MaxCompute provides a data lake analytics solution that lets you create management objects. These objects define the metadata and data access methods for external data sources. Using an external schema mapping mechanism, you can directly access all tables within a database or schema of an external data source. This solution eliminates the barriers between data lakes and data warehouses. It combines the flexibility and rich multi-engine ecosystem of a data lake with the enterprise-grade capabilities of a data warehouse. This helps you build an integrated data management platform. This feature is in public preview.
Data warehouse and data lake
Category | Capabilities |
Data warehouse | A data warehouse emphasizes the management and constraints on structured and semi-structured data. It relies on strong management to achieve better computing performance and more standardized management capabilities. |
Data lake | A data lake emphasizes open data storage and common data formats. It supports multiple engines that produce or consume data as needed. To ensure flexibility, it provides only weak management capabilities. It is compatible with unstructured data and supports a schema-on-read approach, offering a more flexible way to manage data. |
MaxCompute data warehouse
MaxCompute is a cloud-native data warehouse based on a serverless architecture. You can perform the following operations:
Model a data warehouse using MaxCompute.
Use extract, transform, and load (ETL) tools to load and store data in modeled tables with defined schemas.
Process massive amounts of data in the data warehouse using a standard SQL engine and analyze the data using the Hologres OLAP engine.
Scenarios for MaxCompute with data lakes and federated queries
In a data lake scenario, data resides in the lake and is produced or consumed by various engines. The MaxCompute computing engine can act as one of these engines to process and use the data. In this case, MaxCompute needs to read data produced by upstream sources in the data lake, be compatible with various mainstream open source data formats, perform calculations within its engine, and produce data for downstream workflows.
As a secure, high-performance, and cost-effective data warehouse that aggregates high-value data, MaxCompute also needs to retrieve metadata and data from the data lake. This allows for in-engine computation on external data and federated queries with internal data to extract value and consolidate it into the data warehouse.
In addition to data lakes, MaxCompute as a data warehouse also needs to retrieve data from various other external data sources, such as Hadoop and Hologres, to perform federated queries with its internal data. In federated query scenarios, MaxCompute must also support reading metadata and data from external systems.
MaxCompute data lake analytics
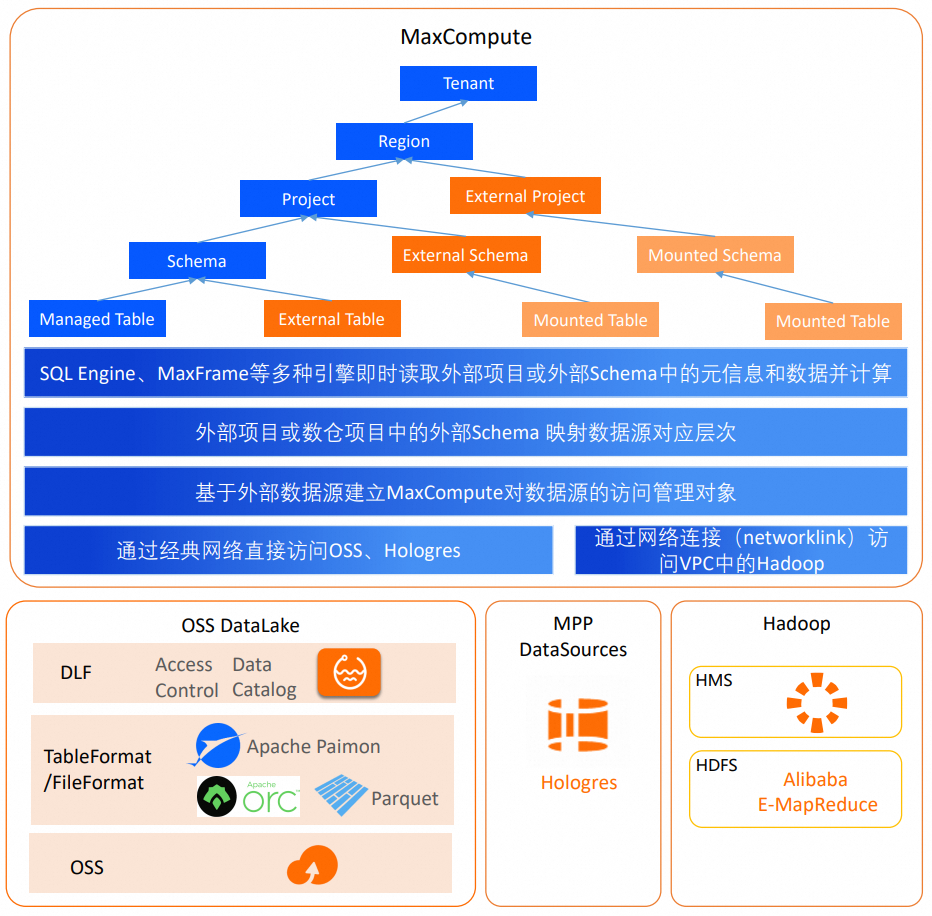
MaxCompute data lake analytics is built on the MaxCompute computing engine. It supports access to Alibaba Cloud metadata or storage services over the interconnected cloud product network. It also supports access to external data sources in a VPC over a leased line. This feature lets you create management objects that define the metadata and data access methods for external data sources. An external schema can map to an external database or schema, which lets you directly access all tables within that scope.
