You can use MongoShake, an open source tool developed by Alibaba Cloud, to synchronize data between MongoDB databases. This feature is suitable for data analytics, disaster recovery, and active-active scenarios. This topic uses real-time data synchronization between ApsaraDB for MongoDB instances as an example to describe the configuration procedure.
MongoShake overview
MongoShake is a general-purpose Platform as a Service (PaaS) tool developed by Alibaba Cloud in the Go language. It reads the operation logs (oplogs) from a MongoDB database to replicate data for various purposes.
MongoShake also provides features to subscribe to and consume log data. You can connect to it using various methods, such as SDKs, Kafka, and MetaQ. This makes it suitable for scenarios such as log subscription, data center synchronization, and asynchronous cache eviction.
For more information about MongoShake, see the MongoShake homepage on GitHub.
Supported data sources
Source database | Destination database |
Self-managed MongoDB database on an ECS instance | Self-managed MongoDB database on an ECS instance |
On-premises self-managed MongoDB database | On-premises self-managed MongoDB database |
ApsaraDB for MongoDB instance | ApsaraDB for MongoDB instance |
Third-party cloud MongoDB database | Third-party cloud MongoDB database |
Usage notes
Do not perform Data Definition Language (DDL) operations on the source database before full data synchronization is complete. Otherwise, data inconsistency may occur.
The local database cannot be synchronized. The admin database can be synchronized. For more information, see Migrate business data from the admin database to a non-admin database.
Required permissions for database users
Data source | Required permissions |
Source MongoDB instance | The readAnyDatabase permission, the read permission on the local database, and the readWrite permission on the mongoshake database. Note The mongoshake database is automatically created by the MongoShake program in the source instance when incremental synchronization starts. |
Destination MongoDB instance | The readWriteAnyDatabase permission or the readWrite permission on the destination database. |
For more information about how to create and grant permissions to MongoDB database users, see Use DMS to manage MongoDB database users or the db.createUser command.
Preparations
For optimal synchronization performance, ensure the source ApsaraDB for MongoDB replica set instance uses a virtual private cloud (VPC). If the instance uses the classic network, switch the network type to VPC. For more information, see Switch the network type of an instance from classic network to VPC.
Create an ApsaraDB for MongoDB replica set instance as the synchronization destination. When you create the instance, select the same VPC as the source ApsaraDB for MongoDB replica set instance to minimize network latency. For more information, see Create a replica set instance.
Create an ECS instance to run MongoShake. When you create the instance, select the same VPC as the source ApsaraDB for MongoDB instance to minimize network latency. For more information, see Create an ECS instance.
Add the private IP address of the ECS instance to the whitelists of the source and destination MongoDB instances. Ensure that the ECS instance can connect to the source and destination MongoDB instances. For more information, see Modify a whitelist.
If your network type does not meet the preceding requirements, you can apply for public endpoints for the source and destination MongoDB instances. Then, add the public IP address of the ECS instance to the whitelists of the source and destination instances. This lets you synchronize data over the Internet. For more information, see Apply for a public endpoint and Modify a whitelist.
Procedure
In this example, MongoShake is installed in the /test/mongoshake directory by default.
Log on to the ECS server.
NoteSelect a logon method based on your business scenario. For more information, see Overview of logon methods for ECS servers.
Run the following command to download the MongoShake program and rename it to
mongoshake.tar.gz.wget "http://docs-aliyun.cn-hangzhou.oss.aliyun-inc.com/assets/attach/196977/jp_ja/1608863913991/mongo-shake-v2.4.16.tar.gz" -O mongoshake.tar.gzNoteThis topic provides the link to download MongoShake 2.4.16. To download the latest version of MongoShake, see the releases page.
Run the following command to decompress the MongoShake package to the /test/mongoshake directory.
tar zxvf mongoshake.tar.gz && mv mongo-shake-v2.4.16 /test/mongoshake && cd /test/mongoshake/mongo-shake-v2.4.16Run the
vi collector.confcommand to modify the collector.conf configuration file of MongoShake. The following table describes the main parameters.Parameter
Description
Example
mongo_urls
The connection string URI of the source MongoDB instance. In this example, the database account is test and it belongs to the admin database.
