This topic describes how to use the modules of the Proxima kernel and configure parameters for each module. The modules are IndexBuilder, IndexConverter, IndexMeasure, and IndexSearcher.
IndexBuilder
IndexBuilder is used to build indexes. The following figure shows the basic process of calling this module.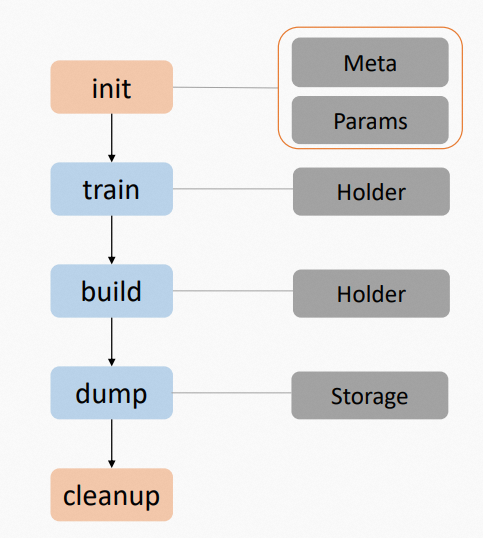
Initialize IndexBuilder.
Perform data training.
Build indexes.
Dump indexes.
Clean up resources.
The Proxima kernel provides multiple built-in Builder plug-ins, such as ClusteringBuilder, LinearBuilder, HnswBuilder, and SsgBuilder. 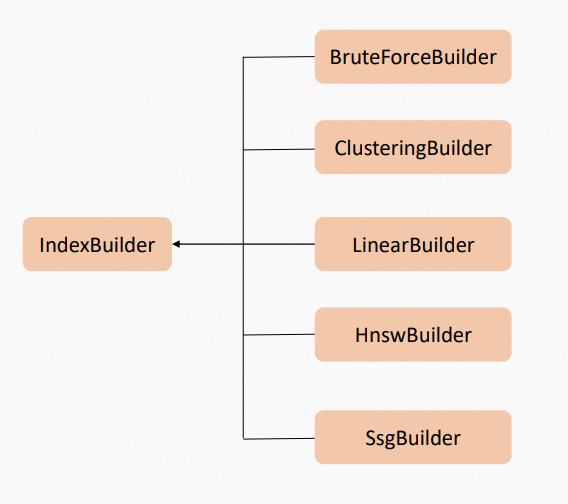
IndexConverter
IndexConverter is used to convert characteristic vectors. For example, the module can perform dimension reduction, half-float conversion, and INT8 quantization for characteristic vectors. This module can be independently used or used as part of the vector search process.
In most cases, IndexConverter is used together with IndexReformer in the vector search process. The relationship between IndexConverter and IndexReformer is similar to the relationship between IndexBuilder and IndexSearcher. IndexConverter is a prerequisite for IndexBuilder. After IndexConverter converts characteristic vectors, IndexBuilder builds indexes. During online search, all query vectors are converted by IndexReformer and then sent to IndexSearcher for the search.
IndexMeasure
IndexMeasure is used to calculate similarities among vectors. A small distance indicates a close similarity. For more information about the names of the plug-ins of IndexMeasure and related parameters, see IndexMeasure parameters.
Distance calculation formulas
Numeric distance
Distance parameter
Formula
Squared Euclidean
$$\sum_{i=0}^n (u_i - v_i)^2$$Euclidean
$$\sqrt{\sum_{i=0}^n (u_i - v_i)^2}$$Normalized Euclidean
$$\sqrt{\frac{1}{2}\frac{\sum_{i=0}^n [(u_i-\bar{u}) - (v_i-\bar{v})]^2}{\sum_{i=0}^n [(u_i-\bar{u})^2 + (v_i-\bar{v})^2]}}$$Normalized Squared Euclidean
$$\frac{1}{2}\frac{\sum_{i=0}^n [(u_i-\bar{u}) - (v_i-\bar{v})]^2}{\sum_{i=0}^n [(u_i-\bar{u})^2 + (v_i-\bar{v})^2]}$$Manhattan
$$\sum_{i=0}^n |u_i - v_i|$$Chebyshev (Chessboard)
$$\max_{i=0} |u_i - v_i|$$Cosine
$$1.0 - \frac{\sum_{i=0}^n u_iv_i}{\sqrt{\sum_{i=0}^n u_i^2}\sqrt{\sum_{i=0}^n v_i^2}}$$Minus Inner Product
$$-\sum_{i=0}^n u_iv_i$$Canberra
$$\sum_{i=0}^n\frac{|u_i-v_i|}{|u_i|+|v_i|}$$Bray Curtis
$$\frac{\sum_{i=0}^n|u_i-v_i|}{\sum_{i=0}^n|u_i+v_i|}$$Correlation
$$1.0 - \frac{\sum_{i=0}^n(u_i-\bar{u})(v_i-\bar{v})}{\sqrt{\sum_{i=0}^n(u_i-\bar{u})^2} \sqrt{\sum_{i=0}^n(v_i-\bar{v})^2}}$$Binary
$$[!u == v]$$Binary image distance
Distance parameter
Formula
Hamming
$$M_{10}+M_{01}$$Jaccard
$$\frac{M_{10}+M_{01}}{M_{11}+M_{10}+M_{01}}$$Matching
$$\frac{M_{10}+M_{01}}{M_{11}+M_{10}+M_{01}+M_{00}}=\frac{M_{10}+M_{01}}{N}$$Dice
$$\frac{M_{10}+M_{01}}{2M_{11}+M_{10}+M_{01}}$$Rogers Tanimoto
$$\frac{2(M_{10}+M_{01})}{M_{11}+2(M_{10}+M_{01})+M_{00}}$$Russell Rao
$$\frac{M_{10}+M_{01}+M_{00}}{N}$$Sokal Michener
$$\frac{M_{10}+M_{01}}{M_{11}+M_{10}+M_{01}+M_{00}}=\frac{M_{10}+M_{01}}{N}$$Sokal Sneath I
$$1.0 - \frac{M_{11}}{M_{11} + 2(M_{10}+M_{01})}=\frac{2(M_{10}+M_{01})}{M_{11}+2(M_{10}+M_{01})}$$Sokal Sneath II
$$1.0 - \frac{2(M_{11} + M_{00})}{2(M_{11} + M_{00}) + M_{10} + M_{01}} = \frac{M_{10} + M_{01}}{2N - (M_{10} + M_{01})}$$Sokal Sneath III
$$1.0 - \frac{M_{11} + M_{00}}{M_{10} + M_{01}} = \frac{2(M_{10} + M_{01}) - N}{M_{10} + M_{01}}$$Sokal Sneath IV
$$1.0 - \frac{1}{4}(\frac{M_{11}}{M_{11} + M_{10}} + \frac{M_{11}}{M_{11} + M_{01}} + \frac{M_{00}}{M_{10} + M_{00}} + \frac{M_{00}}{M_{01} + M_{00}})$$Sokal Sneath V
$$1.0 - \frac{M_{11}M_{00}}{\sqrt{(M_{11} + M_{10}) (M_{11} + M_{01}) (M_{10} + M_{00}) (M_{01} + M_{00})}}$$Kulczynski I
$$1.0-\frac{S_{AB}}{S_A+S_B-2S_{AB}} = 1.0-\frac{M_{11}}{M_{10}+M_{01}} = \frac{M_{10}+M_{01}-M_{11}}{M_{10}+M_{01}}$$Kulczynski II
$$1.0-\frac{1}{2}\left(\frac{S_{AB}}{S_{A}}+\frac{S_{AB}}{S_{B}}\right)$$Yule
$$\frac{2M_{10}M_{01}}{M_{11}M_{00}+M_{10}M_{01}}$$
IndexSearcher
IndexSearcher is mainly used for k-nearest neighbor (kNN) search. This module loads the indexes that are built offline in read-only mode and performs online search.
The following figure shows the process of calling IndexSearcher.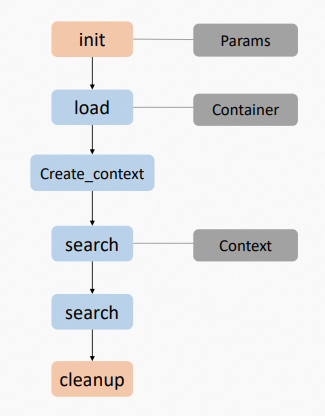
Initialize IndexSearcher.
Load index data.
Create a data context for the search.
Perform a search.
Unload index data.
Clean up resources.
IndexSearcher supports parallel search. However, engine users must have control over parallel search because the scenarios and environments of users vary greatly. Proxima CE supports Searcher Context, which stores the search results and the intermediate data generated in the search process. Each context object can be reused. Threads can access a context object only in sequence. Multiple threads cannot access a context object at the same time. To implement parallel search, you must create multiple context objects. The Proxima kernel provides various built-in Searcher plug-ins, such as ClusteringSearcher, LinearSearcher, HnswSearcher, and SsgSearcher. 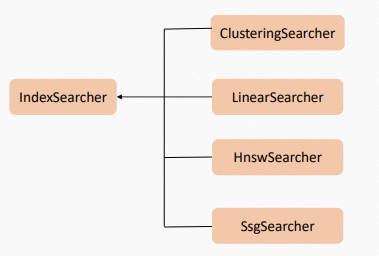
IndexBuilder parameters
ClusteringBuilder
ImportantYou must configure at least one of the proxima.hc.builder.max_document_count and proxima.hc.builder.centroid_count parameters.
Parameter
Data type
Default value
Description
proxima.hc.builder.max_document_count
UNIT32
No default value
If you do not configure the proxima.hc.builder.centroid_count parameter, the proxima.hc.builder.max_document_count parameter is used to calculate the number of cluster centroids.
proxima.hc.builder.centroid_count
STRING
No default value
The number of cluster centroids that you want to use for clusters. Hierarchical clusters are supported. Separate the numbers of centroids at different layers of a hierarchical cluster with an asterisk
(*). If you do not configure this parameter, the number of centroids that are used for clusters is automatically deduced based on the value of the proxima.hc.builder.max_document_count parameter.Sample value for a one-layer cluster: 1000.
Sample value for a two-layer cluster: 100*100.
If you use cluster centroids at two layers, we recommend that you configure more cluster centroids at layer 1 than layer 2. This ensures a high recall rate. Based on empirical values, the number of centroids at layer 1 needs to be set to 10 times the number of centroids at layer 2.
proxima.hc.builder.thread_count
UNIT32
0
The number of threads that are enabled during index building. If you set this parameter to 0, the default number of CPU cores is used.
HnswBuilder
Parameter
Data type
Default value
Description
proxima.hnsw.builder.thread_count
UNIT32
0
The number of threads that are enabled during index building. If you set this parameter to 0, the default number of CPU cores is used.
proxima.hnsw.builder.efconstruction
UNIT32
500
Specifies the graph precision. If this parameter is set to a large value, the graph precision is high but the construction is time-consuming.
proxima.hnsw.builder.max_neighbor_count
UNIT32
100
The number of neighbors in a graph. If this parameter is set to a large value, the graph precision is high but the computing and storage overheads are large. We recommend that you do not set this parameter to a value that is greater than the number of feature dimensions. The maximum value is 65535.
SsgBuilder
Parameter
Data type
Default value
Description
proxima.ssg.builder.thread_count
UNIT32
0
The number of threads that are used for index building.
proxima.ssg.builder.efconstruction
UNIT32
500
Specifies the graph precision. If this parameter is set to a large value, the graph precision is high but the construction is time-consuming.
proxima.ssg.builder.max_neighbor_count
UNIT32
100
The number of neighbors in a graph. If this parameter is set to a large value, the graph precision is high but the computing and storage overheads are large. We recommend that you do not set this parameter to a value that is greater than the number of feature dimensions. The maximum value is 65535.
proxima.ssg.builder.centroid_count
UNIT32
0
The number of cluster centroids that are generated from training samples. If the number of cluster centroids is large, the graph construction cost is high and the graph precision is high. We recommend that you configure this parameter based on the number of data records in the doc table:
If the number of data records in the doc table is less than 2 million, set this parameter to 2000.
If the number of data records in the doc table is between 2 million and 10 million, set this parameter to 5000.
If the number of data records in the doc table is greater than 10 million, set this parameter to 8000.
proxima.ssg.builder.scan_ratio
FLOAT
0.01
The cluster scan rate. Default value: 1%. This value controls the graph precision. If this parameter is set to a large value, the graph precision is high but the graph construction cost linearly increases. We recommend that you configure this parameter based on the number of data records in the doc table:
If the number of data records in the doc table is less than 2 million, the value of this parameter is calculated by using the following formula:
10000/doc_count.If the number of data records in the doc table is between
2 million and 10 million, the value of this parameter is calculated by using the following formula:20000/doc_count.If the number of data records in the doc table is greater than 10 million, the value of this parameter is calculated by using the following formula:
50000/doc_count.
GcBuilder
ImportantThe proxima.gc.builder.centroid_count parameter must be configured.
Parameter
Data type
Default value
Description
proxima.gc.builder.thread_count
UNITt32
0
The number of threads that are enabled during index building. If you set this parameter to 0, the default number of CPU cores is used.
proxima.gc.builder.centroid_count
STRING
No default value
The number of cluster centroids that you want to use for clusters. Hierarchical clusters are supported. Separate the numbers of centroids at different layers of a hierarchical cluster with an asterisk
(*).Sample value for a one-layer cluster: 1000.
Sample value for a two-layer cluster: 100*100.
If you use cluster centroids at two layers, we recommend that you configure more cluster centroids at layer 1 than layer 2. This ensures a high recall rate. Based on empirical values, the number of centroids at layer 1 needs to be set to 10 times the number of centroids at layer 2.
LinearBuilder
Parameter
Data type
Default value
Description
proxima.linear.builder.column_major_order
STRING
false
Specifies how to order the features of an index when the index is being built. The valid values of this parameter are false and true. The value false specifies to order the features of an index by row. The value true specifies to order the features of an index by column.
QcBuilder
NoteThe proxima.qc.builder.centroid_count parameter must be configured.
Parameter
Data type
Default value
Description
proxima.qc.builder.thread_count
UNIT32
0
The number of threads that are enabled during index building. If you set this parameter to 0, the default number of CPU cores is used.
proxima.qc.builder.centroid_count
STRING
No default value
The number of cluster centroids that you want to use for clusters. Hierarchical clusters are supported. Separate the numbers of centroids at different layers of a hierarchical cluster with an asterisk
(*).Sample value for a one-layer cluster: 1000.
Sample value for a two-layer cluster: 100*100.
If you use cluster centroids at two layers, we recommend that you configure more cluster centroids at layer 1 than layer 2. This ensures a high recall rate. Based on empirical values, the number of centroids at layer 1 needs to be set to 10 times the number of centroids at layer 2.
proxima.qc.builder.quantizer_class
STRING
No default value
A quantizer. By default, the system does not use quantizers. Valid values: Int8QuantizerConverter, HalfFloatConverter, and DoubleBitConverter. In most cases, a quantizer can improve the query performance and reduce the index size, but the recall rate decreases.
proxima.qc.builder.quantizer_params
IndexParams
No default value
Specifies the parameters related to the quantizer that you specified for proxima.qc.builder.quantizer_class.
IndexSearcher parameters
ClusteringSearcher
Parameter
Data type
Default value
Description
proxima.hc.searcher.max_scan_count
UNIT32
No default value
The maximum number of data records in the doc table that can be searched for online. This parameter specifies the search range. A large value causes a high recall rate. However, the value cannot exceed the number of data records in the doc table under the cluster centroids that are specified by the proxima.hc.searcher.scan_count_in level parameter.
proxima.hc.searcher.scan_ratio
FLOAT
0.01
This parameter is used to calculate the value of the max_scan_count parameter. Formula:
Total number of data records in the doc table × scan_ratio.HnswSearcher
Parameter
Data type
Default value
Description
proxima.hnsw.searcher.ef
UNIT32
500
The maximum number of data records in the doc table that can be searched for online. This parameter specifies the search range. A large value causes a high recall rate. However, the value cannot exceed the number of data records in the doc table under the cluster centroids that are specified by the proxima.hc.searcher.scan_count_in level parameter.
proxima.hnsw.searcher.max_scan_ratio
FLOAT
0.1f
This parameter is used to calculate the value of the max_scan_count parameter. Formula:
Total number of data records in the doc table × scan_ratio.proxima.hnsw.searcher.brute_force_threshold
INT
1000
A threshold value. If the total number of data records in the doc table is less than this threshold, linear search is performed.
SsgSearcher
Parameter
Data type
Default value
Description
proxima.ssg.searcher.ef
UNIT32
500
The search precision. If this parameter is set to a large value, the number of data records in the doc table that are scanned is large and the recall rate is high.
proxima.ssg.searcher.max_scan_ratio
UNIT32
0
The maximum scan rate for the data records in the doc table. This parameter is used to specify the truncation policy. The default value 0 indicates that this parameter is not used.
GcSearcher
Parameter
Data type
Default value
Description
proxima.gc.searcher.scan_ratio
FLOAT
0.01
This parameter is used to calculate the value of the max_scan_count parameter. Formula:
Total number of data records in the doc table × scan_ratio.LinearSearcher
Parameter
Data type
Default value
Description
proxima.linear.searcher.read_block_size
UNIT32
1024*1024
The size of memory that can be read at a time in the search phase. Approximately 1 MB of memory can be read. If this parameter is set to a small value, queries per second (QPS) is significantly affected. If this parameter is set to a large value, more memory is used. We recommend that you retain the default value 1024*1024.
QcSearcher
Parameter
Data type
Default value
Description
proxima.qc.searcher.scan_ratio
FLOAT
0.01
This parameter is used to calculate the value of the max_scan_count parameter. Formula:
Total number of data records in the doc table × scan_ratio.proxima.qc.searcher.brute_force_threshold
INT
1000
A threshold value. If the total number of data records in the doc table is less than this threshold, linear search is performed.
IndexConverter parameters
MipsConverter
Parameter
Data type
Default value
Description
proxima.mips.converter.m_value
UINT32
No default value
The value of M. This indicates the number of dimensions that can be added. In most cases, a maximum of four dimensions can be added.
proxima.mips.converter.u_value
FLOAT
0.38196601
The value of U. Valid values: 0 to 1.0.
proxima.mips.converter.forced_half_float
BOOLEAN
false
Specifies whether to forcefully convert data from FP32 into FP16.
proxima.mips.converter.spherical_injection
BOOLEAN
false
Specifies whether to use spherical injection for data conversion. After data conversion by using spherical injection, one dimension is added to the data.
HalfFloatConverter
No parameter configuration is required.
DoubleBitConverter
Parameter
Data type
Default value
Description
proxima.double_bit.converter.train_sample_count
INT
0
The amount of data that is used for training. If this parameter is set to 0, full data in the holder is used.
Int8QuantizerConverter
No parameter configuration is required.
Int4QuantizerConverter
No parameter configuration is required.
NormalizeConverter
Parameter
Data type
Default value
Description
proxima.normalize.reformer.forced_half_float
BOOLEAN
false
Specifies whether to forcefully convert data from FP32 into FP16.
proxima.normalize.reformer.p_value
UNIT32
2
The value of P in the P-norm.
IndexReformer parameters
MipsReformer
Parameter
Data type
Default value
Description
proxima.mips.reformer.m_value
UINT32
4
The value of M. This indicates the number of dimensions that can be added. In most cases, a maximum of four dimensions can be added.
proxima.mips.reformer.u_value
FLOAT
0.38196601
The value of U. Valid values: a value that is greater than 0 and less than 1.0.
proxima.mips.reformer.l2_norm
FLOAT
0.0
The value of L2 norm that is obtained from training.
proxima.mips.reformer.normalize
BOOLEAN
false
Specifies whether to normalize the results.
proxima.mips.reformer.forced_half_float
BOOLEAN
false
Specifies whether to forcefully convert data from FP32 into FP16.
HalfFloatReformer
No parameter configuration is required.
IndexMeasure parameters
Canberra
No parameter configuration is required.
Chebyshev
No parameter configuration is required.
SquaredEuclidean
No parameter configuration is required.
Euclidean
No parameter configuration is required.
GeographicalDistance
No parameter configuration is required.
Hamming
No parameter configuration is required.
InnerProduct
No parameter configuration is required.
Manhattan
No parameter configuration is required.
Matching
No parameter configuration is required.
MipsSquaredEuclidean
Parameter
Data type
Default value
Description
proxima.mips_euclidean.measure.injection_type
INT
0
The injection type for inner product feature transformation. Valid values:
0 LocalizedSpherical
1 Spherical
2 RepeatedQuadratic
3 Identity
RogersTanimoto
No parameter configuration is required.
RussellRao
No parameter configuration is required.