OutputStream; import com.aliyun.fc.runtime.Context; import com.aliyun.fc.runtime.Credentials; import com.aliyun.fc.runtime.StreamRequestHandler; import com.aliyun.oss.ClientBuilderConfiguration; import com.aliyun.oss.OSS; import com.aliyun.oss.OSSClientBuilder; import com.aliyun.oss.common.auth.*; import com.aliyun.oss.common.comm.SignVersion; public class App implements StreamRequestHandler { @Override public void handleRequest( InputStream inputStream, OutputStream outputStream, Context context) throws IOException { // Obtain key information. Before execution, ensure that the service where the function resides is configured with role information, and the role has the necessary OSS permissions. We recommend using the AliyunFCDefaultRole role. Credentials creds = context.getExecutionCredentials(); // Use the obtained credentials to create a credential provider instance. CredentialsProvider credentialsProvider = new DefaultCredentialProvider(creds.getAccessKeyId(), creds.getAccessKeySecret(), creds.getSecurityToken()); // Use credentialsProvider to initialize the client. ClientBuilderConfiguration clientBuilderConfiguration = new ClientBuilderConfiguration(); // Explicitly declare the use of the V4 signature algorithm. clientBuilderConfiguration.setSignatureVersion(SignVersion.V4); // Create an OSSClient instance. // When the OSSClient instance is no longer needed, call the shutdown method to release resources. OSS ossClient = OSSClientBuilder.create() .endpoint("endpoint") .credentialsProvider(credentialsProvider) .clientConfiguration(clientBuilderConfiguration) .region("region") .build(); ossClient.shutdown(); outputStream.write(new String("done").getBytes()); } }
Use a CredentialsURI
This method is for applications that need to retrieve Alibaba Cloud credentials from an external system for flexible credential management and keyless access. You can initialize the credential provider with a CredentialsURI. The underlying implementation is based on an STS token. The Credentials tool obtains an STS token from the URI you provide to initialize the credential client. This method eliminates the risk of manually maintaining an AccessKey pair or an STS token because you do not need to provide one.
For the Credentials tool to correctly parse and use the STS token, the URI must follow this response protocol:
Response status code: 200
Response body structure:
{ "Code": "Success", "AccessKeySecret": "AccessKeySecret", "AccessKeyId": "AccessKeyId", "Expiration": "2021-09-26T03:46:38Z", "SecurityToken": "SecurityToken" }
Add the credentials dependency.
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.aliyun/credentials-java --> <dependency> <groupId>com.aliyun</groupId> <artifactId>credentials-java</artifactId> <version>LATEST</version> </dependency>Configure the CredentialsURI as the access credential.
import com.aliyun.credentials.models.CredentialModel; import com.aliyun.oss.ClientBuilderConfiguration; import com.aliyun.oss.OSS; import com.aliyun.oss.OSSClientBuilder; import com.aliyun.oss.common.auth.Credentials; import com.aliyun.oss.common.auth.CredentialsProvider; import com.aliyun.oss.common.auth.DefaultCredentials; import com.aliyun.oss.common.comm.SignVersion; public class CredentialsUriDemoTest { public static void main(String[] args) { com.aliyun.credentials.models.Config config = new com.aliyun.credentials.models.Config(); // Type of access credential. Set to credentials_uri. config.setType("credentials_uri"); // The URI of the credential, which is the address of your server that generates STS tokens, in the format http://local_or_remote_uri/. You can set CredentialsUri through the ALIBABA_CLOUD_CREDENTIALS_URI environment variable. config.setCredentialsUri("<CredentialsUri>"); final com.aliyun.credentials.Client credentialsClient = new com.aliyun.credentials.Client(config); CredentialsProvider credentialsProvider = new CredentialsProvider(){ @Override public void setCredentials(Credentials credentials) { } @Override public Credentials getCredentials() { CredentialModel credential = credentialsClient.getCredential(); return new DefaultCredentials(credential.getAccessKeyId(), credential.getAccessKeySecret(), credential.getSecurityToken()); } }; // Use credentialsProvider to initialize the client. ClientBuilderConfiguration clientBuilderConfiguration = new ClientBuilderConfiguration(); // Explicitly declare the use of the V4 signature algorithm. clientBuilderConfiguration.setSignatureVersion(SignVersion.V4); // Create an OSSClient instance. // When the OSSClient instance is no longer needed, call the shutdown method to release resources. OSS ossClient = OSSClientBuilder.create() .endpoint("endpoint") .credentialsProvider(credentialsProvider) .clientConfiguration(clientBuilderConfiguration) .region("region") .build(); ossClient.shutdown(); } }
Use an auto-rotating AccessKey pair
This method is for applications that require long-term access to OSS but are deployed in an environment with a risk of AccessKey pair leakage that requires frequent manual rotation. Initialize the credential provider with a ClientKey. The underlying implementation is based on an AccessKey pair. When you use a ClientKey, Key Management Service (KMS) can automatically and periodically rotate the managed RAM user's AccessKey pair, turning a static RAM user AccessKey pair into a dynamic one, thus reducing the risk of leakage. In addition to periodic rotation, KMS also supports immediate rotation, which allows for quick replacement of the AccessKey pair in case of a leak. This method eliminates the risk and complexity of manually maintaining an AccessKey pair. To obtain a ClientKey, see Create an application access point.
Add the credential client dependency.