NoteUse a VPC endpoint for interconnection to minimize network latency.
For more information about the connection string URI format, see Connection description for a replica set instance.
mongo_urls = mongodb://test:****@dds-bp19f409d7512****.mongodb.rds.aliyuncs.com:3717,dds-bp19f409d7512****.mongodb.rds.aliyuncs.com:3717NoteThe password cannot contain the at sign (@). Otherwise, the connection fails.
tunnel.address
The connection string URI of the destination MongoDB instance. In this example, the database account is test and it belongs to the admin database.
NoteUse a VPC endpoint for interconnection to minimize network latency.
For more information about the connection string URI format, see Connection description for a replica set instance.
tunnel.address = mongodb://test:****@dds-bp19f409d7512****.mongodb.rds.aliyuncs.com:3717,dds-bp19f409d7512****.mongodb.rds.aliyuncs.com:3717NoteThe password cannot contain the at sign (@). Otherwise, the connection fails.
sync_mode
The data synchronization method. Valid values:
all: Performs both full and incremental data synchronization.
full: Performs only full data synchronization.
incr: Performs only incremental data synchronization.
NoteThe default value is incr.
sync_mode = allNoteFor a complete list of parameters in the collector.conf file, see the Appendix.
Run the following command to start the sync task and output log information.
./collector.linux -conf=collector.conf -verboseObserve the log information. When the following log entry appears, full data synchronization is complete and incremental data synchronization has started.
[09:38:57 CST 2019/06/20] [INFO] (mongoshake/collector.(*ReplicationCoordinator).Run:80) finish full sync, start incr sync with timestamp: fullBeginTs[1560994443], fullFinishTs[1560994737]
Monitor the MongoShake status
After incremental data synchronization starts, open another command-line window and run the following command to monitor MongoShake.
cd /test/mongoshake && ./mongoshake-stat --port=9100mongoshake-stat is a Python script. Before you run the script, install Python 2.7. For more information, see the Python official website.
Sample monitoring output: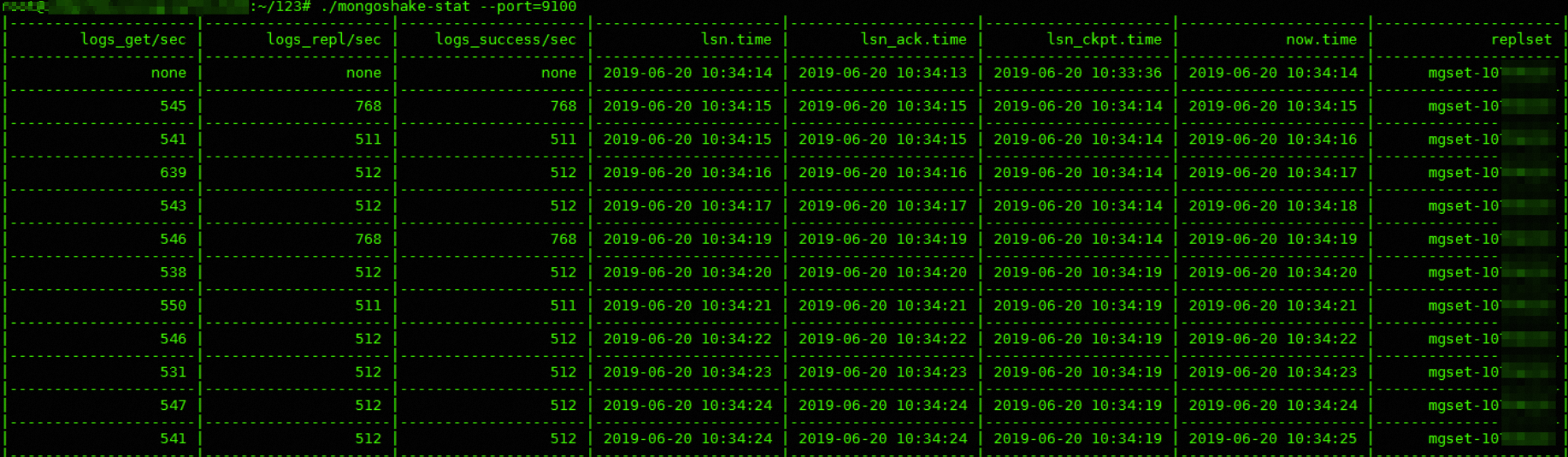
Parameter descriptions:
Parameter | Description |
logs_get/sec | The number of oplogs obtained per second. |
logs_repl/sec | The number of oplog replay operations per second. |
logs_success/sec | The number of successful oplog replay operations per second. |
lsn.time | The time when the last oplog was sent. |
lsn_ack.time | The time when the destination confirmed the write operation. |
lsn_ckpt.time | The time when the checkpoint was persisted. |
now.time | The current time. |
replset | The name of the source database replica set. |
Migrate business data from the admin database to a non-admin database
MongoDB does not recommend storing business data in the admin database. This is because locking behavior and conflicts with internal commands can degrade instance performance.
