This document describes how to use the OpenSearch intelligent Q&A version to provide Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) capabilities for the OpenSearch recall engine version.
Assuming the user has already purchased a recall engine version instance, they only need to purchase an intelligent Q&A version instance. The specific roles of these two instances are as follows:
The recall engine version instance is responsible for:
Storing user document data and vector data
Recalling user document data and vector data
The intelligent Q&A version instance is responsible for:
Slicing and vectorizing user documents (optional)
Vectorizing the user's original query (optional)
Inferring and summarizing the recall results
1. Creating and configuring instances:
1.1. Creating and configuring a recall engine version instance
1.1.1. Purchasing an OpenSearch recall engine version instance
If the user already has a recall engine version instance, there is no need to purchase a new instance.
For more information, see purchasing an OpenSearch recall engine version instance.
1.1.2. Configuring an OpenSearch recall engine version instance
If the user does not want to change the query and recall logic of the existing recall engine version instance, there is no need to modify the configuration of the existing instance. Simply invoke the Q&A interface of the intelligent Q&A version to infer and summarize the existing recall results (refer directly to section 3.3).
If the user wants to slice and vectorize the data content in the existing instance, the existing configuration needs to be modified.
On the instance list page, tap configuration to enter the instance configuration process.
1.1.2.1. Table basic information &&Data source configuration
Configure table basic information: You need to customize the table name, set the number of shards, and set the number of data update resources:
The default number of data update resources is 2 free resources. If the data volume exceeds 2, it will be charged based on n-2, where n is the total number of data update resources for a single table.
Data synchronization: Configure the full data source, select the API data source
After tapping OK, the data source will be saved to the list page. Tap Next to enter the index schema configuration page.
1.1.2.2. Index schema configuration
To save user slice data and vector data, the user table schema must include the following fields:
Document primary key, as shown in the following figure as doc_id;
Document slice content field, as shown in the following figure as split_content;
Document slice content vectorized value, as shown in the following figure as split_content_embedding. This field needs to be set as a multi-value float type vector field and separated by ",".
In addition to the required fields mentioned above, customers can customize and add other business fields and use these fields for query, sort, filter, etc., to meet their business needs.
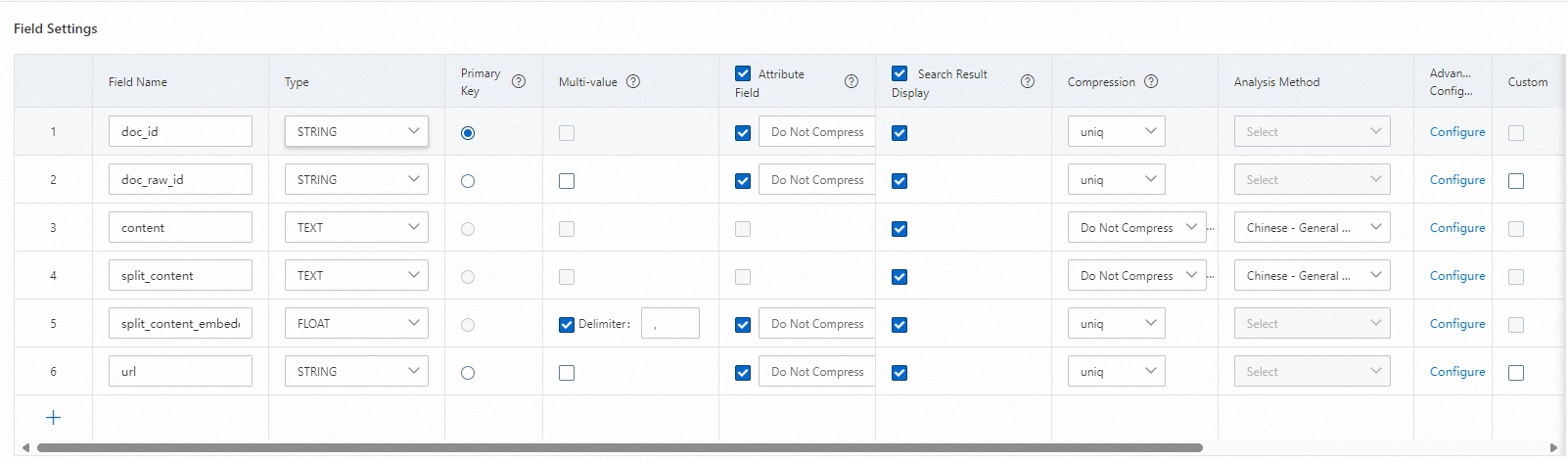
Index configuration instructions:
The primary key id needs to be configured as a primary key index: PRIMARYKEY64
content and split_content need to be configured as PACK index or TEXT index
split_content_embedding needs to be configured as CUSTOMIZED, with a vector index dimension of 1536 dimensions, and other parameters can be default
After the configuration is complete, tap Confirm to create.
You can view the creation progress in Function extension > Change history. After the progress is complete, you can perform a query test.
1.2. Creating and configuring an intelligent Q&A version instance
1.2.1. Purchasing and configuring an OpenSearch intelligent Q&A version instance
For more information, see implementing enterprise knowledge base Q&A through the console.
