The patch management feature predefines a default patch baseline for each operating system. If you want to configure custom rules to scan and install patches for an operating system, you can create a patch baseline to specify the operating system type, patch categories, patch severities, and conditions for automatic approval. After you create the patch baseline, you can specify the patch baseline as the default patch baseline for the operating system to apply the custom rules.
Create a patch baseline
Log on to the CloudOps Orchestration Service console. In the navigation pane on the left, choose .
On the page that appears, click Configure Patch Baseline. On the Patch Baseline page, click Create.
On the Create Patch Baseline page, enter a name and a description for the patch baseline.

Select an operating system from drop-down list.
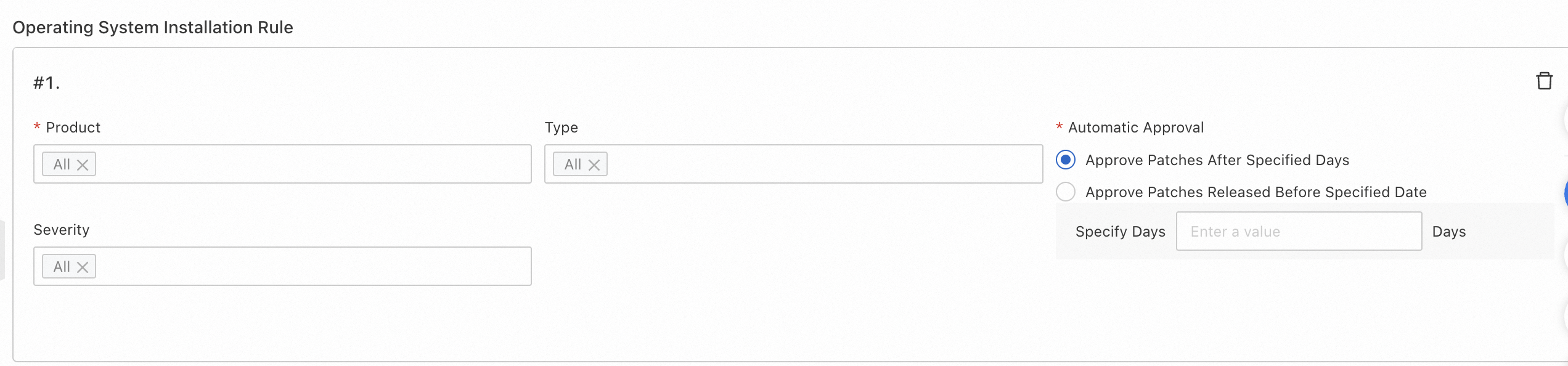
Define rules for the patch baseline, including patch type, severity, and conditions for automatic approval.
(Optional) If some patches cannot be processed by the rules for specific reasons, you can set patch exceptions to explicitly approve or reject these patches.
Click Create.
More operations
Specify the default patch baseline: In the patch baseline list, find the desired patch baseline and click Set as Default Baseline in the Actions column. In the message that appears, click OK.
ImportantThe default patch baseline is used as a reference for patch checks. Therefore, set the default patch baseline with caution.
View the details of a patch baseline: In the patch baseline list, find the desired patch baseline and click Details in the Actions column.
Update a patch baseline: In the patch baseline list, find the desired patch baseline and click Update in the Actions column.
Delete a patch baseline: In the patch baseline list, find the desired patch baseline, click the
 icon in the Actions column, and then select Delete. In the message that appears, click OK. Important
icon in the Actions column, and then select Delete. In the message that appears, click OK. ImportantBefore you delete a patch baseline, make sure that the patch baseline is not used by instances. This prevents patch checks from being affected.