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.aliyun/alibabacloud-secretsmanager-client --> <dependency> <groupId>com.aliyun</groupId> <artifactId>alibabacloud-secretsmanager-client</artifactId> <version>1.3.7</version> </dependency> <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.aliyun/aliyun-java-sdk-core --> <dependency> <groupId>com.aliyun</groupId> <artifactId>aliyun-java-sdk-core</artifactId> <version>4.7.0</version> </dependency>Create the configuration file
secretsmanager.properties.# Type of access credential, fixed as client_key credentials_type=client_key # Decryption password for reading the Client Key: supports reading from an environment variable or a file, only one needs to be set client_key_password_from_env_variable=<your client key private key password environment variable name> client_key_password_from_file_path=<your client key private key password file path> # Path to the Client Key's private key file client_key_private_key_path=<your client key private key file path> # Associated KMS service region cache_client_region_id=[{"regionId":"<regionId>"}]Use the configuration file to pass credential information.
import com.aliyun.oss.ClientBuilderConfiguration; import com.aliyun.oss.OSS; import com.aliyun.oss.OSSClientBuilder; import com.aliyun.oss.common.auth.Credentials; import com.aliyun.oss.common.auth.CredentialsProvider; import com.aliyun.oss.common.auth.DefaultCredentials; import com.aliyun.oss.common.comm.SignVersion; import com.aliyuncs.kms.secretsmanager.client.SecretCacheClient; import com.aliyuncs.kms.secretsmanager.client.SecretCacheClientBuilder; import com.aliyuncs.kms.secretsmanager.client.exception.CacheSecretException; import com.aliyuncs.kms.secretsmanager.client.model.SecretInfo; import org.codehaus.jettison.json.JSONException; import org.codehaus.jettison.json.JSONObject; public class ClientKeyDemoTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws CacheSecretException { final SecretCacheClient client = SecretCacheClientBuilder.newClient(); CredentialsProvider credentialsProvider = new CredentialsProvider() { @Override public void setCredentials(Credentials credentials) { } @Override public Credentials getCredentials() { try { SecretInfo secretInfo = client.getSecretInfo("<secretName>"); JSONObject jsonObject = new JSONObject(secretInfo.getSecretValue()); String accessKeyId = jsonObject.getString("AccessKeyId"); String accessKeySecret = jsonObject.getString("AccessKeySecret"); return new DefaultCredentials(accessKeyId, accessKeySecret); } catch (CacheSecretException | JSONException e) { return null; } } }; // Use credentialsProvider to initialize the client. ClientBuilderConfiguration clientBuilderConfiguration = new ClientBuilderConfiguration(); // Explicitly declare the use of the V4 signature algorithm. clientBuilderConfiguration.setSignatureVersion(SignVersion.V4); // Create an OSSClient instance. // When the OSSClient instance is no longer needed, call the shutdown method to release resources. OSS ossClient = OSSClientBuilder.create() .endpoint("endpoint") .credentialsProvider(credentialsProvider) .clientConfiguration(clientBuilderConfiguration) .region("region") .build(); ossClient.shutdown(); } }
Use a custom access credential
If none of the preceding credential configuration methods meet your requirements, customize the credential provider by implementing the CredentialProviders interface. Note that if the underlying implementation is based on an STS token, you need to provide support for credential updates.
import com.aliyun.oss.ClientBuilderConfiguration;
import com.aliyun.oss.OSS;
import com.aliyun.oss.OSSClientBuilder;
import com.aliyun.oss.common.auth.Credentials;
import com.aliyun.oss.common.auth.CredentialsProvider;
import com.aliyun.oss.common.auth.DefaultCredentials;
import com.aliyun.oss.common.comm.SignVersion;
public class CustomCredentialProviderDemoTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CredentialsProvider credentialsProvider = new CredentialsProvider(){
// Initialize variable
String accessKeyId = null;
// Initialize variable
String accessKeySecrect = null;
// Initialize variable
// String token = null;
@Override
public void setCredentials(Credentials credentials) {
}
@Override
public Credentials getCredentials() {
//TODO
//Customize the method for obtaining access credentials.
// Return long-term credentials: access_key_id, access_key_secrect
return new DefaultCredentials(accessKeyId, accessKeySecrect);
// Return temporary credentials: access_key_id, access_key_secrect, token
// For temporary credentials, you need to refresh them based on their expiration time.
// return new DefaultCredentials(accessKeyId, accessKeySecrect, token);
}
};
// Use credentialsProvider to initialize the client.
ClientBuilderConfiguration clientBuilderConfiguration = new ClientBuilderConfiguration();
// Explicitly declare the use of the V4 signature algorithm.
clientBuilderConfiguration.setSignatureVersion(SignVersion.V4);
// Create an OSSClient instance.
// When the OSSClient instance is no longer needed, call the shutdown method to release resources.
OSS ossClient = OSSClientBuilder.create()
.endpoint("endpoint")
.credentialsProvider(credentialsProvider)
.clientConfiguration(clientBuilderConfiguration)
.region("region")
.build();
ossClient.shutdown();
}
}Use the default credential chain
When you initialize the credential client without passing any parameters, the Credentials tool uses the default credential chain to initialize the client. For information about the logic of reading default credentials, see Default credential chain.
Add the credentials dependency.
