General large language models (LLMs) may struggle to generate precise or correctly formatted answers for specialized tasks. Using a few-shot learning approach, the system retrieves relevant samples from a predefined set of high-quality Q&A pairs. These samples guide the model to produce more accurate and stylistically consistent responses. This feature is ideal for scenarios that require strict adherence to existing knowledge or a fixed style, such as intelligent customer service, domain-specific Q&A, and formatted content generation.
Performance showcase
The following table shows the samples in the sample library.
User input | Model output |
Explain the term: API (Application Programming Interface) | Explanation: An API is an interface specification that defines how software components interact. It allows different applications to exchange data and call functions through preset rules and protocols. Analogy: Imagine a restaurant menu. The menu (API) lists the dishes you can order (functions) and how to order them (request format). The kitchen (service) prepares the food (response) based on the menu's instructions, and you do not need to know how the kitchen operates internally. |
Explain the term: Blockchain | Explanation: Blockchain is a distributed, decentralized digital ledger technology. It records transaction data in a continuously growing chain of cryptographically linked "blocks". This structure makes the data difficult to tamper with and increases transparency and security. Analogy: Think of it as a bank ledger that is jointly maintained and visible to many people. Each new transaction is recorded as a new entry and locked with a password. Once this ledger is written, it is very difficult for one person to secretly modify it. |
