This topic describes how to use OpenTelemetry for distributed tracing in Istio. With the tracing capabilities of Istio, you can visualize service call relationships and dependencies, monitor the health of microservices, identify performance bottlenecks, and troubleshoot issues in distributed systems.
Prerequisites
Istio v1.19 or later has been installed in the cluster.
The OpenTelemetry Collector has been deployed in the cluster. Istio trace data needs to be forwarded to Managed Service for OpenTelemetry through the OpenTelemetry Collector. For information about how to deploy the OpenTelemetry Collector in the cluster, see Forwarding via OpenTelemetry Collector.
The endpoint and authentication information of Managed Service for OpenTelemetry has been obtained. For more information, see Connect to Managed Service for OpenTelemetry and authenticate clients.
Procedure
1. Configure the reporting method for Istio trace data
Istio supports exporting trace data to the OpenTelemetry Collector via the gRPC or HTTP protocol. Choose one of the following methods.
Use the gRPC protocol
Run the following commands. Istio trace data will be exported to the OpenTelemetry Collector via OTLP/gRPC.
Create a configuration file named istio-otel-config.yaml.
cat > istio-otel-config.yaml <<EOF apiVersion: install.istio.io/v1alpha1 kind: IstioOperator spec: meshConfig: defaultConfig: tracingServiceName: APP_LABEL_AND_NAMESPACE enableTracing: true extensionProviders: - name: otel-tracing opentelemetry: port: 4317 service: <service-name>.<namespace>.svc.cluster.local resource_detectors: environment: {} EOFUse the HTTP protocol
Run the following commands. Istio trace data will be exported to the OpenTelemetry Collector via OTLP/HTTP.
Create a configuration file named istio-otel-config.yaml.
cat > istio-otel-config.yaml <<EOF apiVersion: install.istio.io/v1alpha1 kind: IstioOperator spec: meshConfig: enableTracing: true extensionProviders: - name: otel-tracing opentelemetry: port: 4318 service: opentelemetry-collector.observability.svc.cluster.local http: path: "/v1/traces" timeout: 5s headers: - name: "custom-header" value: "custom value" resource_detectors: environment: {} EOFNoteYou need to replace the service address in the configuration with the actual service address of the OpenTelemetry Collector in your environment. In the configuration,
<service-name>refers to the service name of the OpenTelemetry Collector, and<namespace>refers to the namespace where it is deployed. Example:opentelemetry-collector.observability.svc.cluster.local.Istio provides a configuration option
tracingServiceNameto control how the service name (application name) is generated, with three options.APP_LABEL_AND_NAMESPACE(default): uses the format<app label>.<namespace>.CANONICAL_NAME_ONLY: uses only the canonical name of the workload, such as the name of the Deployment.CANONICAL_NAME_AND_NAMESPACE: uses the format<canonical name>.<namespace>.
Apply the istio-otel-config.yaml file.
istioctl install -y -f istio-otel-config.yaml
2. Enable tracing for Istio
After configuring trace data reporting, you need to enable Istio trace data collection and set the sampling ratio. Run the following commands to enable tracing.
Create the configuration file istio-telemetry.yaml.
cat > istio-telemetry.yaml <<EOF apiVersion: telemetry.istio.io/v1 kind: Telemetry metadata: name: otel-demo spec: tracing: - providers: - name: otel-tracing randomSamplingPercentage: 100 EOFNoterandomSamplingPercentagerepresents the trace sampling rate, with values ranging from 0 to 100. Setting it to 100 means recording trace data for all requests. In production environments, we recommend that you adjust this value based on actual traffic conditions.Apply the configuration.
kubectl apply -f istio-telemetry.yamlAfter completing the above configuration, when there are calls between services, Istio will automatically generate trace data and forward it to Managed Service for OpenTelemetry through the OpenTelemetry Collector.