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.aliyun/credentials-java --> <dependency> <groupId>com.aliyun</groupId> <artifactId>credentials-java</artifactId> <version>LATEST</version> </dependency>Configure Credentials as the access credential.
import com.aliyun.credentials.models.CredentialModel; import com.aliyun.oss.*; import com.aliyun.oss.common.auth.Credentials; import com.aliyun.oss.common.auth.CredentialsProvider; import com.aliyun.oss.common.auth.DefaultCredentials; import com.aliyun.oss.common.comm.SignVersion; public class Demo { public static void main(String[] args) { com.aliyun.credentials.Client credentialsClient = new com.aliyun.credentials.Client(); CredentialsProvider credentialsProvider = new CredentialsProvider(){ @Override public void setCredentials(Credentials credentials) { } @Override public Credentials getCredentials() { CredentialModel credential = credentialsClient.getCredential(); return new DefaultCredentials(credential.getAccessKeyId(), credential.getAccessKeySecret(), credential.getSecurityToken()); } }; ClientBuilderConfiguration clientBuilderConfiguration = new ClientBuilderConfiguration(); // Explicitly declare the use of the V4 signature algorithm. clientBuilderConfiguration.setSignatureVersion(SignVersion.V4); // Use credentialsProvider to initialize the client. // Create an OSSClient instance. // When the OSSClient instance is no longer needed, call the shutdown method to release resources. OSS ossClient = OSSClientBuilder.create() .endpoint("endpoint") .credentialsProvider(credentialsProvider) .clientConfiguration(clientBuilderConfiguration) .region("region") .build(); ossClient.shutdown(); } }
FAQ
Package conflicts
Cause
When you use OSS SDK for Java 1.0, an error similar to the following indicates a package conflict in your project.
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: org/apache/http/ssl/TrustStrategy at com.aliyun.oss.OSSClient.<init>(OSSClient.java:268) at com.aliyun.oss.OSSClient.<init>(OSSClient.java:193) at com.aliyun.oss.demo.HelloOSS.main(HelloOSS.java:77) Caused by: java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: org.apache.http.ssl.TrustStrategy at java.net.URLClassLoader$1.run(URLClassLoader.java:366) at java.net.URLClassLoader$1.run(URLClassLoader.java:355) at java.security.AccessController.doPrivileged(Native Method) at java.net.URLClassLoader.findClass(URLClassLoader.java:354) at java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoader.java:425) at sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader.loadClass(Launcher.java:308) at java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoader.java:358) ... 3 moreor
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NoSuchFieldError: INSTANCE at org.apache.http.impl.io.DefaultHttpRequestWriterFactory.<init>(DefaultHttpRequestWriterFactory.java:52) at org.apache.http.impl.io.DefaultHttpRequestWriterFactory.<init>(DefaultHttpRequestWriterFactory.java:56) at org.apache.http.impl.io.DefaultHttpRequestWriterFactory.<clinit>(DefaultHttpRequestWriterFactory.java:46) at org.apache.http.impl.conn.ManagedHttpClientConnectionFactory.<init>(ManagedHttpClientConnectionFactory.java:82) at org.apache.http.impl.conn.ManagedHttpClientConnectionFactory.<init>(ManagedHttpClientConnectionFactory.java:95) at org.apache.http.impl.conn.ManagedHttpClientConnectionFactory.<init>(ManagedHttpClientConnectionFactory.java:104) at org.apache.http.impl.conn.ManagedHttpClientConnectionFactory.<clinit>(ManagedHttpClientConnectionFactory.java:62) at org.apache.http.impl.conn.PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager$InternalConnectionFactory.<init>(PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager.java:572) at org.apache.http.impl.conn.PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager.<init>(PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager.java:174) at org.apache.http.impl.conn.PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager.<init>(PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager.java:158) at org.apache.http.impl.conn.PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager.<init>(PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager.java:149) at org.apache.http.impl.conn.PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager.<init>(PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager.java:125) at com.aliyun.oss.common.comm.DefaultServiceClient.createHttpClientConnectionManager(DefaultServiceClient.java:237) at com.aliyun.oss.common.comm.DefaultServiceClient.<init>(DefaultServiceClient.java:78) at com.aliyun.oss.OSSClient.<init>(OSSClient.java:268) at com.aliyun.oss.OSSClient.<init>(OSSClient.java:193) at OSSManagerImpl.upload(OSSManagerImpl.java:42) at OSSManagerImpl.main(OSSManagerImpl.java:63)The error occurs because OSS SDK for Java 1.0 uses Apache HttpClient 4.4.1, but your project uses a conflicting version of Apache HttpClient or a commons-httpclient JAR package. Run the
mvn dependency:treecommand in your project directory to view the JAR packages and their versions used by your project. As shown in the following figure, the project uses Apache HttpClient 4.3, which conflicts with the standard version: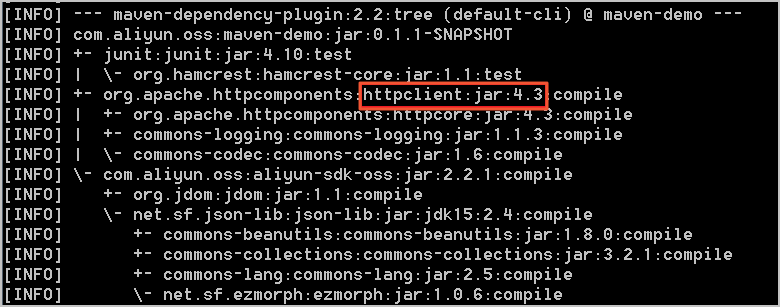
Solution
Resolve package conflicts in one of the following two ways:
Use a unified version: If your project uses a version that conflicts with Apache HttpClient 4.4.1, use version 4.4.1 and remove the dependency on other versions of Apache HttpClient from the pom.xml file. If your project uses commons-httpclient, a conflict may also exist. Remove the commons-httpclient dependency.
