This topic shows you how to use ossfs to mount an Object Storage Service (OSS) bucket as a local file system in Linux.
Prerequisites
You have installed and configured ossfs 1.0.
Mount command format
Command format:
ossfs bucket_name /tmp/ossfs -o url=http://oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com -o sigv4 -o region=cn-hangzhouParameter description
ossfs: The ossfs command.bucket_name: The name of the bucket to mount./tmp/ossfs: The local directory where the bucket will be mounted (the mount point).-o: A flag that precedes a mount option.url=http://oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com: Theurlmount option specifies the endpoint of the target bucket. The option value format ishttp://Endpoint.To view the endpoint of the target bucket, go to the Bucket List page, select the target bucket, and then click Overview in the navigation pane on the left. View the region of the target bucket in the Access Points section on the Overview page. In this example, a bucket in the China (Hangzhou) region is used.

sigv4: Enables signature version 4 for requests. ossfs uses signature version 1 by default.region=cn-hangzhou: The region identifier for OSS bucket requests. Add-oregion=<region_id>when mounting. The default value is empty. When using V4 signatures, you must add this option as the identifier of the region where the request is initiated.
Basic mounting
Mount using configuration files
Create a mount directory.
Run the following command to create custom empty directories
/tmp/ossfs-1and/tmp/ossfs-2as mount directories for the target bucket.mkdir /tmp/ossfs-1 /tmp/ossfs-2Run the following commands.
The following commands mount
bucket-test-1andbucket-test-2to the/tmp/ossfs-1and/tmp/ossfs-2directories, respectively.ossfs bucket-test-1 /tmp/ossfs-1/ -o url=http://oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com -o sigv4 -o region=cn-hangzhou ossfs bucket-test-2 /tmp/ossfs-2/ -o url=http://oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com -o sigv4 -o region=cn-hangzhouThe result should look like this:
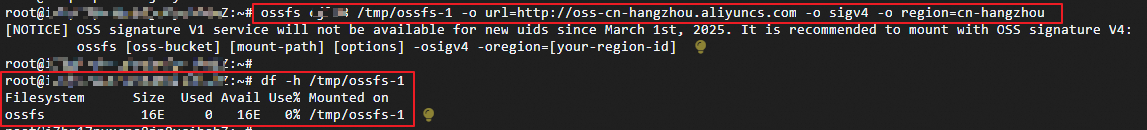
Mount using an ECS RAM role
Create a mount directory.
Run the following command to create an empty directory
/tmp/ossfsas the mount directory for the target bucket.mkdir /tmp/ossfsRun the mount command.
NoteWhen using the instance metadata URL to mount ossfs, only normal mode access is supported. For information about metadata access modes, see Metadata access modes.
Run the following command to mount a bucket named
bucket1to the local/tmp/ossfsdirectory.Note that when mounting with an ECS RAM role, specify the instance metadata URL using the
-o ram_roleparameter.100.100.100.200is the default IP address of the Alibaba Cloud ECS instance metadata service and does not need to be changed.EcsRamRoleOssTestis the name of the RAM role attached to your ECS instance. Replace it with your actual role name.ossfs bucket1 /tmp/ossfs -o url=http://oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com -o ram_role=http://100.100.100.200/latest/meta-data/ram/security-credentials/EcsRamRoleOssTest -o sigv4 -o region=cn-hangzhouThe result should look like this:

Scenario-based mounting
Mount a specific sub-directory or use various mount options for different scenarios. Make sure that the local directory is empty before you run the mount command.
Mount a specific directory
Run the following command to mount the folder directory in bucket-ossfs-test to the local /tmp/ossfs-folder directory.
ossfs bucket-ossfs-test:/folder /tmp/ossfs-folder -o url=http://oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com -o sigv4 -o region=cn-hangzhouMount using a specified configuration file
Mount option: The passwd_file mount option is used to specify the path of a non-default ossfs 1.0 configuration file during mounting. The permissions of the specified configuration file must be set to 600.