Explain the term: Quantum Entanglement | Explanation: Quantum entanglement is a peculiar quantum mechanical phenomenon. When two or more particles are linked, their states are interdependent. No matter how far apart they are, measuring the state of one particle instantly affects the state of the other. Analogy: Imagine you have a pair of magic gloves. When you put on the left glove, the other glove instantly becomes the right one, no matter where it is. Their states are instantly correlated. |
After this prompt sample library is used, the model strictly follows the term explanation structure and analogy style from the samples. The following table compares the results:
Without a prompt sample library
| With a prompt sample library
|
Create and use a prompt sample library
1. Create a prompt sample library
Go to the Sample Library page and click Create Sample Library (on your first use). Alternatively, click
 to create a new library.
to create a new library.
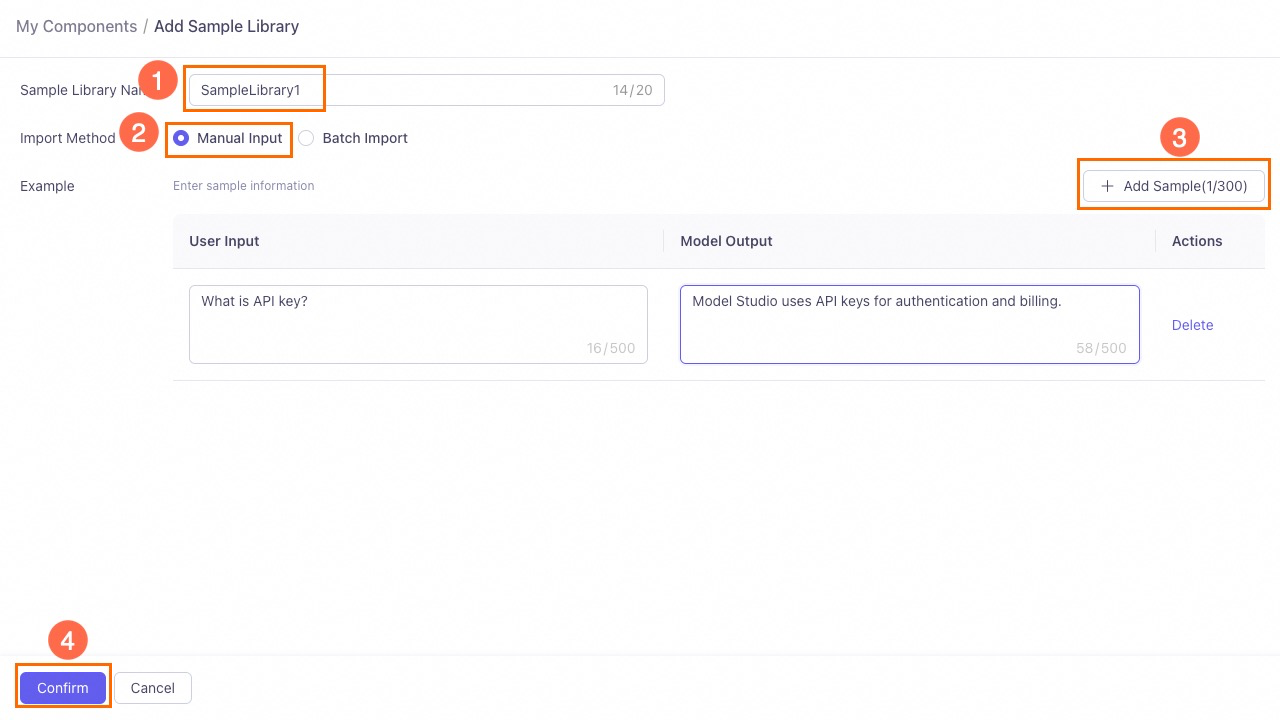
Enter a name for the sample library and select an import method. You can choose between Manual Input and Batch Import.
Manual input
Enter the sample information, including user input and model output, directly on the page. Click Add Sample to add multiple entries.
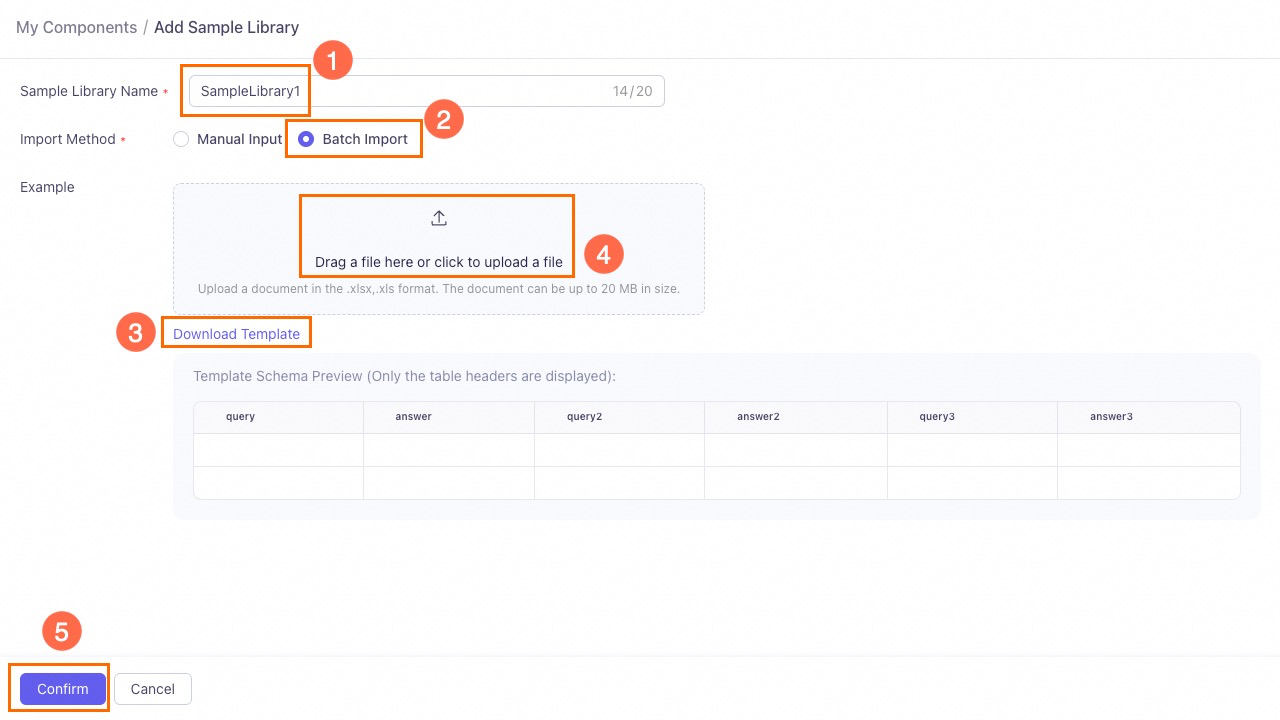
Batch import
First download the template file, fill it out according to the specified format, and then upload it. Excel files smaller than 20 MB are supported. You can import up to 100 samples at a time.