Resolve dependency conflicts: If your project depends on multiple third-party packages, and these packages in turn depend on different versions of Apache HttpClient, your project will have dependency conflicts. Use the exclusion tag to resolve them. For more information, see Maven Guides.
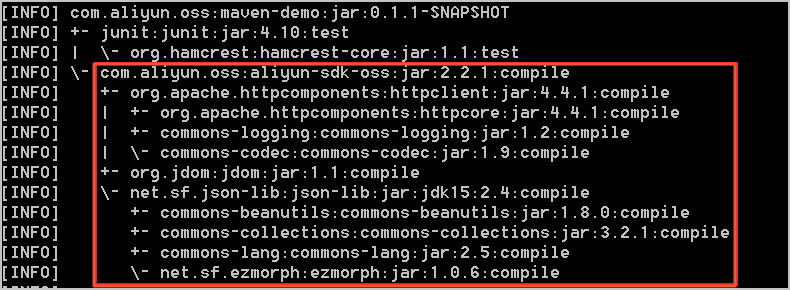
OSS SDK for Java 1.0 depends on the following package versions. The conflict resolution method is similar to that for HttpClient.
Missing packages
Cause
When you use OSS SDK for Java 1.0, an error similar to the following indicates that your project may be missing packages required to compile or run OSS SDK for Java 1.0.
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: org/apache/http/auth/Credentials at com.aliyun.oss.OSSClient.<init>(OSSClient.java:268) at com.aliyun.oss.OSSClient.<init>(OSSClient.java:193) at com.aliyun.oss.demo.HelloOSS.main(HelloOSS.java:76) Caused by: java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: org.apache.http.auth.Credentials at java.net.URLClassLoader$1.run(URLClassLoader.java:366) at java.net.URLClassLoader$1.run(URLClassLoader.java:355) at java.security.AccessController.doPrivileged(Native Method) at java.net.URLClassLoader.findClass(URLClassLoader.java:354) at java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoader.java:425) at sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader.loadClass(Launcher.java:308) at java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoader.java:358) ... 3 moreor
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: org/apache/http/protocol/HttpContext at com.aliyun.oss.OSSClient.<init>(OSSClient.java:268) at com.aliyun.oss.OSSClient.<init>(OSSClient.java:193) at com.aliyun.oss.demo.HelloOSS.main(HelloOSS.java:76) Caused by: java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: org.apache.http.protocol.HttpContext at java.net.URLClassLoader$1.run(URLClassLoader.java:366) at java.net.URLClassLoader$1.run(URLClassLoader.java:355) at java.security.AccessController.doPrivileged(Native Method) at java.net.URLClassLoader.findClass(URLClassLoader.java:354) at java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoader.java:425) at sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader.loadClass(Launcher.java:308) at java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoader.java:358) ... 3 moreor
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: org/jdom/input/SAXBuilder at com.aliyun.oss.internal.ResponseParsers.getXmlRootElement(ResponseParsers.java:645) at … … at com.aliyun.oss.OSSClient.doesBucketExist(OSSClient.java:471) at com.aliyun.oss.OSSClient.doesBucketExist(OSSClient.java:465) at com.aliyun.oss.demo.HelloOSS.main(HelloOSS.java:82) Caused by: java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: org.jdom.input.SAXBuilder at java.net.URLClassLoader$1.run(URLClassLoader.java:366) at java.net.URLClassLoader$1.run(URLClassLoader.java:355) at java.security.AccessController.doPrivileged(Native Method) at java.net.URLClassLoader.findClass(URLClassLoader.java:354) at java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoader.java:425) at sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader.loadClass(Launcher.java:308) at java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass(ClassLoader.java:358) ... 11 moreOSS SDK for Java 1.0 depends on the following packages:
aliyun-sdk-oss-2.2.1.jar
hamcrest-core-1.1.jar
jdom-1.1.jar
commons-codec-1.9.jar
httpclient-4.4.1.jar
commons-logging-1.2.jar
httpcore-4.4.1.jar
log4j-1.2.15.jar
Among these, log4j-1.2.15.jar is an optional dependency. Add this package only when you need logging functionality. The other packages are required.
Solution
Add the packages that OSS SDK for Java 1.0 depends on to your project. You can use one of the following methods:
Eclipse project: For more information, see Install the SDK.
Ant project: Place the packages that OSS SDK for Java 1.0 depends on into the lib directory of your project.
Direct compilation: Use the
-classpathor-cpcommand to specify the path of the packages that OSS SDK for Java 1.0 depends on, or place these packages in the classpath.
Connection timeout
Cause
When you run an OSS SDK for Java 1.0 program, an error similar to the following may occur because of an incorrect endpoint or network connectivity issues.