MongoShake supports synchronizing business data from the admin database to a non-admin database.
Follow the steps in the Procedure section. In Step 4, when you modify the collector.conf file, add the following configuration items:
filter.pass.special.db = admin
# Migrate all business collections from the admin database to newDB.
transform.namespace = admin:newDB
# Alternatively, migrate the abc collection from the admin database to the def collection in the target database. You can configure multiple rules.
transform.namespace = admin.abc:target.defAppendix
Table 1. collector.conf parameters
Category | Parameter | Description | Example |
None | conf.version | The version number of the current configuration file. Do not modify this value. |
|
Global configuration options | id | The ID of the sync task. You can customize this value. It is used for the log name, the name of the database that stores checkpoint information for resumable transmission, and the name of the destination database. |
|
master_quorum | A high availability option. When a primary and a standby MongoShake node synchronize data from the same source, set this parameter to Valid values:
Note The default value is false. |
| |
full_sync.http_port | The HTTP port. Open this port to view the current status of full synchronization from the Internet. Note The default value is 9101. |
| |
incr_sync.http_port | The HTTP port. Open this port to view the current status of incremental synchronization from the Internet. Note The default value is 9100. |
| |
system_profile_port | The profiling port, used to view internal stack information. |
| |
log.level | The log level. Valid values:
Default value: info. |
| |
log.dir | The directory for log files and PID files. If this parameter is not set, the logs directory in the current path is used by default. Note The path for this parameter must be an absolute path. |
| |
log.file | The name of the log file. You can customize this value. Note The default value is collector.log. |
| |
log.flush | The refresh rate of logs on the screen. Valid values:
Note The default value is false. |
| |
sync_mode | The data synchronization method. Valid values:
Note The default value is incr. |
| |
mongo_urls | The connection string URI of the source MongoDB instance. In this example, the database account is test and it belongs to the admin database. Note
|
| |
mongo_cs_url | If the source is a sharded cluster instance, you must enter the endpoint of a Configserver (CS) node. To apply for an endpoint for a Configserver node, see Apply for an endpoint for a shard. In this example, the database account is test and it belongs to the admin database. |
| |
mongo_s_url | If the source is a sharded cluster instance, you must enter the endpoint of at least one Mongos node. Separate multiple Mongos addresses with a comma (,). To apply for an endpoint for a Mongos node, see Apply for an endpoint for a shard. In this example, the database account is test and it belongs to the admin database. |
| |
tunnel | The type of channel for synchronization. Valid values:
Note The default value is direct. |
| |
tunnel.address | The endpoint of the destination. The following addresses are supported:
In this example, the database account is test and it belongs to the admin database. |
| |
tunnel.message | The type of data in the channel. This parameter is valid only when the tunnel parameter is set to
Note The default value is raw. |
| |
mongo_connect_mode | The connection mode for the MongoDB instance. This parameter is valid only when the tunnel parameter is set to
Note The default value is secondaryPreferred. |
| |
filter.namespace.black | Specifies the blacklist for data synchronization. The specified namespaces are not synchronized to the destination database. Separate multiple namespaces with a semicolon (;). Note A namespace is the canonical name for a collection or index in MongoDB. It is a combination of the database name and the collection or index name, for example, |
| |
filter.namespace.white | Specifies the whitelist for data synchronization. Only the specified namespaces are synchronized to the destination database. Separate multiple namespaces with a semicolon (;). |
| |
filter.pass.special.db | Enables synchronization for special databases. During normal synchronization, databases such as admin, local, mongoshake, config, and system.views are filtered out by the system. You can enable synchronization for these databases for special requirements. Separate multiple database names with a semicolon (;). |