3. View Istio trace data
Go to the Managed Service for OpenTelemetry console to view Istio trace data.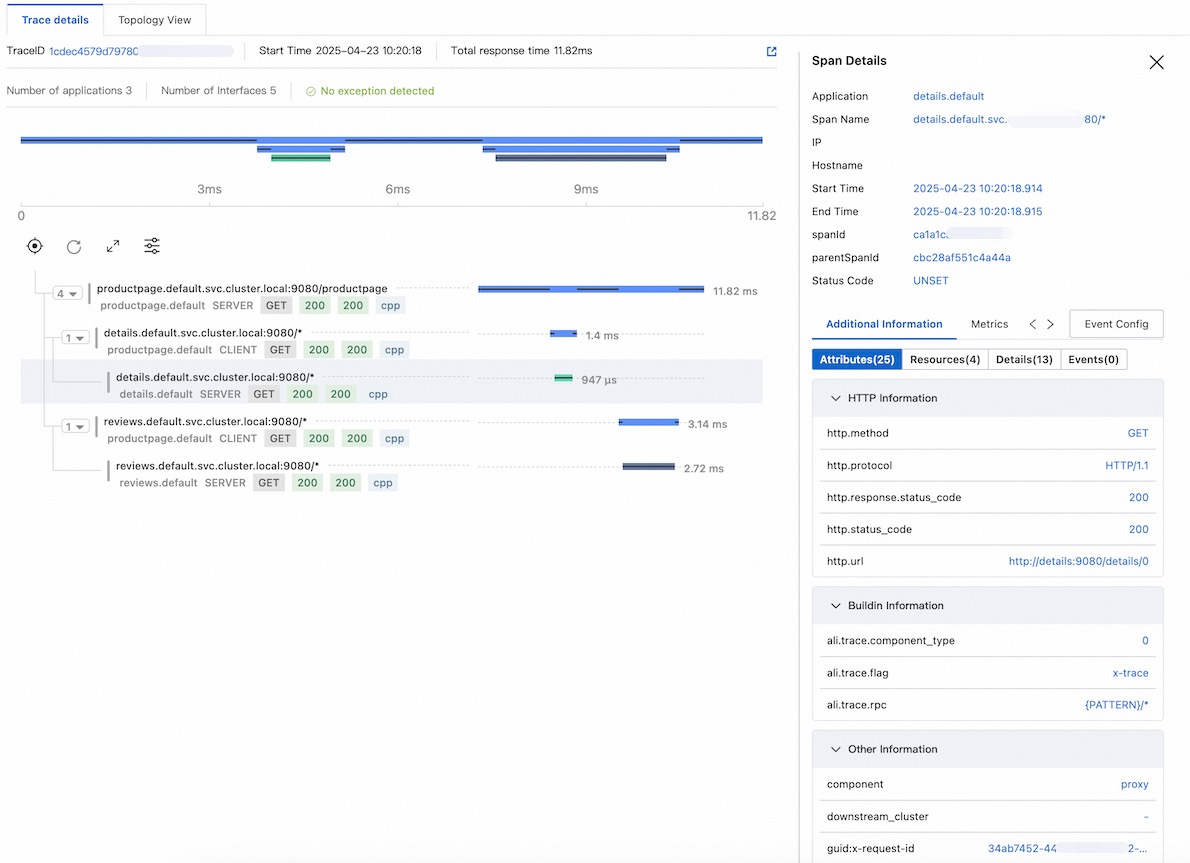
Sample practice
The following sample practice demonstrates how to collect Istio trace data and report it to Managed Service for OpenTelemetry.
1. Install Istio
curl -L https://istio.io/downloadIstio | sh -
cd istio-1.25.2
export PATH=$PWD/bin:$PATH2. Install the OpenTelemetry Collector
Create otel.yaml. Replace <gRPC-Endpoint> and <gRPC-Token> with the endpoint and authentication token obtained in Prerequisites.
