Background information
The procedure of creating a custom template is optimized. When you create a custom template, you do not need to define task outputs. Before the optimization, you must define the task output so that the output can be used as input parameters. After optimization, you do not need to define task outputs. The outputs can be directly used as input parameters. This topic provides best practices for creating a custom template without defining task outputs.
Details
After the optimization, you do not need to define task outputs for each task when you modify a custom template.

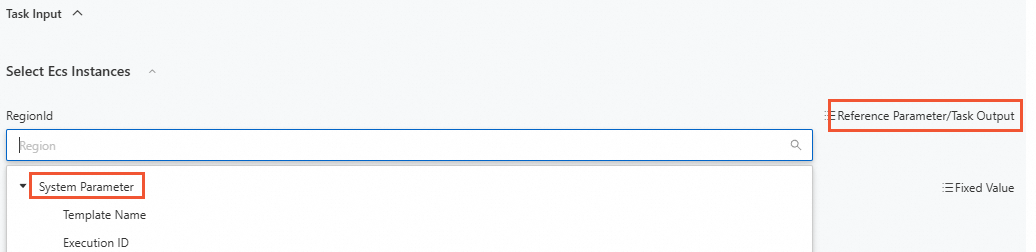
For the subsequent tasks, select Reference Parameter/Task Output and select Task Output Parameters from the drop-down list. The Task Output Parameters section will automatically display all possible outputs. Select parameters based on your requirements.
Sample template syntax:
- Name: ExecuteApi
Action: ACS::ExecuteApi
Description: ''
Properties:
Service: oos
API: DescribeRegions
Outputs: {}
- Action: ACS::ECS::StartInstance
Name: StartInstance
Description: ''
Properties:
regionId: '{{ ExecuteApi.Regions[]?.RegionId }}' # The output of the previous task ExecuteApi is used: RegionId
instanceId: i-xxxxxxxxxExample
Scenario
When you pull Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instances in different regions, you often want to obtain the same environment and image content. In practice, you need to run commands on an existing ECS instance in the ECS console, create an image, and then distribute the image to different regions as needed. This process is usually complex, contains multiple asynchronous operations, and difficult to manage in a unified way. CloudOps Orchestration Service (OOS) supports unified orchestration and management. For the previous scenario, you can create an ECS image based on an existing ECS instance and specified commands, and clone the image to another region. You can create a custom OOS template to include these operations. Then, you can run the template only once to meet your requirements.
Prerequisites
An ECS instance is in the Running state, and make sure that the ECS instance and the OOS template belong to the same region.
The commands to be run are prepared.
The involved actions are prepared.
ACS::ECS::RunCommand: runs a command.
ACS::ECS::CreateImage: creates an image.
ACS::ECS::CopyImage: copies an image.
For more information about actions, see List of actions by function.
Process
0. Preparations
In the left-side navigation pane of the OOS console, click Custom Template. On the Custom Template page, click Create Template.
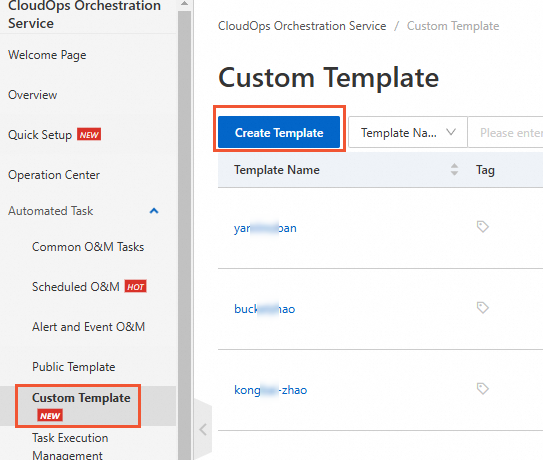
Select an empty template.
Click Add New Task.
Select an action in the Task Type section.