2. Use the sample library in an agent application
To use the prompt sample library, associate it with an agent application in the same workspace.
Make sure that you have an agent application.
Go to the My Applications page, find the target agent application, and click Configure on the application card.
Find and turn on the Sample Library switch. Then, add the sample library that you created in the previous step. An application can be associated with up to five sample libraries and uses a multi-channel recall strategy.
Multi-channel recall strategy: The system retrieves relevant samples from all associated libraries. It then uses a reranking model to select the top K most relevant entries and adds them to the model's input for reference. The number of recalled segments is configurable.
NoteYou cannot manually set the retrieval order.
Optional: Click Configure to adjust the number of recalled segments. The default value is 5, and the maximum value is 10.
Click Publish to apply the configuration.
3. Test and verify
Debug in the console
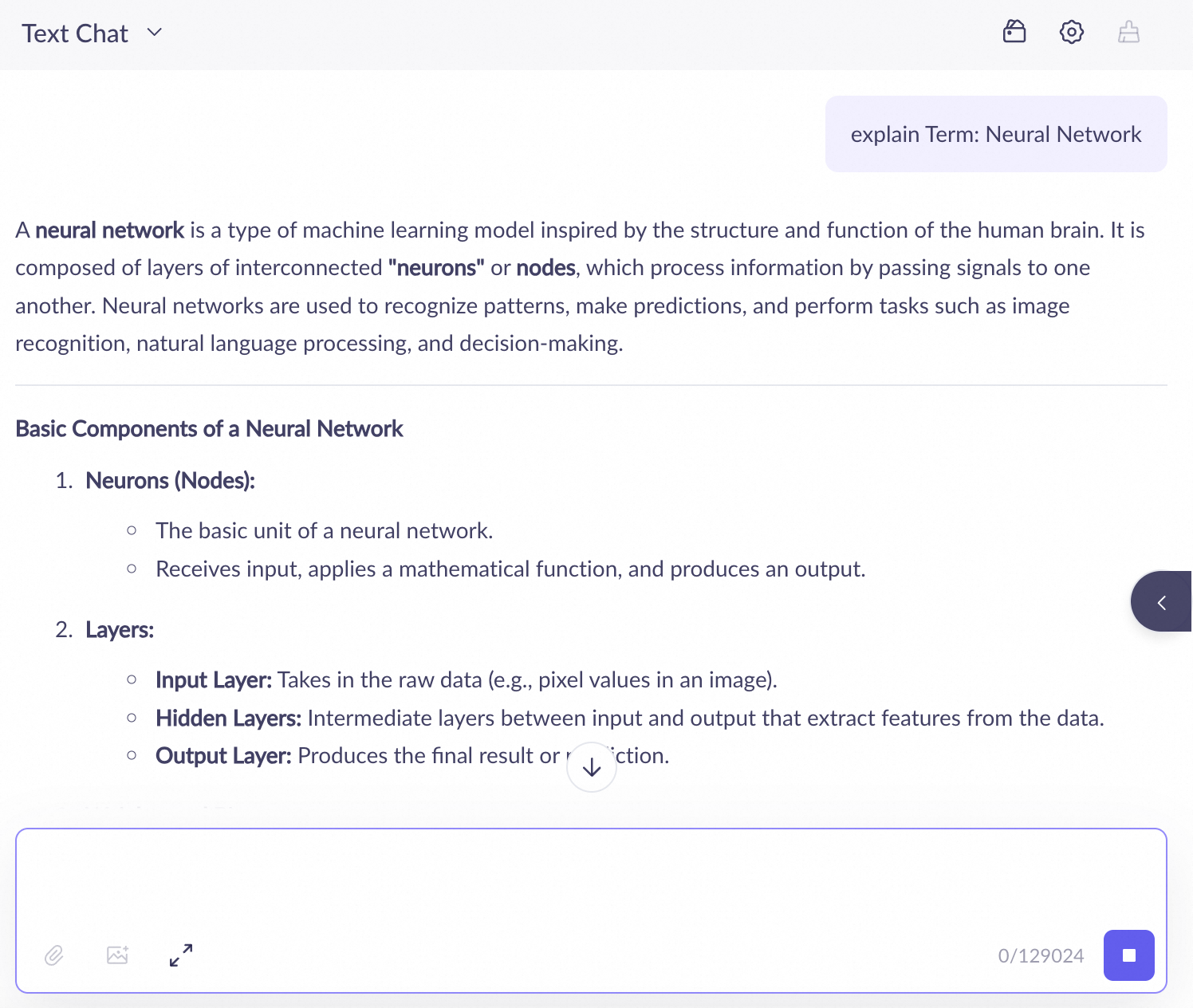
In the application debugging interface, enter a query, such as Explain the term: Neural Network.
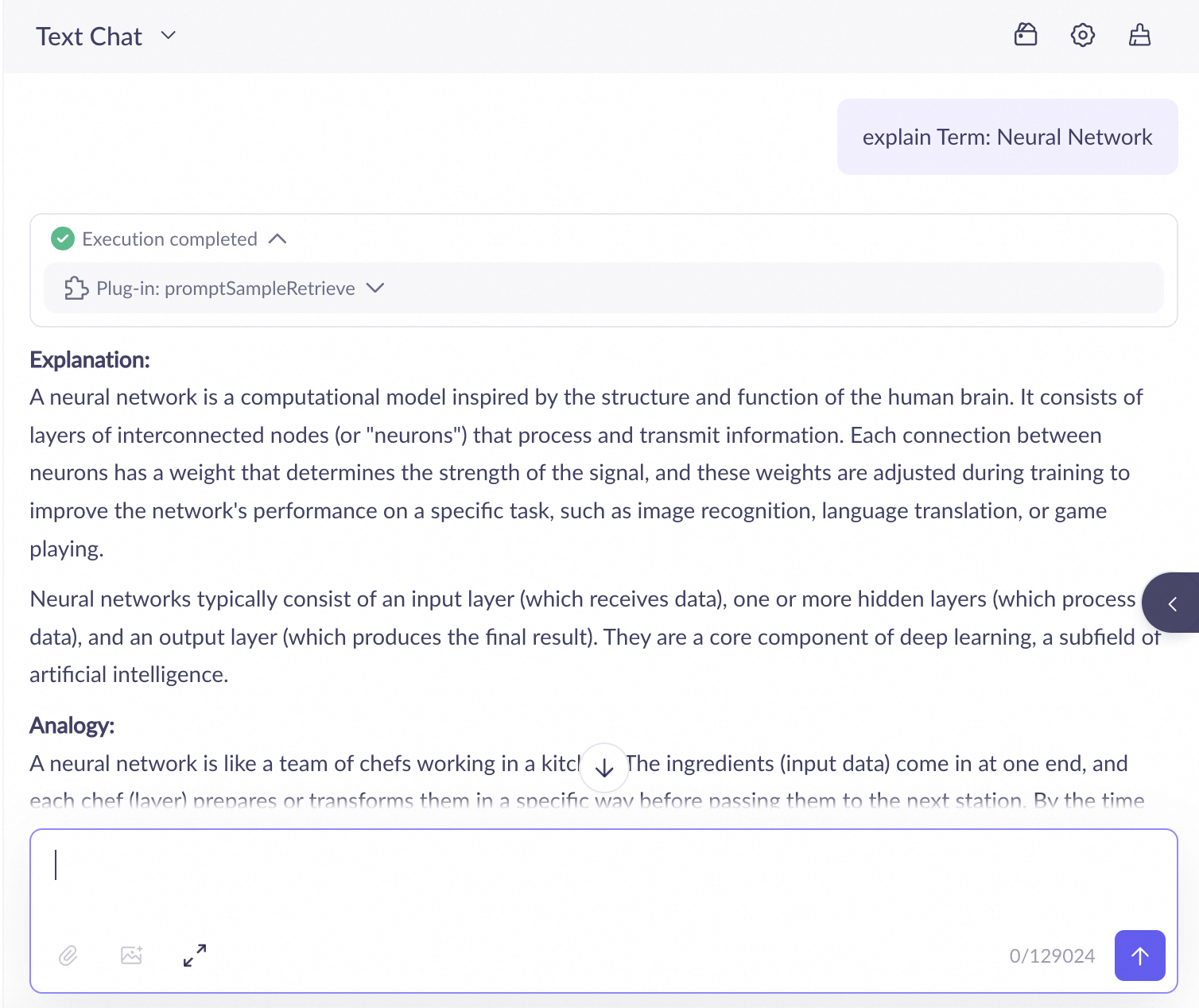
Click promptSampleRetrieve to view the retrieval results.