cat > otel.yaml <<EOF apiVersion: v1 kind: ConfigMap metadata: name: opentelemetry-collector-conf labels: app: opentelemetry-collector data: opentelemetry-collector-config: | receivers: otlp: protocols: grpc: http: processors: batch: exporters: otlp: endpoint: "<gRPC-Endpoint>" headers: Authentication: "<gRPC-Token>" tls: insecure: true logging: loglevel: debug extensions: health_check: port: 13133 service: extensions: - health_check pipelines: logs: receivers: [otlp] processors: [batch] exporters: [logging] traces: receivers: - otlp exporters: - logging - otlp --- apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: opentelemetry-collector labels: app: opentelemetry-collector spec: ports: - name: grpc-opencensus port: 55678 protocol: TCP targetPort: 55678 - name: grpc-otlp # Default endpoint for OpenTelemetry receiver. port: 4317 protocol: TCP targetPort: 4317 - name: http-otlp # HTTP endpoint for OpenTelemetry receiver. port: 4318 protocol: TCP targetPort: 4318 selector: app: opentelemetry-collector --- apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: opentelemetry-collector spec: selector: matchLabels: app: opentelemetry-collector strategy: rollingUpdate: maxSurge: 1 maxUnavailable: 1 type: RollingUpdate template: metadata: labels: app: opentelemetry-collector sidecar.istio.io/inject: "false" # do not inject spec: containers: - command: - "/otelcol" - "--config=/conf/opentelemetry-collector-config.yaml" env: - name: POD_NAME valueFrom: fieldRef: apiVersion: v1 fieldPath: metadata.name - name: POD_NAMESPACE valueFrom: fieldRef: apiVersion: v1 fieldPath: metadata.namespace image: otel/opentelemetry-collector:0.54.0 imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent name: opentelemetry-collector ports: - containerPort: 4317 protocol: TCP - containerPort: 4318 protocol: TCP - name: grpc-opencensus containerPort: 55678 protocol: TCP resources: limits: cpu: "2" memory: 4Gi requests: cpu: 200m memory: 400Mi terminationMessagePath: /dev/termination-log terminationMessagePolicy: File volumeMounts: - name: opentelemetry-collector-config-vol mountPath: /conf dnsPolicy: ClusterFirst restartPolicy: Always schedulerName: default-scheduler terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 30 volumes: - configMap: defaultMode: 420 items: - key: opentelemetry-collector-config path: opentelemetry-collector-config.yaml name: opentelemetry-collector-conf name: opentelemetry-collector-config-vol EOFCreate the namespace named
observability.kubectl create namespace observabilityDeploy the OpenTelemetry Collector.
kubectl apply -f otel.yaml -n observability
3. Configure Istio tracing
Run the following commands in the cluster, and Istio trace data will be exported to the OpenTelemetry Collector via OTLP/gRPC.
cat <<EOF | istioctl install -y -f - apiVersion: install.istio.io/v1alpha1 kind: IstioOperator spec: meshConfig: enableTracing: true extensionProviders: - name: otel-tracing opentelemetry: port: 4317 service: opentelemetry-collector.observability.svc.cluster.local resource_detectors: environment: {} EOFRun the following commands to enable Istio tracing.
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF apiVersion: telemetry.istio.io/v1 kind: Telemetry metadata: name: otel-demo spec: tracing: - providers: - name: otel-tracing randomSamplingPercentage: 100 EOF
4. Deploy the demo application
Enable automatic sidecar injection for the
defaultnamespace.Istio will automatically inject the sidecar proxy (
istio-proxycontainer) into new pods created in this namespace.kubectl label namespace default istio-injection=enabledDeploy the demo application included with Istio (run this command from the extracted Istio directory).
kubectl apply -f samples/bookinfo/platform/kube/bookinfo.yamlCheck the status of pods and services.
kubectl get pods kubectl get servicesVerify that the application is accessible.
kubectl exec "$(kubectl get pod -l app=ratings -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}')" -c ratings -- curl -sS productpage:9080/productpage | grep -o "<title>.*</title>" # Expected output <title>Simple Bookstore App</title>
5. Create external access entry for the demo service
Create an ingress gateway for the demo application.