Network connectivity
For more information about Networklink, see Network Connection Flow. MaxCompute can use a network connection to access data sources in VPCs, such as E-MapReduce (EMR) clusters and ApsaraDB RDS instances (available soon). Data Lake Formation (DLF), Object Storage Service (OSS), and Hologres are located in an interconnected network of cloud services. MaxCompute can directly access data in these services without configuring Networklink.
Foreign Server
A Foreign Server contains information for metadata and data access, including authentication credentials, location information, and connection protocol details for the data source system. A Foreign Server is a tenant-level management object defined by the tenant administrator.
When the project-level tenant resource access control feature is enabled, a tenant administrator attaches the external data source to the project that will use it. The project administrator then uses a Policy to grant users within the project permission to use the external data source.
External Schema
An External Schema is a special type of schema in a MaxCompute data warehouse project. As shown in the figure, it can map to a database or schema of a data source. This allows direct access to the tables and data within that database or schema. Tables that are mapped to an external database through an External Schema are called federated foreign tables.
Federated foreign tables do not store metadata in MaxCompute. Instead, MaxCompute retrieves the metadata in real time from the global meta service specified in the Foreign Server object. When you run a query, you do not need to create an external table in the data warehouse using a DDL statement. You can directly reference the original table name from the data source using the project name and External Schema name as the namespace. If the table schema or data in the data source changes, the changes are immediately reflected in the federated foreign table. The data source level to which an External Schema maps depends on two factors: the level defined in the Foreign Server and the table hierarchy in the data source. The level defined in the Foreign Server is determined by the access permissions of the authentication identity.
External Project
In Data Lakehouse Solution 1.0, an External Project used a two-layer model. Like an External Schema, it mapped to a database or schema of a data source and required a data warehouse project to read and compute external data. However, an External Project was a high-level object. This approach resulted in many External Projects. It was also not compatible with the three-layer model of data warehouse projects. MaxCompute will gradually phase out External Projects from Data Lakehouse Solution 1.0. Existing users can migrate to External Schemas.
In data lake analytics, you can use an External Schema to obtain all the capabilities of an External Project from Data Lakehouse Solution 1.0. The External Schema directly maps to a Catalog or Database of a three-layer model data source. It provides direct visibility into the Databases under a DLF Catalog or the Schemas under a Hologres Database. You can then access the data source tables as federated foreign tables.
Data source type | External Data Source Hierarchy | External Schema mapping level | Data Lakehouse 2.0 External Project mapping level | Data Lakehouse Solution 1.0 External Project (being phased out) mapping level | Authentication method |
DLF+OSS | Region-level DLF and OSS services | DLF Catalog.Database | DLF Catalog | DLF Catalog.Database | RAMRole |
Hive+HDFS | EMR instance | Hive Database | Not supported | Hive Database | No authentication |
Hologres | Database of a Hologres instance | Schema | Database | Not supported | RAMRole |
Different data sources support various types of authentication. MaxCompute will support more authentication methods in future releases, such as using the current user's identity to access Hologres or using Kerberos authentication to access Hive.