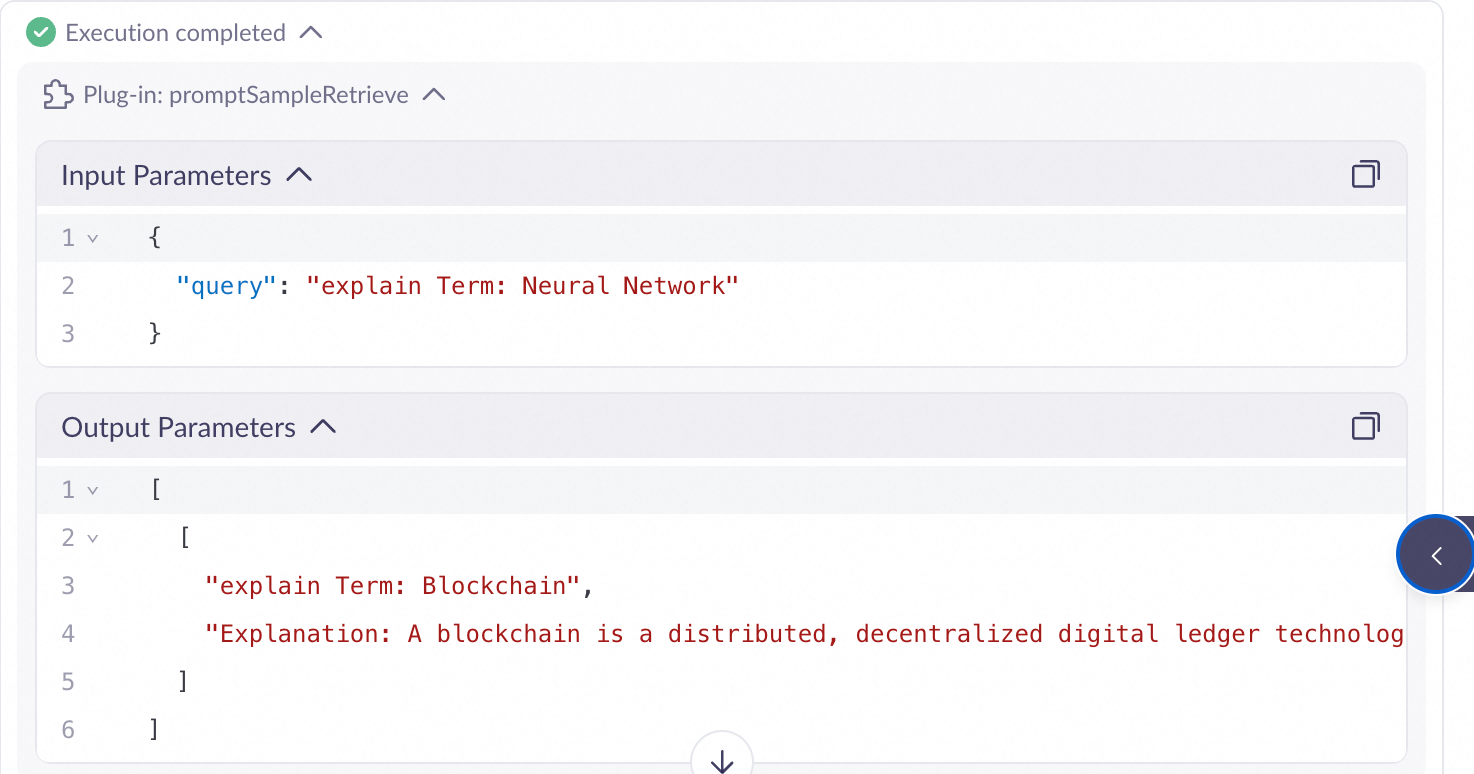
Call using an API
When you call the application API, set the has_thoughts request parameter to true. The thoughts field in the response contains detailed information about the retrieval process for debugging and verification. For code examples, see Call an application.
Manage libraries and samples
On the Sample Library page, you can manage your created libraries and the samples that they contain.
Manage sample libraries

Add: Click
 to the right of Sample Library Management to create a new sample library.
to the right of Sample Library Management to create a new sample library.Delete: Hover over the target sample library and click the
 icon to delete it.
icon to delete it.You cannot directly delete sample libraries that are referenced by an application. To delete such a library, you must first go to the My Applications page and remove it from the application.
Rename: Hover over the sample library that you want to rename and click
 to rename it.
to rename it.
Manage samples
Select a sample library and perform the following operations within it:
Add: Click Enrich Sample or Import Data to add similar samples.
Delete: In the Actions column of the target sample, click Delete.
Modify: In the Actions column of the target sample, click Modify. Change the User Input or Model Output, and then click Save.