kubectl apply -f samples/bookinfo/networking/bookinfo-gateway.yamlexport INGRESS_NAME=istio-ingressgateway export INGRESS_NS=istio-system export INGRESS_HOST=$(kubectl -n "$INGRESS_NS" get service "$INGRESS_NAME" -o jsonpath='{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].ip}') export INGRESS_PORT=$(kubectl -n "$INGRESS_NS" get service "$INGRESS_NAME" -o jsonpath='{.spec.ports[?(@.name=="http2")].port}') export SECURE_INGRESS_PORT=$(kubectl -n "$INGRESS_NS" get service "$INGRESS_NAME" -o jsonpath='{.spec.ports[?(@.name=="https")].port}') export TCP_INGRESS_PORT=$(kubectl -n "$INGRESS_NS" get service "$INGRESS_NAME" -o jsonpath='{.spec.ports[?(@.name=="tcp")].port}') export GATEWAY_URL=$INGRESS_HOST:$INGRESS_PORT # View the generated ingress address echo $GATEWAY_URL # Sample output: 192.168.1.100:80Verify the demo application is accessible.
curl -s "http://${GATEWAY_URL}/productpage" | grep -o "<title>.*</title>" # Expected output <title>Simple Bookstore App</title>
6. View trace data
Use the following command to access the product page 10 consecutive times to generate test traffic.
for i in $(seq 1 10); do curl -s -o /dev/null "http://$GATEWAY_URL/productpage"; doneGo to the Managed Service for OpenTelemetry console to view Istio trace data.
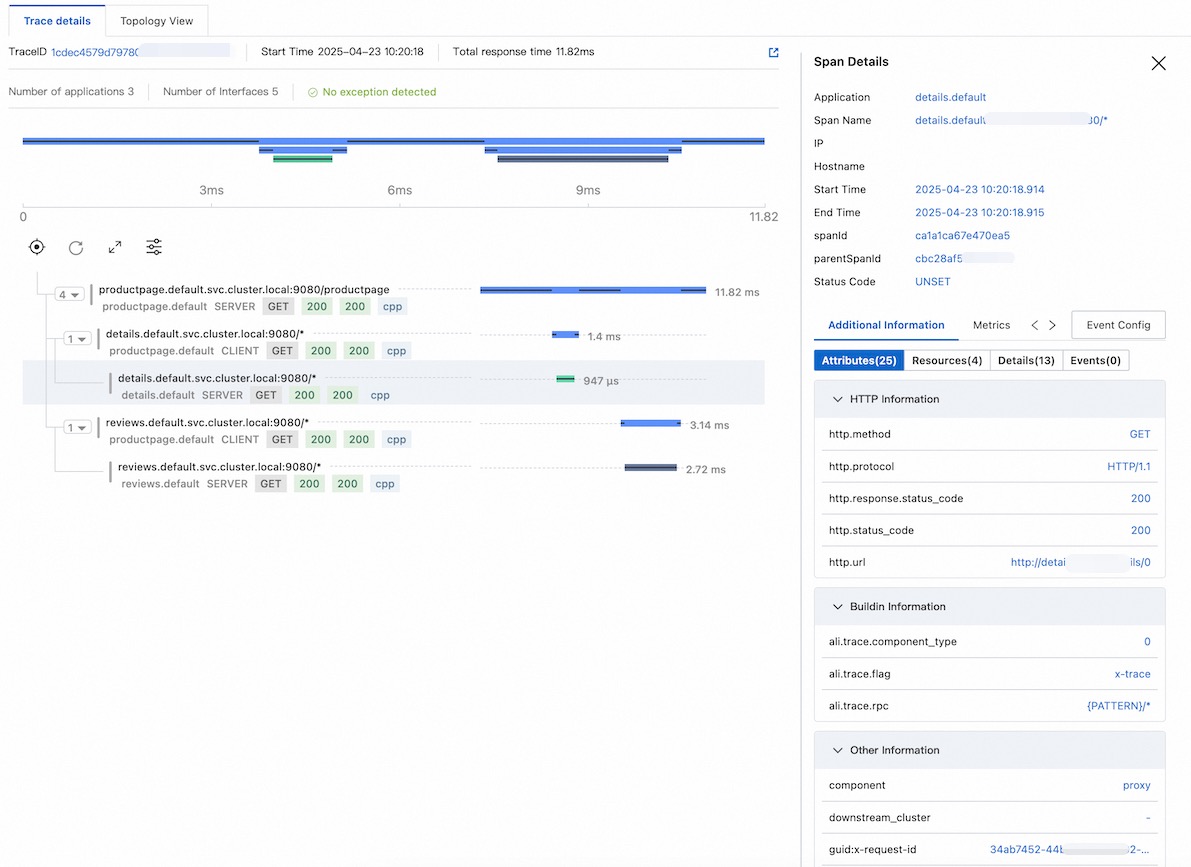
FAQ
Issue: What do I do if no Istio trace data found in the console?