The intelligent Q&A version instance does not require special configuration and can be used once the instance purchase is complete.
2. Data storage:
2.1. Slicing and vectorizing document content
When the user's original document content is relatively large, it is not possible to directly use the original document to invoke the intelligent Q&A version dialog interface for inference and summarization.
This requires invoking the relevant endpoint and API of the intelligent Q&A version instance to slice and vectorize the user's original document content.
Refer to the JAVA SDK Demo at the end of this document, or refer to the article:
SplitDoc - Document slicing and vectorization
2.2. Pushing sliced and vectorized documents to the recall engine version instance
In the results returned in section 2.1:
chunk_id is the ID of the sliced document. It needs to be concatenated with the original document ID to form a new document primary key: doc_id
chunk is the sliced document content, corresponding to split_content;
embedding is the vectorized value of the sliced document content, corresponding to split_content_embedding;
The above results need to be pushed to the recall engine version instance.
To invoke the relevant endpoint and API of the recall engine version instance, refer to the JAVA SDK Demo at the end of this document, or refer to the article:
3. Query and Q&A:
3.1. Query vectorization
Vectorize the user's original query content.
To invoke the relevant endpoint and API of the intelligent Q&A version instance, refer to the JAVA SDK Demo at the end of this document, or refer to the article:
EmbeddingDoc - Text vectorization
3.2. Recalling vectorized result data
Use the vectorized result of the query to recall in the recall engine version
In addition to processing the vectorized recall of the query, users can use other table fields for recall, and can also sort and filter the recall results
To invoke the relevant endpoint and API of the recall engine version instance, refer to the JAVA SDK Demo at the end of this document, or refer to the article:
3.3. Large model inference and summarization
Based on the results recalled by the recall engine version, invoke the large model Q&A interface of the intelligent Q&A version for inference and summarization.
Refer to the JAVA SDK Demo at the end of this document, or refer to the article:
KnowledgeLLM - Large model dialog interface
4. JAVA SDK Demo:
The demo for completing data push and intelligent Q&A using the Java SDK is as follows:
Add maven dependencies:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.aliyun</groupId>
<artifactId>aliyun-sdk-ha3engine</artifactId>
<version>1.3.6</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.aliyun.opensearch</groupId>
<artifactId>aliyun-sdk-opensearch</artifactId>
<version>4.0.0</version>
</dependency>JAVA Demo:
import com.aliyun.ha3engine.Client;
import com.aliyun.ha3engine.models.*;
import com.aliyun.ha3engine.vector.models.QueryRequest;
import com.aliyun.opensearch.OpenSearchClient;
import com.aliyun.opensearch.sdk.generated.OpenSearch;
import com.aliyun.opensearch.sdk.generated.commons.OpenSearchResult;
import com.google.gson.JsonArray;
import com.google.gson.JsonElement;
import com.google.gson.JsonObject;
import com.google.gson.JsonParser;
import java.util.*;
public class RetrievalWithLLMDemo {
/**
* Intelligent Q&A version instance application name
*/
private static String llmAppName = "xxxx";
/**
* Intelligent Q&A version instance access address
*/
private static String llmHost = "http://opensearch-cn-shanghai.aliyuncs.com";
/**
* Intelligent Q&A version instance access key
*/
private static String llmAccessKey = "xxx";
/**
* Intelligent Q&A version instance access secret
*/
private static String llmAccessSecret = "xxx";
/**
* Recall instance API domain name
*/
private static String retrievalEndpoint = "ha-cn-xxx.public.ha.aliyuncs.com";
/**
* Recall engine version instance name
*/
private static String retrievalInstanceId = "ha-cn-xxx";
/**
* Recall engine version document data table name
*/
private static String retrievalTableName = "ha-cn-xxx";
/**
* Recall engine version document push primary key field.
*/
private static String retrievalPkField = "doc_id";
/**
* Recall engine version username
*/
private static String retrievalUserName = "xxx";
/**
* Recall engine version password
*/
private static String retrievalPassword = "xxx";
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//Create an object to access the intelligent Q&A version instance
//Create and construct the OpenSearch object
OpenSearch openSearch = new OpenSearch(llmAccessKey, llmAccessSecret, llmHost);
//Create an OpenSearchClient object and use the OpenSearch object as a constructor parameter
OpenSearchClient llmClient = new OpenSearchClient(openSearch);
//Create an object to access the recall engine version instance
Config config = new Config();
config.setEndpoint(retrievalEndpoint);
config.setInstanceId(retrievalInstanceId);
config.setAccessUserName(retrievalUserName);
config.setAccessPassWord(retrievalPassword);
Client retrievalClient = new Client(config);
//Slice and vectorize content
Map<String, String> splitParams = new HashMap<String, String>() {{
put("format", "full_json");
put("_POST_BODY", "{\"content\":\"OpenSearch is a one-stop commercial intelligent search platform built on Alibaba's self-developed large-scale distributed search engine. It currently provides mid-stage service support for the core search business of Alibaba Group, including Taobao, Tmall, and Cainiao." +
"After years of industry search experience accumulation and the impact of Double 11 promotion traffic, OpenSearch has developed a set of high-performance, high-timeliness, high-availability, and strong-stability search full-service suite, including LLM intelligent Q&A version, industry algorithm version, high-performance retrieval version, recall engine version, and recall engine version, to meet the search needs of various industries." +
"OpenSearch simplifies, lowers the threshold, and reduces the cost of professional search technology in the form of platform services, making search no longer a business bottleneck for customers, achieving product search functions at low cost and quickly iterating\",\"use_embedding\":true}");
}};
String splitPath = String.format("/apps/%s/actions/knowledge-split", llmAppName);
OpenSearchResult openSearchResult = llmClient.callAndDecodeResult(splitPath, splitParams, "POST");
System.out.println("split result:" + openSearchResult.getResult());
JsonArray array = JsonParser.parseString(openSearchResult.getResult()).getAsJsonArray();
// Document push outer structure, you can add the structure of the document operation. The structure supports one or more document operation contents.