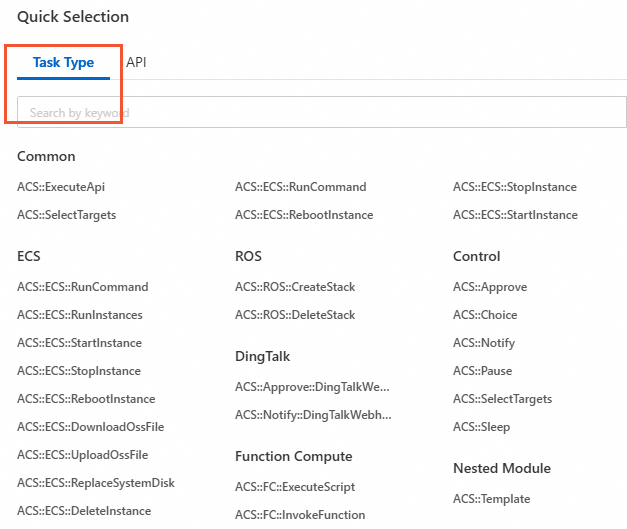
Click Add Template Parameters in the Template Parameters section.
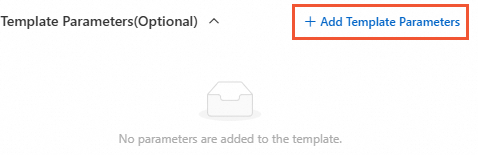
Add the following required parameters: InstanceId, ImageName, and TargetRegionId. Use String for the other parameter types. The default value of ImageName involves system parameters. For more information, see Overview.
CreateImage_from_{{ACS::ExecutionId}}: Add the ID of this execution after the string CreateImage_from_, and the final form is: CreateImage_from_exec-xxxxxxx
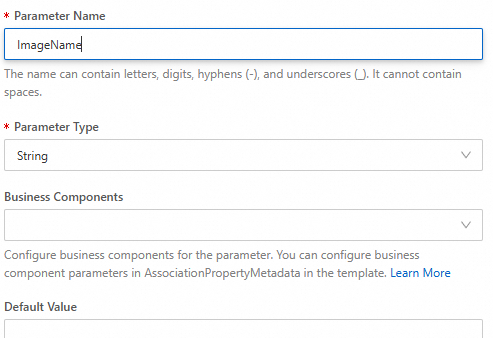
Select Business Components RegionId for TargetRegionId.
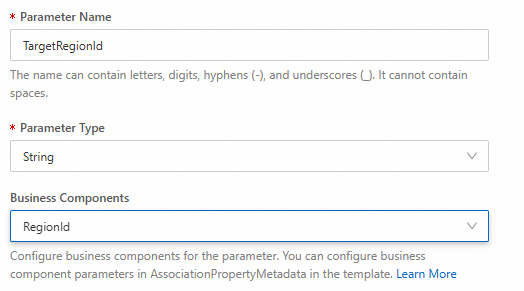
Select Business Components ALIYUN::ECS::Instance::InstanceId for InstanceId.
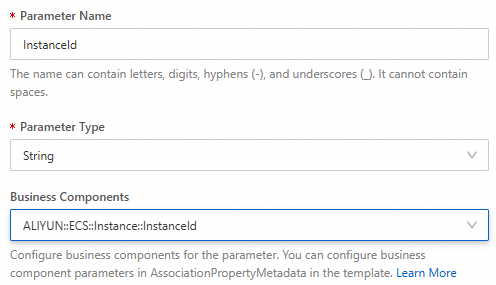
For more information about Business Components, see AssociationProperty and AssociationPropertyMetadata.
1. Configure the RunCommand task
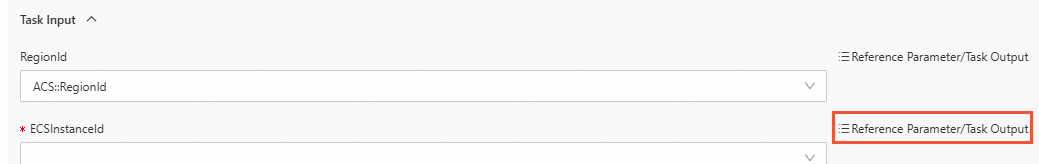
Add a new task and set Task Type to ACS::ECS::RunCommand. Select Reference Parameter/Task Output for Task Input and select the configured parameters and outputs of previous tasks.
