This topic describes how to build a retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) system using Vector Retrieval Service for Milvus (Milvus) and the Dify platform.
Background
RAG
Large language models (LLMs) often hallucinate because their knowledge is limited. The retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) technology solves this pain point by connecting to external knowledge bases. An efficient RAG system requires a powerful vector database.
This topic focuses on Milvus and the Dify low-code artificial intelligence (AI) platform. It shows you how to combine them to quickly build an enterprise-grade RAG application. This demonstrates the core value of a vector database in solving the "last mile" problem in AI.
Dify
Dify is an open source platform for developing AI applications. It features low-code pipelines and a user-friendly interface. Its core mission is to simplify and accelerate the process of building AI applications by integrating backend-as-a-service (BaaS) and LLM Operations (LLMOps) concepts.
Dify is a full-stack solution. On the backend, it provides reliable infrastructure, including API services and data management. This lets developers avoid building from scratch. For LLMOps, Dify offers an intuitive visual interface for prompt engineering, which simplifies complex prompt workflows. The built-in, high-quality RAG engine connects to private knowledge bases, such as company documents and databases. This connection allows the large language model to answer questions using domain-specific knowledge, which reduces hallucinations and ensures that answers are accurate and traceable.
Prerequisites
You have created a Milvus instance. For more information, see Create a Milvus instance.
You have activated Alibaba Cloud Model Studio and obtained an API key. For more information, see Obtain an App ID and a Workspace ID.
You have installed Docker and Docker Compose. For more information, see Install and use Docker and Docker Compose.
Procedure
Step 1: Install Dify
Clone the open-source Dify project from GitHub to your local machine.