com.aliyun.oss.ClientException: SocketException at com.aliyun.oss.common.utils.ExceptionFactory.createNetworkException(ExceptionFactory.java:71) at com.aliyun.oss.common.comm.DefaultServiceClient.sendRequestCore(DefaultServiceClient.java:116) at com.aliyun.oss.common.comm.ServiceClient.sendRequestImpl(ServiceClient.java:121) at com.aliyun.oss.common.comm.ServiceClient.sendRequest(ServiceClient.java:67) at com.aliyun.oss.internal.OSSOperation.send(OSSOperation.java:92) at com.aliyun.oss.internal.OSSOperation.doOperation(OSSOperation.java:140) at com.aliyun.oss.internal.OSSOperation.doOperation(OSSOperation.java:111) at com.aliyun.oss.internal.OSSBucketOperation.getBucketInfo(OSSBucketOperation.java:1152) at com.aliyun.oss.OSSClient.getBucketInfo(OSSClient.java:1220) at com.aliyun.oss.OSSClient.getBucketInfo(OSSClient.java:1214) at com.aliyun.oss.demo.HelloOSS.main(HelloOSS.java:94) Caused by: org.apache.http.conn.HttpHostConnectException: Connect to oss-test.oss-cn-hangzhou-internal.aliyuncs.com:80 [oss-test.oss-cn-hangzhou-internal.aliyuncs.com/10.84.135.99] failed: Connection timed out: connect at org.apache.http.impl.conn.DefaultHttpClientConnectionOperator.connect(DefaultHttpClientConnectionOperator.java:151) at org.apache.http.impl.conn.PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager.connect(PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager.java:353) at org.apache.http.impl.execchain.MainClientExec.establishRoute(MainClientExec.java:380) at org.apache.http.impl.execchain.MainClientExec.execute(MainClientExec.java:236) at org.apache.http.impl.execchain.ProtocolExec.execute(ProtocolExec.java:184) at org.apache.http.impl.execchain.RedirectExec.execute(RedirectExec.java:110) at org.apache.http.impl.client.InternalHttpClient.doExecute(InternalHttpClient.java:184) at org.apache.http.impl.client.CloseableHttpClient.execute(CloseableHttpClient.java:82) at com.aliyun.oss.common.comm.DefaultServiceClient.sendRequestCore(DefaultServiceClient.java:113) ... 9 moreSolution
You can use the ossutil tool to quickly locate the cause of the error and resolve the issue.
SignatureDoesNotMatch error
Cause 1: Mismatched AccessKey pair information
The AccessKey ID and AccessKey secret do not match. For information about how to obtain an AccessKey ID and AccessKey secret, see Create an AccessKey pair.
Cause 2: Incorrect usage of a signed URL
The following is an incorrect example of using a signed URL:
GeneratePresignedUrlRequest request = new GeneratePresignedUrlRequest(bucketName, object); request.setExpiration( new Date(new Date().getTime() + 3600 * 1000)); request.addUserMetadata("author"); URL url = ossClient.generatePresignedUrl(request); Map<String, String> header = new HashMap<String, String>(); header.put("author"); ossClient.putObject(url, new ByteArrayInputStream("Hello OSS".getBytes()), -1, header);If the Method parameter is not specified, the GET method is used by default. However, the preceding example is a PutObject request. Therefore, the Method parameter must be specified and set to PUT.
When you send a PutObject request, custom metadata in the request header must be prefixed with
x-oss-meta-. In the preceding example, the custom metadata should be changed tox-oss-meta-author.Solution:
Specify the Method parameter and modify the header prefix:
request.addUserMetadata("author"); request.setMethod(HttpMethod.PUT); URL url = ossClient.generatePresignedUrl(request); Map<String, String> header = new HashMap<String, String>(); header.put("x-oss-meta-" + "author"); ossClient.putObject(url, new ByteArrayInputStream("Hello OSS".getBytes()), -1, header);Cause 3: HttpClient version compatibility issue
An OSS SDK version earlier than 3.7.0 is used, and HttpClient 4.5.9 or later is introduced in the project.
The name of the uploaded file contains a
+character, and HttpClient 4.5.9 does not URL-encode the+character. This causes the signatures calculated by the client and the server to be inconsistent.
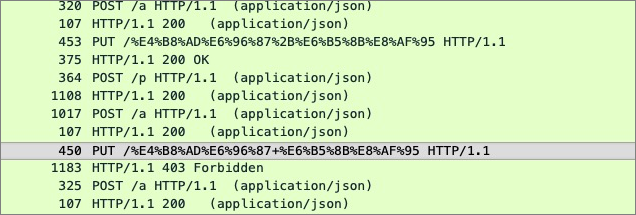
Solution:
Upgrade the OSS SDK to version 3.11.1 or later to be compatible with HttpClient 4.5.9.
Remove redundant HttpClient dependencies. When you introduce the OSS SDK, the HttpClient dependency is automatically introduced. If a third-party library also introduces HttpClient, see the solution for Package conflicts.
Cause 4: HttpClient character set compatibility issue
HttpClient 4.5.10 does not support characters outside the ISO-8859-1 standard in the header. However, a version of HttpClient later than 4.5.10 is introduced in the project, and the request header contains characters outside the ISO-8859-1 standard, such as Chinese characters in custom metadata starting with
x-oss-meta-.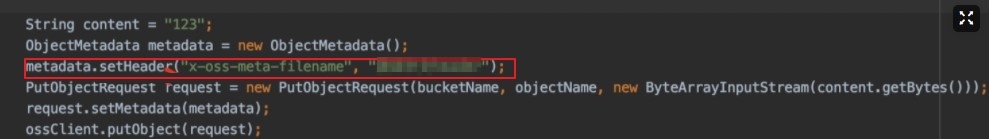
Solution:
See the solution for Package conflicts to remove the conflicting HttpClient version.
Pass only characters that comply with the ISO-8859-1 standard in the request header.
"Failed to parse the response result" exception

Cause
Certain special software on the client side intercepts the HTTP request, or a public network route hijacks the HTTP request.
You are using OSS SDK for Java 1.0 on Java 9 or later, and you have not added the JAXB-related dependencies to the pom.xml file.