Mount example
Run the following command to mount
bucket-test-3configured in the specified configuration file to the local/tmp/ossfs-3directory.ossfs bucket-test-3 /tmp/ossfs-3 -o url=http://oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com -o passwd_file=/etc/passwd-ossfs-3 -o sigv4 -o region=cn-hangzhou
Enable debug logs when mounting
Mount option: The dbglevel option sets the log level. Supported levels are
critical,error,warn,info, anddebug. The default value iscritical. Default log retention path: CentOS systems save logs in /var/log/messages, while Ubuntu systems save logs in /var/log/syslog. You can also specify the target log file path using thelogfilemount option.Mount example 1
Run the following command to mount
bucket-ossfs-test-1to the local/tmp/ossfs-1directory, enablelibfusedebug logs using-d, and set the log information level todebugusing thedbglevelmount option.ossfs bucket-ossfs-test-1 /tmp/ossfs-1 -d -o dbglevel=debug -o sigv4 -o region=cn-hangzhouMount example 2
Run the following command to mount
bucket-ossfs-test-2to the local/tmp/ossfs-2directory, set the log information level todebug, enablelibfusedebug logs, and output the log information to the foreground terminal using the-fmount option.ossfs bucket-ossfs-test-2 /tmp/ossfs-2 -d -o dbglevel=debug -f -o sigv4 -o region=cn-hangzhou
Configure access permissions when mounting
By default, the directory to which ossfs mounts the bucket can be accessed only by the owner of the mount point. The user who runs the mount command becomes the owner of the mount point. To modify the default permission configurations and allow other users or user groups to access the mount point, use the following options when you run ossfs:
Mount option | Description |
allow_other | Grants other users access to the mount point directory itself. Permissions for files within the directory must be managed separately. The permissions for files in the directory need to be set separately. Use the |
uid | Specifies the user ID (UID) of the owner of the directory. |
gid | Specifies the group ID (GID) of the owner of the directory. |
umask | Specifies the permission mask of files and directories on the mount point. For example, to set the permissions of files on the mount point to 770, add -o umask=007. To set the permissions of files on the mount point to 700, add -o umask=077. |
Mount example 1
Run the following command to mount
bucket_nameto the localmount_pointdirectory, and use theallow_othermount option to set the mount directory permissions to 777, allowing all users to access it.ossfs bucket_name mount_point -o url=endpoint -o allow_other -o sigv4 -o region=cn-hangzhouMount example 2
Run the following command to mount
bucket_nameto the localmount_pointdirectory, and use theumaskmount option to set the mount directory and file permissions to 770, allowing only users in the same group to access.ossfs bucket_name mount_point -o url=endpoint -o umask=007 -o sigv4 -o region=cn-hangzhouMount example 3
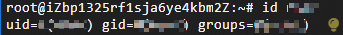
Run the following command to obtain the UID, GID, and groups of a specified user. In this example, the www user is used.
id wwwThe command output is shown in the following figure.
Run the following command to mount
bucket_nameto the localmount_pointdirectory, and use theuidandgidmount options to specify the user and group, allowing only users in the same group to access with permissions set to 770. Theuidandgidinformation uses 1000 as an example. Replace them with the target user'suidandgidinformation before executing the mount command.ossfs bucket_name mount_point -o url=endpoint -o allow_other -o uid=1000 -o gid=1000 -o umask=007 -o sigv4 -o region=cn-hangzhou
Useful tips
Unmount a bucket
To unmount a bucket, use the umount command with the mount point path. For example, unmount the file system mounted to the /tmp/ossfs path.
umount /tmp/ossfsReferences
To mount an OSS bucket in Windows, use Cloud Storage Gateway (CSG). For more information, see Use file gateways in the Alibaba Cloud Management Console and Access SMB shared directories.
Traffic is free when you use an ECS RAM role to mount a bucket via its internal endpoint. For more information, see Traffic fees.
To mount a bucket in a different region from your ECS instance, use a public endpoint or configure cross-region access over the internal network.
If you want to build an IIS website through Cloud Storage Gateway and use OSS as data storage, see How to build an IIS website using Alibaba Cloud Storage Gateway.
To mount OSS on a Windows operating system, see Rclone.
For more information about mounting, permissions, and other related issues, see FAQ.