git clone https://github.com/langgenius/dify.gitGo to the deployment directory and back up the .env configuration file.
cd dify/docker/ cp .env.example .envModify the following configuration information in the .env file.
# Vector storage engine configuration VECTOR_STORE=milvus # Specifies Milvus as the vector storage engine # Milvus connection information MILVUS_URI=http://YOUR_ALIYUN_MILVUS_ENDPOINT:19530 MILVUS_USER=YOUR_ALIYUN_MILVUS_USER MILVUS_PASSWORD=YOUR_ALIYUN_MILVUS_PASSWORDThis example uses the following parameters. Replace them with your actual values.
Parameter
Description
MILVUS_URIThe endpoint of the Milvus instance. The format is
http://<Public IP address>:<Port>.<Public IP address>: You can view this on the Instance Details page of your Milvus instance.<Port>: You can view this on the Instance Details page of your Milvus instance. The default port is 19530.
MILVUS_USERThe username that you specified when you created the Milvus instance.
MILVUS_PASSWORDThe password for the user that you specified when you created the Milvus instance.
Start Dify.
docker compose up -d --build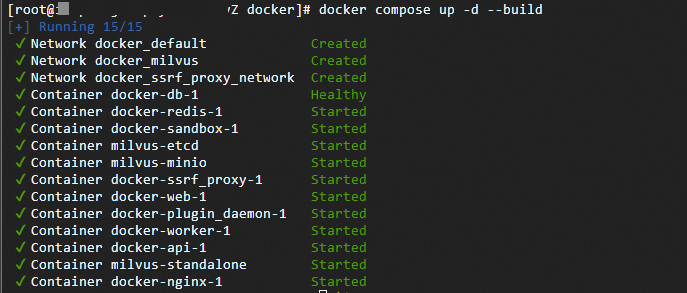
In a browser, navigate to
http://127.0.0.1/to access the Dify service. Set the administrator account and password, and then log on to the console.NoteIf Dify is running on a remote server, such as an Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance or a virtual machine, replace
127.0.0.1with the public IP address or domain name of the server. Make sure that the server is accessible over the network.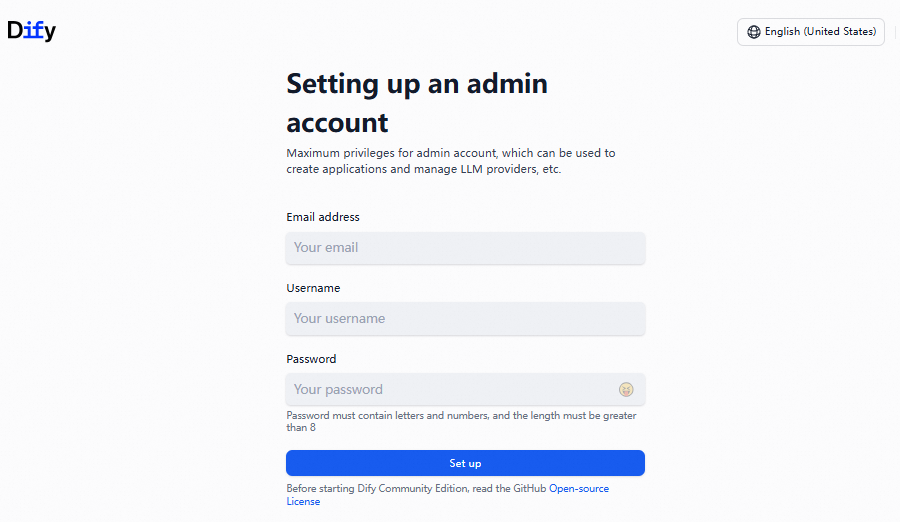
Step 2: Set up the model
After you log on, click your profile picture in the upper-right corner and select Settings from the drop-down menu.
In the navigation pane on the left, select Model Provider. On the right, find Qwen and install it.
After the model is installed, click API-Key Setup. Enter your API key from Alibaba Cloud Model Studio.
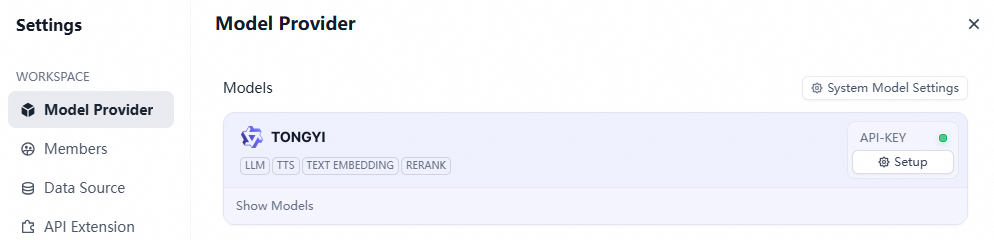
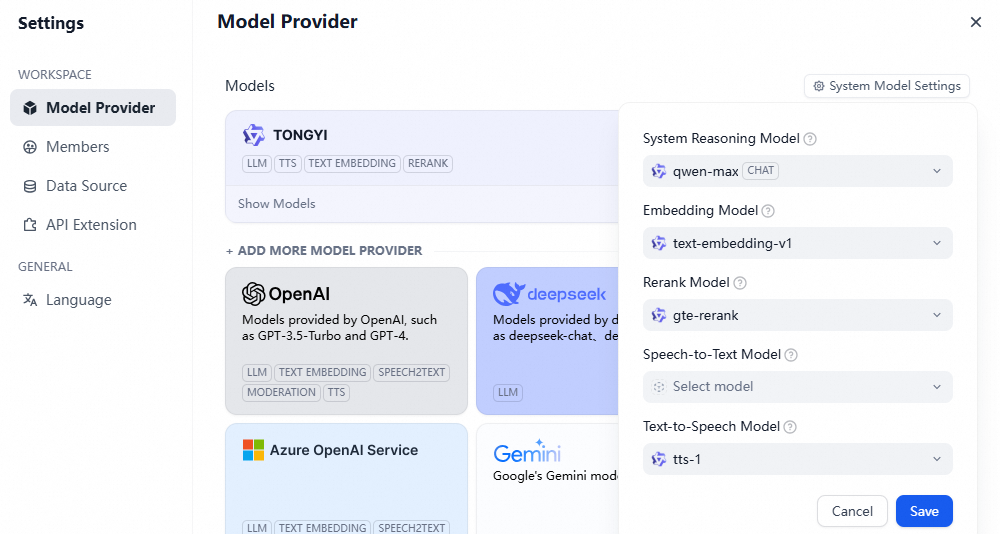
Configure the System Model Settings as needed.