Solution
Switch to an HTTPS request.
Add the JAXB-related dependencies. For the procedure, see Install the SDK.
org.apache.http.NoHttpResponseException: The target server failed to respond
Cause
When you run an OSS SDK for Java 1.0 program, an error similar to the following is reported:
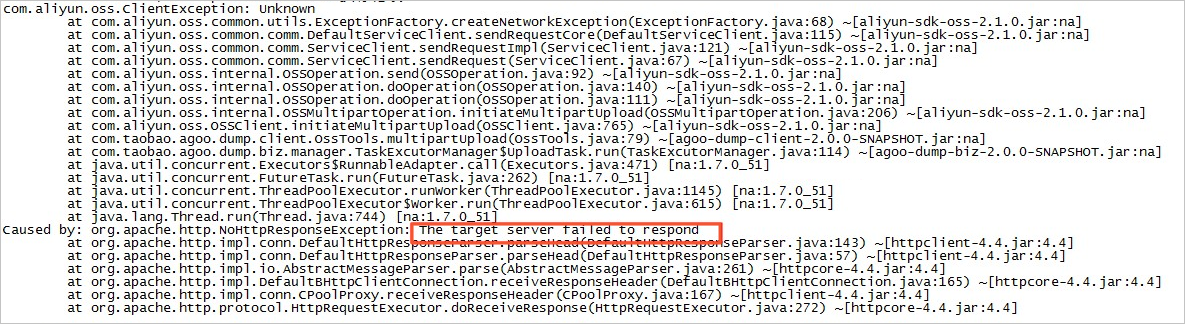
Using an expired connection causes the preceding error. This error only occurs in Java SDK versions earlier than 2.1.2.
Solution
Upgrade OSS SDK for Java 1.0 to version 2.1.2 or later.
Many org.apache.http.impl.conn.PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager instances exist in the JVM
Cause
The ossClient was not closed correctly.
Solution
Close the ossClient after it has finished executing, or use the singleton pattern.
OSS SDK for Java 1.0 call is unresponsive
Cause
An OSS SDK for Java 1.0 call is unresponsive. By running the
jstack -l pidcommand to view the stack, the problem is located at the following position:"main" prio=6 tid=0x000000000291e000 nid=0xc40 waiting on condition [0x0000000002dae000] java.lang.Thread.State: WAITING (parking) at sun.misc.Unsafe.park(Native Method) - parking to wait for <0x00000007d85697f8> (a java.util.concurrent.locks.AbstractQueuedSynchronizer$ConditionObject) at java.util.concurrent.locks.LockSupport.park(LockSupport.java:186) at java.util.concurrent.locks.AbstractQueuedSynchronizer$ConditionObject.await(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.java:2043) at org.apache.http.pool.PoolEntryFuture.await(PoolEntryFuture.java:138) at org.apache.http.pool.AbstractConnPool.getPoolEntryBlocking(AbstractConnPool.java:306) at org.apache.http.pool.AbstractConnPool.access$000(AbstractConnPool.java:64) at org.apache.http.pool.AbstractConnPool$2.getPoolEntry(AbstractConnPool.java:192) at org.apache.http.pool.AbstractConnPool$2.getPoolEntry(AbstractConnPool.java:185) at org.apache.http.pool.PoolEntryFuture.get(PoolEntryFuture.java:107) at org.apache.http.impl.conn.PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager.leaseConnection(PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager.java:276) at org.apache.http.impl.conn.PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager$1.get(PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager.java:263) at org.apache.http.impl.execchain.MainClientExec.execute(MainClientExec.java:190) at org.apache.http.impl.execchain.ProtocolExec.execute(ProtocolExec.java:184) at org.apache.http.impl.execchain.RedirectExec.execute(RedirectExec.java:110) at org.apache.http.impl.client.InternalHttpClient.doExecute(InternalHttpClient.java:184) at org.apache.http.impl.client.CloseableHttpClient.execute(CloseableHttpClient.java:82) at com.aliyun.oss.common.comm.DefaultServiceClient.sendRequestCore(DefaultServiceClient.java:113) at com.aliyun.oss.common.comm.ServiceClient.sendRequestImpl(ServiceClient.java:123) at com.aliyun.oss.common.comm.ServiceClient.sendRequest(ServiceClient.java:68) at com.aliyun.oss.internal.OSSOperation.send(OSSOperation.java:94) at com.aliyun.oss.internal.OSSOperation.doOperation(OSSOperation.java:146) at com.aliyun.oss.internal.OSSOperation.doOperation(OSSOperation.java:113) at com.aliyun.oss.internal.OSSObjectOperation.getObject(OSSObjectOperation.java:229) at com.aliyun.oss.OSSClient.getObject(OSSClient.java:629) at com.aliyun.oss.OSSClient.getObject(OSSClient.java:617) at samples.HelloOSS.main(HelloOSS.java:49)The cause is a connection leak in the connection pool, possibly because ossObject was not closed correctly after use.
Solution
Check your program to ensure there are no connection leaks. Use the following method to close the connection correctly:
// Read the file. OSSObject ossObject = ossClient.getObject(bucketName, objectName); // OSS operation // Close ossObject. ossObject.close();For detailed troubleshooting steps, see Troubleshoot unresponsive OSS SDK for Java 1.0.