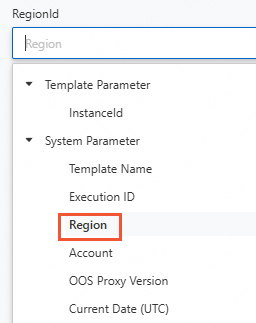
Select Region from the System Parameter drop-down list for RegionId.
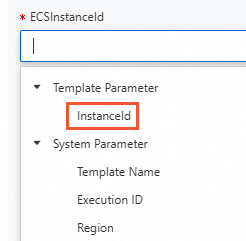
Click Template Parameter for ECSInstanceId to reference an ECS instance ID.
We recommend that you prepare CommandContent in advance and select proper CommandType.
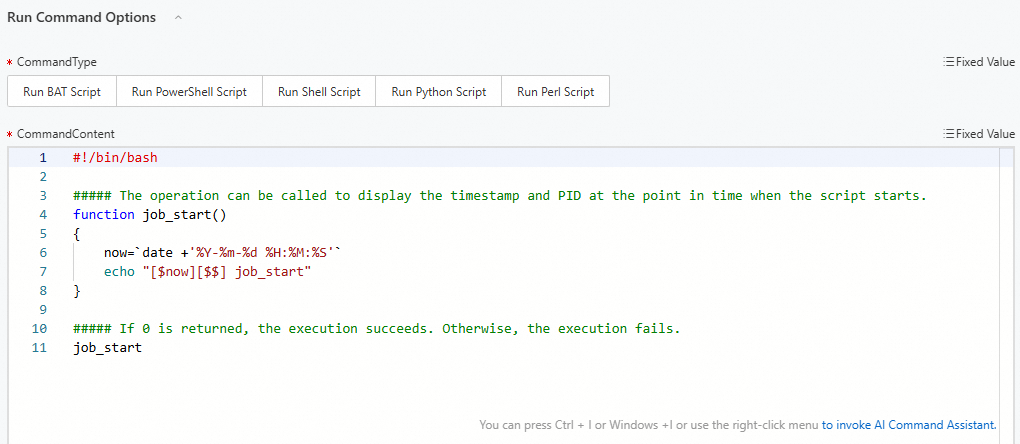 If you want to check the output of the script, you can set it in the template output.
If you want to check the output of the script, you can set it in the template output.
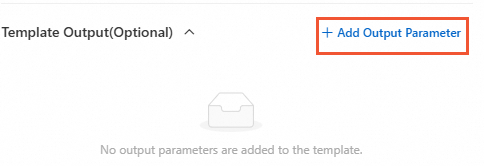
As shown in the following figure, you can select the output of RunCommand.
In the original process, if you want to obtain the result of the execution, you need to define the output to reference the output in the template output. After the optimization, no additional definition is required.
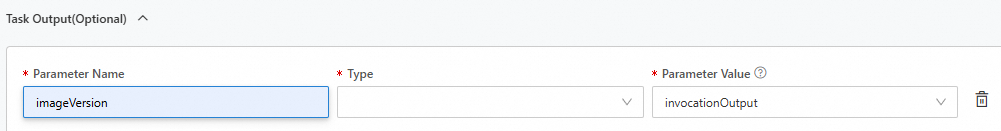
2. Configure the CreateImage task
Specify ACS::ECS::CreateImage for Task Type and select Reference Parameter/Task Output for Task Input.
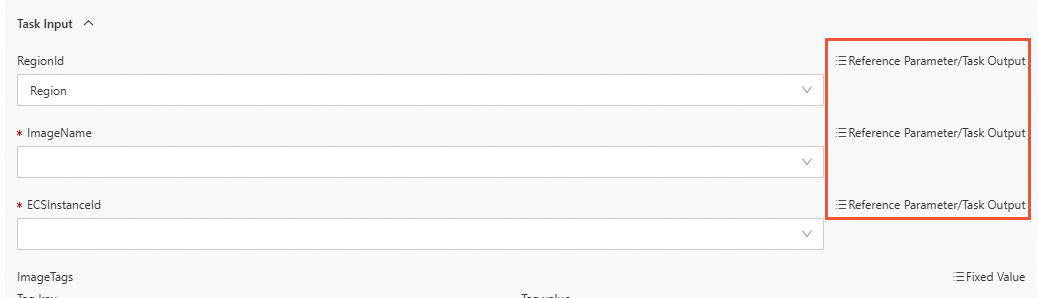
You can select Task Output Parameter, Template Parameter, and System Parameter from the drop-down list.