Step 3: Create a knowledge base
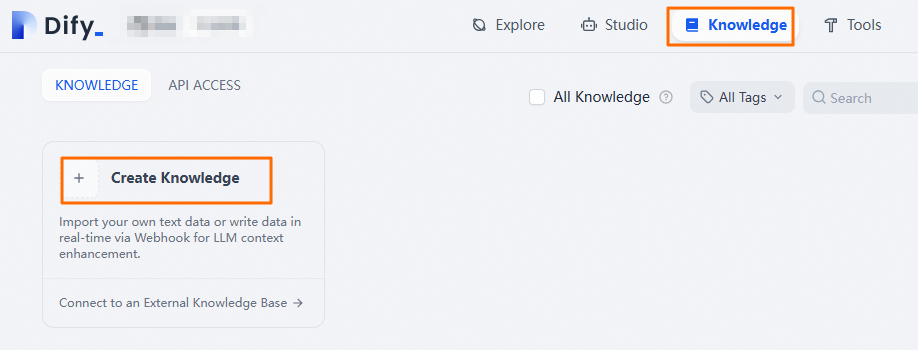
At the top of the page, click Knowledge, and then click Create Knowledge.
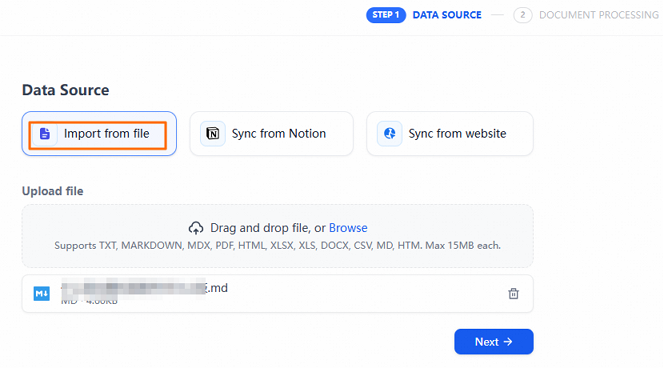
Click Import from file. Download the sample data by clicking README.md. Then, upload the sample data file.
Modify the parameters and click Save & Process.
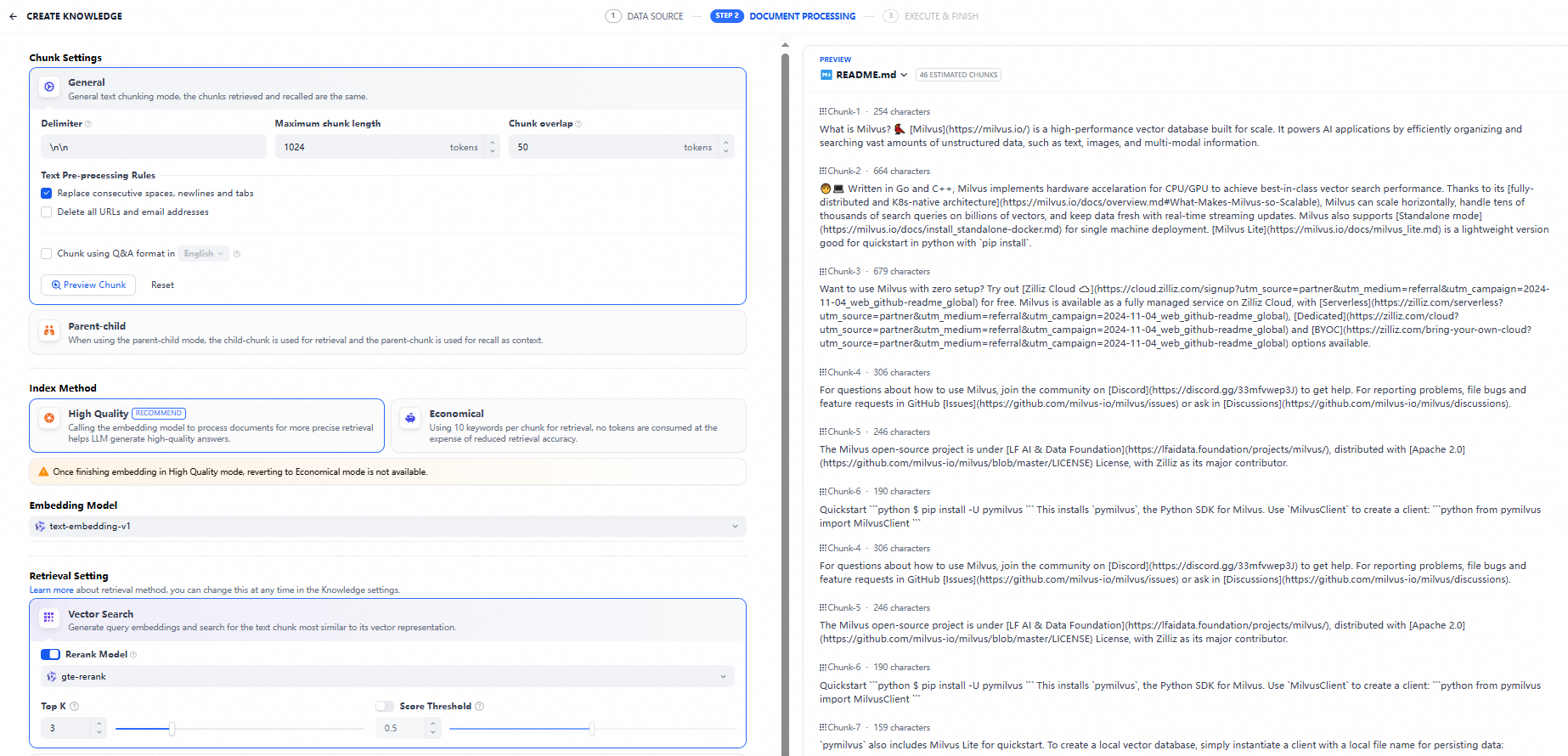
This example modifies the following parameters:
Maximum chunk length: Set it to 1024.