ArrayList<Map<String, ?>> documents = new ArrayList<>();
//Assume the user's original document primary key is 1
String doc_raw_id="001";
for(JsonElement element:array){
JsonObject object = element.getAsJsonObject();
// Add document
Map<String, Object> add2Document = new HashMap<>();
Map<String, Object> add2DocumentFields = new HashMap<>();
// Insert document content information, keyValue pair matching.
// field_pk field needs to be consistent with pkField field configuration.
add2DocumentFields.put("doc_id", doc_raw_id+"_"+object.get("chunk_id").getAsString());
add2DocumentFields.put("doc_raw_id", doc_raw_id);
List<Float> vectors = new ArrayList();
for(String str: object.get("embedding").getAsString().split(",")){
vectors.add(Float.parseFloat(str));
}
add2DocumentFields.put("split_content_embedding", vectors);
add2DocumentFields.put("split_content", object.get("chunk"));
// Add document content to add2Document structure.
add2Document.put("fields", add2DocumentFields);
// Add the corresponding document command: add
add2Document.put("cmd", "add");
documents.add(add2Document);
}
System.out.println("push docs:"+documents.toString());
// Push data to the recall engine version
PushDocumentsRequestModel request = new PushDocumentsRequestModel();
request.setBody(documents);
PushDocumentsResponseModel response = retrievalClient.pushDocuments(retrievalTableName, retrievalPkField, request);
String responseBody = response.getBody();
System.out.println("push result:" + responseBody);
//Vectorize the user's original query
Map<String, String> embeddingParams = new HashMap<String, String>() {
{
put("format", "full_json");
put("_POST_BODY", "{\"content\":\"What is OpenSearch\",\"query\":true}");
}};
String embeddingPath = String.format("/apps/%s/actions/knowledge-embedding", llmAppName);
openSearchResult = llmClient.callAndDecodeResult(embeddingPath, embeddingParams, "POST");
System.out.println("query embedding:"+openSearchResult.getResult());
String embedding = openSearchResult.getResult();
SearchRequestModel haQueryRequestModel = new SearchRequestModel();
SearchQuery haRawQuery = new SearchQuery();
haRawQuery.setQuery("query=split_content_embedding:'"+embedding+"'&&config=start:0,hit:5,format:json&&cluster=general");
haQueryRequestModel.setQuery(haRawQuery);
// Only GET and POST request methods are supported, the default is GET. If the query length exceeds 30K, please use POST request
haQueryRequestModel.setMethod("POST");
SearchResponseModel searchResponse = retrievalClient.Search(haQueryRequestModel);
System.out.println("search results:" + searchResponse.getBody());
JsonObject recallResult = JsonParser.parseString(searchResponse.getBody()).getAsJsonObject().get("result").getAsJsonObject();
long hits = recallResult.get("totalHits").getAsLong();
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
if(hits <=0){
System.out.println("No results recalled");
return ;
}else{
JsonArray items = recallResult.get("items").getAsJsonArray();
for(JsonElement element:items) {
JsonObject object = element.getAsJsonObject();
String splitContent = object.get("fields").getAsJsonObject().get("split_content").getAsString();
list.add(splitContent);
}
}
//Invoke the intelligent Q&A version instance for inference and summarization
StringBuffer sb =new StringBuffer();
sb.append("{ \"question\" : \"What is OpenSearch\" ,");
sb.append(" \"type\" : \"text\",");
sb.append(" \"content\" : [");
for(String str:list){
sb.append("\"");
sb.append(str);
sb.append("\"");
sb.append(",");
}
sb.deleteCharAt(sb.lastIndexOf(","));
sb.append("]}");
Map<String, String> llmParams = new HashMap<String, String>() {{
put("format", "full_json");
put("_POST_BODY", sb.toString());
}};
System.out.println("llm request params:"+llmParams);
String llmPath = String.format("/apps/%s/actions/knowledge-llm", llmAppName);
openSearchResult = llmClient.callAndDecodeResult(llmPath, llmParams, "POST");
System.out.println("llm result:"+openSearchResult.getResult());
}
}