Select Region from the System Parameter drop-down list for RegionId, select ImageName from the Template Parameter drop-down list for ImageName, and select Instances.Instance[].InstanceId from the Task Output Parameter drop-down list for ECSInstanceId.
Specify the other parameters based on your requirements.
In the original process, you need to define the ID of the created image in the output. After the optimization, this is no longer necessary.
3. Configure the CopyImage task
Select ACS::ECS::CopyImage for Task Type. Select the output parameter imageId of the task CreateImage for ImageId.
Select Region from the System Parameter drop-down list for SourceRegionId.
Select TargetRegionId from the Template Parameter drop-down list for TargetRegionId.
Specify a custom name for TargetImageName. In this example, '{{ CreateImage.imageId }}-{{ACS::ExecutionId}}' is used. image ID-execution ID indicates that the outputs of the task CreateImage are referenced and it is combined together with the parameter {{ACS::ExecutionId}} .
In the original process, the outputs of the task need to be defined so that the outputs can be referenced. After the optimization, the outputs can be referenced without the definition.
4. Configure template outputs
After you complete the preceding steps, you can select the outputs to be displayed in the Template Output section. As shown in the preceding figure, the specified outputs are all displayed. You can select the output parameter imageIdsWithRegion from the task CopyImage to directly obtain the image ID.
You can specify an output parameter to obtain the result as needed.
Example for selecting output parameters
After you complete the preceding steps, a custom template is created. You can execute the template and obtain the image ID.
After the template is executed, you can view the result and the image ID on the Output tab.
Template content comparison
The following section shows the sample code for the template:
FormatVersion: OOS-2019-06-01
Description: ''
Parameters:
ImageName:
Type: String
Default: CreateImage_from_{{ACS::ExecutionId}}
TargetRegionId:
Label:
en: TargetRegionIds
zh-cn: the description in Chinese
Type: String
AssociationProperty: RegionId
InstanceId:
Type: String
AssociationProperty: ALIYUN::ECS::Instance::InstanceId
Tasks:
- Action: ACS::ECS::RunCommand
Name: RunCommand
Description: ''
Properties:
regionId: '{{ ACS::RegionId }}'
commandContent: |-
#!/bin/bash
##### When the script starts to run, you can invoke the function to display the timestamp and the process ID.
function job_start()
{
now=`date +'%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S'`
echo "[$now][$$] job_start"
}
##### If 0 is returned, the execution is successful. Otherwise, the execution fails.
job_start
contentEncoding: PlainText
workingDir: /root
timeout: 600
enableParameter: false
parameters: {}
username: ''
windowsPasswordName: ''
maxRetryInterval: 300
instanceId: '{{ InstanceId }}'
commandType: RunShellScript
- Action: ACS::ECS::CreateImage
Name: CreateImage
Description: ''
Properties:
regionId: '{{ ACS::RegionId }}'
tags: []
imageFamily: ''
imageDescription: ''
resourceGroupId: ''
detectionStrategy: ''
instanceId: '{{ InstanceId }}'
imageName: '{{ ImageName }}'
- Action: ACS::ECS::CopyImage
Name: CopyImage
Description: ''
Properties:
targetImageName: '{{ CreateImage.imageId }}-{{ACS::ExecutionId}}'
encrypted: false
KMSKeyId: ''
targetImageDescription: ''
tags: []
regionId: '{{ ACS::RegionId }}'
targetRegionId: '{{ TargetRegionId }}'
imageId: '{{ CreateImage.imageId }}'
Outputs:
CommandOutput:
Type: String
Value: '{{ RunCommand.invocationOutput }}'
Description: the result
ImageIdWithRegion:
Type: String