Connection closed
Cause
If you encounter an error similar to the following when using ossClient.getObject:
Exception in thread "main" org.apache.http.ConnectionClosedException: Premature end of Content-Length delimited message body (expected: 11990526; received: 202880) at org.apache.http.impl.io.ContentLengthInputStream.read(ContentLengthInputStream.java:180) at org.apache.http.impl.io.ContentLengthInputStream.read(ContentLengthInputStream.java:200) at org.apache.http.impl.io.ContentLengthInputStream.close(ContentLengthInputStream.java:103) at org.apache.http.impl.execchain.ResponseEntityProxy.streamClosed(ResponseEntityProxy.java:128) at org.apache.http.conn.EofSensorInputStream.checkClose(EofSensorInputStream.java:228) at org.apache.http.conn.EofSensorInputStream.close(EofSensorInputStream.java:174) at java.io.FilterInputStream.close(FilterInputStream.java:181) at java.io.FilterInputStream.close(FilterInputStream.java:181) at com.aliyun.oss.event.ProgressInputStream.close(ProgressInputStream.java:147) at java.io.FilterInputStream.close(FilterInputStream.java:181) at samples.HelloOSS.main(HelloOSS.java:39)The cause is that the interval between two data reads exceeds 1 minute. OSS closes connections that have been idle for more than 1 minute.
Solution
If you only read part of the data each time and the data processing time is not fixed, use range download to avoid connection closure during data reading. The connection is closed automatically after the range download is complete. For more information, see Range download (Java SDK).
Memory leakage
Cause
A program that calls OSS SDK for Java 1.0 leaks memory after running for a period of time (from a few hours to a few days, depending on the business volume). We recommend using Eclipse Memory Analyzer (MAT) to analyze memory usage. For more information, see Analyze heap dump files with MAT.
If the analysis result is similar to the figure below (PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager occupies 96% of the memory), the cause is that
new OSSClientmay have been executed multiple times in the program, butossClient.shutdownwas not called, which resulted in a memory leak.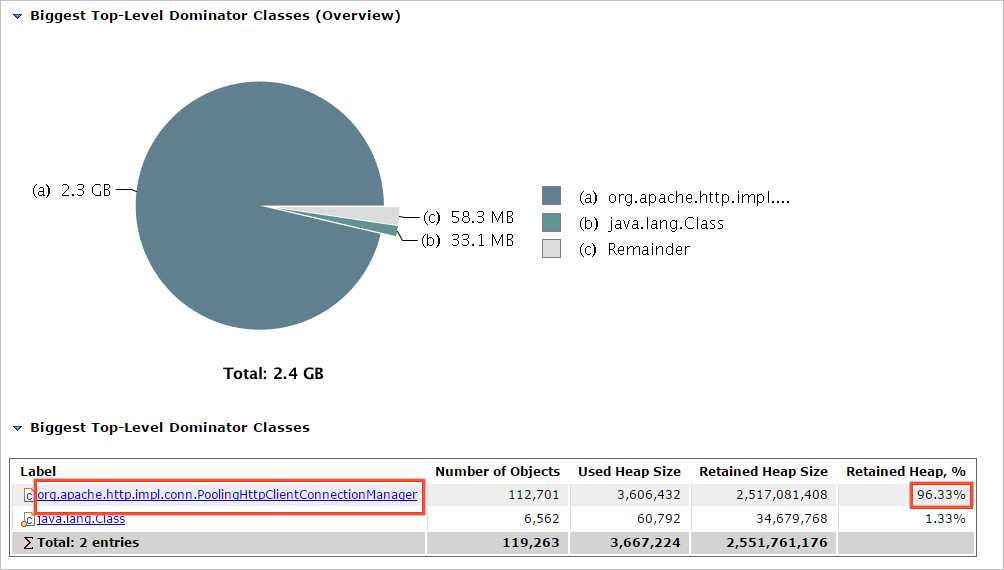
Solution
After the
new OSSClientoperation is complete, call theshutdownmethod to close it. Ensure thatnew OSSClientandossClient.shutdownare used in pairs.
InterruptedException is reported when ossClient.shutdown is called
Cause
Versions of OSS SDK for Java 1.0 earlier than 2.3.0 report the following exception when calling
ossClient.shutdown:java.lang.InterruptedException: sleep interrupted at java.lang.Thread.sleep(Native Method) at com.aliyun.oss.common.comm.IdleConnectionReaper.run(IdleConnectionReaper:76)The cause is that the ossClient backend thread IdleConnectionReaper periodically closes idle connections. If ossClient.shutdown is called while IdleConnectionReaper is in Sleep, the above exception is reported.
Solution
Use the following code to ignore the exception:
try { ossClient.shutdown(); } catch(Exception e) { }
"SDK.ServerUnreachable : Speicified endpoint or uri is not valid" exception
Cause
The client sends too many concurrent requests to STS.
The network connection to the server times out.
The STS SDK and SDK core used are not the latest versions.
Solution
The client is sending too many concurrent requests to STS, and the client's ECS instance or local computer cannot handle the concurrency. Reduce the OSS concurrency.
The network connection from the user to the server times out. Capture packets to verify this.
Upgrade the STS SDK and SDK core to the latest versions.
NoSuchKey

Cause
The source file does not exist.
Solution
For more information, see 404 error.
SocketException
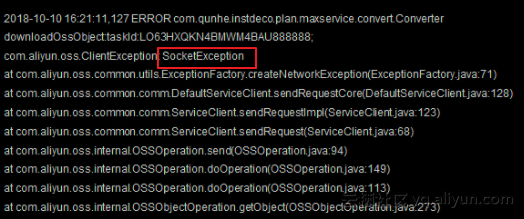
Cause
The socket may have failed during the initialization phase, causing the request to fail before reaching OSS.