Solution
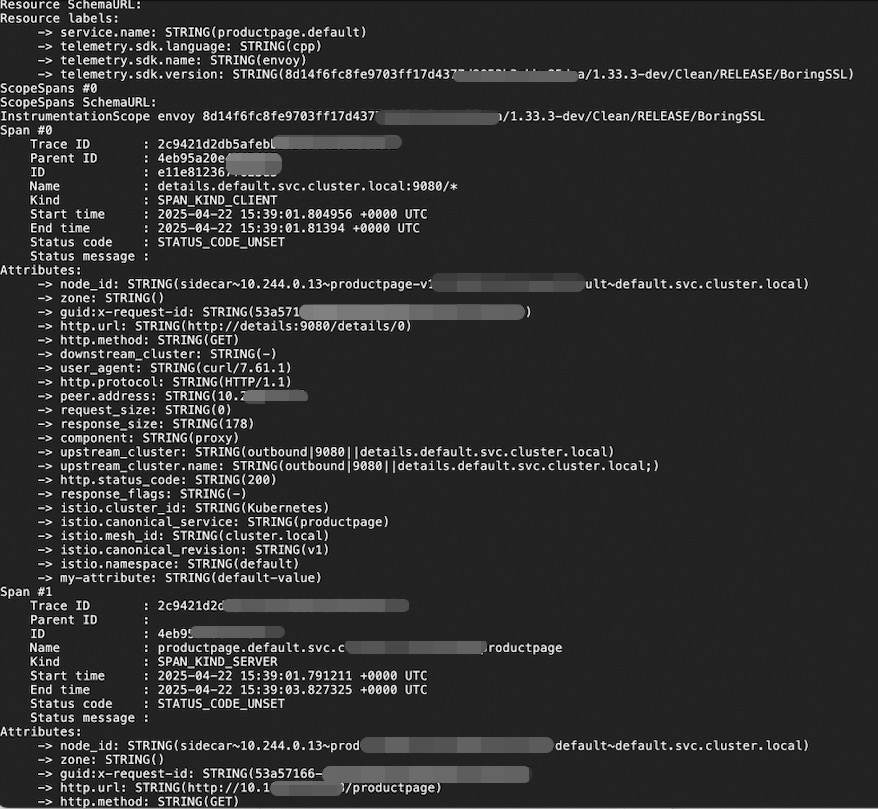
Check the logs of the OpenTelemetry Collector to confirm it is running properly and receiving data reported from Istio.
kubectl logs <collector-pod-name> -n <namespace>Expected output:
Verify that the sidecar has been successfully injected. Run the following command to check whether the
istio-proxycontainer exists in each pod.kubectl get pod -n default -o custom-columns=NAME:.metadata.name,CONTAINERS:.spec.containers[*].nameIf the
istio-proxycontainer does not appear in theCONTAINERSlist, the injection has failed. This may be due to the fact that theistio-injection=enabledlabel was applied to the namespace after the pods were already created. The automatic injection only applies to new pods. Existing pods are not affected unless they are restarted.Check if the Telemetry resource is correctly configured.
Use the following command to check the Telemetry configuration.
kubectl get telemetry otel-demo -o yamlVerify that the OpenTelemetry-related configurations in the Istio ConfigMap are correct.
kubectl get cm istio -n istio-system -o yaml | grep -A 10 extensionProviders