Embedding Model: Select text-embedding-v1.
After the process is complete, the knowledge base is created.
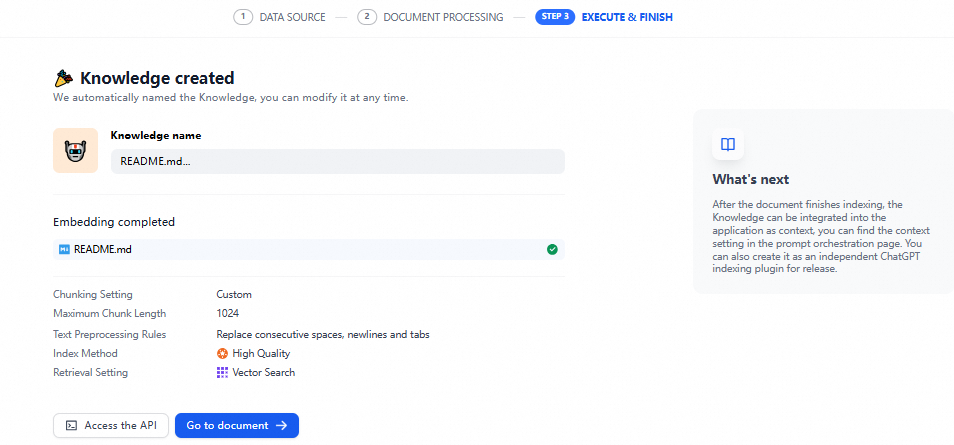
Step 4: Verify vector retrieval
Log on to the Vector Retrieval Service for Milvus console and select your Milvus instance. In the upper-right corner, click Attu Manager to open the Attu page. You can see that the corresponding collection data is imported. For more information, see Manage Milvus instances with Attu.