| |
filter.ddl_enable | Specifies whether to enable DDL synchronization. Valid values:
Note This feature is not supported when the source is a MongoDB sharded cluster instance. |
| |
checkpoint.storage.url | Configures the checkpoint storage address to support resumable transmission. If this is not configured, the program writes to the following databases based on the instance type:
In this example, the database account is test and it belongs to the admin database. |
| |
checkpoint.storage.db | The name of the database that stores checkpoints. Note The default value is mongoshake. |
| |
checkpoint.storage.collection | The name of the collection that stores checkpoints. When you enable a primary and a standby MongoShake node to synchronize data from the same source, you can modify this table name to prevent conflicts caused by duplicate names. Note The default value is ckpt_default. |
| |
checkpoint.start_position | The start position for resumable transmission. This parameter is invalid if a checkpoint already exists. The value format is Note The default value is 1970-01-01T00:00:00Z. |
| |
transform.namespace | Renames the source database or collection and synchronizes it to the destination database. For example, rename |
| |
Full data synchronization options | full_sync.reader.collection_parallel | Sets the maximum number of collections that MongoShake can pull concurrently at a time. |
|
full_sync.reader.write_document_parallel | Sets the number of concurrent threads for MongoShake to write to a single collection. |
| |
full_sync.reader.document_batch_size | Sets the batch size for a single write of documents to the destination. For example, 128 means that 128 documents are aggregated before being written. |
| |
full_sync.collection_exist_drop | Sets how to handle a collection in the destination database that has the same name as a source collection. Valid values:
|
| |
full_sync.create_index | Specifies whether to create an index after synchronization is complete. Valid values:
|
| |
full_sync.executor.insert_on_dup_update | Specifies whether to change an
|
| |
full_sync.executor.filter.orphan_document | Specifies whether to filter orphaned documents when the source is a sharded cluster instance. Valid values:
|
| |
full_sync.executor.majority_enable | Specifies whether to enable the majority write feature on the destination. Valid values:
|
| |
Incremental data synchronization options | incr_sync.mongo_fetch_method | Configures the method for pulling incremental data. Valid values:
Default value: oplog |
|
incr_sync.oplog.gids | Used to set up bidirectional replication for cloud clusters. |
| |
incr_sync.shard_key | The method MongoShake uses to handle concurrency internally. Do not modify this parameter. |
| |
incr_sync.worker | The number of concurrent threads for transmitting oplogs. If the host performance is sufficient, you can increase the number of threads. Note If the source is a sharded cluster instance, the number of threads must be equal to the number of shards. |
| |
incr_sync.worker.oplog_compressor | Enables data compression to reduce network bandwidth consumption. Valid values:
Note This parameter can be used only when the tunnel parameter is not set to |
| |
incr_sync.target_delay | Sets a delayed synchronization between the source and destination. Changes in the source are typically synchronized to the destination in real-time. To prevent accidental operations, you can set this parameter to delay synchronization. For example, Note A value of 0 indicates that delayed synchronization is disabled. |
| |
incr_sync.worker.batch_queue_size | Configuration parameters for MongoShake's internal queue. Do not modify unless necessary. |
| |
incr_sync.adaptive.batching_max_size |
| ||
incr_sync.fetcher.buffer_capacity |
| ||
MongoDB synchronization options (for | incr_sync.executor.upsert | Specifies whether to change an
|
|
incr_sync.executor.insert_on_dup_update | Specifies whether to change an
|
| |
incr_sync.conflict_write_to | Specifies whether to record conflicting documents if a write conflict occurs during synchronization. Valid values:
|
| |
incr_sync.executor.majority_enable | Specifies whether to enable majority write on the destination. Valid values:
Note Enabling this feature affects performance. |
|
FAQ
Refer to the MongoShake FAQ first. If you encounter any other issues when you use MongoShake, provide feedback directly in GitHub Issues.