Limitations
Sample library capacity: Each sample library can contain up to 300 samples.
NoteThis limit balances retrieval performance with recall accuracy. A large library can increase retrieval latency. If you have more than 300 samples, you can split them into multiple independent libraries based on business topics, such as a "Product Features" library and an "After-Sales Policy" library.
Application association limit: Each agent application can be associated with up to 5 sample libraries.
NoteThe system uses a multi-channel recall strategy and retrieves from all associated libraries in parallel.
Recalled chunk limit: Up to 10 sample chunks can be recalled and injected into the context for a single request.
NoteYou can adjust this parameter in the application configuration to control the length of the injected context to balance effectiveness and token costs.
File import limit: For batch imports, Excel files up to 20 MB are supported. You can import up to 100 samples at a time.
Billing
The prompt sample library feature itself does not incur storage or management fees.
However, enabling this feature increases the model's token consumption and your overall costs. The additional tokens consist primarily of the recalled samples that are injected into the context.
Cost estimation formula: Total input tokens ≈ User query tokens + Total tokens of all recalled samples + System prompt tokens
FAQ
What is the relationship between a sample library and a sample?
A sample library is a container for samples. Each sample library can contain up to 300 similar samples, and each sample includes a user input and a model output.
Samples are organized and managed using sample libraries. You can add multiple libraries with different names for application configuration.
What is the difference between a prompt sample library and a knowledge base?
These two features serve different purposes:
Prompt sample library: Uses a few-shot learning approach, primarily to teach the model how to respond. It controls the model's response style, format, and specific facts by providing a small number of high-quality Q&A samples. It is suitable for scenarios that require precise imitation and style control.
Knowledge base: Uses a retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) approach, primarily to tell the model what to say. It provides the model with the external knowledge needed to answer questions by retrieving relevant paragraphs from many documents as context. It is suitable for scenarios that require open-ended Q&A based on extensive documentation.