Solution
We recommend that you check the following aspects:
Whether network jitter occurred when the problem appeared.
Whether the number of socket connections on the host is maxed out.
Confirm whether the number of connections exceeded the maxconnection setting in the SDK when the problem occurred. If the number of connections exceeds the maxconnection setting, a socket exception will also occur.
If there are no issues with the above, we recommend that you deploy tcpdump or Wireshark to capture packets, and then analyze the data packets after the problem recurs.
The callback of OSS PostObject is not triggered
The callback of OSS PostObject is not triggered, but the same callback is triggered by PutObject. Generally, if the JSON format is incorrect or the callback fails, a corresponding message is returned. In this case, you need to test the Put and Post callback effects separately:
Cause
When sending the request, the callback parameter is under the file parameter.

Solution
Adjust the position of the callback and file parameters.
At this point, the test result shows that the business server successfully captured the request.
Connection pool shut down
Caused by: java.lang.IllegalStateException: Connection pool shut down
at org.apache.http.util.Asserts.check(Asserts.java:34)
at org.apache.http.pool.AbstractConnPool.lease(AbstractConnPool.java:184)
at org.apache.http.impl.conn.PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager.requestConnection(PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager.java:251)
at org.apache.http.impl.execchain.MainClientExec.execute(MainClientExec.java:175)
at org.apache.http.impl.execchain.ProtocolExec.execute(ProtocolExec.java:184)
at org.apache.http.impl.execchain.RedirectExec.execute(RedirectExec.java:110)
at org.apache.http.impl.client.InternalHttpClient.doExecute(InternalHttpClient.java:184)
at org.apache.http.impl.client.CloseableHttpClient.execute(CloseableHttpClient.java:82)
at com.aliyun.oss.common.comm.DefaultServiceClient.sendRequestCore(DefaultServiceClient.java:124)
at com.aliyun.oss.common.comm.ServiceClient.sendRequestImpl(ServiceClient.java:133)
... 8 moreCause
You are continuing to send requests through ossClient after calling the
ossClient.shutdown()method.Solution
Check your calling logic to ensure that after you call the
ossClient.shutdown()method, you no longer send requests through ossClient.
A "Request has expired" error occurs for requests generated by generatePresignedUrl of the Java SDK
Cause
An integer overflow causes a timestamp issue related to the year 2038 problem.
An upload request is initiated after the expiration time set for the URL.
Solution
If it is an integer overflow, we recommend that the expiration duration in the Java SDK not exceed the year 2038.
If an upload request is initiated after the expiration time set for the URL, set a reasonable expiration time to ensure that the expiration time is later than the time you initiate the request.
"Invalid Response" or "Implementation of JAXB-API has not been found on module path or classpath" error
Cause
You are using Java 9 or later and have not added the JAXB dependency.
Solution
For information about how to add the JAXB dependency, see Install the SDK.
Is OSSClient in OSS SDK for Java 1.0 thread-safe?
Yes, it is. OSSClient is thread-safe, which allows multiple threads to access the same instance. You can reuse the same OSSClient instance or create multiple OSSClient instances to use separately, based on your business needs.
An OSSClient instance maintains a connection pool internally. When an OSSClient instance is no longer needed, you must call the shutdown method to close it and avoid resource exhaustion from creating too many OSSClient instances.
An "AccessDenied Hierarchical namespace is disabled" error is reported
Cause
Hierarchical namespace was not enabled before you called the CreateDirectory, Rename, or DeleteDirectory API operation.
Solution
Enable hierarchical namespace when you create a bucket. For the specific procedure, see Create a bucket.
The client network is normal, but a "Connection reset" error is reported during HTTP access. How do I handle this?
Carriers in some regions may hijack the OSS domain name. We recommend that you configure the protocol as HTTPS through the endpoint. For more information, see Configure the client.
Java 17 Cannot invoke "java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Object, Object[])" because "com.sun.xml.bind.v2.runtime.reflect.opt.Injector.defineClass" is null
Cause
JAXB was marked as deprecated in Java 9 and removed in Java 11.
Solution
Add the following dependencies:
<dependency> <groupId>com.sun.xml.bind</groupId> <artifactId>jaxb-impl</artifactId> <version>2.3.1</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.sun.xml.messaging.saaj</groupId> <artifactId>saaj-impl</artifactId> <version>1.5.1</version> </dependency>
How do I configure internal log printing for the Java SDK?
The Java SDK uses the Apache Commons Logging (JCL) framework for log printing. JCL can use multiple logging implementation frameworks. For more information, see JCL-Configuration. The most common ones are JCL over log4j or JCL over SLF4j. The implementation methods are as follows:
JCL over log4j: You need to introduce the log4j dependency (log4j 2.x has multiple implementation frameworks to choose from, the default is log4j-api+log4j-core) and configure it according to the log4j configuration method. For the specific process, see APACHE LOG4J-API Separation.
JCL over slf4j: You need to introduce the jcl-over-slf4j and slf4j dependencies (slf4j also has multiple implementation frameworks to choose from, such as slf4j-api+logback-classic) and configure it according to the slf4j configuration method. For the specific process, see SJF4J-Bridging legacy APIs.
Apache Log4j defines different levels of logs, including OFF, FATAL, ERROR, WARN, INFO, DEBUG, TRACE, and ALL.
Enable or disable SDK logs by configuring the log4j properties: