This topic describes how to use Milvus 2.5 for fast full-text search, keyword matching, and hybrid search. Milvus 2.5 enhances search accuracy by improving the flexibility of vector similarity search and data analytics. This topic also shows how to use hybrid search in the retrieval stage of a retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) application to provide more precise context for generating answers.
Background information
Milvus 2.5 integrates the high-performance search engine library Tantivy and includes a built-in Sparse-BM25 algorithm, providing native full-text search capabilities for the first time. This feature complements the existing semantic search function to offer a more powerful search experience.
Built-in analyzer: No extra pre-processing is required. With its built-in analyzer and sparse vector extraction capabilities, Milvus can directly accept text input. It automatically performs tokenization, stop word filtering, and sparse vector extraction.
Real-time BM25 statistics: Term frequency (TF) and inverse document frequency (IDF) are dynamically updated when data is inserted. This ensures real-time and accurate search results.
Enhanced hybrid search performance: Sparse vector retrieval based on the approximate nearest neighbor (ANN) algorithm outperforms traditional keyword systems. It supports millisecond-level responses for hundreds of millions of data entries and is compatible with hybrid queries involving dense vectors.
Prerequisites
You have created a Milvus instance, and its Kernel Version is 2.5. For more information, see Create a Milvus instance.
You have activated the service and obtained an API key.
Limits
This applies to Milvus instances with a Kernel Version of 2.5 or later.
The
pymilvusPython SDK must be version 2.5 or later.You can run the following command to check the current version.
pip3 show pymilvusIf your version is earlier than 2.5, run the following command to update it.
pip3 install --upgrade pymilvus
Procedure
Step 1: Install dependency libraries
pip3 install pymilvus langchain dashscopeStep 2: Prepare data
This topic uses the official Milvus documentation as an example to demonstrate how to chunk text with the LangChain SDK, generate embeddings with the text-embedding-v2 embedding model, and insert the resulting embeddings and original text into Milvus.
from langchain_community.document_loaders import WebBaseLoader
from langchain.text_splitter import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter
from langchain_community.embeddings import DashScopeEmbeddings
from pymilvus import MilvusClient, DataType, Function, FunctionType
dashscope_api_key = "<YOUR_DASHSCOPE_API_KEY>"
milvus_url = "<YOUR_MILVUS_URL>"
user_name = "root"
password = "<YOUR_PASSWORD>"
collection_name = "milvus_overview"
dense_dim = 1536
loader = WebBaseLoader([
'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/milvus-io/milvus-docs/refs/heads/v2.5.x/site/en/about/overview.md'
])
docs = loader.load()
text_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter(chunk_size=1024, chunk_overlap=256)
# Chunk the input documents by chunk_size using LangChain
all_splits = text_splitter.split_documents(docs)
embeddings = DashScopeEmbeddings(
model="text-embedding-v2", dashscope_api_key=dashscope_api_key
)
text_contents = [doc.page_content for doc in all_splits]
vectors = embeddings.embed_documents(text_contents)
client = MilvusClient(
uri=f"http://{milvus_url}:19530",
token=f"{user_name}:{password}",
)
schema = MilvusClient.create_schema(
enable_dynamic_field=True,
)
analyzer_params = {
"type": "english"
}
# Add fields to schema
schema.add_field(field_name="id", datatype=DataType.INT64, is_primary=True, auto_id=True)
schema.add_field(field_name="text", datatype=DataType.VARCHAR, max_length=65535, enable_analyzer=True, analyzer_params=analyzer_params, enable_match=True)
schema.add_field(field_name="sparse_bm25", datatype=DataType.SPARSE_FLOAT_VECTOR)
schema.add_field(field_name="dense", datatype=DataType.FLOAT_VECTOR, dim=dense_dim)
bm25_function = Function(
name="bm25",
function_type=FunctionType.BM25,
input_field_names=["text"],
output_field_names="sparse_bm25",
)
schema.add_function(bm25_function)
index_params = client.prepare_index_params()
# Add indexes
index_params.add_index(
field_name="dense",
index_name="dense_index",
index_type="IVF_FLAT",
metric_type="IP",
params={"nlist": 128},
)
index_params.add_index(
field_name="sparse_bm25",
index_name="sparse_bm25_index",
index_type="SPARSE_WAND",
metric_type="BM25"
)
# Create collection
client.create_collection(
collection_name=collection_name,
schema=schema,
index_params=index_params
)
data = [
{"dense": vectors[idx], "text": doc}
for idx, doc in enumerate(text_contents)
]
# Insert data
res = client.insert(
collection_name=collection_name,
data=data
)
print(f"Generated {len(vectors)} vectors, dimension: {len(vectors[0])}")
This example involves the following parameters. Replace them with your actual values.
Parameter | Description |
| The API key for Alibaba Cloud Model Studio. |
| The Milvus instance's Private Endpoint or Public Endpoint. You can view this information on the Instance Details page of the Milvus instance.
|
| The username and password that you specified when you created the Milvus instance. |
| |
| The name of the collection. You can customize the name. This topic uses `milvus_overview` as an example. |
| The dimension of the dense vector. The `text-embedding-v2` model generates vectors with 1536 dimensions, so `dense_dim` is set to 1536. |
This example uses the latest features of Milvus 2.5. When you create a bm25_function object, Milvus automatically transforms the text column into sparse vectors.
Similarly, when you process Chinese documents, Milvus 2.5 lets you specify a corresponding Chinese analyzer.
After you configure the analyzer in the schema, the setting becomes permanent for the collection. To set a new analyzer, you must create a new collection.
# Define analyzer parameters
analyzer_params = {
"type": "chinese" # Specify the analyzer type as Chinese
}
# Add a text field to the schema and enable the analyzer
schema.add_field(
field_name="text", # Field name
datatype=DataType.VARCHAR, # Data type: string (VARCHAR)
max_length=65535, # Maximum length: 65535 characters
enable_analyzer=True, # Enable the analyzer
analyzer_params=analyzer_params # Analyzer parameters
)
Step 3: Perform full-text search
Milvus 2.5 provides APIs that allow you to easily use the latest full-text search features. The following code shows an example.
from pymilvus import MilvusClient
# Create a Milvus client.
client = MilvusClient(
uri="http://c-xxxx.milvus.aliyuncs.com:19530", # The public endpoint of the Milvus instance.
token="<yourUsername>:<yourPassword>", # The username and password to log on to the Milvus instance.
db_name="default" # The name of the database to connect to. This example uses the default database.
)
search_params = {
'params': {'drop_ratio_search': 0.2},
}
full_text_search_res = client.search(
collection_name='milvus_overview',
data=['what makes milvus so fast?'],
anns_field='sparse_bm25',
limit=3,
search_params=search_params,
output_fields=["text"],
)
for hits in full_text_search_res:
for hit in hits:
print(hit)
print("\n")
"""
{'id': 456165042536597485, 'distance': 6.128782272338867, 'entity': {'text': '## What Makes Milvus so Fast?\n\nMilvus was designed from day one to be a highly efficient vector database system. In most cases, Milvus outperforms other vector databases by 2-5x (see the VectorDBBench results). This high performance is the result of several key design decisions:\n\n**Hardware-aware Optimization**: To accommodate Milvus in various hardware environments, we have optimized its performance specifically for many hardware architectures and platforms, including AVX512, SIMD, GPUs, and NVMe SSD.\n\n**Advanced Search Algorithms**: Milvus supports a wide range of in-memory and on-disk indexing/search algorithms, including IVF, HNSW, DiskANN, and more, all of which have been deeply optimized. Compared to popular implementations like FAISS and HNSWLib, Milvus delivers 30%-70% better performance.'}}
{'id': 456165042536597487, 'distance': 4.760214805603027, 'entity': {'text': "## What Makes Milvus so Scalable\n\nIn 2022, Milvus supported billion-scale vectors, and in 2023, it scaled up to tens of billions with consistent stability, powering large-scale scenarios for over 300 major enterprises, including Salesforce, PayPal, Shopee, Airbnb, eBay, NVIDIA, IBM, AT&T, LINE, ROBLOX, Inflection, etc.\n\nMilvus's cloud-native and highly decoupled system architecture ensures that the system can continuously expand as data grows:\n\n"}}
"""Step 4: Perform keyword matching
Keyword matching is a new feature in Milvus 2.5. You can combine it with vector similarity search to narrow the search scope and improve search performance. To use the keyword matching feature, you must set both enable_analyzer and enable_match to `True` when defining the schema.
Enabling enable_match creates an inverted index for the field, which consumes additional storage resources.
Example 1: Keyword matching combined with vector search
In this code snippet, a filter expression limits the search results to documents that contain the specified words 'query' and 'node'. Then, a vector similarity search is performed on the filtered subset of documents.
filter = "TEXT_MATCH(text, 'query') and TEXT_MATCH(text, 'node')"
text_match_res = client.search(
collection_name="milvus_overview",
anns_field="dense",
data=query_embeddings,
filter=filter,
search_params={"params": {"nprobe": 10}},
limit=2,
output_fields=["text"]
)Example 2: Scalar filtering query
You can also use keyword matching for scalar filtering in query operations. By specifying a TEXT_MATCH expression in query(), you can retrieve documents that match the specified words. In this code snippet, the filter expression limits the search results to documents that match 'scalable' or 'fast'.
filter = "TEXT_MATCH(text, 'scalable fast')"
text_match_res = client.query(
collection_name="milvus_overview",
filter=filter,
output_fields=["text"]
)Step 5: Use hybrid search and RAG
Hybrid search combines vector search and full-text search. It uses the Reciprocal Rank Fusion (RRF) algorithm to merge the results from both searches. This process re-optimizes the sorting and weight allocation to improve the data recall rate and accuracy.
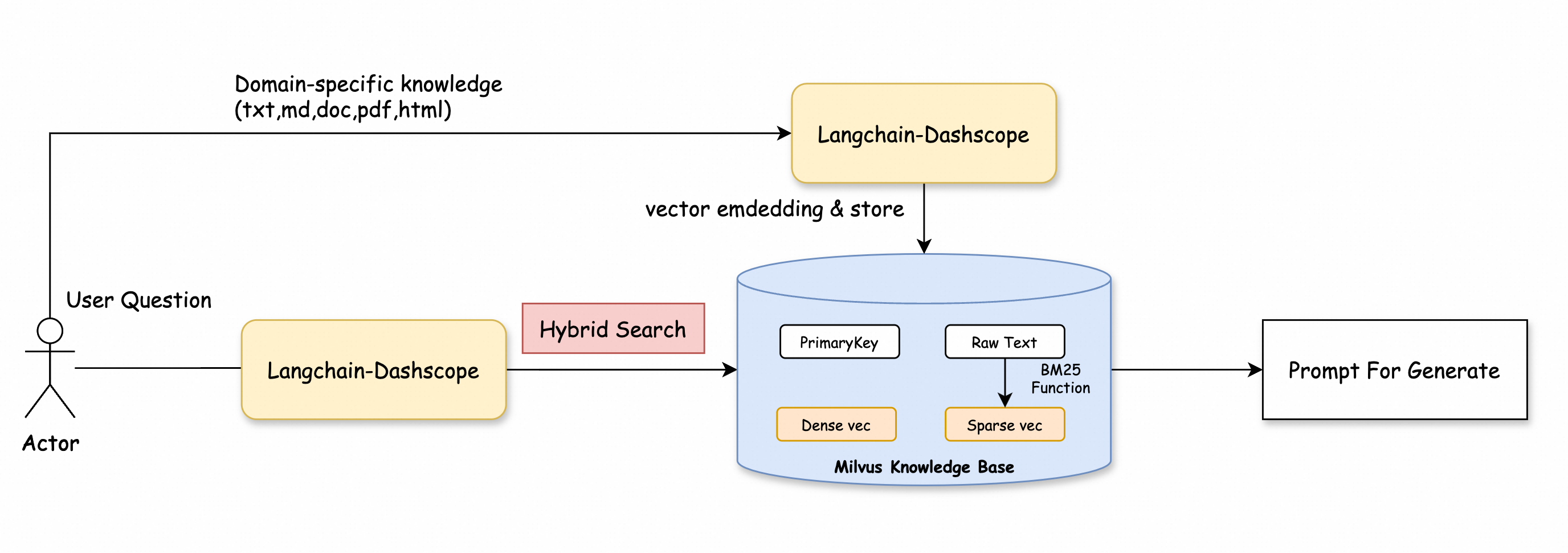
The following code shows an example.
from pymilvus import MilvusClient
from pymilvus import AnnSearchRequest, RRFRanker
from langchain_community.embeddings import DashScopeEmbeddings
from dashscope import Generation
# Create a Milvus client.
client = MilvusClient(
uri="http://c-xxxx.milvus.aliyuncs.com:19530", # The public endpoint of the Milvus instance.
token="<yourUsername>:<yourPassword>", # The username and password to log on to the Milvus instance.
db_name="default" # The name of the database to connect to. This example uses the default database.
)
collection_name = "milvus_overview"
# Replace with your DashScope API key
dashscope_api_key = "<YOUR_DASHSCOPE_API_KEY>"
# Initialize the embedding model
embeddings = DashScopeEmbeddings(
model="text-embedding-v2", # Use the text-embedding-v2 model.
dashscope_api_key=dashscope_api_key
)
# Define the query
query = "Why does Milvus run so scalable?"
# Embed the query and generate the corresponding vector representation
query_embeddings = embeddings.embed_documents([query])
# Set the top K result count
top_k = 5 # Get the top 5 docs related to the query
# Define the parameters for the dense vector search
search_params_dense = {
"metric_type": "IP",
"params": {"nprobe": 2}
}
# Create a dense vector search request
request_dense = AnnSearchRequest([query_embeddings[0]], "dense", search_params_dense, limit=top_k)
# Define the parameters for the BM25 text search
search_params_bm25 = {
"metric_type": "BM25"
}
# Create a BM25 text search request
request_bm25 = AnnSearchRequest([query], "sparse_bm25", search_params_bm25, limit=top_k)
# Combine the two requests
reqs = [request_dense, request_bm25]
# Initialize the RRF ranking algorithm
ranker = RRFRanker(100)
# Perform the hybrid search
hybrid_search_res = client.hybrid_search(
collection_name=collection_name,
reqs=reqs,
ranker=ranker,
limit=top_k,
output_fields=["text"]
)
# Extract the context from hybrid search results
context = []
print("Top K Results:")
for hits in hybrid_search_res: # Use the correct variable here
for hit in hits:
context.append(hit['entity']['text']) # Extract text content to the context list
print(hit['entity']['text']) # Output each retrieved document
# Define a function to get an answer based on the query and context
def getAnswer(query, context):
prompt = f'''Please answer my question based on the content within:
```
{context}
```
My question is: {query}.
'''
# Call the generation module to get an answer
rsp = Generation.call(model='qwen-turbo', prompt=prompt)
return rsp.output.text
# Get the answer
answer = getAnswer(query, context)
print(answer)
# Expected output excerpt
"""
Milvus is highly scalable due to its cloud-native and highly decoupled system architecture. This architecture allows the system to continuously expand as data grows. Additionally, Milvus supports three deployment modes that cover a wide...
"""