Value: '{{ CopyImage.imageIdWithRegion }}'
Metadata:
ALIYUN::OOS::Interface:
ParameterGroups:
- Parameters:
- regionId
- instanceId
Label:
default:
zh-cn: the description in Chinese
en: Select Ecs Instances
- Parameters:
- targetImageName
- tags
Label:
default:
zh-cn: the description in Chinese
en: Image Configure
- Parameters:
- commandType
- commandContent
Label:
default:
zh-cn: the description in Chinese
en: Run Command
- Parameters:
- targetRegionIds
- accountIds
Label:
default:
zh-cn: the description in Chinese
en: Copy Image
- Parameters:
- scalingConfigurationIds
- launchTemplateNames
- rateControl
- OOSAssumeRole
Label:
default:
zh-cn: the description in Chinese
en: Control Options
The following section shows the sample code for the same template before optimization:
FormatVersion: OOS-2019-06-01
Description: ''
Parameters:
ImageName:
Type: String
Default: CreateImage_from_{{ACS::ExecutionId}}
TargetRegionId:
Label:
en: TargetRegionIds
zh-cn: the description in Chinese
Type: String
AssociationProperty: RegionId
InstanceId:
Type: String
AssociationProperty: ALIYUN::ECS::Instance::InstanceId
Tasks:
- Action: ACS::ECS::RunCommand
Name: RunCommand
Description: ''
Properties:
regionId: '{{ ACS::RegionId }}'
commandContent: |-
#!/bin/bash
##### When the script starts to run, you can invoke the function to display the timestamp and the process ID.
function job_start()
{
now=`date +'%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S'`
echo "[$now][$$] job_start"
}
##### If 0 is returned, the execution is successful. Otherwise, the execution fails.
job_start
contentEncoding: PlainText
workingDir: /root
timeout: 600
enableParameter: false
parameters: {}
username: ''
windowsPasswordName: ''
maxRetryInterval: 300
instanceId: '{{ InstanceId }}'
commandType: RunShellScript
Outputs:
commandOutput:
Type: String
ValueSelector: invocationOutput
- Action: ACS::ECS::CreateImage
Name: CreateImage
Description: ''
Properties:
regionId: '{{ ACS::RegionId }}'
tags: []
imageFamily: ''
imageDescription: ''
resourceGroupId: ''
detectionStrategy: ''
instanceId: '{{ InstanceId }}'
imageName: '{{ ImageName }}'
Outputs:
ImageId:
Type: String
ValueSelector: imageId
- Action: ACS::ECS::CopyImage
Name: CopyImage
Description: ''
Properties:
targetImageName: '{{ CreateImage.imageId }}-{{ACS::ExecutionId}}'
encrypted: false
KMSKeyId: ''
targetImageDescription: ''
tags: []
regionId: '{{ ACS::RegionId }}'
targetRegionId: '{{ TargetRegionId }}'
imageId: '{{ CreateImage.ImageId }}'
Outputs:
CopyImageId:
Type: String
ValueSelector: imageId
CopyImageIdWithRegion:
Type: List
ValueSelector: imageIdWithRegion
Outputs:
CommandOutput:
Type: String
Value: '{{ RunCommand.commandOutput }}'
Description: the result
ImageIdWithRegion:
Type: String
Value: '{{ CopyImage.CopyImageIdWithRegion }}'
Metadata:
ALIYUN::OOS::Interface:
ParameterGroups:
- Parameters:
- regionId
- instanceId
Label:
default:
zh-cn: the description in Chinese
en: Select Ecs Instances
- Parameters:
- targetImageName
- tags
Label:
default:
zh-cn: the description in Chinese
en: Image Configure
- Parameters:
- commandType
- commandContent
Label:
default:
zh-cn: the description in Chinese
en: Run Command
- Parameters:
- targetRegionIds
- accountIds
Label:
default:
zh-cn: the description in Chinese
en: Copy Image
- Parameters:
- scalingConfigurationIds
- launchTemplateNames
- rateControl
- OOSAssumeRole
Label:
default:
zh-cn: the description in Chinese
en: Control Options
As you can see, all task outputs can be directly referenced without definition after optimization. This reduces preparation work and allows you to better orchestrate the features that you want to implement by using a custom template.