Step 5: Verify the RAG performance
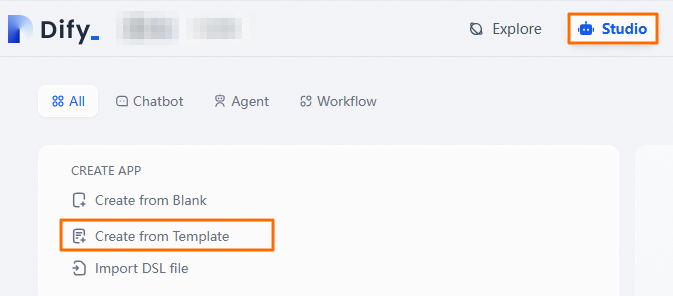
At the top of the page, click Studio to return to the home page. Select Create from Template.
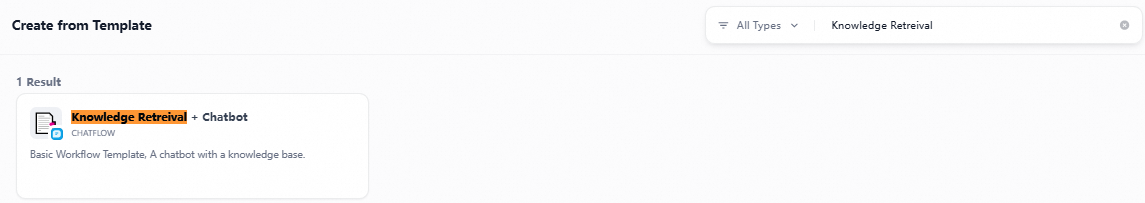
In the search box, search for and use the Knowledge Retrieval + Chatbot template.
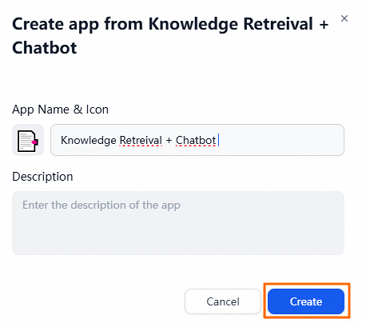
In the dialog box that appears, click Create.
Select the KNOWLEDGE RETRIEVAL node. Set the knowledge base to the one that you created in the previous step.
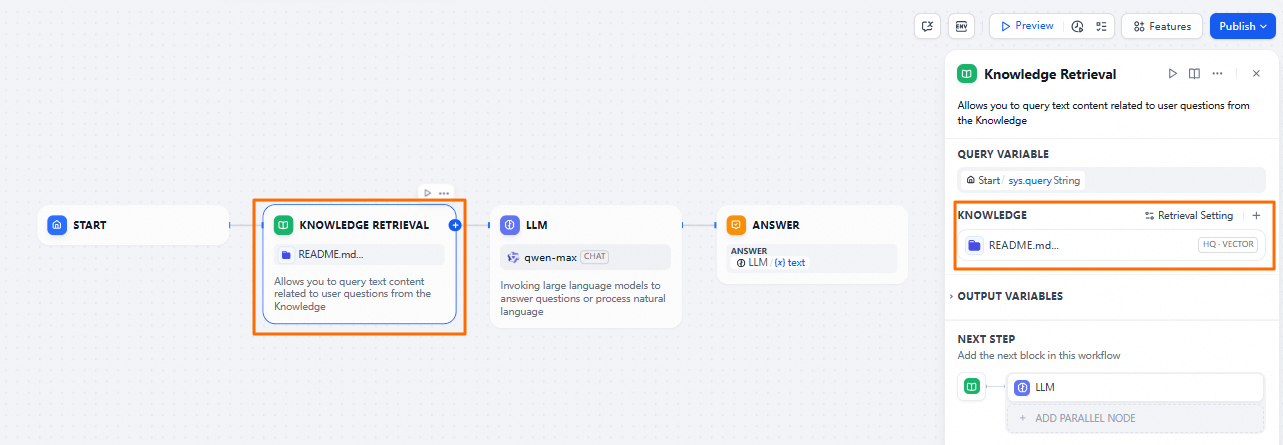
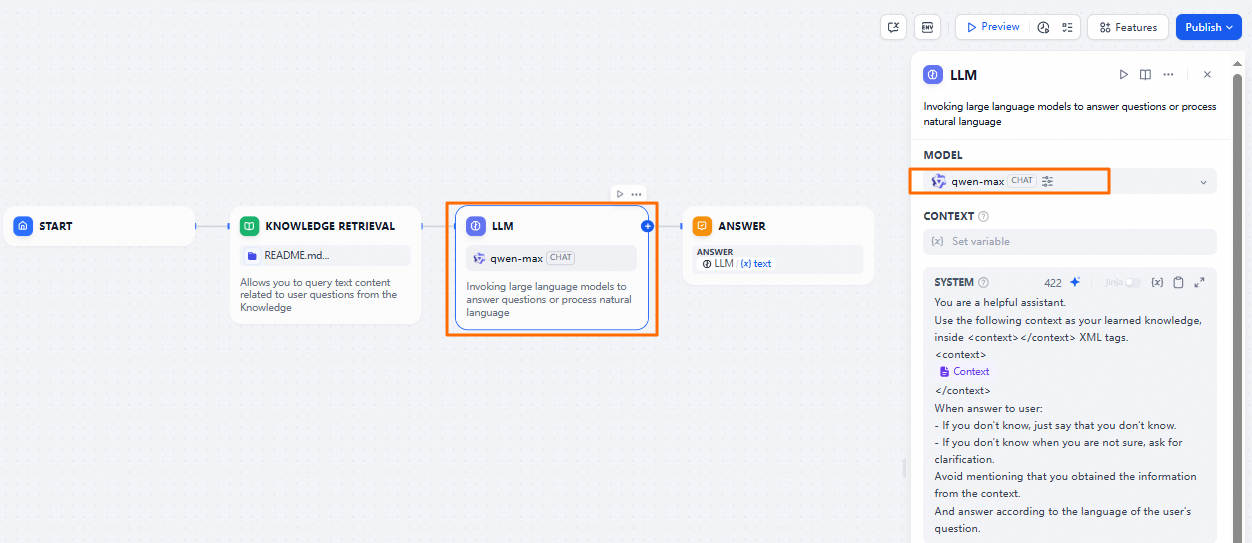
Select the LLM node and set the model to qwen-max.
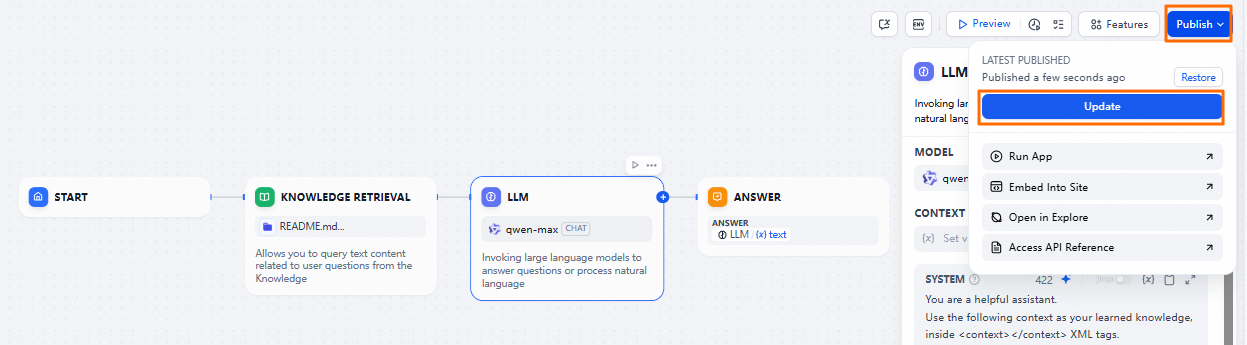
In the upper-right corner, click Publish, and select Update.
Run the workflow to open the test page. Enter a question related to the content in the knowledge base to receive an answer.